Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
1 Low-Voltage Utility Distribution Networks: D - Connecion To The LV Public Distribution Network
Hochgeladen von
tucurici5740Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1 Low-Voltage Utility Distribution Networks: D - Connecion To The LV Public Distribution Network
Hochgeladen von
tucurici5740Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
D - Connecion to the LV public distribution network
1 Low-voltage utility distribution networks
D14
Ba ck
M CB
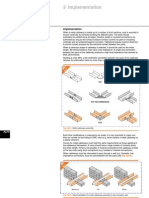
The service cable terminates in a flushmounted wall cabinet which contains the isolating fuse links, accessible from the public way. This method is preferred for esthetic reasons, when the consumer can provide a suitable metering and mainswitch location.
Fig. D8 : Town centre installations
Ba
ck
Interface Utility Service cable Consumer Installation
Isolation by fuse links Meter Meter cabinet Main circuit breaker
Fig. D9 : Typical LV service arrangement for domestic consumers
In the field of electronic metering, techniques have developed which make their use attractive by utilities either for electricity metering and for billing purposes, the liberalisation of the electricity market having increased the needs for more data collection to be returned from the meters. For example electronic metering can also help utilities to understand their customers consumption profiles. In the same way, they will be useful for more and more power line communication and radio-frequency applications as well. In this area, prepayment systems are also more and more employed when economically justified. They are based on the fact that for instance consumers having made their payment at vending stations, generate tokens to pass the information concerning this payment on to the meters. For these systems the key issues are security and inter-operability which seem to have been addressed successfully now. The attractiveness of these systems is due to the fact they not only replace the meters but also the billing systems, the reading of meters and the administration of the revenue collection.
Schneider Electric - Electrical installation guide 2005
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Automated Meter Reading: An Advanced TechnologyDokument3 SeitenAutomated Meter Reading: An Advanced TechnologySkumaran KumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Part 1 SMART GRID TECHNOLOGIESDokument31 SeitenModule 2 Part 1 SMART GRID TECHNOLOGIESRohan AshishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded Edge ComputingforrealtimesmartmeterdataanalyticsDokument5 SeitenEmbedded Edge ComputingforrealtimesmartmeterdataanalyticsSummer TriangleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Metering InfrastructureDokument17 SeitenAdvanced Metering InfrastructurePreetham100% (1)
- Article What Is An Advanced MeterDokument3 SeitenArticle What Is An Advanced MeterAbdulyunus AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Challenges of Advanced Metering InfrastructureDokument7 SeitenChallenges of Advanced Metering InfrastructureAlvaro Jose BazurtoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIGRE-146 Smart Grid 3.0 - A Grid Ready ApproachDokument7 SeitenCIGRE-146 Smart Grid 3.0 - A Grid Ready ApproachkamuikNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPRI - Advanced MeteringDokument2 SeitenEPRI - Advanced Meteringion1212Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Significance of Wireless Communication For The Metering Data Transmission Via Smart GridsDokument11 SeitenThe Significance of Wireless Communication For The Metering Data Transmission Via Smart GridsLeonardo Felipe da Silva Dos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- V6 Brunner Buchholz Naumann PowerGrid+Europe+8-10+Oktober+2010+AmsterdamDokument14 SeitenV6 Brunner Buchholz Naumann PowerGrid+Europe+8-10+Oktober+2010+AmsterdamDavid Jose Poma GuillenNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEminar ReportDokument21 SeitenSEminar ReportRushikesh JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Communications in SmartgridDokument4 SeitenRole of Communications in SmartgridChaitu ChaitanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing DLMS/COSEM in Smart Meters: Gordan Štruklec, Joško MaršiDokument6 SeitenImplementing DLMS/COSEM in Smart Meters: Gordan Štruklec, Joško MaršiKingkulkNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMI TechnologyDokument14 SeitenAMI TechnologyZubab PanniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Meters and Advanced Metering InfrastructureDokument17 SeitenSmart Meters and Advanced Metering InfrastructureRao vmvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing DLMS/COSEM in Smart Meters: Gordan Štruklec, Joško MaršićDokument6 SeitenImplementing DLMS/COSEM in Smart Meters: Gordan Štruklec, Joško MaršićRIZ100% (1)
- Aricent Electrical Utility WhitepaperDokument9 SeitenAricent Electrical Utility Whitepaperap_venezuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-2 Smart Grid Measurement and Automation TechnologiesDokument85 SeitenUnit-2 Smart Grid Measurement and Automation TechnologiessujithNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMI project in Jordan (EDCO PILOT PROJECT) فراس العسلي.ppsxDokument26 SeitenAMI project in Jordan (EDCO PILOT PROJECT) فراس العسلي.ppsxAlexandreRodriguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure Over Power Line CommunicationDokument57 SeitenAdvanced Metering Infrastructure Over Power Line CommunicationAhmad Abu Doush100% (1)
- Cusat Module 1 NotesDokument45 SeitenCusat Module 1 NotesBasil Richard K ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless M2M Communication Networks For Smart Grid ApplicationsDokument7 SeitenWireless M2M Communication Networks For Smart Grid ApplicationsRajIsacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Metering - A Brief Overview of Projects, Benefits and ApplicationsDokument12 SeitenSmart Metering - A Brief Overview of Projects, Benefits and ApplicationsGagan AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Metering in Electric Power Distribution System: December 2013Dokument7 SeitenSmart Metering in Electric Power Distribution System: December 2013Somnath HadpeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch7 Smart Metering&DSI SDokument49 SeitenCh7 Smart Metering&DSI SksajjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Meter PaperDokument7 SeitenSmart Meter PaperAmin AzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Implementaion of A Wireless Automatic Meter Reading SystemDokument5 SeitenDesign and Implementaion of A Wireless Automatic Meter Reading SystemChandru PrasathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Grid Technol-OGY: A Seminar OnDokument26 SeitenSmart Grid Technol-OGY: A Seminar OnTHALLURU SIVA MOHAN KRISHNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Altera Energy-Aware Appliance Platform - A New Approach To Home Energy ControlDokument8 SeitenAltera Energy-Aware Appliance Platform - A New Approach To Home Energy Controlkn65238859Noch keine Bewertungen
- DGSG Notes 5 and 6Dokument40 SeitenDGSG Notes 5 and 6CarlynMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Grid Technology: A Seminar OnDokument26 SeitenSmart Grid Technology: A Seminar Onaarshiya0612aNoch keine Bewertungen
- SG - UNIT II Unit 23-24 - FebDokument185 SeitenSG - UNIT II Unit 23-24 - FebrajaramprathibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei AMI Solution Brochure - v2.0Dokument8 SeitenHuawei AMI Solution Brochure - v2.0jjivkov100% (1)
- Energies 09 00569 PDFDokument19 SeitenEnergies 09 00569 PDFAkabomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Smart MetersDokument17 SeitenIntroduction To Smart MetersDrVikas Singh Bhadoria100% (2)
- Book Chapter - Digital SubstationDokument8 SeitenBook Chapter - Digital SubstationDebasish RahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank EE 6336: Elements of The Smart GridDokument10 SeitenQuestion Bank EE 6336: Elements of The Smart GridSreebash KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upgrading of Traditional Electric Meter Into Wireless Electric Meter Using Zigbee TechnologyDokument11 SeitenUpgrading of Traditional Electric Meter Into Wireless Electric Meter Using Zigbee TechnologyChinchu SasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Grids: For A Brighter FutureDokument6 SeitenSmart Grids: For A Brighter FutureHemanth SairamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication System For Distribution Using CDMA - Tiene Resultados Reales de Uso de Dif TecnolDokument7 SeitenCommunication System For Distribution Using CDMA - Tiene Resultados Reales de Uso de Dif Tecnoledmuarizt7078Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cs RpojectDokument29 SeitenCs RpojectDipanwita DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Smart Grid - Enabling Energy Efficiency and Demand Response - C1Dokument23 SeitenThe Smart Grid - Enabling Energy Efficiency and Demand Response - C1ankenzpro27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Grid ReportDokument27 SeitenSmart Grid ReportLovelesh MalavNoch keine Bewertungen
