Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Rate of Reaction f5 (Worksheet)
Hochgeladen von
Derek MaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Rate of Reaction f5 (Worksheet)
Hochgeladen von
Derek MaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
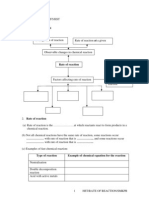
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC RATE OF REACTION 1.
Concept Map Average rate of reaction Rate of reaction at a given time
Observable changes in chemical reaction
Rate of reaction Collision Theory to explain factors affecting rate of reaction
Factors affecting rate of reaction
2. Rate of reaction (a) Rate of reaction is the at which reactants react to form products in a chemical reaction. (b) Not all chemical reactions have the same rate of reaction, some reactions occur with rate of reaction that is .., and some reactions occur with rate of reaction that is ... (c) Examples of fast chemical reaction: Type of reaction Neutralisation Double decomposition reaction Example of chemical equation for the reaction
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC Acid with active metals Combustion of magnesium (d) Examples of slow chemical reaction. Corrosion of iron Photosynthesis Reaction of hydrochloric acid with sodium thiosulphate solution. (e) Time taken for a fast chemical reaction is and the time taken for slow chemical reaction of . Hence the rate of reaction is to time taken for the reaction. Rate of reaction .. (f) The rate of reaction can be determined by measuring the time taken for an observable chemical change to occur. Rate of reaction = Observable chemical change Time taken (g) The observable chemical changes in a chemical reaction are (i) . (ii) (iii) . (iv) (v) ..
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC (h) Rate of reaction can be defined as the rate of change of volume of gas produced per unit time. Rate of reaction = Change in volume of gas produced Time taken = cm3 s-1
(i) Example: If 50.0 cm3 of hydrogen gas is collected in 20 seconds during a chemical reaction between magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid . What is the rate of reaction? Rate of reaction = = cm3 s-1
(ii) Example: If 5.0 gram of magnesium ribbon reacts completely with dilute hydrochloric acid in 25s, what is the rate of reaction? Rate of reaction = = g s-1.
3. To determine the rate of reaction from graph. (a) For a chemical reaction, if the concentration of reactants or mass of reactant is plotted against the time, sketch the graph produced:
Concentration of reactant / mol dm3
Mass of reactant/ g
Time/s
Time/s
(b) For a chemical reaction, if the concentration of products or the volume of gas released is plotted against time, sketch the graph is produced. Volume of gas/cm3 Vmax
Concentration of product / mol dm3
Time/s
Time/s
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC (c) If the concentration of reactant is plotted against 1/time, sketch the graph produced. Concentration of reactant / mol dm3
1/time , s-1 (d) In a chemical reaction involving release of a gas, it is easier to determine the rate of reaction by measuring the .. at a certain time interval. (f) There are 2 methods to determine the rate of reaction, namely (i) average rate or overall rate of reaction Average rate of reaction = Total volume of gas released Time taken = V cm3 s-1 or cm3 min-1 t (ii) rate of reaction at a given time. To determine the rate of reaction at a given time t1 s on the graph at point M, the following steps are taken. - Draw a tangent at the point M on the graph. - Draw a right angle triangle using the tangent as hypotenuse. - Determine the gradient of the tangent. - Rate of reaction at t1 s = y/x cm3 s-1 Example: Volume of gas/cm3 Rate of reaction at t1 = Rate of reaction at t2 = Rate of reaction at t3 = t1 t2 t3 4 Time/s
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC Example: To determine the rate of reaction between zinc and dilute hydrochloric acid. Aim of experiment: To investigate.. Apparatus: Material:
Procedure: (diagram)
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii)
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC Result: Time/minute Burette reading/cm3 Volume of gas collected/cm3 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 6.00 3.5 5.00 4.0 4.00 4.5 4.00 5.0 4.00
49.00 36.00 25.00 17.00 11.00 8.00 0.00
13.00 24.00 32.00 38.00 41.00 43.00 44.00 45.00 45.00 45.00
Discussion: 1. Plot a graph of volume of gas collected against time of reaction. 2. From the graph, calculate the (i) overall average rate of reaction.
(ii) rate of the reaction in the first 3 minutes.
(iii) rate of reaction in the second minute
(iv) rate of reaction at (a) 1 minute
(b) 2 minute
(c) 3 minute
3. Compare the rate of reaction obtained in 2(iv). Explain your answer.
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC
4. Write a balance chemical equation of the reaction between zinc and hydrochloric acid. 5.What is the name of the gas released and suggest a test for the gas.
