Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ivf Pnss
Hochgeladen von
donlynOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ivf Pnss
Hochgeladen von
donlynCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
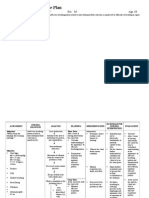
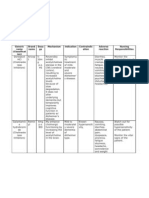
TYPE OF SOLUTION Plain Normal Saline Solution
CLASSIFI CATION Isotonic
CONTENT
MECHANISM OF ACTION Normal saline solution has an osmolality of 308 mOsm/L. Because the osmolality is entirely contributed by electrolytes, the solution remains within the ECF, does not cause red blood cells to shrink or swell. Isotonic fluids expand the ECF volume.
INDICATIONS
CONTRAINDI CATIONS Heart failure pulmonary edema renal impairment sodium retention
HOW SUPPLIE D Parenteral
DOSE
The solution is 9 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolved in 1 liter of water. The mass of 1 milliliter of normal saline is 1.0046 grams at 22C. The molecular weight of sodium chloride is approximat ely 58 grams per mole, so 58 grams of sodium chloride equals 1
Replace Extracellular Fluid Hyponatremia Hypochloremia Water overload mild metabolic acidosis medication diluent IV irrigant compatible with blood.
1L at 20 gtts/ min
NURSING RESPONS I -BILITIES BEFORE: *Obtain history of the patients fluid and electrolyte status before therapy and reassess regularly. *Before giving the bottle, check for the correct patient to be administer ed. *Check for the correct fluid to be given.
mole. Since normal saline contains 9 grams of NaCl, the concentrati on is 9 grams per liter divided by 58 grams per mole, or 0.154 moles per liter. Since NaCl dissociates into two ions sodium and chloride 1 molar NaCl is 2 osmolar. Thus, NS contains 154 mEq/L of Na+ and Cl
DURING: *Upon inserting the chamber to another, make sure that it is inserted well. *Be alert of fluid overload *Check for the patients comfort AFTER: *Infuse the IV well to its prescribed rate *Check for the presence of bubbles in the IV
tube. *Evaluate patients knowledge of therapy
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Power Supply RepairDokument4 SeitenPower Supply RepairterezkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GayDokument15 SeitenGayjulyerwanni100% (2)
- Engine OilDokument14 SeitenEngine OildonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fan RepairDokument22 SeitenFan RepairdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lactated RingersDokument3 SeitenLactated RingersE100% (5)
- Stretch To Win (2017) PDFDokument241 SeitenStretch To Win (2017) PDFmmpersonal2010100% (4)
- MIP17 - HSE - PP - 001 Environment Management Plan (EMP) 2021 REV 3Dokument40 SeitenMIP17 - HSE - PP - 001 Environment Management Plan (EMP) 2021 REV 3AmeerHamzaWarraichNoch keine Bewertungen
- LaPaz Batchoy RecipeDokument10 SeitenLaPaz Batchoy RecipedonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ignition TimingDokument7 SeitenIgnition TimingdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- M265 Lec 13 - Epidemiology and Public HealthDokument10 SeitenM265 Lec 13 - Epidemiology and Public HealthSawsan Z. JwaiedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing DiagnosisDokument34 SeitenNursing DiagnosisZanie Cruz100% (1)
- Construction Project Safety Management Best Practices Handbook PDFDokument332 SeitenConstruction Project Safety Management Best Practices Handbook PDFVENKATESWARA RAO VOONANoch keine Bewertungen
- Copper Toxicity ChecklistDokument12 SeitenCopper Toxicity ChecklistHenia Eden Florin100% (1)
- How To Treat Candida InfectionDokument14 SeitenHow To Treat Candida InfectiondonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNSS Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenPNSS Drug Studyrain peregrinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NootropilDokument2 SeitenNootropilianecunar100% (4)
- Nursing Responsibility Adverse Effects Machanism of Action Drug NameDokument2 SeitenNursing Responsibility Adverse Effects Machanism of Action Drug NameSalwa ZeinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triad Color TestDokument37 SeitenTriad Color TestC.O.M.A research -stopalienabduction-0% (1)
- Humulin RDokument1 SeiteHumulin RZyrah Ziska ZafraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shear and Moment DiagramsDokument38 SeitenShear and Moment DiagramsdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accident Reporting ProcedureDokument2 SeitenAccident Reporting ProcedurebmkallarackalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivf Study D5LRDokument2 SeitenIvf Study D5LRmaria_boyles100% (2)
- AminolebanDokument2 SeitenAminolebanYou know who0% (1)
- Personal SecurityDokument11 SeitenPersonal SecuritydonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivf Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenIvf Drug StudyRyu Bomi0% (2)
- NCP AfDokument3 SeitenNCP AfAngelica Mercado SirotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master in Public Administration (MPA)Dokument106 SeitenMaster in Public Administration (MPA)Mg OoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study MaaloxDokument4 SeitenDrug Study MaaloxJessie Batilo100% (2)
