Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Economics - Elasticity of Demand and Supply
Hochgeladen von
Nadine BacalangcoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Economics - Elasticity of Demand and Supply
Hochgeladen von
Nadine BacalangcoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
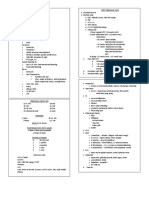
Elasticity - the responsiveness if demand/supply to a change in its determinants Price Elasticity - the percentage change in quantity compared to a percentage
change in price Coefficient Elasticity - absolute value of elasticity Total Revenue - price multiplied by quantity Inferior Goods - goods which are bought when income levels are low, the demand for which tends to decrease when income increases Normal Goods - goods for which demand tends to increase when income increases Substitute Goods - goods used in place of each other Complementary Good - goods that supplement each other and are, therefore used together PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
Is measured by dividing the percentage change in quantity demanded by the percentage in price It has 2 measures Arc Elasticity - the coefficient of price elasticity of demand between two points along the demand curve Point Elasticity - the coefficient of price elasticity of demand at one point along the demand curve
INCOME ELASTICITY DEMAND percentage change in quantity demanded compared to the percentage change income The absolute value of the coefficient of income elasticity is also a measure of how responsive demand is to change in income. As income increases the coefficient of: > 1 means demand is ELASTIC and the good is SUPERIOR < 1 means demand is INELASTIC and the good is INFERIOR = 1 means demand is UNITARY and the good is NORMAL CROSS ELASTICITY OF DEMAND The percentage change in quantity demanded of one good compared to the percentage change in the price of a related good As a result if tue difference degrees of elasticity, there are different ways of presenting the demand curve D is relatively elastic, a change in price leads to significant change in quantity demanded
D is relatively inelastic, a change in price leads to a very slight change in quantity demanded
D is perfectly elastic. At a given price quantity demanded can change infinitely
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Laboratory Slides Book Slides Description: Polycythemia VeraDokument7 SeitenLaboratory Slides Book Slides Description: Polycythemia VeraNadine BacalangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- History First Prenatal VisitDokument8 SeitenHistory First Prenatal VisitNadine BacalangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal CyanosisDokument13 SeitenNeonatal CyanosisNadine BacalangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthyroidism: by CC Nadine BacalangcoDokument2 SeitenHyperthyroidism: by CC Nadine BacalangcoNadine BacalangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAH COD COH: Adventist University of The PhilippinesDokument1 SeiteCAH COD COH: Adventist University of The PhilippinesNadine BacalangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetric Hemorrhage: by CC Nadine D. BacalangcoDokument87 SeitenObstetric Hemorrhage: by CC Nadine D. BacalangcoNadine BacalangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developmental HistoryDokument1 SeiteDevelopmental HistoryNadine BacalangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDokument8 SeitenCell and Molecular BiologyNadine BacalangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Proof of ReincarnationDokument28 SeitenScientific Proof of ReincarnationNadine Bacalangco100% (4)
- Alpha Adrenergic BlockersDokument7 SeitenAlpha Adrenergic BlockersNadine BacalangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aromatic CompoundsDokument55 SeitenAromatic CompoundsNadine Bacalangco100% (1)
- CoevolutionDokument24 SeitenCoevolutionNadine BacalangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tito's Research EditedDokument44 SeitenTito's Research EditedNadine BacalangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)