Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
3T06Bioorg11Physical Properties of Alkanes
Hochgeladen von
nofacejackOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
3T06Bioorg11Physical Properties of Alkanes
Hochgeladen von
nofacejackCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Alkanes
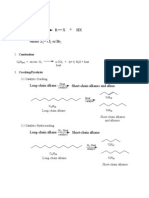
Saturated hydrocarbon; General Formula: CnH2n+2 Primarily used as fuels. solvents and lubricants Physical Properties Solubilities: Non-polar- dissolve in nonpolar or weakly polar solvents Hydrophobic- do not dissolve in water, good lubricants and preservatives because they keep water from reaching the metal surface and causing corrosion Densities Around 0.7 g/mL Separates into two layers with alkanes on top when mixed with water Boiling Points Increase smoothly with increasing carbons Branched alkanes have lower bp than straight-chained alkanes Melting point Increase with increasing molecular weight (increase in melting point is not smooth. Alkanes with even number of C have higher mp than odd number of C because they pack better into a solid structure than odd number alkanes Branched alkane melts higher than normal (n) alkane with the same number of C atoms. Branching gives it more compact 3D structure which packs more easily into a solid structure.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reactions of AlkanesDokument1 SeiteReactions of AlkanesnofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pericyclic Reactions PDFDokument41 SeitenPericyclic Reactions PDFnofacejack67% (3)
- 1-Chemical Analysis - Quantitation - SDokument39 Seiten1-Chemical Analysis - Quantitation - SnofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5-AAS SDokument39 Seiten5-AAS SnofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Light - Matter - SDokument32 Seiten3-Light - Matter - SnofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intsta1 Lecture8Dokument51 SeitenIntsta1 Lecture8nofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intsta1 Lecture5Dokument19 SeitenIntsta1 Lecture5nofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intsta1 Lecture4Dokument40 SeitenIntsta1 Lecture4nofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Continuous Probability DistributionsDokument11 SeitenSpecial Continuous Probability DistributionsnofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intsta1 Lecture3Dokument45 SeitenIntsta1 Lecture3nofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intsta1 Lecture6Dokument26 SeitenIntsta1 Lecture6nofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intsta1 Lecture1Dokument18 SeitenIntsta1 Lecture1nofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intsta1 Lecture2Dokument18 SeitenIntsta1 Lecture2nofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hard QuestionDokument183 SeitenHard QuestionWidodo Muis100% (1)
- The Big Book of Mind-Bending PuzzlesDokument338 SeitenThe Big Book of Mind-Bending PuzzlesAustin Albert93% (14)
- Glycosaminoglycan Monsaccharide Components Function: LinkageDokument1 SeiteGlycosaminoglycan Monsaccharide Components Function: LinkagenofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 9: Rectangular Coordinate PlaneDokument1 SeiteLesson 9: Rectangular Coordinate PlanenofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rev Bio 4th 10-11 (Part 2)Dokument4 SeitenRev Bio 4th 10-11 (Part 2)nofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- WATERDokument2 SeitenWATERnofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rev Bio 4th 10-11 (Part 1)Dokument8 SeitenRev Bio 4th 10-11 (Part 1)nofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To AlgebraDokument1 SeiteIntroduction To AlgebranofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Naming and Chemical Formula WritingDokument47 SeitenRevised Naming and Chemical Formula WritingnofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes Updated Mar 2010Dokument6 SeitenEnzymes Updated Mar 2010nofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates 2 UpdatedDokument7 SeitenCarbohydrates 2 UpdatednofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monosaccharides (Aldoses) : Biochem Structure Sheet 1. CarbohydratesDokument1 SeiteMonosaccharides (Aldoses) : Biochem Structure Sheet 1. CarbohydratesnofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids: C COO H N H CHDokument2 SeitenAmino Acids: C COO H N H CHnofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipids NotesDokument5 SeitenLipids NotesnofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Logic of Life Student NotesDokument4 SeitenMolecular Logic of Life Student Notesnofacejack67% (3)
- Enzymes Updated Mar 2010Dokument6 SeitenEnzymes Updated Mar 2010nofacejackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Pre Stressed Concrete Manual Computer Applications On SAP2000, ETABSDokument259 SeitenPre Stressed Concrete Manual Computer Applications On SAP2000, ETABSGardener AyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sch4uc PTDokument15 SeitenSch4uc PTMarwan MohamudNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP 2 - General Physics II Microwave RadiationDokument9 SeitenGROUP 2 - General Physics II Microwave RadiationRheyven JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samsung CAC Duct S Brochure 20140729 0Dokument16 SeitenSamsung CAC Duct S Brochure 20140729 0Callany AnycallNoch keine Bewertungen
- PV Sol-Main-11014092 (En) Hi PDFDokument56 SeitenPV Sol-Main-11014092 (En) Hi PDFŁukasz Misak100% (1)
- Pressure - Enthalpy Diagram For The Refrigerant R-22: Li Q U IdDokument1 SeitePressure - Enthalpy Diagram For The Refrigerant R-22: Li Q U IdRifki AuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Observational AstronomyDokument427 SeitenObservational AstronomyKorhan KaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science and Health 6Dokument2 SeitenScience and Health 6MA. PATRIA MANDAPNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC Toolbox Users ManualDokument14 SeitenMEC Toolbox Users ManualAntonio Pedro TessaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2 Calibration of Voltmeter: Aim: PrincipleDokument3 SeitenExperiment 2 Calibration of Voltmeter: Aim: PrincipleKEREN EVANGELINE I (RA1913011011002)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Projet RockyDokument19 SeitenProjet RockyCassella AdrianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vishay g200Dokument7 SeitenVishay g200rogerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48 TM 004007Dokument60 Seiten48 TM 004007Joseph DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPS Neuttral EarthingDokument11 SeitenUPS Neuttral Earthingarun kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell and Molecular Biology Module (Lecture and Laboratory)Dokument200 SeitenCell and Molecular Biology Module (Lecture and Laboratory)RM Montemayor100% (2)
- Sink CSMDokument2 SeitenSink CSMZulfiqar AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- C15 and C18 Generator SetDokument4 SeitenC15 and C18 Generator Setspider blackNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Atoms: Level-IIDokument19 Seiten12 Atoms: Level-IIrithiram0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Uk-Lr10 4 PDFDokument2 SeitenUk-Lr10 4 PDFViệt Dương ĐứcNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTV Silicone Rubber CoatingDokument7 SeitenRTV Silicone Rubber CoatingJane ChatsiriphatthanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drift Angle Wind SpeedDokument36 SeitenDrift Angle Wind Speedrahulagarwal33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name:Sajeel Khan ROLL#:M.phil-SSP-03-F19 Class: M.phil SSP (Morning) Subject: X-Ray Diffraction Submitted TO: Dr. Shahid Atiq SBDokument13 SeitenName:Sajeel Khan ROLL#:M.phil-SSP-03-F19 Class: M.phil SSP (Morning) Subject: X-Ray Diffraction Submitted TO: Dr. Shahid Atiq SBAnonymous f7wV1lQKRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kami Export - ALEXA CADENA - PhotosynthesisLabSE - Google Doc VersionDokument5 SeitenKami Export - ALEXA CADENA - PhotosynthesisLabSE - Google Doc VersionALEXA CADENANoch keine Bewertungen
- MD Product Catalogue PROXIMITY ENGDokument194 SeitenMD Product Catalogue PROXIMITY ENGETIENNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Covalent and Metallic Bonding Mcqs by FMDokument17 SeitenCovalent and Metallic Bonding Mcqs by FMfarymemon15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pryda Bracing Design Guide 2022Dokument32 SeitenPryda Bracing Design Guide 2022benjaminsigabalavuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dye Laser: Navigation SearchDokument6 SeitenDye Laser: Navigation SearchselvakanmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No. 4 - 2020-21 PDFDokument2 SeitenAssignment No. 4 - 2020-21 PDFnikhil khanwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- X-Ray Tubes &Dokument45 SeitenX-Ray Tubes &Aakash BhosaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Seal Bonnet Design: Dedication To DeliveryDokument44 SeitenPressure Seal Bonnet Design: Dedication To DeliverylutNoch keine Bewertungen