Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Relative Clauses Theory
Hochgeladen von
crisrolo2538320 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
428 Ansichten1 SeiteRELATIVE CLAUSES are introduced with either a relative pronoun or a relative adverb. Who, which and that can be omitted when they are the object of the relative clause. Whom is always used instead of who or that after a preposition: "She's someone with whom I used to work".
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenRELATIVE CLAUSES are introduced with either a relative pronoun or a relative adverb. Who, which and that can be omitted when they are the object of the relative clause. Whom is always used instead of who or that after a preposition: "She's someone with whom I used to work".
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
428 Ansichten1 SeiteRelative Clauses Theory
Hochgeladen von
crisrolo253832RELATIVE CLAUSES are introduced with either a relative pronoun or a relative adverb. Who, which and that can be omitted when they are the object of the relative clause. Whom is always used instead of who or that after a preposition: "She's someone with whom I used to work".
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
5TH YEAR E.O.
I
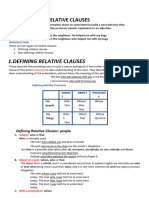
UNIT 7: RELATIVE CLAUSES
• Relative clauses are introduced with either a relative pronoun or a relative
adverb.
• RELATIVE PRONOUNS:
WHO(M) /THAT To refer to people
WHICH/THAT To refer to things
WHOSE With people, animals and objects to show
possession (instead of a possessive adjective).
• Who, which and that can be omitted when they are the object of the
relative clause:
“That is the film (that) I was telling you about”.
• Whom can be used instead of who when it is the object of the relative
clause. Whom is always used instead of who or that after a preposition:
“She´s someone with whom I used to work”.
• Who, which or that is not omitted when it is the subject of a relative
clause:
“The play which won the Tony Award was a musical”.
• Whose is never omitted:
“This is Bruce whose photographs you must have seen”.
• RELATIVE ADVERBS:
WHEN To refer to a time and can be omitted.
/THAT
WHERE To refer to a place.
WHY To give a reason, usually after the word “reason”and
can be omitted.
• DEFINING AND NON-DEFINING RELATIVE CLAUSES
• A defining relative clause gives necessary information essential to the
meaning of the main sentence. It is not put between commas and is
introduced with who, which, that, whose, when, where or the reason
(why).
“Any student who is caught cheating will be expelled”.
• A non-defining relative clause gives extra information and is not essential
to the meaning of the main sentence. It is put between commas and is
introduced with who, whom, which, whose, where or when.
“A student, who was caught cheating, was expelled”.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cleft Sentences+ExercisesDokument5 SeitenCleft Sentences+Exercisescrisrolo25383289% (38)
- Relative ClausesDokument12 SeitenRelative ClausesTấn DũngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative ClausesDokument11 SeitenRelative ClausesannasanjosecbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify Adjective Clauses with Subject and Object Relative PronounsDokument16 SeitenIdentify Adjective Clauses with Subject and Object Relative PronounsEstefane Abigail OyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn About Relative ClausesDokument28 SeitenLearn About Relative ClausesjoloalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn about relative clausesDokument28 SeitenLearn about relative clausesAnonymous HWsv9pBUhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative ClausesDokument28 SeitenRelative ClausesMeyke Jayanti KinasihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Pronouns and Relative Adverbs PDFDokument2 SeitenRelative Pronouns and Relative Adverbs PDFMaria TravagliniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative ClauseDokument22 SeitenRelative ClauseRye EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Adjective Clauses - RepairedDokument10 SeitenRelative Adjective Clauses - RepairedJackie HoffmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Clause?: Independent ClausesDokument5 SeitenWhat Is A Clause?: Independent ClausesRahul DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elative Lauses: Explaining English GrammarDokument20 SeitenElative Lauses: Explaining English Grammarhaymanot aNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Pronouns and ClausesDokument10 SeitenRelative Pronouns and ClausesReham AmmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Clauses: - Defining Clauses - Non-Defining ClausesDokument13 SeitenRelative Clauses: - Defining Clauses - Non-Defining ClausesPedro ArezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Clauses ExplainedDokument4 SeitenRelative Clauses ExplainedChea LincheatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjective Clauses - Part 1Dokument10 SeitenAdjective Clauses - Part 1Naaim EyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative ClausesDokument6 SeitenRelative ClausesEsranur GürgenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of SpeechDokument13 SeitenParts of SpeechAziz RNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFORMEDokument15 SeitenINFORMEYesseniaMedinaTerronesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjective Clause GuideDokument9 SeitenAdjective Clause GuideIntan PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Adjective Clauses PowerPoint ILI MD, Chapter 12, E4 GrammarDokument7 SeitenIntroduction To Adjective Clauses PowerPoint ILI MD, Chapter 12, E4 GrammarPaul NicklasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 9: Lengua Ingelsa IIDokument19 SeitenLesson 9: Lengua Ingelsa IIDavid Bell100% (1)
