Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Standards
Hochgeladen von
api-216728214Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Standards
Hochgeladen von
api-216728214Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
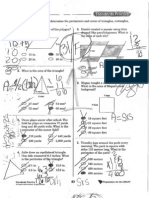
SOUTH CAROLINA ACADEMIC STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICS
Geometry
Standard 5-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of congruency, spatial relationships, and relationships among the properties of quadrilaterals.
Indicators
5-4.1 Apply the relationships of quadrilaterals to make logical arguments about their properties. 5-4.2 Compare the angles, side lengths, and perimeters of congruent shapes. 5-4.3 Classify shapes as congruent. 5-4.4 Translate between two-dimensional representations and three-dimensional objects. 5-4.5 Predict the results of multiple transformations on a geometric shape when combinations of translation, reflection, and rotation are used. 5-4.6 Analyze shapes to determine line symmetry and/or rotational symmetry.
Measurement
Standard 5-5: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the units and systems of measurement and the application of tools and formulas to determine measurements.
Indicators
5-5.1 Use appropriate tools and units to measure objects to the precision of one-eighth inch. 5-5.2 Use a protractor to measure angles from 0 to 180 degrees. 5-5.3 Use equivalencies to convert units of measure within the metric system: converting length in millimeters, centimeters, meters, and kilometers; converting liquid volume in milliliters, centiliters, liters, and kiloliters; and converting mass in milligrams, centigrams, grams, and kilograms. 5-5.4 Apply formulas to determine the perimeters and areas of triangles, rectangles, and parallelograms. 5-5.5 Apply strategies and formulas to determine the volume of rectangular prisms. 5-5.6 Apply procedures to determine the amount of elapsed time in hours, minutes, and seconds within a 24-hour period. 5-5.7 Understand the relationship between the Celsius and Fahrenheit temperature scales. 5-5.8 Recall equivalencies associated with length, liquid volume, and mass:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Geometry Performance IndicatorsDokument10 SeitenGeometry Performance IndicatorsSravan Kumar ChallojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Standard For Grades 6Dokument2 SeitenGeometry Standard For Grades 6Made DwijayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- cmp3 Nyc gr8 Scope and SequenceDokument8 Seitencmp3 Nyc gr8 Scope and Sequenceapi-232678646Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wingett Unitplan2Dokument8 SeitenWingett Unitplan2api-317475882Noch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook MAM2085S 2016Dokument91 SeitenHandbook MAM2085S 2016dylansheraton123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scope & Sequence G10Dokument2 SeitenScope & Sequence G10Olatowode OluwatosinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Honors Syllabus Final 2014-2015Dokument4 SeitenGeometry Honors Syllabus Final 2014-2015api-260883102Noch keine Bewertungen
- PLD GeometryDokument11 SeitenPLD Geometryapi-310256368Noch keine Bewertungen
- GeometryDokument49 SeitenGeometryJennylyn MaraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scope & Sequence G8 1st & 2nd SemesterDokument3 SeitenScope & Sequence G8 1st & 2nd SemesterOlatowode OluwatosinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5-3 AlgebraDokument12 Seiten5-3 AlgebramrkballNoch keine Bewertungen
- Informal GeometryDokument3 SeitenInformal Geometryanon-579447Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learning ObjectivesDokument2 SeitenLearning Objectivesapi-129741358Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 4 Math Unit 3 Concept Map 2013-14 With TasksDokument11 SeitenGrade 4 Math Unit 3 Concept Map 2013-14 With Tasksapi-252811687Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry BookDokument249 SeitenGeometry BookMarizza Bailey100% (1)
- Ccgps Math 5 Unit5frameworkDokument64 SeitenCcgps Math 5 Unit5frameworkapi-288619706Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 BackgroundDokument1 SeiteUnit 6 Backgroundapi-246172196Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Calculus SyllabusDokument5 SeitenPre-Calculus Syllabusapi-300745826Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry TopicsDokument4 SeitenGeometry TopicsRejieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fractions Assessment Marking CriteriaDokument2 SeitenFractions Assessment Marking Criteriaapi-306376059Noch keine Bewertungen