Conclusion:
4. Factors affecting rate of reaction Name the factors that affect the rate of reaction.. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (A) Effect of total surface area of reactant on the rate of reaction. (a) The smaller the size of particle of solid reactant the larger the surface area of reactant exposed, hence the higher is the rate of reaction. Give 3 examples for the above statement. (i) Cube sugar dissolves slower than that of fine sugar of the same mass in same amount of water. (ii) Minced meat cooks faster that solid piece of meat of the same mass. (iii) Powdered zinc reacts faster than granulated zinc of the same mass with hydrochloric acid of the same volume and concentration.
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC (b) Experiment to investigate the effect of total surface area of calcium carbonate on the rate of reaction Problem statement: Hypothesis: Variables: (i) manipulate variable: (ii) responding variable: (iii) fixed variable: Materials: Apparatus: Procedure:
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v)
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC (vi) (vii) (viii) Results: (i) Experiment I using large marble chips: Time/ minute Burette reading/cm3 Volume of gas collected/cm3 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 49.50 45.20 42.0 39.00 36.50 34.00 31.80 29.50 27.80 26.20 24.50 23.50
(ii) Experiment II using crushed marble chips: Time/ minute Burette reading/cm3 Volume of gas collected/cm3 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 49.00 39.00 33.00 28.50 25.00 21.50 19.00 16.70 14.70 13.00 11.50 10.00
1. Plot the graph of total volume of gas collected against time taken for the reaction for experiment I and II on the same axes. 2. Based on the graph , calculate (a) the overall rate of rate of reaction for the first 5 minutes of the reaction between hydrochloric acid and (i) large marble chips:
(ii) crushed marble chips
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC
(b) The rate of reaction at 2.5 minute for (i) large marble chips:
(ii) crushed marble chips:
3. Based on your answers in 2(a) and 2(b) , how does the rate of reaction differ?
4. What is the factor that causes the difference in rate of reaction? 5. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid. 6. Explain why does the rate of reaction decreases with increase of time.
7. If both reactions are allowed to react until completion, is the total volume of gas collected the same? Explain your answer.
8. If the marble chips used in the experiment is in excess, what is the maximum total volume of gas collected? [ 1 mole of gas at room temperature occupies a volume of 24dm3]
Conclusion:
10
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC 5. The effect of concentration of reactant on the rate of reaction. (a)When concentration of reactant increases, the rate of reaction increases. Give one example for the above statement.
(b) Experiment to investigate the effect of concentration of sodium thiosulphate with hydrochloric acid on the rate of reaction Problem statement: Hypothesis: Variables: (i) manipulated variable: (ii) responding variable: (iii) fixed variable: Procedure: (diagram)
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v)
11
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC (vi) (vii) Results: Experiment Volume of 0.2moldm-3 sodium thiosulphate solution, V1 cm3 Volume of distilled water added/cm3 Volume of 1.0mol hydrochloric acid added/cm3 Total volume of reactant /cm3 Concentration of sodium thiosulphate solution used/moldm-3 Time taken/s 1/time , s-1 1. Plot the graph of concentration of sodium thiosulphate solution used against time taken for the reaction. 2. Plot the graph of concentration of thiosuphate solution used against 1/time. 3. What does the value of 1/time represents? 4. Based on your graph, state the relationship between (i) the concentration of sodium thiosulphate and the time taken for the reaction. (ii) the rate of reaction and the concentration of sodium thiosulphate solution. 1 45 0.0 5.0 50.0 2 40 5.0 5.0 50.0 3 35 10.0 5.0 50.0 4 30 15.0 5.0 50.0 5 25 20.0 5.0 50.0
16
20
27
41
83
5. What is colour of the precipitate formed and name the precipitate. 6. What is the time taken for the mark X to disappear if the concentration of sodium thiosulphate solution used is 0.10 mol dm-3? 7. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction in this experiment.
12
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC
8. Write an ionic equation for the reaction in this experiment.
9. If dilute sulphuric acid of the same concentration is used to replace hydrochloric acid in this experiment, predict the rate of reaction and explain your answer.
Conclusion:
6. The effect of temperature on rate of reaction. (a) Increase in temperature of reaction, increases the rate of reaction. Give two examples for the above statement. (i) (ii) (b) Experiment to investigate the effect of temperate on the rate of reaction between thiosulphate solution and dilute hydrochloric acid. Problem statement: Hypothesis: Variables: (i) manipulate variable: (ii) responding variable: (iii) fixed variable: Procedure:
13
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC (diagram)
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii)
Results: Experiment Temperature/oC Time taken/s 1/time, s-1 1 30 55 2 35 48 3 40 42 4 45 37 5 50 33
14
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC 1. Plot the graph of (i) temperature against time and (ii) temperature against 1/time. 2. Based on your graph, what is the relationship between rate of reaction with temperature. 3. Write a balance chemical equation for the reaction of this experiment. 4. why is the volume of sodium thiosulphate solution and hydrochloric acid fixed for each experiment? 5. What is the time taken for the mark X to disappear when the temperature is 60oC?
