Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 8 Endocrine System
Hochgeladen von
Shalu SuntariOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 8 Endocrine System
Hochgeladen von
Shalu SuntariCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DHC 203
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Learning Objectives
At the end of the class the students are able to:-
1.
2. 3.
Define hormone
Explain briefly the role of the hypothalamus in controlling the endocrine system List the hormones produced by the endocrine glands and discuss their functions
4.
Describe the roles of insulin and glucagon in maintaining normal blood glucose levels
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Introduction
Endocrine system is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones to maintain the bodys internal environment within normal range
Consists of ductless glands
The hormones are released into the bloodstream and may affect one or several organs throughout the body.
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
HORMONES
Hormones are chemical messanger produced by the endocrine glands and secreted directly into the bloodstream Hormones only influence a cell with the correct receptor site By binding to receptors, hormones trigger various responses in the tissues containing the receptors.
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
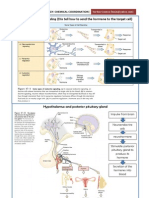
Hypothalamus
located in the lower central part of the brain hypothalamus is responsible for regulating the release of hormones from the pituitary gland It also synthesizes hormones which will be stored in the posterior pituitary gland (ADH & Oxytocin).
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
LOCATION OF THE HYPOTHALAMUS AND PITUITARY GLAND
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Pituitary Gland
located at the base of the brain just beneath the hypothalamus also called as "master gland" because it secrete hormones that control several other endocrine glands - Divided into 2 lobes: - Anterior pituitary lobe
- Posterior pituitary lobe
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Pituitary Gland
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Anterior Pituitary Gland
Hormones released: 1. Growth hormone (GH) 2. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) 3. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) 4. Prolactin 5. Follicle- stimulating hormone (FSH) 6. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
10
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Anterior Pituitary Gland
Hormone
GH ACTH TSH FSH
Function - Regulates metabolism, promotes tissue growth of bones & muscles - Stimulates adrenal cortex to secrete cortisol - Stimulates thyroid gland to produce its hormone
- Stimulates maturation of ovarian follicles and sperm cell production LH - Stimulates ovulation and progesterone production - Helps maintain pregnancy Prolactin - Stimulates milk production in mammary glands
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
11
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Posterior Pituitary Gland
- Does not synthesizes hormones. - Posterior pituitary stores and releases: - oxytocin - causes contraction of the
smooth muscle of the uterus
- antidiuretic hormone (ADH)- promotes water retention. Thus, less urine excreted
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
12
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Hormones of the Pituitary Gland
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
13
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Pineal Gland
attached to the upper part of the thalamus Secretes 2 hormones Melatonin inhibit the growth of sex orgns before puberty Serotonin - acts as neurotransmitter and vasoconstrictor
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
14
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Tyroid Gland
lies in the anterior neck just below the larynyx.
Two lobes, located on either side of the trachea, connected isthmus.
Produce 3 hormones
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Thyroxine (T4) Calcitonin- lowers the amount of calcium in the blood. T3 & T4 regulates metabolism (carbohydrates, fats proteins), increases the basal metabolic rate and heat production
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 15
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Tyroid Gland
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
16
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Paratyroid Gland
pea-shaped glands that located in the neck near the thyroid 4 small parathyroid glands It produces parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Increase the level of
calcium in blood
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
17
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Tymus Gland
lies behind the sternum
Secretes the hormone THYMOSIN Required for the development of immune system
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
18
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
19
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Adrenal Glands
2 small glands that on top of both kidneys Made up of the adrenal medulla (inner part) and the adrenal cortex (outer part)
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
20
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Adrenal Glands (contd)
Adrenal medulla secretes two hormones : Adrenaline Noradrenaline Both involved in immediate response to stress (fight or flight response) by: increasing heart rate & blood pressure
diverting blood to essential organs
Increases metabolic rate
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 21
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Adrenal Glands (contd)
- Adrenal cortex produces 3 types of hormones: 1. Glucocorticoids
2. Mineralocorticoids
3. Androgens (male sex hormones
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
22
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Pancreas
Has both endocrine and exocrine functions Pancreatic hormones are secreted by cells known as the islets of Langerhans (pancreatic islets) - 3 main types of cells in the islets of Langerhans:
- (Alpha) cells: glucagon
- (Beta) cells: insulin - (Delta) cells: somatostatin
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 23
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Pancreas
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
24
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Pancreas
Hormone Function
Insulin Glucagon
Lowers blood glucose levels Elevate blood glucose levels
Somatostatin
Inhibits secretion of insulin and glucagon
25
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
The Reproductive Glands
Comprise of the testes in males and ovaries in females OVARY TESTIS
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
26
WINDFIELD INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED SCIENCES
