Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
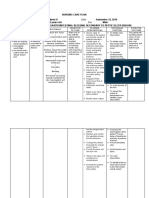
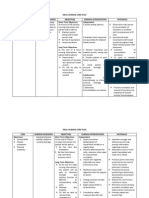
Nursing Care Plan For Inguinal Hernia
Hochgeladen von
Yvonne Joyce Gayagoy GomezOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing Care Plan For Inguinal Hernia
Hochgeladen von
Yvonne Joyce Gayagoy GomezCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing Care Plan for Inguinal Hernia .
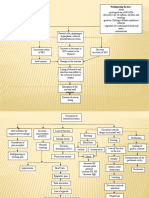
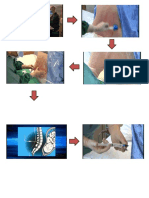
Hernia is a protrusion or projection of an organ ororgan part through an abnormal opening in the containing wall of its cavity, a hernia results. Aninguinal hernia occurs when the omentum, the large or small intestine, or the bladder protrudesinto the inguinal canal. In an indirect inguinal hernia, the sac protrudes through the internalinguinal ring into the inguinal canal and, in males, may descend into the scrotum. In a directinguinal hernia, the hernial sac projects through a weakness in the abdominal wall in the area of the rectus abdominal muscle and inguinal ligament. Strangulated, if part of the herniated intestine becomes twisted or edematous and causingserious complications, possibly resulting in intestinal obstruction and necrosis.Inguinal hernias can be direct which is herniation through an area of muscle weakness, in theinguinal canal, and inguinal hernias indirect herniation through the inguinal ring. Indirecthernias, the more common form, can develop at any age but are especially prevalent in infantsyounger than age 1. This form is three times more common in males. Causes for Inguinal Hernia An inguinal hernia is the result of either a congenital weakening of the abdominal wall, traumaticinjury, aging, weakened abdominal muscles because of pregnancy, or from increased intra-abdominal pressure (due to heavy lifting, exertion, obesity, excessive coughing, or straining withdefecation).Inguinal hernia is a common congenital malformation that may occur in males during the seventhmonth of gestation. Normally, at this time, the testicle descends into the scrotum, preceded bythe peritoneal sac. If the sac closes improperly, it leaves an opening through which the intestinecan slip, causing a hernia.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Von EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study AppendicitisDokument6 SeitenCase Study AppendicitisPrincess Camille ArceoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Dokument34 SeitenOsteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Angelic khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDokument2 SeitenScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Posterior Mold: PurposeDokument3 SeitenPosterior Mold: PurposeSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical Management For Cryptorchidism With Nursing ManagementsDokument4 SeitenSurgical Management For Cryptorchidism With Nursing ManagementsAprille Claire MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP FeuDokument2 SeitenNCP FeuFejlean Angelica AntineoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Ugib Lower MBDokument65 SeitenCase Study Ugib Lower MBQuolette Constante100% (1)
- COMMUNITY-MANUSCRIPT SampleDokument84 SeitenCOMMUNITY-MANUSCRIPT SampleCA SavageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fistula NCPDokument1 SeiteFistula NCPHasna LisnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 51 100Dokument18 Seiten51 100Jaessa Feliciano100% (1)
- AB Critical Thinking ExercisesDokument4 SeitenAB Critical Thinking ExercisesAhmad BaolayyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ampicillin Sodium (Polypen)Dokument3 SeitenAmpicillin Sodium (Polypen)Charlene Serino JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology VolvulusDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology VolvulusHyacinth Bueser Bondad0% (2)
- Stomach CancerDokument7 SeitenStomach CancerSyazmin KhairuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study On Mild Compression Deformity L1Dokument25 SeitenA Case Study On Mild Compression Deformity L1JM UncianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Reduction and Preparedness Equipment ProtectDokument2 SeitenRisk Reduction and Preparedness Equipment ProtectR ArcegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 8 - Activity (Case Scenario)Dokument7 SeitenWeek 8 - Activity (Case Scenario)Jollan Marie BuenvenidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HNP Case Scenario For Case StudyDokument2 SeitenHNP Case Scenario For Case StudyDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study NCP ActualDokument3 SeitenCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryJobelle AcenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP. MOuth SoreDokument1 SeiteNCP. MOuth SoreChriszanie CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Fluid Volume DeficitDokument3 SeitenNCP Fluid Volume DeficitNecheal BaayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Pedia WardDokument2 SeitenDrug Study Pedia WardCayanne ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology AppendicitisDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology AppendicitisIra Krystel ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Appendicitis33342Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis For AppendicitisDokument1 SeiteNursing Diagnosis For AppendicitisTweenie DalumpinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 4 - MEDSURG - Cellular AberrationDokument10 SeitenWEEK 4 - MEDSURG - Cellular AberrationLeslie CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- SildenafilDokument2 SeitenSildenafilSheryl Ann PedinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDokument5 SeitenSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Final PortraitDokument11 SeitenCase Study Final PortraitZhy CaluzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument4 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjomsportg0% (1)
- Bpud, PathoDokument2 SeitenBpud, PathoSheng GosepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Nursing Care Plan: Group A3 - ObDokument4 SeitenFamily Nursing Care Plan: Group A3 - ObErika CadawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Skin IntegityDokument3 SeitenNCP Skin Integityclydell joyce masiarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ClubfootDokument22 SeitenClubfootJhong Xyrus100% (3)
- NCP Background, Demographic Data, Dordon's Functional Health, Drug Study SAint Louis UniversityDokument21 SeitenNCP Background, Demographic Data, Dordon's Functional Health, Drug Study SAint Louis Universitypa3kmedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsDokument33 SeitenDoxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsBibek Singh Mahat100% (2)
- Drug Study - Epidural AnesthesiaDokument5 SeitenDrug Study - Epidural AnesthesiaMarie PotayreNoch keine Bewertungen
- JRMMC - Patho of Ruptured AppendicitisDokument3 SeitenJRMMC - Patho of Ruptured Appendicitis9632141475963Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medications To Continue at Home Exercise Treatments Health Teachings Outpatient Diet Sexuality/ SpiritualityDokument2 SeitenMedications To Continue at Home Exercise Treatments Health Teachings Outpatient Diet Sexuality/ SpiritualityMae EstilloreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaDokument10 SeitenPathophysiology of Transitional Cell CarcinomaJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISDokument2 SeitenNCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISMaria Imogen MilambilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeDokument2 SeitenTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeMiar QuestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy MalaiseDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy Malaise06eltianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsDokument3 SeitenImpaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsKat AlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predisposing Factors Age Diet Dehydration Precipitating Factors Family or Personal History Digestive Diseases and SurgeryDokument2 SeitenPredisposing Factors Age Diet Dehydration Precipitating Factors Family or Personal History Digestive Diseases and SurgeryChloé Jane HilarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Acute AppendicitisDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Acute AppendicitissiarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Colon Cancer Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating Factors: Precipitating FactorsDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Colon Cancer Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating Factors: Precipitating FactorstatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeDokument4 SeitenTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeMiar QuestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDokument5 SeitenAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ov Ov OvDokument15 SeitenOv Ov OvHayyana Mae Taguba LadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final NCP LeptospirosisDokument6 SeitenFinal NCP LeptospirosisKeith Austin100% (1)
- Republic ActDokument36 SeitenRepublic ActjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TAHBSO ReportDokument4 SeitenTAHBSO ReportsachiiMeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity IntoleranceDokument6 SeitenActivity IntoleranceRaidis PangilinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map - Colon CancerDokument2 SeitenConcept Map - Colon Cancerbea pegadNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument10 SeitenNCPbabycheska08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Actual NCPDokument2 SeitenActual NCPbaki0146Noch keine Bewertungen
- HerniaDokument6 SeitenHerniaHirya jamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada Kasus Di Puskesmas Ii KartasuraDokument15 SeitenPenatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada Kasus Di Puskesmas Ii KartasuraDimas HikamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evropski Univerzitet "Kallos" Fakultet Zdravstvenih Nauka Sestrinstvo Predmet: HirurgijaDokument24 SeitenEvropski Univerzitet "Kallos" Fakultet Zdravstvenih Nauka Sestrinstvo Predmet: HirurgijaEnisaBilalicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan PoliDokument16 SeitenLaporan PoliFathya AbadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lichtenstein or Darn Procedure in Inguinal Hernia Repair: A Prospective Randomized Comparative StudyDokument5 SeitenLichtenstein or Darn Procedure in Inguinal Hernia Repair: A Prospective Randomized Comparative StudyFikri AlfarisyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Eponymous Types of HerniaDokument3 SeitenDifferent Eponymous Types of HerniaNizam Mischievous'Lovely Schremo BoyysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Myofascial Trigger Points - Pathophysiology and Evidence-Informed Diagnosis and Management (Contemporary Issues in Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Medicine) (PDFDrive)Dokument306 SeitenMyofascial Trigger Points - Pathophysiology and Evidence-Informed Diagnosis and Management (Contemporary Issues in Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Medicine) (PDFDrive)Christine DiVirgilioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonus - Trigger Points ChartDokument6 SeitenBonus - Trigger Points ChartFaisal Madjid100% (1)
- محمد كارمDokument17 Seitenمحمد كارمmohammed ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- HerniaDokument61 SeitenHerniaAhmed HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HERNIAS in PaediatricsDokument27 SeitenHERNIAS in PaediatricsHugh JacobsNoch keine Bewertungen
- List Dokter Muda Penanggung Jawab Topik IlmiahDokument3 SeitenList Dokter Muda Penanggung Jawab Topik IlmiahYonathanWaisendiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EfusiDokument33 SeitenEfusiPut R MikatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absen Pembacaan Telaah Jurnal Suci RamadhaniDokument2 SeitenAbsen Pembacaan Telaah Jurnal Suci Ramadhanisuci ramadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- DafpusDokument1 SeiteDafpusFitki SuyitnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hernia - SaratogaDokument21 SeitenHernia - SaratogaIndahPurwaningrum100% (1)
- Dr. Ibrahim Bashayreh RN, PHDDokument16 SeitenDr. Ibrahim Bashayreh RN, PHDEndy DestriawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Hernia: (CITATION Amr15 /L 1057)Dokument3 SeitenClassification of Hernia: (CITATION Amr15 /L 1057)dianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal HerniaDokument2 SeitenAbdominal HerniaMichael BoadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- List Pasien Onkologi 05 Agustus 2020: No Identitas Ruan GAN Diagnosa Pemeriksaan Penunjang RencanaDokument2 SeitenList Pasien Onkologi 05 Agustus 2020: No Identitas Ruan GAN Diagnosa Pemeriksaan Penunjang RencanaWahyu IndraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fsurg 01 00020Dokument5 SeitenFsurg 01 00020Ratu AstridNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karakteristik Hernia Inguinalis Di Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah Dr. Pirngadi Medan Tahun 2016Dokument4 SeitenKarakteristik Hernia Inguinalis Di Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah Dr. Pirngadi Medan Tahun 2016Anonymous o7y9x3lGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rekapitulasi Pasien Bedah Januari 2023Dokument18 SeitenRekapitulasi Pasien Bedah Januari 2023lastriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amasi Broucher-Final On 5th Aug 2023Dokument4 SeitenAmasi Broucher-Final On 5th Aug 2023Shaswata SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Februari 2019Dokument45 SeitenLaporan Februari 2019dillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Operasi HerniotomiDokument4 SeitenLaporan Operasi HerniotomiGalihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inguinal Hernia EpidemiologyDokument5 SeitenInguinal Hernia Epidemiologymelon segerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hernia World Conference ProgramDokument112 SeitenHernia World Conference ProgramYovan Prakosa100% (1)
- Hernia NotesDokument2 SeitenHernia NotesEdaManatadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 105-Article Text-258-2-10-20181016Dokument6 Seiten105-Article Text-258-2-10-20181016Aris SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Askes 2014Dokument276 SeitenAskes 2014Tenrisa'na RifaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (24)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (80)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (9)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningVon EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (328)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeVon EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (253)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerVon EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (392)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsVon EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (169)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceVon EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (51)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyVon EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosVon Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (207)