Conclusion:
7. Effect of catalyst on the rate of reaction. (a) A catalyst is a substance which added to a chemical reaction can . the rate of reaction and itself remains . at the end of the reaction. (b) A catalyst does not .. in a chemical reaction. It only .. the rate of reaction if it is a positive catalyst, and the rate of reaction if it is a negative catalyst. (c) Example: When copper(II) sulphate solution is added into a reaction between zinc and hydrochloric acid, the rate of reaction increases but the final quantity of hydrogen produced is the same the reaction of zinc with hydrochloric acid without copper(II) sulphate solution. Sketch the graphs of volume of hydrogen gas against time for comparison of reaction of zinc and hydrochloric acid with catalyst and without catalyst .
Volume of hydrogen released/cm3 15
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC
Time/s (d) Experiment to investigate the effect of catalyst on the rate of reaction for decomposition of hydrogen peroxide solution. Problem statement: Hypothesis: Variables: (i) manipulated variable: (ii) responding variable: (iii) fixed variable: Apparatus: Materials: Procedure:
(i) (ii)
16
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC (iii) (iv) (v) Observation: Test tube A B Discussion: 1. What is the effect of manganese(IV) oxide on the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide solution? 2. What is the function of manganese(IV) oxide in this experiment? 3. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction in this experiment. 4. Will the mass of manganese(IV) oxide change at the end of the reaction in test tube B? Conclusion: (e) Experiment to investigate the effect of the amount of catalyst on the rate of reaction for decomposition of hydrogen peroxide solution. Problem statement: Hypothesis: Variables: (i) manipulated variable: Observation
17
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC (ii) responding variable: (iii) fixed variable: Apparatus: Materials: Procedure:
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii)
Results: (a) Experiment 1, using 0.2g of manganese(IV) oxide
18
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC
Time/s Burette reading/cm3 Volume of gas cm3
0.0
49.70
0.5
48.70
1.0
47.10
1.5
45.70
2.0
44.20
2.5
43.20
3.0
42.00
3.5
41.10
4.0
40.20
4.5
39.50
5.0
39.00
5.5
38.40
6.0
38.00
(b) Experiment II, using 0.6g of manganese(IV) oxide Time/s Burette reading/cm3 Volume of gas cm3 0.0
49.00
0.5
43.60
1.0
40.50
1.5
38.00
2.0
36.00
2.5
34.50
3.0
33.00
3.5
31.70
4.0
30.50
4.5
29.70
5.0
29.00
5.5
28.20
6.0
28.00
1. Plot the graph of total volume of gas against time for experiment I and experiment II on the same axes. 2. Based on your graph, calculate the rate of reaction at 120 seconds for each of the reaction . (i) Experiment I:
(ii) Experiment II:
3. How did the rates of reaction in experiment I and II differ? 4. Which experiment shows the higher rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide? 5. If both experiments are allowed to proceed until completion, is the total volume of gas collected in both experiments the same? Explain your answer. Conclusion: (f) Application of catalyst in industry.
19
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC Most catalysts are transition elements or compounds of transition elements. Catalyst is specific in its action and only a small amount is required in a chemical reaction. Industrial process Haber Process Contact Process Ostwald Process Hydrogenation of vegetable oil Cracking of petroleum (g) Other examples: Table shows the reacting conditions for the following experiments. For the following experiments , sketch graph of (i) volume of gas against time Experiment 1 Experiment 2 5cm3 5 volume of H2O2 + 45cm3 water + MnO2 3cm3 5 volume of H2O2 + 47cm3 water + MnO2 Product produced Equation Catalyst
Volume of oxygen/cm3
(ii) volume of gas against time Experiment 1 Experiment 2
Time/s
5cm3 5 volume of H2O2 + 45cm3 water at 40oC 5cm3 5 volume of H2O2 + 45cm3 water at room temperature
Volume of oxygen/cm3
(iii) Volume of hydrogen against time Time/s 20
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC Experiment 1 Experiment 2 Experiment 3 Volume of hydrogen/cm3 4 g of excess zinc powder + 100 cm3 of sulphuric acid 0.5 mol dm-3 + 5cm3 copper(II) sulphate solution at room temperature 4 g of excess zinc powder + 100 cm3 of sulphuric acid 0.5 mol dm-3 room temperature 4 g of excess zinc powder + 50 cm3 of sulphuric acid 0.5 mol dm-3 at room temperature
Time/s 8. Collision Theory (a) For a chemical reaction to occur, the particles of the reactants must collide with each other. However, not all collisions result in a chemical reaction to form products. (b) According to collision theory, only those collisions which (i) with .. orientation and (ii) posses amount of energy called activation energy , Ea will result in chemical reaction. (c) Collisions of particles of reactants that result in chemical reaction is known as . (d) Activation energy , Ea, is defined as the minimum amount of energy of collision that is required for particles of reactant to react or to produce effective collision. (i) Exothermic reaction Energy (ii) Endothermic reaction Energy
(e) Using Collision Theory to explain the factors affecting the rate of reaction.
