Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Trig P.2 Notes
Hochgeladen von
RabbityHeartCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Trig P.2 Notes
Hochgeladen von
RabbityHeartCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
P.
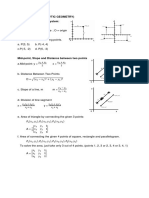
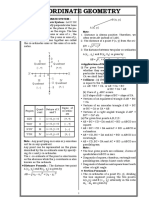
2 Cartesian Coordinate System Cartesian Plane (Rectangular Coordinate System) Pair of perpendicular lines, horizontal and vertical, intersecting at their respective 0-point x-axis Horizontal line in a Cartesian plane y-axis Vertical line is a Cartesian plane Origin Intersection of x- and y-axis; coordinates (0, 0) Ordered Pair (Coordinate) Describes the points on a Cartesian plane; (x,y) x-coordinate intersection of the x-axis with a perpendicular from that point y-coordinate intersection of the y-axis with a perpendicular from that point Quadrants Division of the Cartesian plane by the axes Quadrant 1 (+,+); all points in quadrant 1 have positive x and positive y values Quadrant 2 (,+); all points in quadrant 2 have negative x and positive y values Quadrant 3 (,); all points in quadrant 3 have negative x and negative y values Quadrant 4 (+,); all points in quadrant 4 have positive x and negative y values Absolute Value (magnitude) Distance from 0 *Note Distance is always positive Properties of Absolute Values 1. a 0 Absolute value of a number is always positives 2. a = a 3. ab = a b 4. a a = ,b 0 b b Absolute value of the opposite of a number is still going to be positive It does not matter when we take the absolute value when multiplying It does not matter when we take the absolute value when dividing
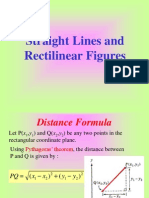
Distance Formulas Distance between two values on a number line D = a b = b a Distance between two points in a Cartesian plane D=
( x1 x2 ) 2 + ( y1 y2 ) 2
Midpoint Formula Midpoint of a segment on a number line a+b M = 2 Midpoint of a segment in a Cartesian plane x + x y + y2 M = 1 2, 1 2 2
Equation of a Circle Standard form equation of a circle with center (h, k) and radius, r ( x h) 2 + ( y k ) 2 = r 2 Homework Assignment P.20 1 53 odds
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Geometry, Matrix and Vector Calculus: Lecture Note Course Code: MAT 102B (For CEP)Dokument56 SeitenGeometry, Matrix and Vector Calculus: Lecture Note Course Code: MAT 102B (For CEP)MUNIA AKTER MOONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathspoint - Co.in Straight Lines-I IIT-JEE (XI)Dokument8 SeitenMathspoint - Co.in Straight Lines-I IIT-JEE (XI)kshitijNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Geometry HandoutsDokument15 SeitenAnalytic Geometry Handoutsdeguzmancarmenfe100% (1)
- Day 2 1analytic GeometryDokument6 SeitenDay 2 1analytic GeometryJhun Michael Locus100% (1)
- Straight LinesDokument127 SeitenStraight LinesVIDYA SRI GANESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lines and CirclesDokument2 SeitenLines and CirclesJohnny MurrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0.2 Lines in The Plane: The Real Number LineDokument14 Seiten0.2 Lines in The Plane: The Real Number Linebenalyn ignacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)Dokument9 SeitenAnalytic Geometry MATH 004 (TIP Reviewer)James Lindo100% (1)
- Unit 10 - Straight LinesDokument3 SeitenUnit 10 - Straight LinesRaffaella LaxaldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three Dimensional GeometryDokument5 SeitenThree Dimensional GeometryAshish AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Analysis I: The Rectangular Coordinate SystemDokument6 SeitenMathematical Analysis I: The Rectangular Coordinate SystemBlack PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- المحاضرة الاولىDokument8 Seitenالمحاضرة الاولىQwaAlmanlawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iii - Analytic Geometry Part 1: Cartesian Coordinate SystemDokument9 SeitenIii - Analytic Geometry Part 1: Cartesian Coordinate System3 stacksNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D GeometryDokument13 Seiten3D GeometryRoshan RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathematicsDokument7 SeitenMathematicsJay LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulas SheetDokument5 SeitenFormulas SheetabdulrehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Geometry HandoutsDokument15 SeitenAnalytic Geometry HandoutsPauSomerhalderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 - Co-Ordinate Geometry BBADokument6 Seiten13 - Co-Ordinate Geometry BBAVeerannaSHiremathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Straight Line Lecture - 1Dokument149 SeitenStraight Line Lecture - 1Aditya TirthakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 (P1)Dokument25 SeitenLecture 1 (P1)Faisal ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.plane Coordinate GeometryDokument10 Seiten1.plane Coordinate GeometryPoh Koon Seng100% (1)
