Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Standard PID Tuning Methods: I. Cohen-Coon Method (Open-Loop Test)
Hochgeladen von
castasoft0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten4 SeitenOriginaltitel
Tuning Methods
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten4 SeitenStandard PID Tuning Methods: I. Cohen-Coon Method (Open-Loop Test)
Hochgeladen von
castasoftCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
Standard PID Tuning Methods
(tbco 2/17/2012)
I.
Cohen-Coon Method (Open-loop Test)
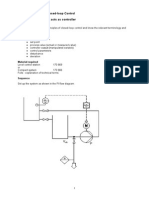
Step 1: Perform a step test to obtain the parameters of a FOPTD (first order plus time delay) model i. Make sure the process is at an initial steady state ii. Introduce a step change in the manipulated variable iii. Wait until the process settles at a new steady state
Figure 1. Step Test for Cohen-Coon Tuning. Step 2: Calculate process parameters: , , , , as follows ln2 1 ln2 Step 3: Using the process parameters, use the prescribed values given by Cohen and Coon.
Table 1. Cohen-Coon Tuning Rules
P 1 1 3 1 0.9 12 1 4 3 4 30 3 9 20 32 6 13 8 4 11 2
PI
PID
II.
Ziegler-Nichols Method (Closed-loop P-ControlTest)
Step 1: Determine the sign of process gain (e.g. open loop test as in Cohen-Coon). Step 2: Implement a proportional control and introducing a new set-point. Step 3: Increase proportional gain until sustained periodic oscillation. Step 4: Record ultimate gain and ultimate period: and . Step 5: Evaluate control parameters as prescribed by Ziegler and Nichols Table 2. Ziegler Nichols Tuning Rules
P 2 2.2 1.7 1.2 2 8
PI
PID
III.
Tyreus-Luyben Method (Closed-loop P-Control test)
Step 1-4: Same as steps 1 to 4 of Ziegler-Nichols method above Step 5: Evaluate control parameters as prescribed by Tyreus and Luyben Table 2. Tyreus-Luyben Tuning Rules for PI and PID
PI 3.2 2.2 2.2 2.2 6.3
PID
IV.
Autotune Method (Closed-loop On-Off test)
Step 1: Let process settle to a steady state Step 2: Move the setpoint to the current steady state Step 3: Implement an on-off (relay) controller If process gain is positive, If process gain is negative,
0 0 0 0
Step 4: Let the process settle to a sustained periodic oscillation
Step 5: Evaluate ultimate gain using autotune formulas ( can be obtain from the plots) 4 Step 6: Use either Ziegler-Nichols or Tyreus-Luyben prescribed tunings
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Matlab Exp 7Dokument9 SeitenMatlab Exp 7Mohd RehanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ziegler - Nichols Pid TuningDokument2 SeitenZiegler - Nichols Pid TuningTrần Ngọc MẩnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ziegler Nichols Pid Tuning MehodsDokument2 SeitenZiegler Nichols Pid Tuning MehodsLQ530Noch keine Bewertungen
- PID tuning methodsDokument14 SeitenPID tuning methodsAbolhasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pid Tuning ClassicalDokument18 SeitenPid Tuning ClassicalVo Quang HuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- L-13 (SS) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel)Dokument8 SeitenL-13 (SS) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel)Darkmatter DarkmatterrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pid TuningDokument10 SeitenPid Tuningmohamed abdelhamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process & Instrumental Control Lab ReportDokument16 SeitenProcess & Instrumental Control Lab ReportJosephine Wong Sian CheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Control Lab ReportDokument23 SeitenProcess Control Lab ReportAnonymous OWdJRM8C100% (1)
- Controller Tuning Methods for Process ControlDokument17 SeitenController Tuning Methods for Process ControltrshaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZN Closed Loop MethodDokument7 SeitenZN Closed Loop MethodJitesh EmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt. 4 - Pressure ControlDokument16 SeitenExpt. 4 - Pressure Controlpleco4meNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACT - Ziegler-Nichols TuningDokument3 SeitenACT - Ziegler-Nichols TuningMadan BhojleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report PIDDokument11 SeitenReport PIDSaiman ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID Controller PerformanceDokument27 SeitenPID Controller PerformanceJose Heli Vallejos CoronadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective of The StudyDokument9 SeitenObjective of The StudyFnur FatihahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture09 - 5. Feedback Control Systems-2. Ziegler-Nichols Rules For Tuning PID ControllersDokument5 SeitenLecture09 - 5. Feedback Control Systems-2. Ziegler-Nichols Rules For Tuning PID ControllersjonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date:. - Experiment # 12 Roll No.: - : To Complete Your TasksDokument4 SeitenDate:. - Experiment # 12 Roll No.: - : To Complete Your TasksRasheed ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- P-I-D Controller Literature ReviewDokument12 SeitenP-I-D Controller Literature ReviewMalek Marry AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controller Tuning Methods for PID LoopsDokument5 SeitenController Tuning Methods for PID LoopsSubham SikdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open loop PID tuning for 1st order systemsDokument18 SeitenOpen loop PID tuning for 1st order systemskarmoweldingNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXP-9 Cohen and Coon Tuning MethodDokument3 SeitenEXP-9 Cohen and Coon Tuning MethodAyush SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- PIDTuningClassical - ControlsWikiDokument14 SeitenPIDTuningClassical - ControlsWikiksameer_coepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 1Dokument12 SeitenExp 1Anonymous T7vjZG4otNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID Tuning Classical Methods GuideDokument10 SeitenPID Tuning Classical Methods GuideTolga DurudoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID Controller Tuning Using "Ziegler-Nichols" TechniqueDokument5 SeitenPID Controller Tuning Using "Ziegler-Nichols" Technique;(Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acfrogdgl836ldvbuspou Eyl6uhjugculhmtzdojwbgtlkkup E7yn7z3wkk04xjugsulhx0ouzu9rws3smog3t9o06r7-Cs1zavkubqcfvimg43ogdym21jddxoevtgcy ZznougjhwjcxkhnDokument40 SeitenAcfrogdgl836ldvbuspou Eyl6uhjugculhmtzdojwbgtlkkup E7yn7z3wkk04xjugsulhx0ouzu9rws3smog3t9o06r7-Cs1zavkubqcfvimg43ogdym21jddxoevtgcy ZznougjhwjcxkhnMOHAMED THARIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report ControlDokument33 SeitenReport Controlajwadalfatani100% (5)
- Feedback Controller TuningDokument23 SeitenFeedback Controller Tuningso cool100% (1)
- Applied Control CW2Dokument2 SeitenApplied Control CW2uflillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExercisesDokument18 SeitenExercisescetec1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mukriz: PV (What Is PV?)Dokument5 SeitenMukriz: PV (What Is PV?)Mukriz MahaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two tank non-interacting liquid level PID controlDokument9 SeitenTwo tank non-interacting liquid level PID controlHimanshu JatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report ControlDokument6 SeitenLab Report Controlrolllings3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Finn Haugen - Basic Dynamics - CH 010 - Tuning PID - Skogestad's Method - Integrator Processes - CA6B81DDd01Dokument27 SeitenFinn Haugen - Basic Dynamics - CH 010 - Tuning PID - Skogestad's Method - Integrator Processes - CA6B81DDd01Larissa CarolineNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC1 SE270 Modular Level ControlDokument6 SeitenPC1 SE270 Modular Level ControlYuveraj ThanasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Control ReportDokument14 SeitenRatio Control ReportKoi Zi KangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinjal Shah M.Tech Inst.& Cont. Mi-09: Intrnal Guide Asst. Prof. J.G.bhattDokument9 SeitenKinjal Shah M.Tech Inst.& Cont. Mi-09: Intrnal Guide Asst. Prof. J.G.bhattGaurav MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Good Gain Method For Simple Experimental TuninDokument12 SeitenThe Good Gain Method For Simple Experimental TuninANVESH DONTULANoch keine Bewertungen
- C7 Temperature Control ExperimentDokument5 SeitenC7 Temperature Control ExperimentSzeQiLungNoch keine Bewertungen
- WINSEM2023-24_BEIE303L_TH_VL2023240502899_2024-02-02_Reference-Material-I (1)Dokument56 SeitenWINSEM2023-24_BEIE303L_TH_VL2023240502899_2024-02-02_Reference-Material-I (1)Affan AhmmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Z-L MethodDokument1 SeiteZ-L MethodSutha SangapillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuning-Ryan and AlexDokument21 SeitenTuning-Ryan and AlexPrincess CutabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Reaction CurveDokument6 SeitenProcess Reaction Curveindra100% (1)
- Ijst 120605Dokument3 SeitenIjst 120605srinathgudur11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Empirical Tuning Rules According To Ziegler and NicholsDokument3 SeitenEmpirical Tuning Rules According To Ziegler and NicholskalajamunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2: Optimum Controller Chapter 2: Optimum Controller Settings Settings GGDokument5 SeitenChapter 2: Optimum Controller Chapter 2: Optimum Controller Settings Settings GGLakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PID Controller Tuning ProcessDokument3 SeitenPID Controller Tuning ProcessSasmilah KandsamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labsheet3-Controlsystem v1Dokument11 SeitenLabsheet3-Controlsystem v1Aina FarzanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE402 RecitationDokument64 SeitenEE402 Recitationvignesh0617Noch keine Bewertungen
