Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nursing Care Plan Community Acquired Pneumonia
Hochgeladen von
deric92%(50)92% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (50 Abstimmungen)
83K Ansichten2 SeitenA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Community Acquired Pneumonia.
Originaltitel
NursingCrib.com Nursing Care Plan Community Acquired Pneumonia
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Community Acquired Pneumonia.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
92%(50)92% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (50 Abstimmungen)
83K Ansichten2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Community Acquired Pneumonia
Hochgeladen von
dericA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Community Acquired Pneumonia.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
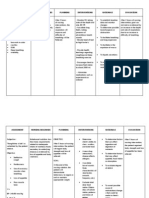
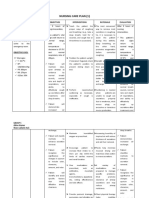
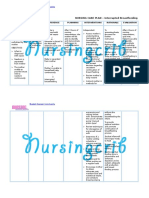
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Independent:
Subjective: Acute pain r/t • Pneumonia is • After 4 hours • Elevate head of • Lowers • After 4
localized of nursing the bed, change diaphragm, hours of
“Masakit ang inflammation and
inflammation
interventions position promoting nursing
dibdib ko” as persistent cough. of the terminal , the patient frequently. chest intervention
verbalized by airways and will display expansion s, the
patient. alveoli caused patent and patient was
by acute airway with expectoration able to
Objective: breath of secretions. display
infection by
sounds • Assist patient • Deep patent
• Use of various clearing and with deep breathing airway with
accessory agents. absence of breathing facilitates breath
muscle. Pneumonia dyspnea. exercises. maximum sounds
can be divided expansion of clearing and
• Dyspnea into three the lungs and absence of
smaller dyspnea.
groups:
• Fatigue. airways.
community • Demonstrate or • Coughing is a
• V/S taken as acquired, help patient natural self
follows: hospital or learn to perform cleaning
nursing home activity like mechanism.
T: 37.3 acquired splinting chest Splinting
P: 80 and effective reduces chest
(nosocomial), coughing while discomfort,
R: 25
Bp: 120/80 and in upright and an upright
pneumonia in position. position favors
an deeper, more
immunocompr forceful cough
effort.
omised
• Force fluids to at • Fluids
person. least 3000 ml especially
Causes per day and offer warm liquids
include warm, rather aid in
bacteria than cold fluids. mobilization
(Streptococcu and
expectoration
s,
of secretions.
Staphylococcu
s,
Haemophilus Collaborative:
influenzae, • Administer • Aids in
medications as reduction of
Klebsiella,
prescribe: bronchospas
Legionella). mucolytics or m and
Community expectorants. mobilization of
Acquired secretions.
Pneumonia • Provide • Fluids are
(CAD) is a supplemental required to
fluids. replace losses
disease in and aid in
which mobilization of
individuals secretions.
who have not
recently been
hospitalized
develop an
infection of the
lungs. It is an
acute
inflammatory
condition
that’s result
from
aspiration of
oropharyngeal
secretions or
stomach
contents in the
lungs.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Cap NCPDokument2 SeitenCap NCPkyshb100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan - CAP-MRDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan - CAP-MRCarmela Mabel Ansay Principe100% (3)
- NCP PcapDokument2 SeitenNCP PcapGacutan Jonathan88% (25)
- NCP PneumoniaDokument2 SeitenNCP Pneumonia_garonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cap NCPDokument6 SeitenCap NCPMarlo Parayno100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceKenj Pereña100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- NCP PCAP CDokument4 SeitenNCP PCAP CRio Bonifacio100% (2)
- NCP For Community Acquired PnuemoniaDokument7 SeitenNCP For Community Acquired PnuemoniaAshley Gaton Alindogan100% (1)
- Pcap PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenPcap PathophysiologyAko Gle C Mariz80% (10)
- Pneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument2 SeitenPneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceNursesLabs.com86% (7)
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDokument1 SeiteNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeLaidy Aizahlyn Indoc Angod0% (3)
- Assessing and Treating a Child with CroupDokument4 SeitenAssessing and Treating a Child with CroupChristian Paul Reyes100% (1)
- SAMPLE NCP For PneumoniaDokument3 SeitenSAMPLE NCP For Pneumoniakana_mercado100% (6)
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPAbegail Abaygar100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for PneumoniaDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan for PneumoniaJazzmin Angel ComalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis and Interventions for Impaired Gas Exchange and Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument4 SeitenNursing Diagnosis and Interventions for Impaired Gas Exchange and Ineffective Airway ClearanceKen Simon100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For PcapDokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plan For PcapMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumonia NCPDokument7 SeitenPneumonia NCPitsmeaya100% (3)
