Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Rules For Subject-Verb Agreement
Hochgeladen von
pragya_rai5090Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Rules For Subject-Verb Agreement
Hochgeladen von
pragya_rai5090Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Rules for Subject-Verb agreement
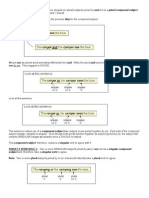
Make the subject and verb agree when words intervene between them.
The grammatical number of the subject does not change with the addition of
expressions beginning with such words as the following: accompanied by, along with, as
well as, in addition to, including, no less than, not to mention, together with.
Subjects joined by and are usually plural
Singular subjects joined by or, either . . . or, neither . . . nor take a singular verb.
If one subject is singular and one is plural, the verb agrees with the nearer subject.
The verb also agrees with the nearer subject in person.
Do not let inverted word order cause you to make a mistake in agreement.
When used as subjects, such words as each, either, one, everybody, and anyone
regularly take singular verbs.
Every or each preceding singular subjects joined by and calls for a singular verb.
Collective nouns take a singular verb when they refer to the group as a unit.
Collective nouns take a plural verb when they refer to individuals or parts of the
group.
Some nouns (such as athletics, politics, series, deer, and sheep) can be either singular
or plural depending on meaning.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Subjects Verbs AgreementDokument19 SeitenSubjects Verbs AgreementPuvanes SomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Verb AgreementDokument2 SeitenSubject Verb AgreementNorlene L. MenguanNoch keine Bewertungen
- by Group 5 Ikm-7Dokument15 Seitenby Group 5 Ikm-7NURUL FIFI ALAYDANoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject-Verb AgreementDokument20 SeitenSubject-Verb AgreementLyka CasillanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject - Verb AgreementDokument17 SeitenSubject - Verb AgreementCharmain Mae A. MamacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject-Verb Agreement ModuleDokument16 SeitenSubject-Verb Agreement Modulekhairulrasyid100% (1)
- 9T Lesson Plan On Subject-Verb AgreementDokument3 Seiten9T Lesson Plan On Subject-Verb AgreementTeika Knott-AndersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUBJECT Verb AgreementDokument12 SeitenSUBJECT Verb AgreementmymytrangNoch keine Bewertungen
- HS-001A Subject-Verb AgreementDokument39 SeitenHS-001A Subject-Verb AgreementS KohliNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Noun?Dokument4 SeitenWhat Is Noun?Christian GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 Linguistic CompetenceDokument15 SeitenLesson 4 Linguistic CompetenceShinji100% (1)
- Subject-Verb Agreement 1Dokument16 SeitenSubject-Verb Agreement 1Agan PrasetianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject-Verb AgreementDokument13 SeitenSubject-Verb AgreementIsmail KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Teaching UnitDokument12 SeitenSelf Teaching UnitELOISA CASANENoch keine Bewertungen
- Subj Verb Agreement (g5)Dokument23 SeitenSubj Verb Agreement (g5)Reycel Miravalles TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules On Subject-Verb AgreementDokument19 SeitenRules On Subject-Verb Agreementapi-374208995% (22)
- Assessment Reviewer and CoverageDokument11 SeitenAssessment Reviewer and CoverageLEGASPI EUGENE L.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Subjects VerbsDokument6 SeitenSubjects VerbsKyle GatdulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUBJECT VERB AGREEMENT Students'Dokument5 SeitenSUBJECT VERB AGREEMENT Students'Kashif BuzdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usage - Subject-Verb Agreement: Subjects VerbsDokument15 SeitenUsage - Subject-Verb Agreement: Subjects VerbsAubrey EuropeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 1 BeDokument115 SeitenUnit - 1 Bevicky PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUBJECT B. InggrisDokument11 SeitenSUBJECT B. InggrisTrianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hunter College Reading/Writing Center: Grammar and Mechanics The Verb System: Subject-Verb AgreementDokument7 SeitenHunter College Reading/Writing Center: Grammar and Mechanics The Verb System: Subject-Verb AgreementSuchan KhankluayNoch keine Bewertungen
