Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chem Insights Chapter 7 WS
Hochgeladen von
wakakkaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chem Insights Chapter 7 WS
Hochgeladen von
wakakkaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 7 Worksheets 1C 1 2C 3C 4A 5A 6B 7D 8B 9C 10 B
2(a) (i) 3C + SiO2 SiC + 2CO (ii) 180 kg (b) (i)
A lot of heat energy is needed to break the strong covalent bonds. (ii) It should not conduct electricity and it should not dissolve in water.
3(a) (b)(i) A lot of heat energy is neede to break the strong electrostatic forces of attraction that make up the ionic bond (ii) the magnesium ion and the oxide ion have double the charge of potassium ion and chloride ion so the electrostatic forces of attraction is stronger in magnesium oxide. (c)(i) the ions are in a fixed position and cannot move about freely to carry the electric current (ii) in the molten (liquid) state and when dissolved in water to form an aqueous solution 4 (a)(i) the electrons between the positive ions in the metallic structure are able to move about freely so the electrons can carry the electric current (ii) high melting point (b) (i) liquid (ii) covalent bonds. The low melting and boiling points suggest a simple molecular structure rather than an ionic lattice structure (iii) simple molecular structure (iv) titanium is a metal and chlorine is a non-metal so it should form an ionic compound. 5 (a)(i) Copper consist of a lattice of positive ions surrounded by a sea of electrons. The electrons are free to move about. (ii) E (b) D or F (c)(i) B (ii)
Section B 1(a) low melting point and does not conduct electricity (b) C60 (c) graphite and diamond 2(a)
(b)(i) all atoms in silicon dioxide are joined by strong covalent bonds. A lot of heat energy is needed to break these bonds. In carbon dioxide, there are weak forces of attraction between the molecules so only a little heat energy is needed to break the forces of attraction. (ii) No because there are no free moving electrons.
3(a)(i) the flat layers of atoms can slide (ii) the strong rigid structure prevents atoms from sliding (b)(i) cutting and drilling rock (ii) graphite has a very high melting point because a lot of heat energy is needed to break the strong covalent bonds between the carbon atoms in graphite.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 5054 s20 Ms 21 PDFDokument11 Seiten5054 s20 Ms 21 PDFJack KowmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 444323735-Chem-Matters-Workbook-2E-Teacher-s-Edn-pdf 1-1Dokument1 Seite444323735-Chem-Matters-Workbook-2E-Teacher-s-Edn-pdf 1-1whatis100% (1)
- O Level Physics P1 June 77 - London University Examination BoardDokument10 SeitenO Level Physics P1 June 77 - London University Examination Boarddjenner100% (1)
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2006 Question PaperDokument4 Seiten0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2006 Question PaperVarun PanickerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Particles, Atomic Structure, Ionic Bonding, The Periodic Table CIE iGCSE 0620 PPQDokument12 SeitenParticles, Atomic Structure, Ionic Bonding, The Periodic Table CIE iGCSE 0620 PPQsanaahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 10.1Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet 10.1SavithaBroonanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1123 w10 Ms 22Dokument12 Seiten1123 w10 Ms 22Fatima HashmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Periodic Table: Test Yourself 16.1 and 16.2 (Page 312)Dokument2 SeitenThe Periodic Table: Test Yourself 16.1 and 16.2 (Page 312)khalil rehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2000 - Paper 2Dokument12 SeitenJune 2000 - Paper 2theyaasir67% (3)
- Igcse Chem Model AnswersDokument24 SeitenIgcse Chem Model AnswersNoah MarvelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet O Levels Physics PressureDokument30 SeitenWorksheet O Levels Physics PressureHZNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIE IGCSE Chemistry (0620 & 0971) Revision - PMTDokument1 SeiteCIE IGCSE Chemistry (0620 & 0971) Revision - PMThanthi winkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes - Topic 5 Forces, Density and Pressure - CAIE Physics A-LevelDokument5 SeitenNotes - Topic 5 Forces, Density and Pressure - CAIE Physics A-LevelMahamIsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Physics - Oup - Com.pk Download (252 Pages - Free)Dokument2 SeitenFundamental Physics - Oup - Com.pk Download (252 Pages - Free)patrick shulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igcse Coordinated Sciences 0654 Combined Science 0 - 59cc8a591723ddab3bbdfff3 PDFDokument50 SeitenIgcse Coordinated Sciences 0654 Combined Science 0 - 59cc8a591723ddab3bbdfff3 PDFBank Yossy WoluslaweNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 26 - Motion in The UniverseDokument2 SeitenIGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 26 - Motion in The UniverseAishath Waheeda0% (1)