- Noun ClausesDokument9 SeitenNoun Clausesnyu tsukiyomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RELATIVE CLAUSES DEFINING NON-DEFININGDokument9 SeitenRELATIVE CLAUSES DEFINING NON-DEFININGDomingo de LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SN 8Dokument2 SeitenSN 8New SupplierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of ClausesDokument11 SeitenTypes of ClausesChristineNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Use Relative Pronouns Who, Which and ThatDokument2 SeitenHow to Use Relative Pronouns Who, Which and Thatkhlis81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clause: - There Are Two Types of ClausesDokument10 SeitenClause: - There Are Two Types of ClausesSarlita NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of ClausesDokument12 SeitenTypes of ClausesCorazon ReymarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pronouns: Standing in For NounsDokument38 SeitenPronouns: Standing in For NounsVERNADETTE ESTRELLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Noun ClauseDokument3 SeitenNoun ClauseAlfianizza AufanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Clauses TheoryDokument5 SeitenRelative Clauses TheoryireneNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIZ 1054 DeterminersDokument18 SeitenBIZ 1054 DeterminersChuah Jia HuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative ClausesDokument22 SeitenRelative ClausesmariabetaniaalbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Relative ClausesDokument6 SeitenUnderstanding Relative ClausesEpifánio António De OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- PronounsDokument4 SeitenPronounschilufyampundu03Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Parts of Speech in English: Verb Noun Adjective Adverb Pronoun Preposition Conjunction InterjectionDokument14 SeitenThe Parts of Speech in English: Verb Noun Adjective Adverb Pronoun Preposition Conjunction InterjectionJufri NstNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defining and Non-Defining Relative Clauses 1Dokument12 SeitenDefining and Non-Defining Relative Clauses 1juan gomez del angelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rel ClausesDokument4 SeitenRel ClausesMagalí StylesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd PPT On Pronouns 1 1 - 1659120080391Dokument7 Seiten2nd PPT On Pronouns 1 1 - 1659120080391ARIYAN PALITNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 13 Relative Pronouns PADokument8 SeitenUNIT 13 Relative Pronouns PAP. AlmeidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative ClausesDokument11 SeitenRelative Clausessaeed100% (1)
- Presentation About Noun ClausesDokument13 SeitenPresentation About Noun Clausesclaudia clavioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of Speech: The 8 "Building Blocks" of The English LanguageDokument9 SeitenParts of Speech: The 8 "Building Blocks" of The English LanguageArman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative ClausesDokument9 SeitenRelative ClausesSandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Pronouns and ClausesDokument6 SeitenRelative Pronouns and ClausesRolando ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative ClausesDokument9 SeitenRelative ClausesTania Samael Uribe HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Clauses ExplainedDokument15 SeitenRelative Clauses Explainedander oviedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Clauses Grammar ReferenceDokument2 SeitenRelative Clauses Grammar ReferencemariecbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defining Relative ClausesDokument13 SeitenDefining Relative Clauses10elNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Clauses Grammar Guides 140856Dokument16 SeitenRelative Clauses Grammar Guides 140856Roberta OrlandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cald3 1326036100156Dokument1 SeiteCald3 1326036100156oprea silvia elenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What you need to know about clausesDokument34 SeitenWhat you need to know about clausesgood girlNoch keine Bewertungen
- LOG101 Week 4 Definition (20230217170330)Dokument90 SeitenLOG101 Week 4 Definition (20230217170330)John Rey Operaña IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Noun ClausesDokument48 SeitenNoun ClausesLili_Hzn_nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles 6Dokument9 SeitenIngles 6Laura ZamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- PronounDokument18 SeitenPronounCaliph JagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative ClausesDokument11 SeitenRelative ClausesVictoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 2 PronounDokument29 SeitenGroup 2 PronounJacob Clint LipuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Clauses: English GrammarDokument10 SeitenRelative Clauses: English GrammarDr MontyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEF. U6B By Cristina Rodríguez - Prepositions of PlaceDokument21 SeitenNEF. U6B By Cristina Rodríguez - Prepositions of Placecrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- I M Starving!! Soami. Me Too. I Am Too.: Nef: U-1A by Cristina RodríguezDokument7 SeitenI M Starving!! Soami. Me Too. I Am Too.: Nef: U-1A by Cristina Rodríguezcrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cooking VerbsDokument2 SeitenCooking Verbscrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Object PronounsDokument10 SeitenObject Pronounscrisrolo253832100% (2)
- KEY To Food Vocab 1aDokument2 SeitenKEY To Food Vocab 1acrisrolo2538320% (1)
- DVD TranscriptDokument12 SeitenDVD Transcriptcrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cooking VerbsDokument2 SeitenCooking Verbscrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- FoodDokument17 SeitenFoodcrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cooking VerbsDokument2 SeitenCooking Verbscrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cooking VerbsDokument2 SeitenCooking Verbscrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Complete With A or AnDokument3 SeitenComplete With A or Ancrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cooking VerbsDokument2 SeitenCooking Verbscrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Saying HelloDokument2 SeitenSaying Hellocrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Famous PeopleDokument9 SeitenFamous Peoplecrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dancing QueenDokument1 SeiteDancing Queencrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Relative ExercisesDokument2 SeitenRelative Exercisescrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dancing QueenDokument1 SeiteDancing Queencrisrolo253832100% (1)
- Word FormationDokument5 SeitenWord Formationcrisrolo2538320% (2)
- Review AnswersDokument3 SeitenReview Answerscrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- If I Had A Secretary, I Wouldn T Have Done All The Typing MyselfDokument3 SeitenIf I Had A Secretary, I Wouldn T Have Done All The Typing Myselfcrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review AnswersDokument1 SeiteReview Answerscrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- ConditionalsDokument2 SeitenConditionalscrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- In Versions After Negative AdverbialsDokument2 SeitenIn Versions After Negative Adverbialscrisrolo253832100% (2)
- Warming Up ConditionalsDokument2 SeitenWarming Up Conditionalscrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formal LettersDokument3 SeitenFormal Letterscrisrolo25383250% (2)
- Plans and ArrangementsDokument3 SeitenPlans and Arrangementscrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen
- BlogDokument1 SeiteBlogcrisrolo253832100% (1)
- UNIT 3: 5th E.O.I. Inversion 1: Actually Lived ThereDokument3 SeitenUNIT 3: 5th E.O.I. Inversion 1: Actually Lived Therecrisrolo253832Noch keine Bewertungen