- 1823 - Part - A - DCHB - Kamrup Metropolitan PDFDokument224 Seiten1823 - Part - A - DCHB - Kamrup Metropolitan PDFSaddam FaruqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- IVF Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenIVF Drug StudyHannah Angelu CabadingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassRheegell Ellar-Fuertes100% (3)
- D5WDokument1 SeiteD5WBreena Reubee EstilloreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Sodium BicarbonateDokument2 SeitenDrug Study Sodium BicarbonateSheena Kristine0% (1)
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChlorideDokument4 SeitenCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study Sodium ChloridehahahahaaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D5LRDokument2 SeitenD5LRMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (2)
- Name of Drugs Kaligen 8Dokument2 SeitenName of Drugs Kaligen 8mellany100% (1)
- Ivf Study d5lrDokument2 SeitenIvf Study d5lrryan0% (1)
- d5lr Ivf StudyDokument2 Seitend5lr Ivf Studyjames_delica100% (5)
- Drug Study - D5NSSDokument1 SeiteDrug Study - D5NSSCerie Anne Olay100% (1)
- D5 0.3%Dokument1 SeiteD5 0.3%Aloyan Rose Joy0% (1)
- D5imb IvDokument2 SeitenD5imb IvLegendXNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNSS Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenPNSS Drug Studyabrokenheartedgirl86% (14)
- Discharge Plan For CVADokument1 SeiteDischarge Plan For CVAPhoebe Guevarra100% (2)
- D5NMDokument3 SeitenD5NMjonoelc100% (2)
- Plain LRDokument3 SeitenPlain LRlovlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tia DrugsDokument2 SeitenTia DrugsPorxa MalolosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivf StudyDokument2 SeitenIvf StudyDanePepitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PnssDokument2 SeitenPnssFrances Oscar GaviolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D5LRDokument2 SeitenD5LRjonoelc100% (5)
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDokument1 SeiteDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- D 5 IMBDokument2 SeitenD 5 IMBAloyan Rose JoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)Dokument1 SeiteSilvadene (Silver Sulfadiazine)ENoch keine Bewertungen
- D5LRDokument2 SeitenD5LRLouiseville Ann Arcilla PilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aminoleban Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteAminoleban Drug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- MetronidazoleDokument2 SeitenMetronidazoleJm RomancapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetaminophen (Paracetamol, Tylenol, Tempra, Panadol)Dokument3 SeitenAcetaminophen (Paracetamol, Tylenol, Tempra, Panadol)Jocelyn Rivera0% (1)
- Fluimucil Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenFluimucil Drug StudyDenzel Ivan A. TadusNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALZHEIMER's - Drug Study.Dokument2 SeitenALZHEIMER's - Drug Study.Christian UretaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)Dokument2 SeitenAcetaminophen (Tylenol)amelia hearonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study ProglinDokument2 SeitenDrug Study ProglinChris Denver BancaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chlorhexidine Gluconate 0.2% W/V Mouth Wash: Class: IndicationsDokument3 SeitenChlorhexidine Gluconate 0.2% W/V Mouth Wash: Class: IndicationsAnonymous Bt6favSF4YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthermia NCPDokument2 SeitenHyperthermia NCPMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez0% (1)
- D5IMBDokument1 SeiteD5IMBPrincess Garrote50% (2)
- Senna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeDokument2 SeitenSenna Concentrate: The Medicine at BedtimeTempoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinDokument1 SeiteDRUG ORDER Generic Name: - Ampicillin Brand Name: - AmpicinRadicalRay100% (3)
- CatapresDokument1 SeiteCatapres去約翰Noch keine Bewertungen
- MultivitaminDokument1 SeiteMultivitaminKatie McPeek88% (8)
- NeoblocDokument2 SeitenNeoblocianecunar100% (2)
- Drug Study For FractureDokument4 SeitenDrug Study For FractureitsmeayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atracurium BesylateDokument4 SeitenAtracurium BesylateStill DollNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For FrostbiteDokument2 SeitenNCP For FrostbiteRommar RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- IvfDokument16 SeitenIvfJohnRev Fundal Lopez LorenzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contain Small Particles That That Pass Easily From The Bloodstream To Cells andDokument3 SeitenContain Small Particles That That Pass Easily From The Bloodstream To Cells andMimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Resuscitation NewDokument32 SeitenFluid Resuscitation Newffattimu667Noch keine Bewertungen