- Electricity and Chemical ChangeDokument2 SeitenElectricity and Chemical ChangeTia WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charles Law PDFDokument3 SeitenCharles Law PDFIvan BayonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gcesoln 2Dokument3 SeitenGcesoln 2api-3734333100% (1)
- 5054 s04 Ms 2Dokument5 Seiten5054 s04 Ms 2adilkhan42301Noch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Dokument4 SeitenO Level Pure Physics Topic by Topic 3 109 112Kugan KishurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Displacement Reaction Word Equations HWDokument1 SeiteDisplacement Reaction Word Equations HWjaig78Noch keine Bewertungen
- IG General PhyDokument155 SeitenIG General PhyJun QiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write A Story Where A Text Message Plays An Important Part. (528 Words)Dokument6 SeitenWrite A Story Where A Text Message Plays An Important Part. (528 Words)Huma EssaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1988 1998 Physics Past PapersDokument168 Seiten1988 1998 Physics Past PapersAnthony Benson100% (1)
- Physics: Revising For Your Physics ExamsDokument10 SeitenPhysics: Revising For Your Physics ExamsKamrul Hasan SagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- FREETESTPAPER.com - Your Source for Free Papers OnlineDokument42 SeitenFREETESTPAPER.com - Your Source for Free Papers OnlineUZAIR MAHBUB BHUYAINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sec 4 Chem Prelim Paper 1Dokument16 SeitenSec 4 Chem Prelim Paper 1TeckluckyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 1: Group 1 - The Alkali MetalsDokument4 SeitenTask 1: Group 1 - The Alkali MetalsNeen NaazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet On The Reactivity SeriesDokument2 SeitenWorksheet On The Reactivity SeriesPramudith LiyanageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turning Effect of Forces (Worksheet)Dokument3 SeitenTurning Effect of Forces (Worksheet)Usman Ameen100% (1)
- Radioactive Worksheet IGCSEDokument2 SeitenRadioactive Worksheet IGCSESyakti PerdanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet Chemistry Electrolysis Ks4Jeffrey PiggottNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why I Hate Squirrels!: Chapter 6, Ex.1, Page 80 - 82Dokument7 SeitenWhy I Hate Squirrels!: Chapter 6, Ex.1, Page 80 - 82Iva Sivaraja100% (1)
- 5090 w01 QP 2Dokument12 Seiten5090 w01 QP 2Ahmed Kaleem Khan NiaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 1999 Paper 1Dokument16 SeitenJune 1999 Paper 1YasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Particulate Nature of Matter 1 MSDokument7 SeitenThe Particulate Nature of Matter 1 MSKHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Contents for Chemistry GuidebookDokument16 SeitenTable of Contents for Chemistry GuidebookMariam ShehabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3Dokument22 SeitenTopic 3ChaudhryAbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sankey Diagram Efficiency + Energy TransferDokument4 SeitenSankey Diagram Efficiency + Energy TransferSelwah Hj AkipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 Unit B ExamDokument8 SeitenScience 9 Unit B Examapi-427321002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel Chemistry A2 (Student Book) Examzone PDFDokument11 SeitenEdexcel Chemistry A2 (Student Book) Examzone PDFGhaith AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Chemistry Topic 1 Quantitative Chemistry TestDokument9 SeitenIB Chemistry Topic 1 Quantitative Chemistry TestPak Hei Marcus CHOWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Substitution and EliminationDokument79 SeitenSubstitution and Eliminationjana srutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Matter and Materials WorksheetDokument16 SeitenProperties of Matter and Materials Worksheetrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter08 Deformation of Solids SsDokument6 SeitenChapter08 Deformation of Solids SseltytanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2 Jun 2000 PhysicsDokument4 SeitenPaper 2 Jun 2000 Physicssolarixe100% (3)
- Electrolysis BreakdownDokument14 SeitenElectrolysis BreakdownBaryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: Chapter 9 Industrial Inorganic ChemistryDokument2 SeitenAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: Chapter 9 Industrial Inorganic ChemistryMP3 MusicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checkpoint ChemistryDokument18 SeitenCheckpoint ChemistryNgoc Quang NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Tests For Cations and AnionsDokument1 SeiteIGCSE Tests For Cations and AnionsCoolman Poon100% (2)