21
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC 1. The effect of increase in total surface area of reactant. Using solid reactant that is smaller in size. When size of solid reactant is smaller, the total surface area increases The frequency of collision of particles of reactant increases The frequency of effective collision increases The rate of reaction increases.
2. The effect of increase in concentration of reactant. Increasing the concentration of reactant will increase the number of particles of reactant per unit volume. The frequency of collision of particles of reactant increases. The frequency of effective collision increases. The rate of reaction increases. 3. The effect of increase in temperature of reaction o By increasing the temperature of the reactant o Increased in temperature, increases the kinetic energy of the reactant particles. o The frequency of colliding particles possesses energy higher than the activation energy increases. o The frequency of effective collision increases o The rate of reaction increases. 4. The effect of catalyst on the rate of reaction. Energy Addition of a positive catalyst to a chemical reaction provides an alternative path of reaction that requires a lower activation energy. The frequency of effective collision increases The rate of reaction increases. Energy profile diagrams to show the effect of catalyst on rate of reaction. Energy
9. The effect of pressure on rate of reaction. 22
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC
(i) The effect of pressure only affects the rate of chemical reaction when the reactants are in the gaseous state. Eg: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g)
(ii) Increased in pressure by increasing the concentration of gas or by reducing the volume of the vessel, o the number of particles per unit volume increases. o The frequency of collision among the reactant particles increases o The frequency of effective collision increases o Hence the rate of reaction increases. Reinforce exercise; 1. Which of the following can be used to determine the rate of the reaction? I Release of gas per unit time. II Change of colour intensity per unit time. III Formation of precipitate per unit time. IV Increase in the mass of reactant per unit time. A. I and II B. III and IV C. I, II and III D. II, III and IV An equation of a reaction is as follows 2Fe2+ Green + Cl2 2Fe3+ + Brown 2Cl
2.
In the reaction represented by the equation above, it was found that the change of colour from green to brown was faster when the reactant mixture was heated. This was due to the I. decrease in the activation energy. II. increase in the frequency of effective collision . III. increase in the kinetic energy of ferrum(II) ions and chlorine molecules. IV. increase in the frequency of collision between ferrum(II) ions and chlorine molecules. A. I and II only B. II and III only C. I, III and IV only D. II, III and IV only 3. Table 4 shows the total volume of gas collected at regular intervals in a reaction.
23
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC
Time / s Volume of gas/ cm3
0 0
30 2.0
60 3.7
90 5.2
120 6.4
150 7.3
180 8.6
210 8.6
What is the average rate of reaction in the second minute ? A. B. C. D. 4. 0.040 0.045 0.053 0.062 cm3s-1 cm3s-1 cm3s-1 cm3s-1
The equation below represents the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide solution. 2H2O2(aq) 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
Which of the following are produced when 1 mole of hydrogen peroxide is decomposed completely ? [1 mole of gas occupies 24 dm3 at room condition; Avogadros constant : 6 X 1023 mol-1] I II III IV A B C D 5 2 moles of water 12 dm3 of oxygen gas 3 X 1023 of oxygen molecules 1.2 X 1024 of water molecules I and III only I and IV only II and III only II and IV only
An experiment is carried out to study the rate of reaction between marble and hydrochloric acid to produce carbon dioxide gas. Experiment Substances I Excess marble and 50.0 cm3 of 2 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid II A Volume of CO2/cm3 Excess marble and 100.0cm3 of 1 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid C Volume of CO2/cm3 II
I II
Time/s B Volume of CO2/cm3 24 D
Time/s
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC Volume of CO2/cm3
II I Time/s 6
I II Time/s
The reaction between hydrochloric acid and zinc produces hydrogen gas. The reaction is complete in 50 seconds and the maximum volume of gas produced is 25 cm3. What is the average rate of the reaction? A. 0.5 cm3 s-1 B. 1.0 cm3 s-1 C. 2.0 cm3 s-1 D. 4.0 cm3 s-1
The diagram shows the energy profile of a reaction. Ea is the activation energy for this reaction. Energy Ea Reactant Ea Products Reaction path What will change the activation energy from Ea to Ea? A. Temperature C. Concentration B. Catalyst D. Total surface area
Which of the following explains the meaning of effective collision? A. B. C. D. The collision where its energy is less than the activation energy. The collision that has a low energy The collision which takes place before a reaction The collision that causes a reaction
The diagram shows the set up of the apparatus for an experiment to determine the rate of reaction between sodium thiosulphate and sulphuric acid.
25
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC
Which of the conditions take mark X to Sulphuric acid Volume/cm3 Concentration/ mol dm-3 A 10 1.0 B 10 1.0 C 10 0.5 D 20 0.5 In an experiment, 0.1 mol dm-3 produces oxygen gas. Volume of oxygen gas/cm3
following combination of the shortest time for the diappear from sight? Sodium thiosulphate Temperature 3 Volume/cm Concentration/ /oC mol dm-3 50 0.5 30 50 0.5 40 50 0.5 30 40 0.5 40 the decomposition of 25cm3 of hydrogen peroxide solution
10
P Q Time/s
If the experiment is repeated using another solution, which solution will produce curve Q? A. 25 cm3 of 0.15 mol dm-3 hydrogen peroxide B. 20 cm3 of 0.15 mol dm-3 hydrogen peroxide C. 15 cm3 of 0.15 mol dm-3 hydrogen peroxide D. 10 cm3 of 0.25 mol dm-3 hydrogen peroxide 11 The following statements are related to the collision theory of a reaction. I. The total surface area of the reactant particles increases. II. The kinetic energy of the reactant particles increases. III. The frequency of the collision between the reactant particles increases. IV. The number of the reactant particles per unit volume increases. Which of the following combinations is true about the effect of the rise in temperature on the reactant particles? A I and II only C III and IV only B II and III only D I and IV only
26
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC 12 If you want to cook 100 potatoes within a short time, which is the most suitable method? A Boil the potatoes in a pan B Boil the potatoes in a pressure cooker C Steam the potatoes in a steamer D Fry the potatoes in a wok Which of the following reactants produces the highest rate of reaction with zinc powder? A 25 cm3 of sulphuric acid 0.1 mol dm-3. B 25 cm3 of ethanoic acid 0.1 mol dm-3. C 25 cm3 of nitric acid 0.1 mol dm-3. D 25 cm3 of hydrochloric acid 0.1 mol dm-3.
13
Reinforce Exercise for Structural Questions and Essay Questions. 1. The rate of reaction is affected by several factors. One of the factors is the size of particles. One kilogramme of meat, cut into big pieces, takes a longer time to cook compared to one kilogram of meat cut into smaller pieces. (a) Explain the above statement based on the size of the particles. [2 marks] (b) A student carried out three experiments to investigate the effects of the factors influencing the rate of reaction. Table 1 shows the results of the experiments.
27
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC (i) Write the chemical equation for the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid. Calculate the maximum volume of hydrogen gas produced. [ Relative atomic mass: Mg,24; molar mass volume: 24 dm3 mol-1 at room condition] [4 marks]
(ii) Sketch the graphs for the volume of hydrogen gas against time for Experiment I, II and III on the same axes. [3 marks] (iii) Calculate the average rate of reaction for Experiment I, II and III in cm3 s-1. [3 marks]
(iv) Compare the rates of reaction between Experiment I and Experiment II, and between Experiment II and Experiment III. With reference to collision theory, explain why there are differences in the rates of reaction in the experiments. [8 marks]
28
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC 2. An experiment was conducted to find out the effects of temperature on the rate of reaction. 50cm3 of sodium thiosulphate solution 0.05 mol dm-3 at 30oC was put into a 250cm3 conical flask. Then the conical flask was placed on an X sign on a piece of white paper. 10cm3 of hydrochloric acid 1.0 mol dm-3 was added to the sodium thiosulphate solution and shaken. At the same time, the stop watch was started. The stop watch was stopped as soon as the X sign was no longer visible. The same steps of the experiment were repeated for sodium thiosulphate solution which was heated to 35oC, 40oC, 45oC and 50oC. Figure 1 shows the readings of the stop watch for each of the reaction at different temperatures.
(a)
Record the time for each reaction in the spaces provided in Figure 1. (b) Construct a table and record temperature, time and 1/time for this experiment.
29
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC
(c) (i) Draw a graph of temperature against 1/time on the graph paper. (ii) Based on the graph in c(i) , state the relationship between the rate of reaction and temperature. (d) Predict the time taken as soon as the sign X to be not longer visible if this experiment is repeated at 55oC.
(e)(i) State the variables involved in this experiment. Manipulated variable: Responding variable: Constant variable: (ii) State how you would manipulate one variable while keeping the other variables constant.
(f) State the hypothesis for this experiment.
(g) From the above experiment, the student found a relationship between temperature and rate of reaction. The same situation can be applied in our daily lives, for example, keeping food that is easily spoiled in the refrigerator.
30
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC Using your knowledge of chemistry, state the relationship between temperature and the rate at which food turns bad.
3(a) Food stored in a refrigerator last longer than food stored in a kitchen cabinet. Explain why. [4 marks]
(b) A group of pupils carried out three experiments to investigate the factors affecting the rate of a reaction. Table 7 shows information about the reactants and the temperature used in each experiment. Experiment I II III Reactants Excess calcium carbonate chips and 30 cm3 of 0.5 mod dm-3 hydrochloric acid Excess calcium carbonate chips and 30 cm3 of 0.5 mod dm-3 hydrochloric acid Excess calcium carbonate powder and 30 cm3 of 0.5 mod dm-3 hydrochloric acid Table 7. Graph 7 shows the results of these experiments. Temperature /oC 30 40 40
31
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC (i) Calculate the average rate of reaction for experiment I.
[2 marks] (ii) Based on Table 7 and graph 7, compare the rate of reaction between: Experiment I and Experiment II Experiment II and Experiment III In each case explain the difference in rate of reaction with reference to the collision theory. [ 10 marks]
(iii) The chemical equation below shows the reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid. CaCO3 + 2HCl CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O Given that the relative atomic mass of C=12, O=16, Ca=40 and the molar volume of any gas is 24 cm3 mol-1 at room temperature and pressure. Calculate the maximum volume of carbon dioxide gas produced in Experiment II. [4 marks]
32
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC
4. Diagram 6 shows two experiments to investigate one factor that influences the rate of a reaction.
(a) What is the factor that influences the rate of reaction in both experiments? [1 mark] (b) The reaction in the experiment is represented by the following equation: CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
(i) Among the products stated in the equation, which is the most suitable to be chosen to determine the rate of reaction? [1 mark]
33
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC (ii) State one reason for choosing the product in 6(b)(i) [1 mark] (c) State two controlled variables in both experiments. 1. 2. [2 marks] (d) The results for both experiments are represented by graph 6. Quantity of Key: product
Experiment I Experiment II
x Based on Graph 6:
Time
(i) Experiment II has a higher rate of reaction. How does the graph show this? [1 mark] (ii) What has happened to the reactants at time x? [1 mark]
34
RATE OF REACTION/F5/MZ/SMKCC
35
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Solubility Curve WorksheetDokument5 SeitenSolubility Curve WorksheetAtulya BharadwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Reactions Chapter 6 ReviewDokument11 SeitenOrganic Reactions Chapter 6 ReviewKatie Wilson67% (3)
- Kinetic particle theory part 2: Factors affecting diffusion rateDokument8 SeitenKinetic particle theory part 2: Factors affecting diffusion rateizzatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Reactivity Series ks3Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet Reactivity Series ks3siau chingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Worksheet - WaveDokument3 SeitenPhysics Worksheet - WaveMegan Lapida100% (1)
- Rate of Reaction (Multiple Choice) QP PDFDokument18 SeitenRate of Reaction (Multiple Choice) QP PDFimran100% (1)
- A Hybrid System For Battery Thermal Management For PDFDokument152 SeitenA Hybrid System For Battery Thermal Management For PDFHARSHIT KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy changes in reactionsDokument2 SeitenEnergy changes in reactionsSamandarbek Numonov100% (1)
- Diffusion and Osmosis WorksheetDokument5 SeitenDiffusion and Osmosis Worksheetskeltenboi100% (1)
- Unit 2 Acids Bases Salts Past QuestionsDokument49 SeitenUnit 2 Acids Bases Salts Past QuestionsDwiyasa Irin100% (2)
- Acid and Base Worksheet 1-07-08 Ans KeyDokument4 SeitenAcid and Base Worksheet 1-07-08 Ans KeyShazia FarheenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Kinetics Problems and SolutionsDokument15 SeitenChemical Kinetics Problems and SolutionsRhea CelzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reaction EngineeringDokument93 SeitenChemical Reaction EngineeringGuru Raj BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Rates of Reaction 2014Dokument90 SeitenCSEC Rates of Reaction 2014Carl Agape Davis100% (2)
- The Reactivity SeriesDokument25 SeitenThe Reactivity SeriesFatema KhatunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5TH FORM CHEMISTRY - POLYMER WORKSHEET ON GLUCOSE, STARCH AND PROTEINSDokument4 Seiten5TH FORM CHEMISTRY - POLYMER WORKSHEET ON GLUCOSE, STARCH AND PROTEINSZantaye Thomas100% (1)