- Risk For Infection Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDokument1 SeiteRisk For Infection Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_sane100% (1)
- Pneumonia NCPDokument5 SeitenPneumonia NCPElbert Aquitania Mutuc RN100% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaDokument5 SeitenNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaKullin Rain100% (1)
- Discharge Plan For PneumoniaDokument1 SeiteDischarge Plan For PneumoniaSaf Tanggo Diampuan0% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument2 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearancemichelle_010379Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For PneumoniaDokument3 SeitenNCP For PneumoniaKahMallari100% (10)
- Final Case Study PCAPDokument71 SeitenFinal Case Study PCAPGabriel Lorenz S. ParongNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument4 SeitenNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceMary Joyce Limoico100% (1)
- Benign Febrile ConvulsionDokument9 SeitenBenign Febrile ConvulsionRoxanne Mae Marcelo BadongenNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For PCAPCDokument6 SeitenNCP For PCAPCEnrique Lu100% (1)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaDokument2 SeitenNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaAdrian Mallar100% (6)
- NCP For AsthmaDokument1 SeiteNCP For AsthmaMelvin Martinez100% (1)
- Goal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionDokument4 SeitenGoal:: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Cumulation of SecretionWyen CabatbatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pcap PathoDokument2 SeitenPcap PathoDiana Jean Abad Dacumos69% (13)
- Nursing Care Plan For InflammationDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For InflammationJobelle AcenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan CoughDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Coughderic90% (89)
- Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Bronchial Asthmaderic93% (60)
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPUgalde AlyssakyleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student NurseDokument2 SeitenStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Dokument6 SeitenNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Karissa GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difficulty Breathing Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenDifficulty Breathing Nursing Care PlanOPERAñA ELLAYZA RB DECANONoch keine Bewertungen
- Santillaruby NCPDokument3 SeitenSantillaruby NCPRuby SantillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On CAPDokument4 SeitenCase Study On CAPjcarysuitosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Assessment and Plan for Pneumonia PatientDokument9 SeitenNursing Assessment and Plan for Pneumonia PatientKen IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - CopdDokument3 SeitenNCP - CopdhystericoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDokument2 SeitenIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - CapDokument2 SeitenNCP - CapbercoaprilgraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP of PnuemoniaDokument13 SeitenNCP of PnuemoniaFrando kenneth100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Improving Airway Clearance (40 charactersDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Improving Airway Clearance (40 charactersAkira A. AtomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisAkira A. AtomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Effective Airway ClearanceDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Effective Airway ClearanceAnnahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Airway ClearanceDokument8 SeitenImproving Airway ClearanceNikael Patun-ogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessm ENT Nursing Diagnos IS Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluati ON Subjectiv eDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Assessm ENT Nursing Diagnos IS Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluati ON Subjectiv eJ. TSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Dokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)deric95% (41)
- Nursing Care Plans: Republic of The Philippines University of Northern Philippines Tamag, Vigan City 2700 Ilocos SurDokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plans: Republic of The Philippines University of Northern Philippines Tamag, Vigan City 2700 Ilocos SurNo EulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As VerbalizedDokument2 SeitenAssessment Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalizedmayla_jordan3666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Asthma Attack Nursing Care Plan for Married Female PatientDokument5 SeitenAsthma Attack Nursing Care Plan for Married Female PatientMarivic Yuson MalagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Background Knowledge Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument4 SeitenAssessment Background Knowledge Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apis Mellifica; or, The Poison of the Honey-Bee, Considered as a Therapeutic AgentVon EverandApis Mellifica; or, The Poison of the Honey-Bee, Considered as a Therapeutic AgentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPderic79% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic71% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPDokument14 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (23)
- Proposal Anguria Pasta NewDokument24 SeitenProposal Anguria Pasta NewNOOR IRDINA HAFIZAH BT TAUPISNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Analysis and Financial Projections for Gerbera Cultivation ProjectDokument26 SeitenCost Analysis and Financial Projections for Gerbera Cultivation ProjectshroffhardikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canon imageFORMULA DR-X10CDokument208 SeitenCanon imageFORMULA DR-X10CYury KobzarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1989 GMC Light Duty Truck Fuel and Emissions Including Driveability PDFDokument274 Seiten1989 GMC Light Duty Truck Fuel and Emissions Including Driveability PDFRobert Klitzing100% (1)
- Progibb LV Plus PGR - Low Voc FormulationDokument2 SeitenProgibb LV Plus PGR - Low Voc FormulationDodik Novie PurwantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sibuyan Island ResiliencyDokument12 SeitenSibuyan Island ResiliencyEndangeredSpeciesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is.4162.1.1985 Graduated PipettesDokument23 SeitenIs.4162.1.1985 Graduated PipettesBala MuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Note Taker Saves Time With Air WritingDokument17 SeitenSmart Note Taker Saves Time With Air WritingNagarjuna LokkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjoint Analysis Basic PrincipleDokument16 SeitenConjoint Analysis Basic PrinciplePAglu JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Binder 2Dokument23 SeitenProject Binder 2Singh DhirendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 - Energy Transfers: I) Answer The FollowingDokument3 SeitenChapter 16 - Energy Transfers: I) Answer The FollowingPauline Kezia P Gr 6 B1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Monster of The Week Tome of Mysteries PlaybooksDokument10 SeitenMonster of The Week Tome of Mysteries PlaybooksHyperLanceite XNoch keine Bewertungen
- DENSO COMMON RAIL INJECTOR REPAIR GUIDEDokument22 SeitenDENSO COMMON RAIL INJECTOR REPAIR GUIDEMarcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oecumenius’ Exegetical Method in His Commentary on the RevelationDokument10 SeitenOecumenius’ Exegetical Method in His Commentary on the RevelationMichał WojciechowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic First AidDokument31 SeitenBasic First AidMark Anthony MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sattvik Brochure - Web VersionDokument4 SeitenSattvik Brochure - Web Versionudiptya_papai2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- GLOBAL Hydro Turbine Folder enDokument4 SeitenGLOBAL Hydro Turbine Folder enGogyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasonic Weld Examination ProcedureDokument16 SeitenUltrasonic Weld Examination ProcedureramalingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet PDFDokument6 SeitenDatasheet PDFAhmed ElShoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Brewing Log Sheet PDFDokument2 SeitenHome Brewing Log Sheet PDFStefanita0% (1)
- ML AiDokument2 SeitenML AiSUYASH SHARTHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Sradham ChecklistDokument9 SeitenSradham ChecklistpswaminathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSC 405 Grant ProposalDokument23 SeitenHSC 405 Grant Proposalapi-355220460100% (2)
- APLICACIONES PARA AUTOS Y CARGA LIVIANADokument50 SeitenAPLICACIONES PARA AUTOS Y CARGA LIVIANApancho50% (2)
- Activities and Assessments:: ASSIGNMENT (SUBMIT Your Answers at EDMODO Assignment Section)Dokument5 SeitenActivities and Assessments:: ASSIGNMENT (SUBMIT Your Answers at EDMODO Assignment Section)Quen CuestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Placenta Previa Case Study: Adefuin, Jay Rovillos, Noemie MDokument40 SeitenPlacenta Previa Case Study: Adefuin, Jay Rovillos, Noemie MMikes CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundermax Exterior Technic 2011gb WebDokument88 SeitenFundermax Exterior Technic 2011gb WebarchpavlovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Implementation: Name: Rasheed Campbell School: Kingston College Candidate #.: Centre #: 100057Dokument12 SeitenChemistry Implementation: Name: Rasheed Campbell School: Kingston College Candidate #.: Centre #: 100057john brownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokument24 SeitenPeptic Ulcer Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentOktaviana Sari Dewi100% (1)
- Essentials For Professionals: Road Surveys Using SmartphonesDokument25 SeitenEssentials For Professionals: Road Surveys Using SmartphonesDoly ManurungNoch keine Bewertungen