- Identification of Ions and GasesDokument5 SeitenIdentification of Ions and GasesJobelle Aleli Perez EhinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Alkalis Worksheet-1452166521Dokument3 SeitenAcids and Alkalis Worksheet-1452166521Jomon ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 7.1Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet 7.1markusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Techniques (TOPIC 2)Dokument17 SeitenExperimental Techniques (TOPIC 2)ChaudhryAbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8: SaltsDokument23 SeitenChapter 8: SaltsWong Wai LunNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8 Preparation of Salts Lab ExperimentDokument4 SeitenG8 Preparation of Salts Lab Experimentaswin100% (1)
- Vibrational SpectrosDokument82 SeitenVibrational SpectrosPedro CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- DreamSpark InstallDokument1 SeiteDreamSpark InstallwakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConceptsDokument7 SeitenConceptswakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social media's impact on sociability is complexDokument3 SeitenSocial media's impact on sociability is complexwakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MeasurementDokument9 SeitenMeasurementDaizLee AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Singapore Factsheet For AQDokument1 SeiteSingapore Factsheet For AQwakakka67% (3)
- Lecture 1 - Intro To OM - HandoutDokument40 SeitenLecture 1 - Intro To OM - HandoutStephen BaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEM2900 ProbabilityDokument2 SeitenGEM2900 ProbabilitywakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emily of Emerald Hill AnalysisDokument2 SeitenEmily of Emerald Hill AnalysiswakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP Article 2 NeuroscienceDokument2 SeitenGP Article 2 NeurosciencewakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Envmt Compiled NotesDokument3 SeitenEnvmt Compiled NoteswakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poem AnalysisDokument1 SeitePoem AnalysiswakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS Diplomacy, Singapore's InvolvementDokument4 SeitenSS Diplomacy, Singapore's InvolvementwakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of Conflict in Sri LankaDokument3 SeitenCauses of Conflict in Sri LankawakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and BasesDokument6 SeitenAcids and Basescharlene1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Limitations of Hdi and GDP EssayDokument1 SeiteLimitations of Hdi and GDP EssaywakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classes of CompoundsDokument3 SeitenClasses of CompoundswakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Map ReadingDokument2 SeitenMap ReadingwakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mole Concept (Stoichiometry) 5 LevelsDokument4 SeitenMole Concept (Stoichiometry) 5 LevelswakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Acids & Bases April 10Dokument8 SeitenNotes On Acids & Bases April 10wakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed of Reaction (Key Points and Q&A)Dokument8 SeitenSpeed of Reaction (Key Points and Q&A)wakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the Periodic TableDokument2 SeitenUnderstanding the Periodic TablewakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metals (Key Points and Q&A)Dokument7 SeitenMetals (Key Points and Q&A)wakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Notes On Chemical Formulae: Name: - Date: - ClassDokument4 SeitenRevision Notes On Chemical Formulae: Name: - Date: - ClasswakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table Chemical Bonding Atomic Structure Plastics (Q&A)Dokument3 SeitenPeriodic Table Chemical Bonding Atomic Structure Plastics (Q&A)wakakka100% (1)
- Summary of Chemical BondingDokument1 SeiteSummary of Chemical Bondingchong56Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8.1-8.3Dokument8 SeitenChapter 8.1-8.3wakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic BondingDokument2 SeitenIonic BondingwakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUMMARY - Reactions of Amines Phenylamine AmidesDokument1 SeiteSUMMARY - Reactions of Amines Phenylamine AmideswakakkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Question Banks AyDokument67 SeitenChemistry Question Banks AyOni AyomideNoch keine Bewertungen
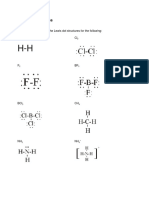
- Lewis DotDokument9 SeitenLewis DotLing Wang100% (1)
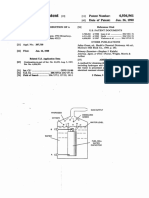
- Us 4936961Dokument8 SeitenUs 4936961PratikNoch keine Bewertungen
- KISCO Company Brochure Renewal WebDokument9 SeitenKISCO Company Brochure Renewal WebNguyễn Huy CườngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms Elements and Compounds WorksheetDokument2 SeitenAtoms Elements and Compounds WorksheetNubar MammadovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- +3 Chemistry SyllabusDokument53 Seiten+3 Chemistry SyllabusArindam DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2a-Water and The Aqueous EnvironmentDokument42 SeitenChapter 2a-Water and The Aqueous EnvironmentAra Jean AgapitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Monomers of Macromolecules-Gummi BioregDokument7 SeitenBuilding Monomers of Macromolecules-Gummi Bioregapi-267079239Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Dokument36 SeitenChemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Kavitha VijeandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry 1: Groups in The Periodic TableDokument4 SeitenGeneral Chemistry 1: Groups in The Periodic TableShane G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Planets Outermost Neptune Vitamin DeficienciesDokument27 SeitenPlanets Outermost Neptune Vitamin DeficienciesFayaz JumaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- HC 2 Nech 07Dokument38 SeitenHC 2 Nech 07Aditya TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1 Chem Book 1 PDFDokument292 SeitenA1 Chem Book 1 PDFsheuli rahman100% (1)
- Physical and Chemical Properties of BiomaterialsDokument4 SeitenPhysical and Chemical Properties of BiomaterialsMelvin Ariel Bautista100% (2)
- Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (3Rd Ed 2001 Academic Press) - AstronomyDokument353 SeitenEncyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (3Rd Ed 2001 Academic Press) - AstronomyDildar Khan Bhati100% (3)
- Advances in Organometallic Chemistry 01 (1964) PDFDokument338 SeitenAdvances in Organometallic Chemistry 01 (1964) PDFYugenthira Cholan100% (1)
- CH 4 Energy Transport by Heat Work MassDokument47 SeitenCH 4 Energy Transport by Heat Work MassgfsfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v8Dokument24 SeitenCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v8Rashi GhadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry P2 Questions (2020-2023)Dokument28 SeitenOrganic Chemistry P2 Questions (2020-2023)moiz.8450Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry SK015 Pre-Lab EXP 1Dokument3 SeitenChemistry SK015 Pre-Lab EXP 1FATIN FARHANAH BINTI HALIDIN MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual 02Dokument158 SeitenLab Manual 02Stephen VivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- IX - Chemistry KAT Worksheet - IIIDokument3 SeitenIX - Chemistry KAT Worksheet - IIIVrindavanchandra Animation StudiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Chem STOICHIOMETRYDokument46 SeitenPrinciples of Chem STOICHIOMETRYALIGARBES, Rhonna May L.Noch keine Bewertungen
- IMO55 2021 T2 Problems EngDokument15 SeitenIMO55 2021 T2 Problems EngTrần Phạm Gia BảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Properties of WaterDokument9 SeitenChemical Properties of WaterMohammad Cipto SugionoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Living Things Are Highly Organized Sahar HassannejadDokument20 SeitenLiving Things Are Highly Organized Sahar HassannejadFarhang PrintingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Chemistry An Active Learning Approach 6th Edition Cracolice Test BankDokument17 SeitenIntroductory Chemistry An Active Learning Approach 6th Edition Cracolice Test Banka5563409580% (1)
- Chemical Bonding Detailed Lesson PlanDokument18 SeitenChemical Bonding Detailed Lesson PlanAiah Rica Sumalinog100% (2)
- 3-1 Boundary of CellDokument20 Seiten3-1 Boundary of CellAndrey_gpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeVon EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolVon EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryVon EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (25)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (90)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionVon EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsVon EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (146)
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsVon EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableVon EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (22)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilVon EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (9)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingVon EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksVon EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementVon EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsVon EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (14)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (150)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableVon EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldVon EverandStuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (289)
- The Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastVon EverandThe Long Hangover: Putin's New Russia and the Ghosts of the PastBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (76)