Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
cs2402 2 Marks Question Bank-With Answer
Hochgeladen von
Frousper29Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
cs2402 2 Marks Question Bank-With Answer
Hochgeladen von
Frousper29Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CS2402- MOBILE AND PERVASIVE COMPUTING TWO MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT 1
1. What is wireless communication? Wireless communication is the transfer of information over a distance without the use of electrical conductors or wires.The distance involved may be short , long. 2. What are the uses of wireless Technology ? To span a distance beyond the capabilities of typical cabling To avoid obstacles such as physical structures To provide a backup communication link in case of normal network failure To overcome situations where normal cabling is difficult or financially impractical. 3. What are the challenges in wireless communication? Very limited resources Unstable channel characteristics Multi- user Interference Line of sight for frequencies Mobility issues 4. List the type of wireless networks Personal area networks Local area networks Metropolitan area networks Wire area networks. 5. Define CDMA ? Code Division Multiple Access systems use codes with certain characteristic to separate
different users. To enable access to the shared medium without interference. The users use the same frequency and time to transmit data. The main problem is to find good codes and to separate this signal from noise. The good code can be found by two characteristics 1. orthogonal 2. auto correlation. 6. What is meant by non-persistent CSMA ? n Non-persistent CSMA, stations sense the carrier and start sending immediately if the medium is idle, if the medium is busy the stations passes a random amount of time before sensing the medium again and repeating this pattern. 7. What is FDD ? In FDMA, the base stations and the mobile stations establish a duplex channel. The two directions, mobile stations to base stations and vice versa are separated using different frequencies. This scheme is called Frequency Division Duplex. 8. What is a signal ? signals are the physical representation of data. The users of a communication system can only exchange data through the transmission of signals. Signals are functions of time and location. Signal parameters : Parameters representing the value of data. Signal parameter of periodic signal 9. What is polarization? Polarization is an important factor for antennas. Both antennas and electromagnetic waves are said to have a polarization. For the electromagnetic wave it is effectively the plane in which the electric vibrate. This is important when looking at antenna because they are sensitive Period T frequency f = 1/T amplitude A
to polarization and generally receive or transmit a signal with a particular r polarization 10. What is Polling? Polling is a centralized scheme with one master and several slave stations. The master can collect the list of stations during the connection phase and can poll these slaves according to many schemes like round robin, random access, reservation schemes etc. 11. List out the types of multiplexing? Space Division Multiplexing Frequency Division Multiplexing Time Division Multiplexing Code Division Multiplexing 12. What are the advantages and disadvantages of CDMA ? Adv. All terminals can use the same frequency no planning needed. Huge code space used Interference is not coded. Dis adv. Higher complexity of a receiver All signals should have the same strength at a receiver 13. What are the types of communication? Simplex communication Duplex communication Half Duplex Communication 14. What are the types of antenna? The Dipole antenna the Folded Dipole antenna Quarter wave Vertical Antenna
J Pole Vertical Antenna Yagi Antenna Log periodic Beam antenna Parabolic Reflector/dish antenna Horn antenna Discone Antenna 15. What is SDMA? Space Division Multiple Access is used for allocating separated spaces to users in wireless Networks. The basis for the SDMA algorithm is formed by cells and sectorized antennas which constitute the infrastructure implementing space division multiplexing . 16.Define SAMA. Spread Aloha Multiple Access is a combination of CDMA and TDMA. The CDMA better suits for connection oriented services only and not for connection less bursty data traffic because it requires to program both sender and receiver to access different users with different codes. 17. What are the several versions in CSMA? There are several versions in CSMA, they are as follows a) non-persistent CSMA b) p-persistent CSMA c) 1-persistent CSMA 18.What is meant by non-persistent CSMA? In, non-persistent CSMA, stations sense the carrier and start sending immediately if the medium is idle., if the medium is busy, the station pauses a random amount of time before sensing the medium again and repeating this pattern. 19.What is meant by p-persistent CSMA? In p-persistent CSMA system nodes also sense the medium, but only transmit with a probability of p. With the station deferring to the next slot with the probability 1-p, i.e. access is
slotted in addition. 20.What is SDMA? Space Division Multiple Access (SDMA) is used for allocating separated spaces to users in wireless networks. The basis for the SDMA algorithm is formed by cells and sectorized antennas which constitute the infrastructure implementing space division multiplexing (SDM)
UNIT 2 1. What are the Subsystem in GSM ? Radio Subsystem (RSS) Network & Switching Subsystem (NSS) Operation Subsystem (OSS) 2. List the Services of GSM ? Bearer services ii) Tele services iii) Supplementary services 3. What is meant by GPRS ? The General Packet Radio Services provides Packet mode transfer for applications that exhibit traffic patterns such as frequent transmission of small volumes. Provide flexible series at relatively low costs. Possibility for connectivity to the Internet. Provide fast access time 4. How the data is transferred? The most common methods used for data transfer are Circuit Switching. Packet Switching In circuit switching the dedicated circuit is first established across a sequence of links and then the whole channel is allocated to a single user for the whole duration of the call. 5. What are the different types of Satellite Orbits?
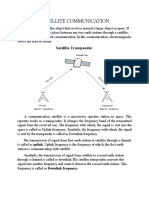
Low Earth Orbit (LEO: 200 -1200 km) Medium Earth Orbit (MEO or ICO 1200 35790km) Geosynchronous Orbit(GEO: 35790 km above earth surface ) High Earth Orbit (HEO : above 35790 km) 6. What is handover? The satellite is the base station in satellite communication systems and that it is moving. So additional instance of handover are necessary due to the movement of the satellite. 7. What are the advantages of LEO? Data rate is 2400 bits/s Packet delay is relatively low Smaller footprints of LEO allows frequency reuse Provide high elevations 8 Define the elevation and foot print? The elevation angle is defined as the angle between the centre of satellite beam and the plane tangential the earths surface. The foot-print can be defined as the area on the earth where the signal of the satellite can be received 9 What is DAB ? The DAB system offers sound in a CD quality and also it eliminate the interference and multi-path propagation effects. When transmitting an audio transmission, a limited information such as the secion- id can be include with transmission, a limited information such as the station id can be included with the data. 10. What are the mechanism that is used in DAB Main service channel (MSC)
Fast information channel (FIC) 11. What is SFN ? in early days all senders transmitting the same radio program operand at the same frequency. But today different frequencies to avoid interference. DAB systems uses the SFN to avoid such situation. By using SFN a ratio station uses one frequency to transmit their program throughout their country. 12. List out the services of GSM? The key advantages of GSM systems to consumers has been higher voice quality and low cost alternatives to making cells, such as the Short Message Service. The advantages for network operator has been the ease of deploying equipments from any vendors that implement the standard. Like other cellular standards, GSM allows network operators to offer roaming services so that subscribers can use their phones on GSM networks all over the world. 13. What is LEO and GEO ? these are satellites that appear fixed in the sky GEO are enough for a complete coverage of almost any spot on earth. Senders and receivers can use fixed antenna positions. LEO circulate on a lower orbit. It is obvious that they exhibit a much shorter period. Additionally LEO systems try to ensure a high evaluation communication link. 14.What is the use of flat disk? By using a flat disk all blocks are repeated one after the another. Every block is for every spot on earth to provide a high quality
transmitted for an equal amount of time. Average waiting time for receiving a block is the same 15. Write about multi path effects and interference ? the digital audio broadcasting DAB was developed for eliminating multipath effects and interference. Whenever a strong signal is available it is possible to eliminate multipath effects and interference. 16. Explain about DAB & DVB? Digital Audio Broadcasting systems can use single frequency networks(SFN). The fully digital DAB system does not only offer sound in a CD-like quality, it is also practically immune to interference although they are transmitting the same radio program. Digital Video Broadcasting is to introduce digital television broadcasting using satellite transmission. Audio/video streams can be recorded, processed and replayed using digital versatile disk 17. List the process of DAB sender ? the process of DAB sender are as follows audio services are encoded and coded for transmission (FEC) data services are multiplexed and coded with redundancy the MSC multiplexes combines all data streams and forwards them to transmission multiplexer transmission multiplexer creates the frame structure by interleaving the FIC 18.Write about DVB container ? DVB transmits MPEG-2 container High flexibility for the transmission of digital data No restrictions regarding the type of information DVB service information specifies the content of a container.
19.What are the logical channels in GSM? Traffic channel(TCH) Control channel(CCH) What is the function of Medium Access Control Layer? The functions of Medium Access Control Layer is responsible for establishes, maintains, and releases channels for higher layers by activating and deactivating physical channels. 20. What is meant by GEO? GEO means Geostationary or Geosynchronous earth orbit. GEO satellites have a distance of almost 36000 km to the earth. Examples are almost all TV and radio broadcast satellites, many weather satellites and satellites operating as backbone for the telephone network. 21. what are the advantages of GEO? Three GEO satellites are enough for a complete coverage of almost any spot on earth, senders and receivers can use fixed antennas positions, no adjusting is needed. Therefore GEOs are ideal for T.V and radio 22.What is Handover? The satellite is the base station in satellite communication systems and that it self is moving. So, additional instance of handover are necessary due to the movement of the satellite 1.Intra Satellite handover: 2.Inter Satellite handover. 3.Gateway handover. 4.Inter System handover. 23. What are the registers maintained by the gateway of satellite?
1.Home Location Register(HLR). 2.Visitor Location Register(VLR). 3.Satellite User Mapping Register(SUMR). 24.Advantages of MEO Orbits around 10,000Km, the system only requires a dozen satellites which is more than the GEO system, but much less than a LEO system. Further more these satellites move slower relative to the earths rotation allowing a simpler system design.Depending on the inclination a MEO can cover larger populations, thus requiring less handovers. 25. Applications of Satellite ? Satellites can be used in the Following Areas Weather Forecasting Radio and TV broadcast Satellites Military Satellites Satellites for Navigation 26.What are the applications in satellites? Weather forecasting satellites Radio & TV broadcast satellites Military satellites Satellites for navigation Mobile communication 27. What are the advantages of LEO? Data rate is 2400 bit/s Packet delay is relatively low
Smaller footprints of LEO allows frequency reuse Provide high elevations 28. Define the inclination angle and perigee. The inclination angle is defined as the angle between the equatorial plane and the plane described by the satellite orbit. An inclination angle of 0 degrees means that the satellite is exactly above the equator. If the satellite does not have a circular orbit, the point to the earth is called the perigee. 29. Define the elevation angle and footprint. The elevation angle is defined as the angle between the centre of satellite beam and The plane tangential to the earths surface. The foot-print can be defined as the area on earth where the signals of the satellite can be received. 30. Define Header core. Seven bytes field contains the sizes of the header and the body, the content type of the object. Depending on this header information, the receiver may decide if it has enough resources(memory, cpu, power, display etc) available to decode and further process the object. 31. What is MSC? Main Service Channel(MSC) carries all user data. eg. audio, multimedia data. 32. What is FIC? The Fast Information Channel(FIC) contains Fast Information Block(FIB) with 256bits each(16 bit checksum). An FIC carries all control information which is required for interpreting the configuration and content of the MSC. 33. What are the different types of disk?
A flat disks Skewed disks Multi disks 34. What are the goals of DVB? The goal of DVB is to introduce digital TV broadcasting using satellite transmission (DVB-5) cable technology (DVB-c) and terrestrial transmission (DVB-7). 35) What is the function of Medium Access Control Layer? The functions of Medium Access Control Layer is responsible for establishes, maintains, and releases channels for higher layers by activating and deactivating physical channels. 36) What is meant by GEO? GEO means Geostationary or Geosynchronous earth orbit. GEO satellites have a distance of almost 36000 km to the earth. Examples are almost all TV and radio broadcast satellites, many weather satellites and satellites operating as backbone for the telephone network. 37) what are the advantages of GEO? Three GEO satellites are enough for a complete coverage of almost any spot on earth, senders and receivers can use fixed antennas positions, no adjusting is needed. Therefore GEOs are ideal for T.V and radio broadcasting 38) What are the registers maintained by the gateway of satellite? 1.Home Location Register(HLR). 2.Visitor Location Register(VLR). 3.Satellite User Mapping Register(SUMR). 40)Advantages of MEO Using Orbits around 10,000Km, the system only requires a dozen satellites
which is more than the GEO system, but much less than a LEO system. Further more these satellites move slower relative to the earths rotation allowing a simpler system design. Depending on the inclination a MEO can cover larger populations, thus requiring less handovers. 41) Applications of Satellite ? Satellites can be used in the Following Areas Weather Forecasting Radio and TV broadcast Satellites Military Satellites Satellites for Navigation 42)What are the applications in satellites? Weather forecasting satellites Radio & TV broadcast satellites Military satellites Satellites for navigation Mobile communication
UNIT 3 1. Name some of the formats supported by MOT?. _Multimedia and Hypermedia information coding experts group(MHEG) _Join photographs experts group(JPEG) _American standard code for information interchange(ASCII) _Moving pictures expert group(MPEG) _Hypertext markup language(HTML)
_Hypertext transfer protocol(HTTP) _Bitmap(BMP) _Graphics interchange format(GIF) 2. Give structure MOT object. 1. variable size 2. variable size 3. Header core 4. Header Extension Body 5. Header core : contain the size of the header and body and the content type of the object. 6. Header Extension : contains additional object handling data such as repetition distance to 7. support caching, segmentation information and priority of the data. 8. Body : contains arbitrary data to be transmitted. 3.What are different interleaving and repetition schemes applied by DAB to objects and segments? 1.Object Repetition. 2.Interleaved Objects. 3.Segment repetition. 4.Header repetition. 4. What are the advantages of DAB? 1.DAB can offer sound in CD like quality. 2.DAB can use single frequency network where all senders transmitting the same radio program can operate at the same frequency. 3.DAB use VHF and UHF frequency bands.
4.DAB uses DQPSK modulation scheme. 5.DAB user COFDM and FEC. 6.DAB can transmit up to six stereo audio programmes with a data rate of 192kbit/s each. 5. What is object repetition? DAB can repeat objects several times. If an object A consists of four segments(A1,A2,A3,A4) a single repetition pattern would be A1A2A3A4A1A2A3A4A1A2A3A4.. 6. What is EIT? Event Information Table(EIT) contains status information about the current transmission and some additional information for set-top boxes. 7. What are the service information sent by DVB? Digital Video Broadcast Containers are basically MPEG-2 frames. DVB sends service information. These information are, 1.Network information table(NIT). 2.Service Description Table(SDT). 3.Event Information Table(EIT). 4.Time and Date Table(TDT) 8. What are the advantages of DVB? 1.Data rates planned for users are 6-38mbit/s for the downlink and 33-100kbit/s for the uplink. 2.Transmitted along with TV programmes and doesnt require additional lines or hardware per customer. 3.Can be used in remote areas and developing countries where there is no high band width wired network. 9. what is meant by beacon?
A beacon contains a timestamp and other management information used for power management and roaming. e.g., identification of the base station subsystem(BSS) 10. What is Active scanning? Active scanning comprises sending a probe on each channel and waiting for response. Beacon and Probe response contain the information necessary to join the new BSS. 11. What is Passive Scanning? Passive Scanning Simply means listening into the medium to find other networks, i.e. receiving the beacon of another network issued by the synchronization function within an access point 12. what is the primary goal of IEEE 802.11? The primary goal of the standard was the specification of a simple, robust, WLAN which offers time bounded and asynchronous services also it should be able to operate with multiple physical layers. 13. what is meant by SIFS? SIFS means Short Inter Frame Spacing. The shortest waiting time defined for short control message such as acknowledgements or polling response. 14. What are Advantages of wireless LAN? Flexibility, Planning, Design, Robustness, Quality Service, Cost,
Proprietary Solution, Restriction, Safety and Security 15. What are Design Goals of Wireless LAN? Global Operation Low Power License-free Robust transmission technology Simplified spontaneous co-operation Easy to use protection of investment Safety and Security Transparency for application 16)What are different interleaving and repetition schemes applied by DAB to objects and segments? 1.Object Repetition. 2.Interleaved Objects. 3.Segment repetition. 4.Header repetition. 17)What are the three Low Power States provided by Bluetooth? PARK state HOLD state 18)What is SCO? SCO-stands for Synchronous Connection Oriented Link Standard telephone (voice) connection require symmetrical, circuit-switched, point-topoint
connections. For this type of link, the master reserves two consecutive slots at fixed intervals. 19)What are the three phases in EY-NPMA? i. Prioritization: Determine the highest priority of a data packet ready to be sent on competing nodes. ii. Contention: Eliminate all but one of the contenders, if more than one sender has the highest current priority. iii. Transmission: Finally, transmit the packet of the remaining node. 20)What are Advantages and Disadvantages of Infrared? Advantages: i. Simple and extremely cheap senders and receivers which integrated in almost all mobile devices ii. No licenses are needed for infrared technology and shielding is very simple. iii. Electrical devices do not interfere with infrared transmission. Disadvantages: i. Low bandwidth ii. Quite easily shielded iii. