Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ileus T/C Sbo, HPN 2 Pathophysiology
Hochgeladen von
Charlayne AnneOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ileus T/C Sbo, HPN 2 Pathophysiology
Hochgeladen von
Charlayne AnneCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
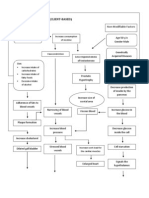
Modifiable Risk Factors: GI Surgery Constipation Medications Electrolyte Imbalance Spinal Cord Injury (T5) Stress
Non - Modifiable Risk Factors: Age (60+) Gender (Females are more affected than males Genetics
Infrequent defecation withholding the Stool
Decrease blood flow to organs
Maximum heart rate declines due to aging
Infrequent bowel movements Damages blood vessels throughout the body overtime
Alterations in blood pressure
Decreased diastolic filling of the ventricles
Difficulty in defecating
High blood pressure Hypertension Kidney filters (Glomerulus) may not function due to damage
Constipation Kidneys blood vessels are narrowed or possibly damaged (+) Abdominal Colic
After load rises secondary to increase stiffness in the ascending aorta
Decreased/impaired Bowel movement
Impairment of the ventricles Inability of ventricles to empty the chamber
Accumulation of Gas and Fluids within the bowel
Intestinal/Abdominal Distention
Diaphragm is compressed due to abdominal distention
Higher end diastolic feeling pressure reduces myocardial blood flow
Accumulation of waste products in the intestinal lining
Shortness of breathing Waste products and excess fluid cannot be excreted Large molecules can pass through Glomeruli
Inadequate supply to other organs
Bowel Obstruction
Inadequate supply of blood to the brain
Proteins may pass through and are excreted through the urine Proteinuria:
Excessive fluid volume Edema Bed ridden
One part of the brain losses function
Stroke Coma GCS: E1 V1 M1 = 3
Prolonged Catheterization
Bed sores/ulcers may occur Some wounds are not medicated or treated
Infection
WBC:
Chief Complaint: Cannot defecate
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Discharge Plan EndoDokument3 SeitenDischarge Plan EndoCharlayne AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- History of Philippine LiteratureDokument2 SeitenHistory of Philippine LiteratureCharlayne AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Nursing Care Plan For Stroke PatientsDokument7 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Stroke Patients_cezca_85% (89)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Urinary SystemDokument2 SeitenUrinary SystemCharlayne AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- FDARDokument2 SeitenFDARCharlayne Anne40% (5)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Cva PPT Case PresDokument19 SeitenCva PPT Case PresCharlayne AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Modifiable Factors: Ix. Pathophysiology (Client-Based)Dokument3 SeitenModifiable Factors: Ix. Pathophysiology (Client-Based)Charlayne AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenDrug StudyCharlayne AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- VIII. Drug StudyDokument11 SeitenVIII. Drug StudyCharlayne AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- CD NursingDokument43 SeitenCD NursingCharlayne AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIII. Drug StudyDokument11 SeitenVIII. Drug StudyCharlayne AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)