- New Format MasterDokument34 SeitenNew Format MasterMuhammad FurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy - SeblewongelDokument47 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte Therapy - SeblewongelSeblewongel AsemeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DKAPPTxDokument34 SeitenDKAPPTxMuhammad FurqanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid & Electrolyte TherapyDokument33 SeitenFluid & Electrolyte Therapyhendra_darmawan_4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids & ElectsDokument61 SeitenFluids & ElectsYousif Ahmed DANoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering (Manual)Dokument6 SeitenSteering (Manual)donlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perations Anual: Project or System NameDokument13 SeitenPerations Anual: Project or System NameViren SehgalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Perfect Tenses Present Perfect Past Perfect Tense Future Perfect TenseDokument1 SeiteTense Perfect Tenses Present Perfect Past Perfect Tense Future Perfect TensedonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials For Septic Tank Using BarrelsDokument2 SeitenMaterials For Septic Tank Using BarrelsdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wheel AlignmentDokument4 SeitenWheel AlignmentdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials For Septic Tank Using BarrelsDokument2 SeitenMaterials For Septic Tank Using BarrelsdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar 1Dokument1 SeiteGrammar 1donlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bring Dead Lead Acid Battery To Live AgainDokument14 SeitenBring Dead Lead Acid Battery To Live AgaindonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Maintenance Section - Non-Turbo - PDF Montero PDFDokument17 Seiten2015 Maintenance Section - Non-Turbo - PDF Montero PDFdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Rebuild An AlternatorDokument29 SeitenHow To Rebuild An AlternatordonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accident Reporting Procedure2Dokument1 SeiteAccident Reporting Procedure2donlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obd CodesDokument2 SeitenObd CodesdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security TemplateDokument89 SeitenSecurity TemplatedonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Richard WagnerDokument2 SeitenRichard Wagnerdonlyn100% (1)
- PhilosophyDokument3 SeitenPhilosophydonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accident Investigation Report Reviews: Health & Safety Committee (Worker Members)Dokument1 SeiteAccident Investigation Report Reviews: Health & Safety Committee (Worker Members)donlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Running CostDokument6 SeitenRunning CostdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Witness Statement FormDokument1 SeiteWitness Statement FormdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accident Investigation ReportDokument1 SeiteAccident Investigation ReportdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrective Action FormDokument1 SeiteCorrective Action FormdonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accident/Incident Investigation: PurposeDokument1 SeiteAccident/Incident Investigation: PurposedonlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Details Received From Collectorate - Excellent Dedicated Work - During Pandemic COVID - 19Dokument2 SeitenDetails Received From Collectorate - Excellent Dedicated Work - During Pandemic COVID - 19Vimal kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Patpka#-Yvxv, : Circuit-Breaker IZMDokument42 Seiten4 Patpka#-Yvxv, : Circuit-Breaker IZMJames IzquierdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BingggDokument12 SeitenBingggZulham YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msds Material Safety Data Sheet For #2 Diesel: of TermsDokument7 SeitenMsds Material Safety Data Sheet For #2 Diesel: of TermsAndrew PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course 1.2: What You Should KnowDokument27 SeitenCourse 1.2: What You Should KnowGeorgios MilitsisNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Village Square Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenA Village Square Lesson PlanShivaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet For NEBNext End Prep Reaction BufferDokument9 SeitenSafety Data Sheet For NEBNext End Prep Reaction BufferNabilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Korean Vocabulary ListttDokument31 SeitenKorean Vocabulary ListttAireeneMhaePanenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ept, PoDokument2 SeitenEpt, PoStacieNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To PrescribingDokument12 SeitenAn Introduction To PrescribingNelly AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM - CompleteDokument12 SeitenHRM - Completedhou_4Noch keine Bewertungen
- BTEC - Assignment - Brief A2 Unit 21 2Dokument3 SeitenBTEC - Assignment - Brief A2 Unit 21 2Dariusz LangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PreviewpdfDokument62 SeitenPreviewpdfImtiazAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Albumin CPDokument4 SeitenAlbumin CPLAB. GATOT SUBROTONoch keine Bewertungen
- Cannistra 2007Dokument4 SeitenCannistra 2007amdreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purpose 1Dokument4 SeitenPurpose 1Rizzah MagnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shofa Aji Setyoko (N101 12 051)Dokument4 SeitenShofa Aji Setyoko (N101 12 051)ShofaajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sonographic Evaluation of The DiaphragmDokument1 SeiteSonographic Evaluation of The DiaphragmAngelo LongoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Business Model Canvas v1.1.8 A2Dokument1 SeitePersonal Business Model Canvas v1.1.8 A2Laura Natalia SalcedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 State of The StateDokument26 Seiten2018 State of The StateRuss LatinoNoch keine Bewertungen