- College Algebra SyllabusDokument5 SeitenCollege Algebra Syllabusanon-579447Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Preliminary & HSC Course OutlineDokument10 SeitenMathematics Preliminary & HSC Course OutlineTrungVo369Noch keine Bewertungen
- Course Outline (Math 2041)Dokument2 SeitenCourse Outline (Math 2041)Nahom EliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Syllabi 2015-2016Dokument1 SeiteCourse Syllabi 2015-2016api-294397535Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Map Math 8thDokument41 SeitenCurriculum Map Math 8thapi-241650432Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cmo 13, S. 2008 - Annex III - Course Specifications For The Bscpe ProgramDokument52 SeitenCmo 13, S. 2008 - Annex III - Course Specifications For The Bscpe ProgramChris ArguellesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Division - Lesson 1Dokument4 SeitenDivision - Lesson 1magicklaxonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engaa SpecificationDokument24 SeitenEngaa SpecificationdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 8 Commom Core SyllabusDokument6 SeitenMath 8 Commom Core Syllabusapi-261815606Noch keine Bewertungen
- Course Syllabus in Mathematics IIDokument9 SeitenCourse Syllabus in Mathematics IIGena ClarishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Standards Adopted 1997 7Dokument6 SeitenMath Standards Adopted 1997 7establoid1169Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCTM Statement of Beliefs: M A T H E M A T I C SDokument6 SeitenNCTM Statement of Beliefs: M A T H E M A T I C SFreddy Reyes FalckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformations ProjectDokument15 SeitenTransformations Projectapi-278805077Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geo 1 4Dokument4 SeitenGeo 1 4rmullen82Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus II Textbook OptionsDokument6 SeitenCalculus II Textbook OptionsMohsen SharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- A15 201-NYC Linear AlgebraDokument5 SeitenA15 201-NYC Linear AlgebraNicole GuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus Trigonometry 1Dokument8 SeitenSyllabus Trigonometry 1Rogelio PontejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide to Math 38 - Mathematical Analysis IIIDokument2 SeitenGuide to Math 38 - Mathematical Analysis IIIPau BorlagdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Geometry SyllabusDokument18 Seiten12 Geometry SyllabusSri KondabattulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lessonplan RubricDokument2 SeitenLessonplan Rubricapi-248927320Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fourth Grade English Language ArtsDokument18 SeitenFourth Grade English Language ArtshnlfranzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mcv4u Course Outline 16Dokument4 SeitenMcv4u Course Outline 16api-323266544Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Nine-Point CircleDokument9 SeitenThe Nine-Point CircleMr. Bran100% (1)
- Fourth Grade Syllabus 2015Dokument8 SeitenFourth Grade Syllabus 2015api-274977607Noch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Description of Content of CourseDokument2 SeitenDetailed Description of Content of CourseAhmadMoaazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Math 2033 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDokument4 Seiten2 Math 2033 Plane and Spherical Trigonometrynoli90100% (1)
- 4 Standards HorizontalDokument2 Seiten4 Standards Horizontalapi-327901674Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Pacing Guide 2016-2017Dokument2 SeitenGeometry Pacing Guide 2016-2017api-325084503Noch keine Bewertungen
- UnitOutline-MM1 2022Dokument7 SeitenUnitOutline-MM1 2022Sreeya DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Plan Cartesian Planes Year 5:6Dokument18 SeitenUnit Plan Cartesian Planes Year 5:6magicklaxonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra I Outline - Eligible ContentDokument1 SeiteAlgebra I Outline - Eligible Contentapi-234130682Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diana Curriculum AnalysisDokument14 SeitenDiana Curriculum Analysisapi-245618390Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade/Subject: Mathematics/Grade 8 Unit 6: Congruence and SimilarityDokument18 SeitenGrade/Subject: Mathematics/Grade 8 Unit 6: Congruence and SimilaritySabrina Maula AfdahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry: Approximate Grade Level: 9 - 10 M/W or T/TH 11:00 AM - 11:55 AM Course DescriptionDokument3 SeitenGeometry: Approximate Grade Level: 9 - 10 M/W or T/TH 11:00 AM - 11:55 AM Course Descriptionapi-308781855Noch keine Bewertungen