- BHCOE Project Description - FinalDokument2 SeitenBHCOE Project Description - Finallxd.hepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Meters For Smart GridsDokument103 SeitenSmart Meters For Smart GridsKwangrok ChangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control and Monitoring of Electrical Distribution Grid Using Automatic Reader SystemsDokument4 SeitenControl and Monitoring of Electrical Distribution Grid Using Automatic Reader SystemsAdriana AfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv Cellular Comm Smart MeteringDokument9 SeitenAdv Cellular Comm Smart MeteringRajesh ChinthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexible Wireless Sensor Network For Smart Lighting ApplicationsDokument6 SeitenFlexible Wireless Sensor Network For Smart Lighting ApplicationsmonikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Implementation of Control Unit For Railways Using Power Line Data TransmissionDokument5 SeitenDesign and Implementation of Control Unit For Railways Using Power Line Data TransmissionEditor IJRITCCNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZF ASTronic Error CodesDokument12 SeitenZF ASTronic Error Codesमुकेश कुमार झाNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Implementation of Low-Cost Universal Smart Energy Meter With Demand Side Load ManagementDokument8 SeitenDesign and Implementation of Low-Cost Universal Smart Energy Meter With Demand Side Load Managementdan_intel6735Noch keine Bewertungen
- Smart GridDokument35 SeitenSmart GridSanjana Ganesh100% (2)
- 1.) What Is The Advantage of Smart Grid in The Following?Dokument3 Seiten1.) What Is The Advantage of Smart Grid in The Following?Carlnagum 123456789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Andthe SmartGridDokument13 SeitenCellular Andthe SmartGridamitjain310Noch keine Bewertungen
- Book 2 DefinitionsDokument4 SeitenBook 2 DefinitionsrhsiboneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ami MDMDokument42 SeitenAmi MDMMuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Challenges and Opportunities of Smart Meters in Smart Homes and Smart GridsDokument7 SeitenOn The Challenges and Opportunities of Smart Meters in Smart Homes and Smart GridsGILBERT DJIDIACK FAYENoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument24 SeitenUnit 2Omkar Shete100% (1)
- Protection Against Electric Shocks: Chapter FDokument5 SeitenProtection Against Electric Shocks: Chapter Ftucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- Simplify Fiber Optic Cabling Migrations With A Multi-Path™ SystemDokument8 SeitenSimplify Fiber Optic Cabling Migrations With A Multi-Path™ Systemtucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Earthing Schemes: 2.4 Selection Criteria For The TT, TN and IT SystemsDokument1 Seite2 Earthing Schemes: 2.4 Selection Criteria For The TT, TN and IT Systemstucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Low-Voltage Utility Distribution Networks: D - Connecion To The LV Public Distribution NetworkDokument1 Seite1 Low-Voltage Utility Distribution Networks: D - Connecion To The LV Public Distribution Networktucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 LV Distribution Schemes: 1.4 Safety or Emergency-Services Installations and Standby Power SuppliesDokument4 Seiten1 LV Distribution Schemes: 1.4 Safety or Emergency-Services Installations and Standby Power Suppliestucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- E17 18Dokument2 SeitenE17 18tucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Installation Guide: According To IEC International StandardsDokument3 SeitenElectrical Installation Guide: According To IEC International Standardstucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Coupling Mechanisms and Counter-Measures: 4.1 GeneralDokument1 Seite4 Coupling Mechanisms and Counter-Measures: 4.1 Generaltucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Supply of Power at High Voltage: 1.2 Different HV Service ConnectionsDokument3 Seiten1 Supply of Power at High Voltage: 1.2 Different HV Service Connectionstucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Power Monitoring and Control: 5.1 Main User's BenefitsDokument2 Seiten5 Power Monitoring and Control: 5.1 Main User's Benefitstucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ap 10Dokument1 SeiteAp 10tucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Power Monitoring and Control: 5.4 Technical Inputs On Communicating SystemsDokument2 Seiten5 Power Monitoring and Control: 5.4 Technical Inputs On Communicating Systemstucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- Himel Enclosures 2008Dokument107 SeitenHimel Enclosures 2008tucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guide IbcsDokument92 SeitenGuide Ibcstucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen
- Explosionproof Performance: That Exceeds ExpectationsDokument2 SeitenExplosionproof Performance: That Exceeds Expectationstucurici5740Noch keine Bewertungen