- DS Part B 4Dokument3 SeitenDS Part B 4DHANESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4 KaranDokument7 SeitenLab 4 KaranSamyak DhutaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pic Final DraftDokument37 SeitenPic Final DraftEeHuey ChooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification and Optimization of Pi Parameters Based On Genetic Algorithm For Non Linear System Using MatlabDokument51 SeitenIdentification and Optimization of Pi Parameters Based On Genetic Algorithm For Non Linear System Using Matlabjagateesan50% (2)
- A) Ziegler-Nichols Method:: Exercises Simulator Automatisation 3th Bachelor Marine EngineeringDokument3 SeitenA) Ziegler-Nichols Method:: Exercises Simulator Automatisation 3th Bachelor Marine EngineeringvivekvkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Control Lab ManualDokument30 SeitenProcess Control Lab ManualAkash Sundar50% (2)
- Instrument Technology: Telemetering and Automatic ControlVon EverandInstrument Technology: Telemetering and Automatic ControlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis within the Systems Development Life-Cycle: Book 4 Activity Analysis—The MethodsVon EverandAnalysis within the Systems Development Life-Cycle: Book 4 Activity Analysis—The MethodsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic Control of Quality of Manufactured ProductVon EverandEconomic Control of Quality of Manufactured ProductNoch keine Bewertungen
- RailDokument2 SeitenRailsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rail 012Dokument2 SeitenRail 012sagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filter Code MDokument1 SeiteFilter Code MsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read LocoDokument1 SeiteRead LocosagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- FilteringDokument1 SeiteFilteringsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epl PlayersDokument1 SeiteEpl PlayerssagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- RailDokument1 SeiteRailsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete FiltersDokument1 SeiteDiscrete FilterssagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- BookDokument3 SeitenBooksagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOC and DTCDokument69 SeitenFOC and DTCRaed MohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read LocoDokument1 SeiteRead LocosagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Texas InstrumentsDokument1 SeiteTexas InstrumentssagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor 55Dokument1 SeiteMotor 55sagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- DISCRETE EQUIVALENTS OF CONTINUOUS SYSTEMSDokument10 SeitenDISCRETE EQUIVALENTS OF CONTINUOUS SYSTEMSsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- BookDokument1 SeiteBooksagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prekidačka NapajanjaDokument48 SeitenPrekidačka NapajanjaDamir PranjkovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCB power supply and motor control circuitsDokument1 SeitePCB power supply and motor control circuitssagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- 064Dokument1 Seite064sagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Text DocumentDokument1 SeiteNew Text DocumentsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wakefield PWR Semi HeatsinkDokument7 SeitenWakefield PWR Semi HeatsinksagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tata Institute of Fundamental Research: Advertisement No. 4/2013Dokument5 SeitenTata Institute of Fundamental Research: Advertisement No. 4/2013apurva_khandekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series and Parallel Equations From A de PerspectiveDokument6 SeitenSeries and Parallel Equations From A de PerspectivealenagroupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features: Schematic:: Global Supplier of Optoelectronic SolutionsDokument3 SeitenFeatures: Schematic:: Global Supplier of Optoelectronic SolutionssagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- 32 Volt-100 AmpDokument4 Seiten32 Volt-100 AmpsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicrochipDokument1 SeiteMicrochipsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicrochipDokument1 SeiteMicrochipsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- JPE JournalDokument9 SeitenJPE JournalsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- K Inetic Engineering LimitedDokument6 SeitenK Inetic Engineering Limitedatul_raj4Noch keine Bewertungen
- S Roy NewDokument1 SeiteS Roy NewsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Injected CalibrationDokument2 SeitenInjected CalibrationsagarscorpionNoch keine Bewertungen