- GMAT® Official Guide Supplement: Sentence Correction BasicsVon EverandGMAT® Official Guide Supplement: Sentence Correction BasicsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- English Grammar Made EasyDokument17 SeitenEnglish Grammar Made EasyAyaz Latif Siyal84% (19)
- Subject Verb AgreementDokument11 SeitenSubject Verb Agreementjazmin yasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Merry Ann A. Barbon DATE: APRIL 21, 2021 Section: Bse-Filipino 1Dokument11 SeitenName: Merry Ann A. Barbon DATE: APRIL 21, 2021 Section: Bse-Filipino 1Ronnie BarbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the basics Words: Unit 1 - Nouns - ءامسلااDokument4 SeitenUnderstanding the basics Words: Unit 1 - Nouns - ءامسلااosama aboualamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Verb AgreementDokument7 SeitenSubject Verb AgreementNica Barroso100% (1)
- Advanced Syntax Part 1 2Dokument34 SeitenAdvanced Syntax Part 1 2wg7hh2tmbdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sentence CorrectionDokument10 SeitenSentence CorrectionsanjivsingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject-Verb AgreementDokument7 SeitenSubject-Verb Agreementtsuna banaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahasa Inggris - GrammarDokument53 SeitenBahasa Inggris - GrammarFirda ExRock NeverDies Mncud-BeibzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Verb AgreementDokument18 SeitenSubject Verb AgreementBasilas Ace Dominic T.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aljerose DolorDokument6 SeitenAljerose DolorJaime PandoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Subject Verb AgreementDokument6 SeitenUnit 1 Subject Verb AgreementAdeb Mutalib100% (1)
- Unit 1 PDFDokument24 SeitenUnit 1 PDFRana pichaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Grammar Glossary For ParentsDokument6 SeitenPrimary Grammar Glossary For ParentsJack EdieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usage Problems of EnglishDokument4 SeitenUsage Problems of EnglishRachel MochNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usage - Subject-Verb Agreement: Subjects VerbsDokument8 SeitenUsage - Subject-Verb Agreement: Subjects VerbsAnonymous c4pPO7YphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject-Verb AgreementDokument9 SeitenSubject-Verb AgreementYash JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject-Verb Agreement - RulesDokument11 SeitenSubject-Verb Agreement - RulesdfmnNoch keine Bewertungen
- AttachmentDokument7 SeitenAttachmentOgunbiyi SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Verb AgreementDokument13 SeitenSubject Verb AgreementFlorivee Garcia EreseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maya Sukma (Kel. 4)Dokument4 SeitenMaya Sukma (Kel. 4)Maya SukmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agreement Between The Subject and The VerbDokument5 SeitenAgreement Between The Subject and The VerbLuz M. SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 8 Principal Parts of SpeechDokument24 SeitenThe 8 Principal Parts of SpeechChelsea LandiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject and Verb AgreementDokument23 SeitenSubject and Verb AgreementKaren Joy ViterboNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementDokument4 Seiten20 Rules of Subject Verb AgreementJohn Walter TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- INGLES Actividad 1Dokument4 SeitenINGLES Actividad 1Chiquinquira MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes ReviewerDokument23 SeitenNotes ReviewerJoanne JoanneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syntactic Linkage: by Haryono Lekat BaktiDokument7 SeitenSyntactic Linkage: by Haryono Lekat Baktiamelia100% (1)
- Subject-Verb Agreement - Handout 24Dokument7 SeitenSubject-Verb Agreement - Handout 24Veasna ChannNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Parts of SpeechDokument4 SeitenThe Parts of SpeechSoelapa 88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eight Parts of SpeechDokument41 SeitenEight Parts of SpeechAldrin AponNoch keine Bewertungen
- Other Parts of SpeechDokument7 SeitenOther Parts of SpeechLilibeth MalayaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Verb AgreementDokument17 SeitenSubject Verb AgreementAnne PaulinNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUBJECT - VERB - AGREEMENT Material PDFDokument11 SeitenSUBJECT - VERB - AGREEMENT Material PDFSameerNoch keine Bewertungen
- English for Execs: And Everyone Who Desires to Use Good English and Speak English Well!Von EverandEnglish for Execs: And Everyone Who Desires to Use Good English and Speak English Well!Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7A Verb+InfinitiveDokument1 Seite7A Verb+InfinitiveJuanCarlosPayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adverbs - 5Dokument4 SeitenAdverbs - 5Ebtihal Al-AwdhaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- B1 Reading Comprehension 10Dokument1 SeiteB1 Reading Comprehension 10Carolina LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gic1 U4Dokument24 SeitenGic1 U4Steven LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types and Styles: Arlene Joy CastilloDokument76 SeitenTypes and Styles: Arlene Joy CastilloKhiem AmbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Language Course: GermanDokument210 SeitenLanguage Course: German2004007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar BergañoDokument230 SeitenGrammar BergañoJohn Paulo Dizon SarsagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapa Conceptual EnglishDokument1 SeiteMapa Conceptual EnglishOscar AceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Big City: VocabularyDokument46 SeitenThe Big City: VocabularyRaul Alejandro Celis MaturanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Too-EnoughDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan Too-EnoughBenediktus R. Rattu89% (9)
- Universidad Del Pacifico Communicative English CourseDokument4 SeitenUniversidad Del Pacifico Communicative English CourseAnonymous iAomQwKDuENoch keine Bewertungen
- Collocation Radi PratamaDokument4 SeitenCollocation Radi PratamaSMK Taruna WiyatamandalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar I Appositives AppositiveDokument1 SeiteGrammar I Appositives Appositivemarcela noemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verbals: Gerunds, Infinitives, and ParticiplesDokument2 SeitenVerbals: Gerunds, Infinitives, and ParticiplesEstefaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar CopDokument47 SeitenGrammar CopEC Pisano Riggio100% (9)
- French Learning1Dokument89 SeitenFrench Learning1Amit BhanawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Grammar SuggestionDokument35 SeitenEnglish Grammar SuggestionmejbahuddinjabedNoch keine Bewertungen
- L3 15 Ref01 PDFDokument2 SeitenL3 15 Ref01 PDFNohan OlivanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Level Term Notes PDFDokument13 SeitenAdvanced Level Term Notes PDFNoël PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tag Question Lecture SheetDokument8 SeitenTag Question Lecture SheetJewel AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Verb Agreement RulesDokument4 SeitenSubject Verb Agreement RulesTay Kai XianNoch keine Bewertungen
- HF6 ApoioEstudo Grammar U1Dokument5 SeitenHF6 ApoioEstudo Grammar U1lizete.capelas8130Noch keine Bewertungen
- Semana7 1Dokument5 SeitenSemana7 1marita :3 atiram xDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Simple Find Someone Who PDFDokument2 SeitenPast Simple Find Someone Who PDFIng. Luis Alberto García CórdovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjectives Circling Writing P 1 BeginnerDokument1 SeiteAdjectives Circling Writing P 1 BeginnerNella Diane Ismael BiabanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - The 1990sDokument8 SeitenUnit 1 - The 1990sblaphemous gloryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Words Often ConfusedDokument24 SeitenWords Often ConfusedEddy TudorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1a Sec - Present Perfect Tense - PracticeDokument2 Seiten1a Sec - Present Perfect Tense - PracticeAngi Quincho YaulliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Intermediate Unit 9bDokument2 SeitenUpper Intermediate Unit 9bHuitzcuauhtlahuac CeyolcoatlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of English Words 1Dokument39 SeitenStructure of English Words 1emman leonardoNoch keine Bewertungen