- Askeland Science and Engineering 7e ISM Chapter 05Dokument24 SeitenAskeland Science and Engineering 7e ISM Chapter 05Ian Gabriel Cañas Fernández50% (2)
- Reaction Kinetics NotesDokument40 SeitenReaction Kinetics Notesapi-234602673Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet 1Dokument2 SeitenDiffusion and Osmosis Worksheet 1yojhanvargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matter Practice Worksheet 1 - 8 ChemDokument2 SeitenMatter Practice Worksheet 1 - 8 ChembhaveshkhantedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrochemistry WorksheetDokument4 SeitenElectrochemistry WorksheetLtHenry0% (1)
- S 495160Dokument4 SeitenS 495160Khondokar Tarakky0% (1)
- Acids Bases and Salts Worksheet 1Dokument2 SeitenAcids Bases and Salts Worksheet 1api-251783882100% (3)
- Worksheet Grade 8Dokument5 SeitenWorksheet Grade 8willadahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsDokument18 Seiten4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsVictor VC100% (5)
- 4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsDokument18 Seiten4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsVictor VC100% (5)
- Chapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseDokument5 SeitenChapter 7 Chemical Energetics ExerciseAri Adiantari100% (1)
- States of Matter AssessmentDokument2 SeitenStates of Matter AssessmentYAD91250% (2)
- Chapter 18 AssessmentDokument23 SeitenChapter 18 Assessmentmilemike67% (6)
- Diffusion and Osmosis GR 8 WorksheetDokument1 SeiteDiffusion and Osmosis GR 8 WorksheetDeddy Kismana100% (1)
- Solubility Curve Practice Problems Worksheet 1Dokument2 SeitenSolubility Curve Practice Problems Worksheet 1MobiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Rate of ReactionDokument23 Seiten1.1 Rate of ReactionAnonymous uK5JEjNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02-04 Atomic Structure Worksheet - AnswersDokument2 Seiten02-04 Atomic Structure Worksheet - AnswersRSLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Chapter 10 - Simple MachineDokument23 SeitenNotes Chapter 10 - Simple MachineNoraslina Binti Abdul Wahab100% (2)
- Air and Water Worksheet B1Dokument2 SeitenAir and Water Worksheet B1GBENGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample PDF of STD 12th Science English Medium Perfect Chemistry 1Dokument27 SeitenSample PDF of STD 12th Science English Medium Perfect Chemistry 1Tanisha ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromatography Lab WorksheetDokument4 SeitenChromatography Lab WorksheetBradley Wolf100% (1)
- Worksheet 10.6Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet 10.6SavithaBroonanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.6 Sound WavesDokument16 Seiten1.6 Sound WavesIshraqi Ilyas100% (1)
- Chemistry Chapter 10 Rate of ReactionDokument23 SeitenChemistry Chapter 10 Rate of ReactionAbdul ManafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rates of ReactionsDokument54 SeitenRates of ReactionsjohnyeapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating molar enthalpy of reactions in calorimetry experimentsDokument2 SeitenCalculating molar enthalpy of reactions in calorimetry experimentsNayeemAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate of Reaction f5 (Worksheet)Dokument35 SeitenRate of Reaction f5 (Worksheet)Derek Ma67% (3)
- Chemical Formula Writing WorksheetDokument4 SeitenChemical Formula Writing Worksheetapi-286295321Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 The Reactivity Series of MetalsDokument17 Seiten3.1 The Reactivity Series of MetalsWafa OsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers Rates of ReactionDokument1 SeiteAnswers Rates of Reactionkaran79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Chemistry Chapter 1: Rate of ReactionsDokument101 SeitenForm 5 Chemistry Chapter 1: Rate of ReactionscikgufiezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Population DemographicDokument63 Seiten2 Population Demographicapi-296317938100% (3)
- Modul Sains Ting 1Dokument10 SeitenModul Sains Ting 1miznaqibahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual LevenSpiel by 13BCH@ITNUDokument370 SeitenSolution Manual LevenSpiel by 13BCH@ITNUManishMakwana87% (156)
- Rate of Reaction 2Dokument12 SeitenRate of Reaction 2Baskaran ManogaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate of Reaction 2Dokument13 SeitenRate of Reaction 2MalaysiaBoleh100% (9)
- Rate of ReactionDokument5 SeitenRate of ReactionlettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases and Salts Worksheet 1Dokument2 SeitenAcids, Bases and Salts Worksheet 1Abhaydev KA100% (1)
- Problems On PressureDokument4 SeitenProblems On Pressurevinod kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan For Diffusion and OsmosisDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan For Diffusion and Osmosisapi-298754116Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acids & Alkalis For KS3 Science - WorksheetDokument2 SeitenAcids & Alkalis For KS3 Science - WorksheetMfanafuthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson PlanDokument9 SeitenLesson PlanneethulalminiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MYP 3 Criterion D-MetallurgyDokument6 SeitenMYP 3 Criterion D-Metallurgywama ojhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Paper 1 - 2018-2003 - QP PDFDokument539 SeitenChemistry Paper 1 - 2018-2003 - QP PDFal_helu26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in Integrated ScienceDokument6 SeitenLesson Plan in Integrated Sciencerhyme_jiji50% (2)
- Pressure MCQ Physics TopicDokument3 SeitenPressure MCQ Physics TopicFahimDayhan67% (3)
- Good Student Sand-Salt Lab ReportDokument4 SeitenGood Student Sand-Salt Lab ReportKrystalLovejoy67% (3)
- Waves - Worksheet 2Dokument7 SeitenWaves - Worksheet 2Ricardo Johnson0% (2)
- 10.rate of Reaction f5Dokument33 Seiten10.rate of Reaction f5khayranizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry F5C1Dokument9 SeitenChemistry F5C1Mohammad Nur SyafiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sains - Chemistry Form 5Dokument61 SeitenSains - Chemistry Form 5Sekolah Portal100% (8)
- Form 5 Chapter 2: Region of Inequalities 1Dokument8 SeitenForm 5 Chapter 2: Region of Inequalities 1Derek MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan (Form4)Dokument20 SeitenYearly Plan (Form4)Derek MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 往年应用文考题Dokument2 Seiten往年应用文考题Derek MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimia Mid Year 2010 T4 p3Dokument9 SeitenKimia Mid Year 2010 T4 p3Derek MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM F4C2 Structure of AtomDokument30 SeitenCHEM F4C2 Structure of AtomDerek MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 16 PMR Trapezium and Scale Drawing ProblemsDokument6 SeitenModule 16 PMR Trapezium and Scale Drawing ProblemsDerek MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S1093326323000165 MainDokument13 Seiten1 s2.0 S1093326323000165 MainDanso MichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 10th Edition Solomon Solutions ManualDokument5 SeitenBiology 10th Edition Solomon Solutions Manualspawnerminutiaxae7n100% (34)
- Kromatografi Gas PDFDokument8 SeitenKromatografi Gas PDFWigeSudirmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Organic and Biological Chemistry 3rd Edition Frost Test BankDokument24 SeitenGeneral Organic and Biological Chemistry 3rd Edition Frost Test Bankjacobmoralesynjdpksxob100% (29)
- Student Guide: Enzymes - AP STEM Case and HandbookDokument4 SeitenStudent Guide: Enzymes - AP STEM Case and HandbookNicholas CrowellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics of a Reaction Rate LawDokument15 SeitenKinetics of a Reaction Rate LawSebatHian Santiago60% (5)
- Gen Chem 2 - Answer KeyDokument11 SeitenGen Chem 2 - Answer KeyJessie CentillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic analysis of non-isothermal thermal dataDokument13 SeitenKinetic analysis of non-isothermal thermal dataoreamigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsDokument11 SeitenChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Chemical KineticsAyush singh PrinceNoch keine Bewertungen
- H432 01 Mark Scheme Set 2Dokument23 SeitenH432 01 Mark Scheme Set 2JeronNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Chemistry Activation EnergyDokument3 SeitenAP Chemistry Activation Energyctremblaylcsd150Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction KineticsDokument37 SeitenReaction KineticsDaisyNoch keine Bewertungen
- J. Appl. Chem. Biotechnol. 1974, 24, 759-768Dokument10 SeitenJ. Appl. Chem. Biotechnol. 1974, 24, 759-768Robert L JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 6070954144254919518Dokument32 Seiten5 6070954144254919518sujal thawareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics and Applications of Solid State Kinetics A Pharmaceutical PerspectiveDokument27 SeitenBasics and Applications of Solid State Kinetics A Pharmaceutical PerspectiveMadiha RashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6Dokument17 SeitenLecture 6Nurshuhada Nordin0% (1)
- Chem 2Dokument17 SeitenChem 2Mohsen Haj HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 3 MCQ MedDokument20 SeitenChem 3 MCQ Medbrighter716Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thin-Layer Drying Behaviour of Mint Leaves: - Ibrahim DoymazDokument6 SeitenThin-Layer Drying Behaviour of Mint Leaves: - Ibrahim DoymazJanela FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- PharmacyDokument39 SeitenPharmacyGanesh DalabhanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TAM AIR BrochureDokument19 SeitenTAM AIR BrochureErica MagnagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Biology Sec.2.4Dokument33 SeitenGrade 10 Biology Sec.2.4zakaria AlshurmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction KineticsDokument26 SeitenReaction Kineticssuhaila ramleyNoch keine Bewertungen