Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Addison's Disease - CONCEPT MAP
Hochgeladen von
ninapotOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Addison's Disease - CONCEPT MAP
Hochgeladen von
ninapotCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
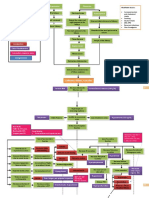
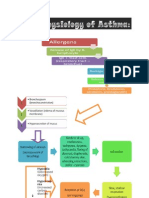
Autoimmune Idiopathic atrophy of the adrenal glands Iatrogenic due to surgical removal of both glands Infections (e.g.
e.g.,TB/Histoplasmosis) Administration of medications a. Hydrocortisone (Solu-cortef) given thru IV b. Vasopressor amine if hypotension persist Monitor vital signs Over secretion, exposure to cold, acute infections Anorexia Gastrointestinal symptoms Severe/chronic dehydration Muscular weakness To restore blood circulation Oral intake as tolerated to prevent hypovolemic shock Administer fluids (5% dextrose in NSS and Place patient in recumbent position with legs elevated Supplementary dietary intake (i.e., pickles) Emaciation (haggard looking/extreme leanness) Mental status changes (depression, apathy, emotional lability) Addisonian crisis with disease progression and acute hypotension Dark pigmentation of the skin
LEGEND Disease Definition Etiology Signs and symptoms Nursing Interventions Medical Management Goal of Therapy
Due to decreased cortisol/aldosterone Results when adrenal cortex function is inadequate to meet the patients need for cortical hormones Prevention of infection
Addisons Disease
To combat shock
Restoring fluid balance
Improving activity intolerance (Quiet and non-stressful activities) Monitoring for Addisonian crisis s/sx : a. Hypotension b. Rapid, weak respiratory rate c. Extreme weakness d. Pallor Promoting community and home-based care
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ACS PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenACS PathophysiologyFerliza OblenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map HypertensionDokument1 SeiteConcept Map Hypertensionninapot100% (1)
- Ards Concept MapDokument1 SeiteArds Concept Mapchristine louise bernardo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of VSDDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of VSDMarlon CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP CopdDokument14 SeitenNCP CopdJanine ClaudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Pulmonary EbolismneuronurseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Reasoning Questions - CollaborationDokument4 SeitenClinical Reasoning Questions - CollaborationMohammad OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)Dokument3 SeitenDrug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)mikErlhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of DMDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of DMShelly_Ann_Del_9959Noch keine Bewertungen
- Addisons DiseaseDokument12 SeitenAddisons DiseaseChinju CyrilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cushing's Disease - PathophysiologyDokument1 SeiteCushing's Disease - Pathophysiologyninapot67% (3)
- Addison'sDokument4 SeitenAddison'sKoRnflakesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For AsthmaDokument2 SeitenNCP For AsthmawaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3. COURSE TASK - Acute PancreatitisDokument3 SeitenWeek 3. COURSE TASK - Acute PancreatitisqwertNoch keine Bewertungen
- MI BrochureDokument2 SeitenMI BrochureAbedin Mehmedovic100% (1)
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenAngina Pectoris PathophysiologyALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of HyperthyroidismDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology of HyperthyroidismKitty YuffieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity IntoleranceDokument1 SeiteActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cystic Mass PathophysiologyDokument1 SeiteCystic Mass PathophysiologyMa Cheryll DueñasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionDokument50 SeitenPathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionPryo UtamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYPERTENSION Health TeachingDokument3 SeitenHYPERTENSION Health TeachingPaulo JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDokument4 SeitenDecreased Cardiac OutputAdnan Khan100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDokument3 SeitenImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument1 SeiteNursing Care PlanMikki lor PuaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDokument3 SeitenHypertension Obstruction: Chronic Renal FailureDiane-Richie PezLo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology On DementiaDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology On Dementiaiamjulzcurtis50% (2)
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDokument6 SeitenWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Final PortraitDokument11 SeitenCase Study Final PortraitZhy CaluzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addisons Disease PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenAddisons Disease PathophysiologyHanna NocumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDokument2 SeitenImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 1 (Pneumonia)Dokument13 SeitenCase Study 1 (Pneumonia)Kate EscotonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDokument4 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Breathing PatternDokument1 SeiteImpaired Breathing PatternHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPDokument2 SeitenRisk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPPaula AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTP of AsthmaDokument1 SeiteHTP of AsthmaMarland Faith Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlavixDokument2 SeitenPlavixianecunar100% (2)
- CKD - For Concept MappingDokument7 SeitenCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Dokument6 SeitenRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan On HypertensionDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Plan On Hypertensionbhavana100% (1)
- Concept Map - Colon CancerDokument2 SeitenConcept Map - Colon Cancerbea pegadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureLeng Royo BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDokument1 SeiteDecreased Cardiac OutputPrecious Heart Sotero TababaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decreased Cardiac Output FinalDokument2 SeitenDecreased Cardiac Output FinalSandraDeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism PathophysiologyDokument1 SeiteHypothyroidism PathophysiologyCleo Joyce C. CristalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schematic Diagram of StrokeDokument1 SeiteSchematic Diagram of StrokeMaricar K. BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- A: Hydrolyzed To Active Drug: Cebu Normal University - College of Nursing Drug StudyDokument1 SeiteA: Hydrolyzed To Active Drug: Cebu Normal University - College of Nursing Drug StudyMaki Dc100% (1)
- NCP CvaDokument4 SeitenNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyVic MagtotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument5 SeitenNursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Ugib Lower MBDokument65 SeitenCase Study Ugib Lower MBQuolette Constante100% (1)
- NCP CKDDokument3 SeitenNCP CKDRiel TumandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For Bladder CaDokument4 SeitenNCP For Bladder CaChris Tine CaccamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDokument5 SeitenHypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseAna Katrina OcanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Dokument6 SeitenIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Addison's DiseaseDokument3 SeitenAddison's Diseaseavinash dhameriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCMB 316 Cu14 AdrenalDokument39 SeitenNCMB 316 Cu14 AdrenalJanine Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- HipotiroidDokument27 SeitenHipotiroidJuwitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HyfrhDokument34 SeitenHyfrhmebibegNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addison DiseaseDokument23 SeitenAddison DiseaseKompari EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Exclusions A. This Policy Shall Not Cover Claims Arising FromDokument1 SeiteStandard Exclusions A. This Policy Shall Not Cover Claims Arising FromninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument18 SeitenChapter 3ninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative Community ExtentionDokument5 SeitenNarrative Community ExtentionninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I: Introduction To Human RelationsDokument62 SeitenUnit I: Introduction To Human RelationsninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic Inflammatory Response SyndromeDokument12 SeitenSystemic Inflammatory Response SyndromeninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (Mods)Dokument16 SeitenMultiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (Mods)ninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Ventilation: Presented By: Joahnna Marie A. Abuyan, RNDokument24 SeitenMechanical Ventilation: Presented By: Joahnna Marie A. Abuyan, RNninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Survey AnalysisDokument39 SeitenCustomer Survey AnalysisninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calayan Educational Foundation, Inc.: Lucena City, PhilippinesDokument1 SeiteCalayan Educational Foundation, Inc.: Lucena City, PhilippinesninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- His Grandfather Was Father Pedro CasanasDokument2 SeitenHis Grandfather Was Father Pedro CasanasninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map TOFDokument1 SeiteConcept Map TOFninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Path o PhysiologyDokument3 SeitenPath o PhysiologyninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Classification Drug Name Adverse EffectsDokument3 SeitenDrug Classification Drug Name Adverse EffectsninapotNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCCCCCC CC CDokument14 SeitenCCCCCCC CC CninapotNoch keine Bewertungen