Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
4mat Shelter
Hochgeladen von
api-198669584Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
4mat Shelter
Hochgeladen von
api-198669584Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
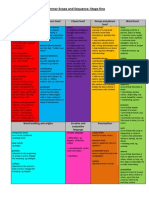
4 Mat Unit HSIE: The need for shelter Stage 1
Outcomes: ENS1.6 Demonstrates an understanding of the relationship between environments and people. - Identifies ways in which people depend on the environment - Identifies ways in which peoples interactions with the environment can change the environment - Recognises that Aboriginal peoples have interacted with the environment positively for a long time
Orla Page
ENS1.5 Compares and contrasts natural and built features in their local area and the ways people interact with these features and sites - Examines the difference between built and natural features and sites - Identifies similarities and differences between natural features and sites in their local area and those in other areas - Associates geographical terms for places and features with visual images - Makes and interprets 3D models of features and places - Expresses feelings for particular environments and why they have these feelings
Quadrant One - Creating an Experience: Connect (right brain activity) Examine (Left Brain activity) Students will explore things they want but may not need. Discuss going on a camping trip or being shipwrecked on a deserted island. What might you take with you? What will you want? What might you need? On small card students draw what they need to take camping. Discuss drawings as a whole class. Repeat activity for wants. Discuss the difference in what students need to take camping and what they want to take camping.
Students look at needs through classifying them in order of importance to them. Using the students drawings, classify the pictures as need or want. Discuss differences. Jointly define needs and wants Using need drawings students work in small groups and rank four needs in order of importance. Students report back to whole class and discuss why they made their choices. View on DET intranet TALES HSIE Interactive island needs and wants Students create an image of their own shelter. Ask students to describe their picture and how they feel in this environment Discuss different types of shelters that students have drawn units/flats, town houses, semi-detached, free standing houses. What features do they have that are similar? Different? Discuss and take a look at shelters around the local area (streets bordering the school). Observe and draw/sketch pictures of homes/buildings. Create a streetscape for the classroom wall. Discuss how these buildings provide shelter.
Quadrant Two - The Concept: Imaging the concepts (right brain activity)
Developing the concepts (left brain activity)
Quadrant Three Practise and personalise (right brain activity)
1. Brainstorm the main features of a house/ shelter, providing vocab for students to describe their own shelter. Students label their shelter drawing. 2. Jointly construct a definition of a shelter. Referring to a dictionary to verify or amend. 3. Jointly view text/websites about homes in other parts of Australia and the world http://www.hgpho.to/wfest/house/house-e.html - Discuss how these shelters are suited to particular environments or climates eg stilts, wide veranda, steep roof - Compare similarities and differences - Discuss materials used and why they are used 4. Aboriginal shelters. - View images of Aboriginal shelters. Discuss materials used and the environment they were built in. - Look at text and investigate the way Aboriginal people have adapted to harsh environments such as the desert. - Visit from an Aboriginal Elder to school 5. Jointly construct a flow chart of building a shelter 6. Write a procedure on how to build a cubby house - Students will complete a web quest on various types of housing around the world - Create a collage of different types of dwellings - Homework task: students could build an inside cubby house at home using sheets, pegs, blankets etc. Students can draw their cubby house and report back to the class what design features worked/didnt work; what materials they used; and how they built their cubby.
Actively experimenting (left brain) Quadrant Four Reinforcement and manipulation Refining for application and relevance (right brain activity) Doing it themselves and sharing with others (left brain)
Analyse pictures of different shelters Provide a picture of a shelter and in small groups students use a retrieval chart (below)to gather information about their picture of a shelter. Students can report back using Think/pair/share. Makes 3D model of a shelter suited to a specific environment In pairs students will be allocated a climate/environment to design and build a 3D model of a shelter that would be suited to that specific environment. - Students will need to design their shelter, draw, label, list materials used (as if it was in the real world) and build.
Students will present their design/models to the class (or other class) - Need to explain their design for that climate features and materials used Discuss how we alter the environment to create shelters for humans - Brainstorm ways that we can keep environmental impact to a minimum
Environment
Climate
Materials used
Design features
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Faust Part Two - Johann Wolfgang Von GoetheDokument401 SeitenFaust Part Two - Johann Wolfgang Von GoetherharsianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharingtheplanet 8-12upDokument4 SeitenSharingtheplanet 8-12upapi-147600993Noch keine Bewertungen
- Opal Lee and What It Means to Be Free Educator's Guide: The True Story of the Grandmother of JuneteenthVon EverandOpal Lee and What It Means to Be Free Educator's Guide: The True Story of the Grandmother of JuneteenthBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- NSW Handwriting Scope and Sequence k-2Dokument2 SeitenNSW Handwriting Scope and Sequence k-2api-198669584100% (3)
- Social Unit PlanDokument20 SeitenSocial Unit Planapi-489862967Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sharing The PlanetDokument4 SeitenSharing The Planetapi-147600993100% (2)
- InfoVista Xeus Pro 5 TMR Quick GuideDokument76 SeitenInfoVista Xeus Pro 5 TMR Quick GuideNguyen Dang KhanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Where We Are in Place in Time 1 17 13Dokument4 SeitenWhere We Are in Place in Time 1 17 13api-147600993Noch keine Bewertungen
- Art Integrated Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenArt Integrated Lesson Planapi-248641854100% (1)
- Software Quality Metrics MethodologyDokument17 SeitenSoftware Quality Metrics MethodologySumit RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Melanie Cella Unit Plan 3 Grade Topic: Animals and EcosystemsDokument42 SeitenMelanie Cella Unit Plan 3 Grade Topic: Animals and Ecosystemsapi-384066525Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices and Electronic Circuits: QuestionsDokument51 SeitenElectronic Devices and Electronic Circuits: QuestionsRohit SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- How The World WorksDokument3 SeitenHow The World Worksapi-250808296100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Marketing Management: by Prabhat Ranjan Choudhury, Sr. Lecturer, B.J.B (A) College, BhubaneswarDokument53 SeitenFundamentals of Marketing Management: by Prabhat Ranjan Choudhury, Sr. Lecturer, B.J.B (A) College, Bhubaneswarprabhatrc4235Noch keine Bewertungen
- All Kinds of Bears: An Integrated Unit for Elementary SchoolVon EverandAll Kinds of Bears: An Integrated Unit for Elementary SchoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Art Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenArt Lesson Planapi-269199367Noch keine Bewertungen
- LTC 4240 Art Integration Lesson PlanDokument6 SeitenLTC 4240 Art Integration Lesson Planapi-254257614Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kremmel ArtintegratedunitDokument4 SeitenKremmel Artintegratedunitapi-254251035Noch keine Bewertungen
- Saturday Art - Lesson Plan Adaptations Flip BookDokument6 SeitenSaturday Art - Lesson Plan Adaptations Flip Bookapi-264233549Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Focus: Environments Grade: 2Dokument8 SeitenUnit Focus: Environments Grade: 2api-320610068Noch keine Bewertungen
- Art Integration Lesson Plan Template: (Please Circle)Dokument5 SeitenArt Integration Lesson Plan Template: (Please Circle)api-302379773Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sustainability UnitDokument17 SeitenSustainability Unitapi-285314391Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indigenous STEM Sample Lesson 1: (Junior High)Dokument7 SeitenIndigenous STEM Sample Lesson 1: (Junior High)api-543824384Noch keine Bewertungen
- Draft Unit PlanDokument12 SeitenDraft Unit Planapi-265334535Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jennerra LppolishedDokument4 SeitenJennerra Lppolishedapi-312080780Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Mat Wet Dry Environ 2Dokument7 Seiten4 Mat Wet Dry Environ 2api-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pba Lesson 5Dokument5 SeitenPba Lesson 5api-302824532Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hsie Our Place Term 2Dokument4 SeitenHsie Our Place Term 2api-208000806Noch keine Bewertungen
- Float Sink Lesson Plan 2Dokument6 SeitenFloat Sink Lesson Plan 2api-388627256Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching and LearningDokument6 SeitenTeaching and Learningapi-247416806Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan SCNDokument3 SeitenLesson Plan SCNapi-253740903Noch keine Bewertungen
- Block Plan EinselenDokument2 SeitenBlock Plan Einselenapi-272786644Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arts Assignment 2Dokument7 SeitenArts Assignment 2isabellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit PresentationDokument20 SeitenUnit Presentationapi-404422607Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sose Unit CompleteDokument18 SeitenSose Unit Completeapi-263184946Noch keine Bewertungen
- LTC 4240 Art Integration Unit Plan TemplateDokument5 SeitenLTC 4240 Art Integration Unit Plan Templateapi-251299147Noch keine Bewertungen
- FinalartDokument6 SeitenFinalartapi-265174867Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Lesson PlanDokument6 Seiten1 Lesson Planapi-427935712Noch keine Bewertungen
- One Persons Trash Is Another's Treasure Art Unit - Grade 7Dokument4 SeitenOne Persons Trash Is Another's Treasure Art Unit - Grade 7hellkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 LetterDokument5 SeitenUnit 3 Letterapi-237760840Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Project TemplateDokument14 SeitenFinal Project TemplateMAT2986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inquiry Assesment Project 2017 Part OneDokument4 SeitenInquiry Assesment Project 2017 Part Oneapi-362162791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Place Es1Dokument5 SeitenPlace Es1api-260443196Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geography 2Dokument5 SeitenGeography 2api-561111966Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calendar 2Dokument4 SeitenCalendar 2api-263471389Noch keine Bewertungen
- Haury LessonsixDokument3 SeitenHaury Lessonsixapi-240991456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sse Azure Gipson LP Template 2015Dokument5 SeitenSse Azure Gipson LP Template 2015api-284046416Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coast Miwok Unit 3 Grade Class: Description of The Integrated Curriculum UnitDokument11 SeitenCoast Miwok Unit 3 Grade Class: Description of The Integrated Curriculum Unitapi-269754690Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Lesson Plan 1Dokument4 SeitenIntegrated Lesson Plan 1api-456004455Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Unit OutlineDokument2 SeitenIntegrated Unit Outlineapi-299096655Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Reset 6th Grade Unit Layout and Materials 4 1 24Dokument11 SeitenRevised Reset 6th Grade Unit Layout and Materials 4 1 24api-735929865Noch keine Bewertungen
- Identify Desired Results (Stage 1) Content Standards: and TopicsDokument6 SeitenIdentify Desired Results (Stage 1) Content Standards: and Topicsapi-229802853Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nature Walk Lesson PlanDokument7 SeitenNature Walk Lesson PlanKatelin SchroederNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backward DesignDokument5 SeitenBackward Designapi-334865072Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 3Dokument3 SeitenLesson Plan 3api-261801340Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Complete Answers in Purple Font) : STEM 433/533 Lesson Planning TemplateDokument4 Seiten(Complete Answers in Purple Font) : STEM 433/533 Lesson Planning Templateapi-510369386Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 4 HabitatsandcommunitiesframeworkDokument7 SeitenGrade 4 Habitatsandcommunitiesframeworkapi-337088263Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 RelativedatingDokument5 Seiten1 Relativedatingapi-382026608Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPGDokument5 SeitenEdtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPGapi-636480355Noch keine Bewertungen
- Creativity Science Reading LessonDokument6 SeitenCreativity Science Reading Lessonapi-272909297Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Unit Planner TemplateDokument16 Seiten2015 Unit Planner Templateapi-265554130Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hibernation Play ReneeDokument6 SeitenHibernation Play Reneeapi-489881515Noch keine Bewertungen
- Art Lesson PlanDokument8 SeitenArt Lesson Planapi-285019687Noch keine Bewertungen
- Social Science Unit For EDU 383 Social Science Methods Name Emily DarterDokument8 SeitenSocial Science Unit For EDU 383 Social Science Methods Name Emily Darterapi-316811443Noch keine Bewertungen
- National Parks Thematic UnitDokument13 SeitenNational Parks Thematic Unitapi-497358383Noch keine Bewertungen
- English DramaDokument1 SeiteEnglish Dramaapi-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2h Grammar ProgramDokument4 Seiten2h Grammar Programapi-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Es 1 S 1 TeachingprogramDokument14 SeitenEs 1 S 1 Teachingprogramapi-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pdhpe Scope and SequenceDokument2 SeitenPdhpe Scope and Sequenceapi-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Timetable 2014Dokument1 SeiteTimetable 2014api-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- JourneysDokument9 SeitenJourneysapi-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fms OverviewDokument1 SeiteFms Overviewapi-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Story of Our Lives t1 2014Dokument9 SeitenThe Story of Our Lives t1 2014api-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year Overview 14Dokument3 SeitenYear Overview 14api-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Are We There YetDokument7 SeitenAre We There Yetapi-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stage 1 English Outcomes OverviewDokument1 SeiteStage 1 English Outcomes Overviewapi-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hsie Stage OneDokument1 SeiteHsie Stage Oneapi-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dps Grammar Stage 1Dokument3 SeitenDps Grammar Stage 1api-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- t4 Literacy ProgramDokument11 Seitent4 Literacy Programapi-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transport 0Dokument1 SeiteTransport 0api-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths t3 w1Dokument1 SeiteMaths t3 w1api-198669584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Long-Distance HADR ConfigurationsDokument73 SeitenAutomated Long-Distance HADR ConfigurationsKan DuNoch keine Bewertungen
- TesisDokument388 SeitenTesisHadazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPA Digital Media Owners Survey Autumn 2010Dokument33 SeitenIPA Digital Media Owners Survey Autumn 2010PaidContentUKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Đại Từ Quan Hệ Trong Tiếng AnhDokument5 SeitenĐại Từ Quan Hệ Trong Tiếng AnhNcTungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsJonyzhitop TenorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simplified Cost Accounting Part Ii: Solutions ManualDokument58 SeitenSimplified Cost Accounting Part Ii: Solutions ManualAnthony Koko CarlobosNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGMT 400-Strategic Business Management-Adnan ZahidDokument5 SeitenMGMT 400-Strategic Business Management-Adnan ZahidWaleed AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2-EER and Relational Database SchemaDokument146 SeitenChapter 2-EER and Relational Database Schemagirmay tadeseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabre, Intro To Unfinished Quest of Richard WrightDokument9 SeitenFabre, Intro To Unfinished Quest of Richard Wrightfive4booksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Art of Insight PDFDokument409 SeitenArt of Insight PDF31482Noch keine Bewertungen
- Extraction of Non-Timber Forest Products in The PDFDokument18 SeitenExtraction of Non-Timber Forest Products in The PDFRohit Kumar YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Character Skills Snapshot Sample ItemsDokument2 SeitenCharacter Skills Snapshot Sample ItemsCharlie BolnickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mod B - HSC EssayDokument11 SeitenMod B - HSC EssayAryan GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Recall and SkepticismDokument4 SeitenTotal Recall and Skepticismdweiss99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test A NN4 2020-2021Dokument2 SeitenTest A NN4 2020-2021Toska GilliesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer in Auditing Problems by Reynaldo Ocampo PDFDokument1 SeiteReviewer in Auditing Problems by Reynaldo Ocampo PDFCarlo BalinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ghosh, D. P., 1971, Inverse Filter Coefficients For The Computation of Apparent Resistivity Standard Curves For A Horizontally Stratified EarthDokument7 SeitenGhosh, D. P., 1971, Inverse Filter Coefficients For The Computation of Apparent Resistivity Standard Curves For A Horizontally Stratified EarthCinthia MtzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Exam 201460 UpdatedDokument12 Seiten2nd Exam 201460 UpdatedAlbert LuchyniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidated PCU Labor Law Review 1st Batch Atty Jeff SantosDokument36 SeitenConsolidated PCU Labor Law Review 1st Batch Atty Jeff SantosJannah Mae de OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occ ST 1Dokument3 SeitenOcc ST 1Rona Marie BulaongNoch keine Bewertungen
- They Cried MonsterDokument13 SeitenThey Cried MonstermassuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of AIDokument27 SeitenHistory of AImuzammalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hanssen, Eirik.Dokument17 SeitenHanssen, Eirik.crazijoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Vs Health and Safety Vs Reputation Vs Opportunity CostsDokument11 SeitenFinancial Vs Health and Safety Vs Reputation Vs Opportunity Costschanlego123Noch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Document 2Dokument12 SeitenPDF Document 2Nhey VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen