Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Alignment Tolerances
Hochgeladen von
bendutsCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Alignment Tolerances
Hochgeladen von
bendutsCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
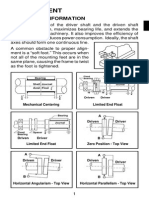
Machinery Alignment Tolerance Tables
The suggested alignment tolerances shown here are general values based upon experience and general industry standards and should not be exceeded. (Note: If a manufacturer of a machine or coupling require tighter alignment tolerances, those should be used) Consider all values listed to be the maximum allowable deviation from the alignment target, be it zero, or some desired value to compensate for thermal growth. In most cases, a quick glance at the table will tell whether coupling misalignment is allowable or not. Metric tolerances are given for machines with a 50Hz supply running at multiples/fractions of 3000 RPM. Imperial tolerances are given for machines with a 60 Hz supply running at multiples/fractions of 3600 RPM. Angularity is usually measured in terms of gap width at the edge of the coupling. For a given amount of angularity, the larger the diameter, the wider the gap at the coupling edge. The table lists values for coupling diameters of 100 mm or 10". If actual coupling diameter is required, multiply the value from the table by the appropriate factor.
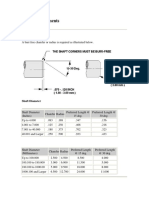
(RPM) metric (mm) 0.06mm Excellent Acceptable Offset 600 750 1500 1800 3000 3600 6000 7200 600 750 1500 1800 3000 3600 6000 7200 0.19 0.09 0.06 0.03 0.09 0.06 3.0 0.03 1.5 0.02 1.0 15.0 0.13 0.07 0.04 0.03 0.09 0.05 5.0 0.03 3.0 0.02 2.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 0.5 10.0 1.0 2.0 Acceptable 9.0 inch (mils) 2.0 mils Excellent
Align machine to within Acceptable Soft foot tolerances based upon coupling type and RPM Short "flexible"
couplings
any
5.0
Angularity (gap difference at coupling edge per 100 millimeters diameter
Complements of Pruftechnik, dB There Is A Better Way
For spacer shafts, the corresponding table gives the maximum allowable offset for each 100 mm or inch of spacer shaft length.
Spacer shafts and membrane (disk) couplings Offset (per 100 millimeters spacer length or per inch of spacer length)
600 750 1500 1800 3000 3600 6000 7200
3.0 0.25 0.12 0.07 0.03 0.15 0.07 1.0 0.04 0.5 0.02 0.3
1.8
0.6 0.3 0.2
"Acceptable" limits are calculated from sliding velocity of lubricated steel on steel, using a conservative value of 12 mm/sec. (0.5 in./sec.) for allowable sliding velocity. These values also coincide with those derived from elastomer shear rates, so they also apply to short couplings with flexible elements. The "excellent" values draw on vibration observations made upon a wide variety of industrial machines to determine the critical misalignment for vibration; however, compliance with these tolerance values does not guarantee vibration-free operation of a particular machine. Rigid couplings have no tolerance for misalignment, they should be aligned as accurately as possible.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Dynamic Movement White Paper: Vibralign, Inc. 530G Southlake BLVD Richmond, Va 232326 804.379.2250Dokument0 SeitenDynamic Movement White Paper: Vibralign, Inc. 530G Southlake BLVD Richmond, Va 232326 804.379.2250SreenivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alignment TolerancesDokument1 SeiteAlignment TolerancesbederinadmlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometrical TolerancingDokument12 SeitenGeometrical TolerancingItalo Venegas100% (1)
- Alignment Tolerance TableDokument1 SeiteAlignment Tolerance TableAlagar Samy ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Limits & Fits - Types of Fits Explained & Tolerance Charts - FractoryDokument10 SeitenLimits & Fits - Types of Fits Explained & Tolerance Charts - FractoryMangesh KetkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elastomeric Bearing PadDokument4 SeitenElastomeric Bearing PadMohammad Fikrie Bahrul Hayat100% (2)
- Shaft Alignment White PaperDokument14 SeitenShaft Alignment White PaperHamed HamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laser Alignment Standards PDFDokument10 SeitenLaser Alignment Standards PDFrohit singh100% (1)
- MH pgs0700Dokument15 SeitenMH pgs0700Hamza Nouman100% (1)
- 00.00.tolerancing and Engineering StandardsDokument55 Seiten00.00.tolerancing and Engineering StandardsJosh De LoeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ServoClass RohsDokument8 SeitenServoClass RohsManel MontesinosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tolerancing and Engineering StandardsDokument69 SeitenTolerancing and Engineering StandardsAnoj pahathkumburaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EN Prevent Turbomachinery Thrust FailuresDokument4 SeitenEN Prevent Turbomachinery Thrust FailuresUmair NaseemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla de Tolerancias PDFDokument1 SeiteTabla de Tolerancias PDFCesar Cedano VivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 400-10 (Meters & Accessories 49093) PDFDokument52 Seiten400-10 (Meters & Accessories 49093) PDFmetal_dung2Noch keine Bewertungen
- TC V1 28 enDokument40 SeitenTC V1 28 enJesus Hernandez AmezcuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix A - Tolerances For Impression DieDokument21 SeitenAppendix A - Tolerances For Impression Diekkozak99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alignment Tolerances: 9:1 Methods For Evaluating The Alignment QualityDokument5 SeitenAlignment Tolerances: 9:1 Methods For Evaluating The Alignment Qualityمنذر بوجازيةNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screen Amplite Testing-MetsoDokument3 SeitenScreen Amplite Testing-MetsoPRASHANTH100% (1)
- Limits&TolerancesDokument7 SeitenLimits&Tolerancessekar507Noch keine Bewertungen
- MSZ Selection CalculationDokument20 SeitenMSZ Selection Calculationlojzemulec5966Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rack and Pinion CatalogDokument12 SeitenRack and Pinion CatalogMatei AlexandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Carbon Brush Technical Guide MersenDokument40 Seiten5 Carbon Brush Technical Guide Mersenpiojezior100% (1)
- Journal BearingsDokument32 SeitenJournal Bearingsa_salehiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LECTURE 2B Limits and Fits NewDokument17 SeitenLECTURE 2B Limits and Fits Newmanishkrbarnwal13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Din 3967-1978 EngDokument24 SeitenDin 3967-1978 EngLatha Pundi100% (4)
- A Necessary EvilDokument7 SeitenA Necessary EvilAlfredo MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO Bar TolerancesDokument1 SeiteISO Bar TolerancesBaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit2 - Limits Fits & Tolerance NotesDokument19 SeitenUnit2 - Limits Fits & Tolerance NotesvrmgiteduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejemplo de Variables de InstrumentacionDokument16 SeitenEjemplo de Variables de InstrumentacionEduardo JiménezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Limits Fits and TolerancesDokument22 Seiten3-Limits Fits and TolerancesAbhay Sharma100% (1)
- Shaft AlignmentDokument13 SeitenShaft AlignmentSushant MoundekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eccentricity Measurement in STGDokument7 SeitenEccentricity Measurement in STGKarthick Velayutham100% (1)
- Tolerances FabDokument1 SeiteTolerances FabAnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMM Module2Dokument19 SeitenMMM Module2SUNIL SWAMY SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tolerancias de Forja Segun F.I.A.Dokument20 SeitenTolerancias de Forja Segun F.I.A.Carlos EspinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tolerancing SystemDokument24 SeitenTolerancing SystemLenis Enrique Julio QuintanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conditions Influencing PerformancesDokument3 SeitenConditions Influencing PerformancesbhageshlNoch keine Bewertungen
- RESM Angle EncoderDokument8 SeitenRESM Angle EncoderJaswinder SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Truing Commutators and Slip-RingsDokument4 SeitenTruing Commutators and Slip-RingsTariq AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoples TramecDokument26 SeitenAcoples TramecAndres ValderramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B 502 - 02 - QjuwmgDokument3 SeitenB 502 - 02 - QjuwmghamidharvardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument17 SeitenChapter 2Gaurav AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Factors When Using Small Bearings: Part 1: Bearing GeometryDokument7 SeitenDesign Factors When Using Small Bearings: Part 1: Bearing Geometryhittaf_05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Lovejoy Serie JawDokument26 SeitenCatalogo Lovejoy Serie JawJuan Pablo CirizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaw Type Coupling LOVEJOY PDFDokument26 SeitenJaw Type Coupling LOVEJOY PDFRafo Vega GuerovichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shaft RequirementsDokument4 SeitenShaft RequirementsMr ShrekNoch keine Bewertungen
- FALLSEM2019-20 MEE2001 ELA VL2019201005431 Reference Material II 12-Jul-2019 Conventional TolerancingDokument22 SeitenFALLSEM2019-20 MEE2001 ELA VL2019201005431 Reference Material II 12-Jul-2019 Conventional TolerancingNikhil VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lovejoy CouplingDokument13 SeitenLovejoy Couplingsandulupeni100% (1)
- D400-10 (Meters & Accessories 49093) PDFDokument52 SeitenD400-10 (Meters & Accessories 49093) PDFLazzarus Az GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ysteresis Rakes AND LutchesDokument20 SeitenYsteresis Rakes AND LutchesRahul SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsVon EverandBearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Ultrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentVon EverandUltrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Mercedes - Benz Vito & V-Class Petrol & Diesel Models: Workshop Manual - 2000 - 2003Von EverandMercedes - Benz Vito & V-Class Petrol & Diesel Models: Workshop Manual - 2000 - 2003Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Band Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsVon EverandBand Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Checklist For NP CO2 Compressor Overhauling - Rev 0 PDFDokument6 SeitenChecklist For NP CO2 Compressor Overhauling - Rev 0 PDFMohsin MurtazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Couplings - A Basic Introduction To Different Types of CouplingsDokument38 SeitenCouplings - A Basic Introduction To Different Types of CouplingsMohsin MurtazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Turbine IntroductionDokument57 SeitenGas Turbine IntroductionMohsin Murtaza100% (3)
- Jo Rukey To Koh e Giran Thy Hum Episode 17 To 29Dokument158 SeitenJo Rukey To Koh e Giran Thy Hum Episode 17 To 29Mohsin MurtazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cataylyst Tubes North CellDokument13 SeitenCataylyst Tubes North CellMohsin MurtazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stainless Steel Designation SystemsDokument6 SeitenStainless Steel Designation SystemsMohsin MurtazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Series BrochureDokument8 SeitenE Series BrochureMohsin MurtazaNoch keine Bewertungen