Hormone Testosterone
Function Development of male reproductive structures and secondary male sexual characteristics
Estrogen Progesterone
Development of female reproductive structures and secondary female sexual characteristic
DHC 203 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
27
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Caroline Myss, Norm Shealy - The Science of Medical Intuition-WorkBookDokument88 SeitenCaroline Myss, Norm Shealy - The Science of Medical Intuition-WorkBookCristian Catalina100% (2)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Hormonal Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismDokument11 SeitenHormonal Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismpuchioNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Endocrine GlandsDokument9 SeitenEndocrine Glandstadashii100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology For Emergency Care, 3e Bryan Bledsoe, Frederic Martini, Edwin BartholomewDokument48 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology For Emergency Care, 3e Bryan Bledsoe, Frederic Martini, Edwin BartholomewDing BoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapt10 - PPT Endocrine SystemDokument57 SeitenChapt10 - PPT Endocrine SystemBtaman Rock100% (1)
- Nervous & Endocrine Systems Maintain HomeostasisDokument4 SeitenNervous & Endocrine Systems Maintain Homeostasismaricar relatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry of HormoneDokument58 SeitenBiochemistry of HormoneSofi Nur FitriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ninja Nerd Science & MedicineDokument3 SeitenNinja Nerd Science & MedicineG-cell at Work33% (24)
- Lesson Plan EndocrineDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan Endocrineelrasc0685% (13)
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDokument8 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerBeverly DatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 115 - Anitha Sundrum - STUDENTS - PERCEPTION ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF TEAMWORK BASED ACTIVITIES IN ENHANCING THE LEARNING PROCESS PDFDokument9 Seiten115 - Anitha Sundrum - STUDENTS - PERCEPTION ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF TEAMWORK BASED ACTIVITIES IN ENHANCING THE LEARNING PROCESS PDFShalu SuntariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Body As A Whole Done (Autosaved)Dokument36 SeitenChapter 1 Body As A Whole Done (Autosaved)Shalu SuntariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Transaction For Internet Banking and Its Perception To Malaysian Online CustomersDokument12 SeitenElectronic Transaction For Internet Banking and Its Perception To Malaysian Online CustomersShalu SuntariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multicultural EducationDokument8 SeitenMulticultural EducationNurul Afifah Zainal AbidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 MathsDokument3 SeitenForm 2 MathsSharmila SathiaselanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sains (Kertas 2) PMR PerakDokument17 SeitenSains (Kertas 2) PMR PerakShalu SuntariNoch keine Bewertungen
- NguyenThanh - Tung Full SurveyDokument54 SeitenNguyenThanh - Tung Full SurveyShalu SuntariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 01Dokument4 SeitenChap 01Jamaliah Daud76% (33)
- Relationship between employer branding, attraction & productivityDokument13 SeitenRelationship between employer branding, attraction & productivityShalu SuntariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic ManagementDokument20 SeitenStrategic ManagementShalu Suntari67% (3)
- Case Study of Pepsi Co IncDokument14 SeitenCase Study of Pepsi Co IncShalu SuntariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chinese Herbs That Impact HormonesDokument7 SeitenChinese Herbs That Impact HormonesnepretipNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10bio AssignmentDokument4 Seiten10bio AssignmentKrishna GovilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11b. For Students Animal Form and FunctionDokument71 Seiten11b. For Students Animal Form and FunctionAlessiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HomeostasisDokument21 SeitenHomeostasisapi-294162496Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemical Coordination SummaryDokument7 SeitenThe Chemical Coordination SummaryTee Bio-ScienceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehensive Stress Management 13th Edition Greenberg Test BankDokument45 SeitenComprehensive Stress Management 13th Edition Greenberg Test BankJacquelineSinghwoad100% (12)
- Endocrine Glands & Their Functions: Anatomy & Physiology II Georgia Perimeter College K. Donaldson, InstructorDokument55 SeitenEndocrine Glands & Their Functions: Anatomy & Physiology II Georgia Perimeter College K. Donaldson, InstructorIsaacJ22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDokument25 SeitenEndocrine System Feedback SystemsEthan Miles VigilanciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study on Managing Type 2 Diabetes and DyslipidemiaDokument46 SeitenCase Study on Managing Type 2 Diabetes and DyslipidemiaMary Angelique BanogonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicinal Chemistry Receptors and MessengersDokument41 SeitenMedicinal Chemistry Receptors and MessengersMehak SarfrazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Odisha PG Zoology SyllabusDokument35 SeitenOdisha PG Zoology SyllabusThe IdyllicxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q3 Science 3 10 Bow Sy 2023 2024Dokument24 SeitenQ3 Science 3 10 Bow Sy 2023 2024marife gupaalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual Variation in Body Odor FactorsDokument14 SeitenIndividual Variation in Body Odor FactorsHisshanthini NavarethinarasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasite DetoxDokument42 SeitenParasite Detoxedurodica7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Endocrinology LectureDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To Endocrinology LectureRhaymark ParraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BB Training Tests Med Physiology 2nd Sem - Answ 120 OrderDokument19 SeitenBB Training Tests Med Physiology 2nd Sem - Answ 120 OrderGandam SwadeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- What proteins do and their 9 important functionsDokument11 SeitenWhat proteins do and their 9 important functionsmuhammad aslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System ReviewDokument18 SeitenEndocrine System ReviewJessa SuacitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atar Notes Endorcine SystemDokument12 SeitenAtar Notes Endorcine Systembella.wenman6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus First Year BNYS Course Duration-12 MonthsDokument22 SeitenSyllabus First Year BNYS Course Duration-12 MonthsShubham PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen