Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Optical Mineralogy - Sample Exam 1
Hochgeladen von
Zarina AdilbekovaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Optical Mineralogy - Sample Exam 1
Hochgeladen von
Zarina AdilbekovaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Optical Mineralogy First Lecture Exam Closed Book
Name: Score (dont write below)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 - bonus Total w/o bonus Total w. bonus Grade:
GEOL 4320
1. Define the following terms (2 points each): a. wave front
b. phase retardation
c. refractive index
d. dispersion
e. orthoscopic light
f. double refraction
g. pleochroism
2. Write an equation that relates wave frequency (f), wavelength () and speed (v). (6 points).
3. How do the properties (f, , v) of a wave ray change when it passes from a gas into a solid? (3 points).
4. Given the major refractive indices for the following fictitious minerals. Rank these minerals in order of highest to lowest birefringence. (4 points) a. N = 1.45, n = 1.35 b. N = 1.50, n = 1.45 c. N = 2.65, n = 1.55 d. N = 1.65, n = 1.55
5. Which of the above minerals (in problem 4) has (3 points): a) the fastest ray b) the slowest ray c) the highest density
6. Briefly discuss ordinary and extraordinary rays. What is the main difference between them? (12 points)
7. The pictures below show cross-sections of indicatrixes in 3 different mineral grains. Rank these minerals according to the relief that they would display in plane-polarized light. (6 points)
8. Rank the above minerals in terms of the birefringence they would display (6 points).
9. In the diagram below illustrate how double refraction works in a calcite crystal. Identify the rays (what are their names) and show their vibration directions (6 points).
randomly polarized light
10. Define retardation, , (path difference) and write an equation describing how it relates to mineral properties (5 points).
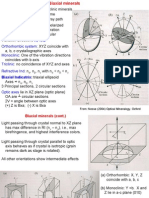
11. What is an optical indicatrix? Draw and describe the 3 main types of indicatrixes. Identify primary planes and axis as appropriate (15 points).
12. Name and describe two different methods for determining the refractive indices of minerals in oils. Describe the microscope setup and how each method works in some detail (20 points).
13. Monochromatic light ( = 500 nm) passes through the wedge below (in a 45 position). How will the light intensity vary along the length of the wedge (maximum thickness is 2000 nm) and why? (15 points bonus).
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- An Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsVon EverandAn Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision WorksheetDokument3 SeitenRevision WorksheetkrisshivNoch keine Bewertungen
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesVon EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bsc-II PhysicsDokument5 SeitenBsc-II Physicskaranspawar007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Radiation and Electronic StructureDokument3 SeitenElectromagnetic Radiation and Electronic StructureAjay NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Prvs-Qn-2. Structure of Atom Q & ADokument13 SeitenHsslive-Xi-Chem-Prvs-Qn-2. Structure of Atom Q & Aaromalssatheesh02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Physics: B.Tech I Year (R07) Supplementary Examinations, June 2013Dokument1 SeiteApplied Physics: B.Tech I Year (R07) Supplementary Examinations, June 2013sivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT 2 Exam 2005 - Answer KeyDokument8 SeitenMT 2 Exam 2005 - Answer KeySamuel WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM 2030 Inorganic Chemistry I EXAM I Example QuestionsDokument6 SeitenCHEM 2030 Inorganic Chemistry I EXAM I Example Questionscoolusername95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Minimum Learning Material (XII)Dokument6 SeitenMinimum Learning Material (XII)Abhi VarnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Physics Text - QuizDokument20 SeitenFinal Physics Text - QuizSus NortonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ach 110 AssignmentDokument8 SeitenAch 110 AssignmentJoseph NyabugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms & NucleiDokument15 SeitenAtoms & NucleixkryxxzNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemDokument2 SeitenChemJathin NakkellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave DynamicsDokument5 SeitenWave DynamicspothirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11th Full Book PaperDokument3 Seiten11th Full Book PaperAhsan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIT 5.112 Exam 1 Fall 2009Dokument12 SeitenMIT 5.112 Exam 1 Fall 2009bitternessinmymouthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Question Paper Engineering Physics (14PHY12/14PHY22)Dokument3 SeitenModel Question Paper Engineering Physics (14PHY12/14PHY22)prabs20069178Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment EDokument2 SeitenAssignment EWilson Jones0% (1)
- X-Ray Diffraction and Bragg's LawDokument24 SeitenX-Ray Diffraction and Bragg's LawYagnesh Rohit100% (1)
- Stress OpticsDokument11 SeitenStress Opticschantaiah100% (1)
- DP Physics Unit 7 Quiz 1 AnswersDokument7 SeitenDP Physics Unit 7 Quiz 1 AnswersStif Alifan GanendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared Spectroscopy of Triatomics for Space ObservationVon EverandInfrared Spectroscopy of Triatomics for Space ObservationNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTERWISETEST - D09 Dec 2022Dokument4 SeitenCHAPTERWISETEST - D09 Dec 2022Atharva SisodiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4PYQ TW N&P Phy.Dokument13 Seiten4PYQ TW N&P Phy.IAS SANWARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Atom-hsslive-AnilDokument4 SeitenStructure of Atom-hsslive-AnilDhana Aryal100% (1)
- Exam 1 Answer KeyDokument9 SeitenExam 1 Answer KeyVictor DinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank For First Year First Sem Question Bank For Physics-I Regulation 20913Dokument21 SeitenQuestion Bank For First Year First Sem Question Bank For Physics-I Regulation 20913PRIYA RAJINoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 Physics Volume 2Dokument5 SeitenGrade 12 Physics Volume 2sudhir2009knrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes For: Solid State Electronic Devices: With Modifications by M. Nadeem Akram and Per OhlckersDokument45 SeitenLecture Notes For: Solid State Electronic Devices: With Modifications by M. Nadeem Akram and Per OhlckersSaleha QuadsiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBCS Scheme: Model Question Paper With Effect From 2017-18Dokument2 SeitenCBCS Scheme: Model Question Paper With Effect From 2017-18Sidharth PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of AtomsDokument42 SeitenChapter 6 Electronic Structure of AtomsTommy NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Science March 2022Dokument6 SeitenMaterials Science March 2022Narjeena ThanveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 3 MarkDokument4 SeitenPhysics 3 MarkVishnu DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021-22 Term 2 - NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA SAMITI PRE-BOARD - TERM II EXAMINATIONDokument5 Seiten2021-22 Term 2 - NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA SAMITI PRE-BOARD - TERM II EXAMINATIONnewtonfogg123Noch keine Bewertungen
- MLM Paper - 2Dokument5 SeitenMLM Paper - 2Akshay RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of The Atom - ExamDokument4 SeitenStructure of The Atom - Examzehra giyoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyVon EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework Assignment 12-07-2020 - PDFDokument2 SeitenHomework Assignment 12-07-2020 - PDFUtkarsh Bhauji Kannake ep19b014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction For CandidatesDokument4 SeitenInstruction For CandidatesAmit PokhariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1ST YEAR INTERMEDIATE CHEMISTRY MLMDokument63 Seiten1ST YEAR INTERMEDIATE CHEMISTRY MLMRajesh MeghawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 4 2 Electronic Structure of ComplexesDokument13 SeitenActivity 4 2 Electronic Structure of ComplexesAgilen MagalingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Work Must Be Shown To Receive Full Credit: Dr. Woodward Chemistry 123 Sample Quiz 1 Spring 2007 Quiz 5 20 MinutesDokument2 SeitenAll Work Must Be Shown To Receive Full Credit: Dr. Woodward Chemistry 123 Sample Quiz 1 Spring 2007 Quiz 5 20 MinutesEsther WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6. Atomic Structure: Upon Successful Completion of This Unit, The Students Should Be Able ToDokument7 SeitenUnit 6. Atomic Structure: Upon Successful Completion of This Unit, The Students Should Be Able TobillingsleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmftDokument6 SeitenEmftsyamalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Theory of Relativity, Crystallography)Dokument9 SeitenSpecial Theory of Relativity, Crystallography)Otim Daniel EmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure ChapterDokument36 SeitenQuantum Theory and Atomic Structure ChapterLAVTOLNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssddgfghhfDokument9 SeitenAssddgfghhfbahasismanogluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 410Dokument3 SeitenPhys 410Joram MuiruriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 05 04 11 58 26 PDFDokument8 Seiten2017 05 04 11 58 26 PDFOm KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- XRDDokument26 SeitenXRDAnonymous dvuYynfXNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Year Chemistry Chapter No. 5-6 - SQs - NOTESPKDokument14 Seiten1st Year Chemistry Chapter No. 5-6 - SQs - NOTESPKZeeshan ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure - Workbook SolutionsDokument20 SeitenAtomic Structure - Workbook SolutionsJee AspirantNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUCCESS STUDY CIRCLE CHEMISTRY REVISIONDokument3 SeitenSUCCESS STUDY CIRCLE CHEMISTRY REVISIONAshok PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam-23 UDokument8 SeitenExam-23 UIjaz AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conoscopic Patterns Near Isotropic PointDokument12 SeitenConoscopic Patterns Near Isotropic PointBayer MitrovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank of Chemistry (BSC-105) for 2018 onwards Batch Students (1)Dokument8 SeitenQuestion Bank of Chemistry (BSC-105) for 2018 onwards Batch Students (1)interestingfacts2525Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nuclei QB XiiDokument23 SeitenNuclei QB XiiToshani GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology Syllabus KeralaDokument43 SeitenGeology Syllabus KeralaSidney HillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Mineralogy in A Nutshell: Use of The Petrographic Microscope in Three Easy LessonsDokument29 SeitenOptical Mineralogy in A Nutshell: Use of The Petrographic Microscope in Three Easy LessonsMavin arellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nesse - Introduction To Optical Mineralogy - 3th Edition PDFDokument328 SeitenNesse - Introduction To Optical Mineralogy - 3th Edition PDFRaúl Iglesias86% (35)
- Laboratorium Geologi Optik: Borang Laporan Resmi Praktikum Mineral Optik Acara: Pengamatan Polarisasi Bersilang (XPL)Dokument5 SeitenLaboratorium Geologi Optik: Borang Laporan Resmi Praktikum Mineral Optik Acara: Pengamatan Polarisasi Bersilang (XPL)Anonymous g7XbMgcL8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Mineralogy PropertiesDokument51 SeitenOptical Mineralogy PropertiesAkqueza MendonçaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Mineralogy A ReviewDokument49 SeitenOptical Mineralogy A Reviewjose villaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock Forming Minerals in Thin SectionDokument235 SeitenRock Forming Minerals in Thin Sectionyaku16180% (1)
- Plane Polarised Light Cross Polarised Light: Optical Properties PlagioclaseDokument5 SeitenPlane Polarised Light Cross Polarised Light: Optical Properties PlagioclaseOmkar SagavekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Min3Dokument28 SeitenOptical Min3Deybis Jhonny JuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratorium Geologi Optik: Laporan Resmi Praktikum Mineral Optik Acara: Feldspar Dan KuarsaDokument6 SeitenLaboratorium Geologi Optik: Laporan Resmi Praktikum Mineral Optik Acara: Feldspar Dan KuarsaAldi Hendra HermawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mineralogy and Optical Mineralogy: Lab Manual Compiled by Brittani D. Mcnamee and Mickey E. GunterDokument51 SeitenMineralogy and Optical Mineralogy: Lab Manual Compiled by Brittani D. Mcnamee and Mickey E. GunterKlaus KauffmannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 - Microscopic Study of Minerals Under The MicroscopeDokument23 SeitenLecture 4 - Microscopic Study of Minerals Under The MicroscopeAnonymous 8KPGnFtB4100% (1)
- Petrological MicroscopeDokument2 SeitenPetrological MicroscopeNand B. VidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Define An IndicatrixDokument4 SeitenDefine An IndicatrixTYron AnotidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mineralogy and Optical Mineralogy by Dyar, Gunter, and Tasa: Images, Animations, and VideosDokument3 SeitenMineralogy and Optical Mineralogy by Dyar, Gunter, and Tasa: Images, Animations, and VideosKevin Tjoeng0% (1)
- The Polarized Ligh Microscopy - Should We Teach The Use of 19thDokument11 SeitenThe Polarized Ligh Microscopy - Should We Teach The Use of 19thJuanchofarrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Mineralogy - Optical Properties of Uniaxial MineralsDokument19 SeitenAnalytic Mineralogy - Optical Properties of Uniaxial Mineralsseed3dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 10 IGNOU NOTE ON GEOLOGYDokument28 SeitenUnit 10 IGNOU NOTE ON GEOLOGYMeenakshi AshokNoch keine Bewertungen
- McNamee Gunter Lab ManualDokument51 SeitenMcNamee Gunter Lab ManualFrancNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSCDokument13 SeitenBSCrajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Optical AccessoriesDokument15 Seiten4 Optical AccessoriesYash BagkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.9 Interference FiguresDokument33 Seiten1.9 Interference FigureswessilissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah 5.1 - Indicatrix PDFDokument27 SeitenKuliah 5.1 - Indicatrix PDFBERNARDUS ANGGIT WINAHYUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biaxial MineralDokument11 SeitenBiaxial MineralRivdhal SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPTICAL ANOMALIES IN MINERALS GoodDokument3 SeitenOPTICAL ANOMALIES IN MINERALS GooddeshmukhgeolNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Make Rock Thin Sections, Without Much Equipment - How - To - Make - Rock - Thin - SectionsDokument2 SeitenHow To Make Rock Thin Sections, Without Much Equipment - How - To - Make - Rock - Thin - SectionstwinscrewcanoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biaxial Interference Figures F12Dokument20 SeitenBiaxial Interference Figures F12dcegarciamapuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microscopc Determination of Nonopaqe MineralsDokument272 SeitenMicroscopc Determination of Nonopaqe MineralsdmbgddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Mineralogy Tutorial 3Dokument16 SeitenOptical Mineralogy Tutorial 3Istrate IsabelaNoch keine Bewertungen