- Analytic Geometry 1Dokument39 SeitenAnalytic Geometry 1Jan Jhezer LimpinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP 5 MathsDokument4 SeitenDPP 5 MathsAnurupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circles: Circle Is A Set of Points On A Plane That Are EquidistantDokument34 SeitenCircles: Circle Is A Set of Points On A Plane That Are EquidistantJheromeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19vectors 3dDokument8 Seiten19vectors 3djuhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Straight Lines ArjunaDokument5 SeitenStraight Lines ArjunaRishiraaj KhurmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit1 SummaryDokument1 SeiteUnit1 SummaryknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Booklet (Study Material + Model Paper) For SA-2 Class 10Dokument32 SeitenSample Booklet (Study Material + Model Paper) For SA-2 Class 10Apex Institute88% (8)
- Analytic Geometry: Engr. RenDokument48 SeitenAnalytic Geometry: Engr. RenTristan100% (1)
- Analytic GeometryDokument45 SeitenAnalytic Geometrylynser chuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 3 1 1 3Dokument13 Seiten1 3 1 1 3Himanshu GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CST Math 2015 - Day 4 - Analytic GeometryDokument19 SeitenCST Math 2015 - Day 4 - Analytic Geometryapi-245317729Noch keine Bewertungen
- 13 - Three-Dimensional Geometry PDFDokument20 Seiten13 - Three-Dimensional Geometry PDFthinkiitNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAT 104 2d Coordinate GeometryDokument14 SeitenMAT 104 2d Coordinate GeometryBolaji OgunlanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-D Graphics: Mathematics For Computer GraphicsDokument13 Seiten2-D Graphics: Mathematics For Computer GraphicsSumit Kumar VohraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordinate Geometry Recent QuestionsDokument8 SeitenCoordinate Geometry Recent Questionsrayaat770Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Analytic: Group 7Dokument10 SeitenGeometry Analytic: Group 7Viani AstutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Geometry 1Dokument2 SeitenAnalytic Geometry 1ggomo15100% (1)
- Maths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XDokument16 SeitenMaths Concepts and Formulae: y FX F y XAt TanwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Points and Formulae: e Markedpric Discount Loss ProfitDokument5 SeitenImportant Points and Formulae: e Markedpric Discount Loss ProfitNyasha GweruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quant - Co-Ordinate, P&C, ProbDokument9 SeitenQuant - Co-Ordinate, P&C, Probharshalshah3110Noch keine Bewertungen
- Day 6 - Straight Line (Ok)Dokument32 SeitenDay 6 - Straight Line (Ok)Daniel Piamonte100% (1)
- Vector Calculus ReviewDokument45 SeitenVector Calculus ReviewJoshua CookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Straight Lines and Rectilinear FiguresDokument40 SeitenStraight Lines and Rectilinear FiguresChona Escoton AlcaydeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Sheet - Straight Lines: Section (A)Dokument5 SeitenPractice Sheet - Straight Lines: Section (A)Sushma ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co-Ordinate Geometry: Y I II Quadrant Quadrant (-.,+) (+,+) 1 2 3Dokument11 SeitenCo-Ordinate Geometry: Y I II Quadrant Quadrant (-.,+) (+,+) 1 2 3Aarti Sharma100% (1)
- c1 Idiot GuideDokument3 Seitenc1 Idiot GuideJames LeungNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Coordinate PlaneDokument2 SeitenThe Coordinate PlaneJosé Antonio Luque LamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARML TheoremsDokument27 SeitenARML Theoremsfreefall014Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Rise Up) - Straight Lines - Sep 1Dokument238 Seiten(Rise Up) - Straight Lines - Sep 1prakhar100% (1)
- Cartesian-Plane 7th TopicDokument91 SeitenCartesian-Plane 7th TopicFranklin BuisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordinate Geometry Assignment - NTA AbhyasDokument95 SeitenCoordinate Geometry Assignment - NTA AbhyasKshreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordinate GeometryDokument2 SeitenCoordinate GeometryZakir AhemadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet MathDokument5 SeitenFormula Sheet MathMata Pronoob100% (1)
- CXC MATHS Formula SheetDokument7 SeitenCXC MATHS Formula SheetEric D Medeci100% (1)
- Circles by NV Sir - JEE BriefDokument55 SeitenCircles by NV Sir - JEE BriefdahaleswaroopNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1705808131Dokument134 Seiten1705808131Study EasyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths-Straight Line IIIDokument7 SeitenMaths-Straight Line IIIShubham JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Trig P.4 NotesDokument1 SeiteTrig P.4 NotesRabbityHeartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trig P.3 NotesDokument1 SeiteTrig P.3 NotesRabbityHeartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Round One Notes Pre Contact-Fall of The Kapu SystemDokument2 SeitenRound One Notes Pre Contact-Fall of The Kapu SystemRabbityHeartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 Age of Religious Wars NotesDokument3 SeitenChapter 12 Age of Religious Wars NotesRabbityHeartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Reading QuestionsDokument2 SeitenChapter 10 Reading QuestionsRabbityHeartNoch keine Bewertungen