Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Torque, HP, and Speed The Speed On A Conveyor Is Increased by Increasing The AC Drive
Hochgeladen von
sanshinde10Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Torque, HP, and Speed The Speed On A Conveyor Is Increased by Increasing The AC Drive
Hochgeladen von
sanshinde10Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
If the effective tension of a conveyor were calculated to be 2000 pounds and the maximum speed is 750 FPM, then
the required horsepower is 45.5.
Starting torque of a conveyor can be 1.5 to 2 times full load torque. A motor capable of driving a fully loaded conveyor may not be able to start and accelerate the conveyor up to speed. AC drives can typically supply 1.5 times full load torque for starting. An engineer may need to choose a larger motor and drive in order to start and accelerate the conveyor. Torque, HP , and Speed The speed on a conveyor is increased by increasing the AC drive frequency (F) to the motor. Torque (T) is affected by flux ()) and working current (IW). The drive will maintain constant flux by keeping the voltage and frequency ratio constant. To do this the drive increases voltage and frequency in proportion. During acceleration working current will increase, however, causing a corresponding increase in torque. Once at its new speed the working current and torque will be the same as its old speed. The conveyor cannot be operated above the rated frequency of the motor (60 Hz) without losing available torque. Since torque is proportional to (volts/Hz)2 any increase in speed will cause available torque to decrease by the square. As a result, the motor will be unable to supply rated torque. Horsepower (HP) is affected by torque and speed. There will be a corresponding increase in horsepower as speed (RPM) increases.
100
Variable Torque Applications
A variable torque load implies that torque and horsepower increase with an increase in speed. Overloads, as a rule of thumb, are not possible at lower speeds. Peak torques are typically limited to rated torque. Fans and pumps are examples of variable torque. A pump used on a chilled water system is shown below.
101
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Liquid Horsepower Liquid Horsepower Is The Hydraulic Power Transferred To TheDokument2 SeitenLiquid Horsepower Liquid Horsepower Is The Hydraulic Power Transferred To Thesanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Knee Point Here Gives The Rated SpeedDokument2 SeitenThe Knee Point Here Gives The Rated SpeedtankimsinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variable Frequency Drive Based On Load CharacteristicsDokument6 SeitenVariable Frequency Drive Based On Load CharacteristicsarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Performance Characteristics and Application Guidelines - Fe 3100Dokument6 SeitenMotor Performance Characteristics and Application Guidelines - Fe 3100proteuscarrillusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variable TorqueDokument2 SeitenVariable TorqueKrrishNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Torque VFDDokument3 SeitenHP Torque VFDcaibillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yaskawa Electric America: The Basics of AC Drive ApplicationsDokument123 SeitenYaskawa Electric America: The Basics of AC Drive Applicationsnikika1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Converting Our Generators From 60Hz To 50Hz PowerDokument2 SeitenConverting Our Generators From 60Hz To 50Hz PowerZahid Mehmood100% (3)
- AC Drive Theory and Application1Dokument66 SeitenAC Drive Theory and Application1satyendra kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load Inertia Motor SelectionDokument3 SeitenLoad Inertia Motor Selectiondanferreiro8318100% (1)
- VFD Pump RelationshipsDokument15 SeitenVFD Pump RelationshipsMohcyn MunyrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Droop Setting in TurbineDokument2 SeitenDroop Setting in TurbinepurnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Droop Setting in TurbineDokument2 SeitenDroop Setting in TurbinepurnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap4 Hydrodynamic TransmissionDokument5 SeitenChap4 Hydrodynamic TransmissionIsaac NjorogeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Motor Formulas and Calculations PDFDokument11 SeitenBasic Motor Formulas and Calculations PDFAditya Shrivastava100% (2)
- VFDDokument49 SeitenVFDkisan singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Change of Voltage and Frequency On Electrical EquipmentDokument17 SeitenEffect of Change of Voltage and Frequency On Electrical EquipmentAhmed ElsharkawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loads Adjustable Speed Drives: Starting Inertia ONDokument6 SeitenLoads Adjustable Speed Drives: Starting Inertia ON1977julNoch keine Bewertungen
- If You Have A Speedtronic Mark IV or Mark V or Mark VIDokument55 SeitenIf You Have A Speedtronic Mark IV or Mark V or Mark VIAnonymous fDP5ceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pointless - Important Thing Is To Understand Philosophy of Droop Control Once You Understand That, It Becomes Self Evident. inDokument2 SeitenPointless - Important Thing Is To Understand Philosophy of Droop Control Once You Understand That, It Becomes Self Evident. inGolu kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variable Freequency Drive (VFD) : (A Theory and Practical Guide)Dokument43 SeitenVariable Freequency Drive (VFD) : (A Theory and Practical Guide)sanskriti123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Drive: FundamentalsDokument45 SeitenAc Drive: FundamentalsShivaji ThubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Shunt MotorDokument9 SeitenDC Shunt MotorPeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isn't It Obvious? It Does So Because It Is Commanded To Do So, You Said So Yourself. All Good Generators Do As Commanded, Don't They?Dokument10 SeitenIsn't It Obvious? It Does So Because It Is Commanded To Do So, You Said So Yourself. All Good Generators Do As Commanded, Don't They?abhijit.adgube3376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power and Torque PDFDokument10 SeitenPower and Torque PDFGhssoüb GhssoubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 1.3 Hydraulic System Power RequirementDokument4 SeitenSection 1.3 Hydraulic System Power Requirementaerogem618Noch keine Bewertungen
- DC Shunt MotorDokument9 SeitenDC Shunt MotorPeterNoch keine Bewertungen
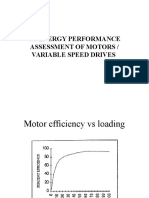
- 4.5 Energy Performance Assessment of Motors / Variable Speed DrivesDokument24 Seiten4.5 Energy Performance Assessment of Motors / Variable Speed DrivesranveerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed Regulation, Percent Slip and Start CurrentDokument3 SeitenSpeed Regulation, Percent Slip and Start Currentabdulyunus_amirNoch keine Bewertungen
- DriveMotorBasics01 PDFDokument11 SeitenDriveMotorBasics01 PDFSundar Kumar Vasantha GovindarajuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor TechNotes OverspeedsDokument2 SeitenMotor TechNotes OverspeedsramoebpNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Generator Works and Compete With Load Set PointDokument7 SeitenHow Generator Works and Compete With Load Set PointLakshmi NarayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequency Controlled Ac Motor Drive: 1.0 Features of Standard AC MotorsDokument12 SeitenFrequency Controlled Ac Motor Drive: 1.0 Features of Standard AC MotorsvenikiranNoch keine Bewertungen
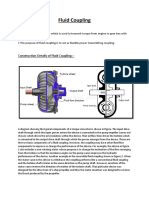
- Construction Details of Fluid CouplingDokument4 SeitenConstruction Details of Fluid CouplingSagar Patil100% (1)
- Fluid Coupling & Fluid Torque ConverterDokument5 SeitenFluid Coupling & Fluid Torque ConverterMahmoud Magdy RizkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torque Conveter TA22-42E Training TextDokument8 SeitenTorque Conveter TA22-42E Training TextPHÁT NGUYỄN THẾNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static Thrust For PropellerDokument9 SeitenStatic Thrust For PropellerDr.S.RamamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Motor FrequencyDokument3 SeitenElectric Motor FrequencyPriya JakoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- VFD TutorialDokument21 SeitenVFD TutorialDaniel Taiti Kimathi100% (3)
- Nameplate PDFDokument8 SeitenNameplate PDFobida adailehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6.2 - Speed Control of Ac MotorDokument45 SeitenChapter 6.2 - Speed Control of Ac MotorWeehao SiowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed Control Methods of Induction MotorDokument6 SeitenSpeed Control Methods of Induction MotorsahebraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Can We Run A VFD Motor With Higher SpeedDokument1 SeiteCan We Run A VFD Motor With Higher SpeedMarey MorsyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accelerating and Breakdown TorqueDokument44 SeitenAccelerating and Breakdown TorqueekonurudinahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power and TorqueDokument5 SeitenPower and Torqueanappan0% (1)
- DC Motor Transient Response Lab ReportDokument9 SeitenDC Motor Transient Response Lab ReportErick OderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion Lab 2Dokument2 SeitenDiscussion Lab 2cameenNoch keine Bewertungen
- TP2-Satya PrakashDokument13 SeitenTP2-Satya Prakashm_azhagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequency Shifting Power To and From 60 HZ To 50 HZDokument3 SeitenFrequency Shifting Power To and From 60 HZ To 50 HZALPHONCENoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens - Motor SpecificationsDokument50 SeitenSiemens - Motor SpecificationsArtifoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Low Voltage On MotorDokument3 SeitenEffect of Low Voltage On MotorLuisito RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesVon EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesVon EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetVon EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetVon EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetVon EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Fengshui Santosh Page1Dokument1 SeiteFengshui Santosh Page1sanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hi My Name Is Santosh I Will Be Training You One Fengshui BasicDokument1 SeiteHi My Name Is Santosh I Will Be Training You One Fengshui Basicsanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hi My Name Is Santosh I Will Be Training You One Fengshui BasicDokument1 SeiteHi My Name Is Santosh I Will Be Training You One Fengshui Basicsanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cbt13 Schooldays.1Dokument1 SeiteCbt13 Schooldays.1sanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1. What's The Story?Dokument5 SeitenChapter 1. What's The Story?sanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics 45Dokument1 SeiteBasic Electronics 45sanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics 9Dokument1 SeiteBasic Electronics 9sanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Enno 3Dokument1 SeiteEnno 3sanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics 6Dokument1 SeiteBasic Electronics 6sanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics 10Dokument1 SeiteBasic Electronics 10sanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- PLD (Programmable Logic Device) : - All Layers Already ExistDokument1 SeitePLD (Programmable Logic Device) : - All Layers Already Existsanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Semi-Custom: - Lower Layers Are Fully or Partially BuiltDokument1 SeiteSemi-Custom: - Lower Layers Are Fully or Partially Builtsanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- General-Purpose Processors: - Programmable Device Used in A Variety of Applications - FeaturesDokument1 SeiteGeneral-Purpose Processors: - Programmable Device Used in A Variety of Applications - Featuressanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- IC Technology: - Three Types of IC TechnologiesDokument1 SeiteIC Technology: - Three Types of IC Technologiessanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Full-custom/VLSI: - All Layers Are Optimized For An Embedded System's Particular Digital ImplementationDokument1 SeiteFull-custom/VLSI: - All Layers Are Optimized For An Embedded System's Particular Digital Implementationsanshinde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- NullDokument10 SeitenNullapi-25932525Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report of NumericalsDokument7 SeitenReport of Numericals79Jay ShethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nzgp1 Scenarios Update: NZGP1 Scenarios and Modelling Results For An Unconstrained Transmission GridDokument44 SeitenNzgp1 Scenarios Update: NZGP1 Scenarios and Modelling Results For An Unconstrained Transmission GridIBA PUNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 ProblemsDokument17 Seiten4 ProblemsJairo Fernandez100% (1)
- Pressure, Density, Temperature, Velocity and Mach No. Changes Across A Normal Shock WaveDokument7 SeitenPressure, Density, Temperature, Velocity and Mach No. Changes Across A Normal Shock WaveJeremy GorospeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Harmonic FilterDokument8 SeitenActive Harmonic FilterKanai BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry 2Dokument13 SeitenGeneral Chemistry 2MarianneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 6 Electromagnetism in Everyday LifeDokument68 SeitenScience: Quarter 2 - Module 6 Electromagnetism in Everyday LifeJacob Dy67% (3)
- Physics I Problems PDFDokument1 SeitePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNoch keine Bewertungen
- An 4134Dokument14 SeitenAn 4134shri.bhairavkar6977Noch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet 2Dokument10 SeitenDatasheet 2miguel angel jaramilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improvement in Patel Teja Eqn of StatesDokument10 SeitenImprovement in Patel Teja Eqn of StatesSumukh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasonics PDFDokument3 SeitenUltrasonics PDFSankalpa psNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi VerseDokument82 SeitenMulti VerseAntito123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Activity 3 Application of Bernoullis TheoremDokument13 SeitenLaboratory Activity 3 Application of Bernoullis TheoremChardel PorlaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 2 Examination Trials PhysicsDokument15 SeitenForm 2 Examination Trials PhysicsBoaz BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentasi ICT-PEP FinalDokument14 SeitenPresentasi ICT-PEP FinalIndriyanto PeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neutral Grounding Resistors: MeasuringDokument3 SeitenNeutral Grounding Resistors: MeasuringRajendra Prasad ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bushing CapacitivoDokument19 SeitenBushing Capacitivo434lapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 8: Alternating Current (A.C.)Dokument29 SeitenUnit 8: Alternating Current (A.C.)kayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ficha Tecnica SkyAir CODokument1 SeiteFicha Tecnica SkyAir COErnesto Garza - CN8 ProyectosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opti 6104Dokument3 SeitenOpti 6104Nenad MitrovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raoult's Law: Solution Solvent o SolventDokument8 SeitenRaoult's Law: Solution Solvent o SolventAbdul Azeem KhosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SB2011-10 Online EN PDFDokument66 SeitenSB2011-10 Online EN PDFAmanda KaizerNoch keine Bewertungen
- LHB Eog Power CarDokument41 SeitenLHB Eog Power Carvishak MkNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANALYTICAL CHEM LEC 3 - Unit 2, Chapter 2 (Sample Problems)Dokument3 SeitenANALYTICAL CHEM LEC 3 - Unit 2, Chapter 2 (Sample Problems)ARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONoch keine Bewertungen
- Bulk Weight OF AggregatesDokument15 SeitenBulk Weight OF AggregatesKyle SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kcet Mathematics Question Paper 2023 2282Dokument11 SeitenKcet Mathematics Question Paper 2023 2282Teja CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Lab Manual Volume OneDokument60 SeitenElectrical Lab Manual Volume OneMahesh M P NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bhel TG RollingDokument26 SeitenBhel TG RollingAnand Swami100% (2)