- Determining Height With TrigonometryDokument5 SeitenDetermining Height With TrigonometryMus'ab UsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Grade Math Staar Teks ChecklistDokument5 Seiten4th Grade Math Staar Teks Checklistheatherw123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Priyar MSC MathsDokument20 SeitenPriyar MSC MathsJothi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miap20s Course Content WeightsDokument7 SeitenMiap20s Course Content Weightsapi-683027695Noch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Self Assessment FormDokument2 SeitenProfessional Self Assessment Formapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Self Assessment 1Dokument2 SeitenProfessional Self Assessment 1api-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Long Range PlanDokument17 SeitenLong Range PlanWhitleyHurdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Time TestDokument5 Seiten2nd Time Testapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math DataDokument1 SeiteMath Dataapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Video Consent FormDokument1 SeiteVideo Consent Formapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Praxis ScoresDokument2 SeitenPraxis Scoresapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Browns EvaluationsDokument7 SeitenBrowns Evaluationsapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adept Evaluation SummaryDokument1 SeiteAdept Evaluation Summaryapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- New EvalsDokument6 SeitenNew Evalsapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Claflin University School of EducationDokument4 SeitenClaflin University School of Educationapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Time TestDokument5 Seiten1st Time Testapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Readers TheaterDokument4 SeitenReaders Theaterapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes TogetherDokument5 SeitenNotes Togetherapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- AreaDokument8 SeitenAreaapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- PerimeterDokument3 SeitenPerimeterapi-216728214100% (1)
- TransformationsDokument16 SeitenTransformationsapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Standards SsDokument3 SeitenStandards Ssapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Video Lesson Plan-Tech Aviation and CommunicationDokument4 SeitenVideo Lesson Plan-Tech Aviation and Communicationapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instructional Strategies WkstsDokument4 SeitenInstructional Strategies Wkstsapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Using DataDokument2 SeitenUsing Dataapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- AreaDokument8 SeitenAreaapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- World War II Booklet RubricDokument1 SeiteWorld War II Booklet Rubricapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Objective: Test ScoresDokument1 SeiteObjective: Test Scoresapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Work Sample-WwiiDokument11 SeitenUnit Work Sample-Wwiiapi-216728214100% (1)
- AreaDokument4 SeitenAreaapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom ManagementDokument4 SeitenClassroom Managementapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Video Lesson Plan-Tech Aviation and CommunicationDokument4 SeitenVideo Lesson Plan-Tech Aviation and Communicationapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Claflin University School of Education: EDUC 450: Professional Clinical Practice Reflective Lesson Plan ModelDokument3 SeitenClaflin University School of Education: EDUC 450: Professional Clinical Practice Reflective Lesson Plan Modelapi-216728214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arabian Mathematics: Prepared By: Mark Rolando Tabbu Angelica GuzmanDokument15 SeitenArabian Mathematics: Prepared By: Mark Rolando Tabbu Angelica GuzmanronatabbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3-ME2617 Forced Vibration of SDOF SystemsDokument53 SeitenLecture 3-ME2617 Forced Vibration of SDOF SystemsHamzah QadriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making Clocks Workshop GuideDokument65 SeitenMaking Clocks Workshop GuideGOUTHAM RATHINAM100% (1)
- KREBS Products For COAL Mining Industry - DigitalDokument24 SeitenKREBS Products For COAL Mining Industry - DigitalTobias De SomerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Usuario Microcentrifuga Clay AdamsDokument19 SeitenManual Usuario Microcentrifuga Clay AdamsNARIÑO CONSACANoch keine Bewertungen
- 26.3 - Mass Defect and Nuclear Binding EnergyDokument8 Seiten26.3 - Mass Defect and Nuclear Binding EnergyDellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compound Glass Systems PV 2503: KonzernnormDokument6 SeitenCompound Glass Systems PV 2503: KonzernnormStefany BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BASICS OF AN INSTRUMENT AIR SUPPLY SYSTEM - Instrumentation and Control EngineeringDokument4 SeitenBASICS OF AN INSTRUMENT AIR SUPPLY SYSTEM - Instrumentation and Control EngineeringAhmadTaufikMuradNoch keine Bewertungen
- LD - 1 MSDokument28 SeitenLD - 1 MSDr. Love TrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat 2Dokument58 SeitenHeat 2Ayush SrivastavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crossword English Global WarmingDokument2 SeitenCrossword English Global WarmingADRIANA SOFIA RODRIGUEZ HERNANDEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Concrete Column Slenderness Flowchart Process CSA A23.3-19Dokument1 Seite02 Concrete Column Slenderness Flowchart Process CSA A23.3-19hichem titouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For College Physics 5th Edition Alan GiambattistaDokument24 SeitenTest Bank For College Physics 5th Edition Alan Giambattistaalexiscastillorbtjcdazng100% (46)
- Review - Physics Semester Exam - 1Dokument28 SeitenReview - Physics Semester Exam - 1techzealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differences Between Electrical Power and Electrical EnergyDokument4 SeitenDifferences Between Electrical Power and Electrical EnergyCatherine TabujaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET Pre-Medical Major Test ScheduleDokument1 SeiteNEET Pre-Medical Major Test ScheduleSUBHAM DASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joey G. Carillo, Lord Boy C. Silong, & Engr. Jack O. BertulfoDokument1 SeiteJoey G. Carillo, Lord Boy C. Silong, & Engr. Jack O. BertulfoLORD BOY SILONGNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument169 SeitenUntitledle huyNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Book) McElreath, Richard. Statistical RethinkingDokument483 Seiten(Book) McElreath, Richard. Statistical RethinkingR0% (1)
- The Mathematical Quotezine NotebookDokument24 SeitenThe Mathematical Quotezine NotebookScribb DbircsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustics Module 1: Factors and DefectsDokument11 SeitenAcoustics Module 1: Factors and DefectsKrupa NidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitinol in Plain LanguageDokument105 SeitenNitinol in Plain LanguagesilviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mustang Series M116-52 or M6116-52 (Globe), M1116-52 or M61116-52 (Angle) Installation InstructionsDokument2 SeitenMustang Series M116-52 or M6116-52 (Globe), M1116-52 or M61116-52 (Angle) Installation InstructionsWattsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lathi Ls SM Chapter 3Dokument52 SeitenLathi Ls SM Chapter 3Dr Satyabrata JitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsDokument97 SeitenChapter 1 - Electric Charges and FieldsPriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beer Lambert's Law MCQsDokument95 SeitenBeer Lambert's Law MCQsKaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identification of 2H and 3R Polytypes of MoS2 Layered Crystals Using Photoluminescence SpectrosDokument7 SeitenIdentification of 2H and 3R Polytypes of MoS2 Layered Crystals Using Photoluminescence SpectroswesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- File:Number-line-4.svg - Wikimedia CommonsDokument1 SeiteFile:Number-line-4.svg - Wikimedia CommonsAiden BallesterosNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review of Terrain Aided Navigation For Underwater VehiclesDokument16 SeitenA Review of Terrain Aided Navigation For Underwater VehiclesPrasad PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Sesion 14: Lecturer: Dra. Hariani, M.PDDokument11 SeitenModul Sesion 14: Lecturer: Dra. Hariani, M.PDMfatanj100% (1)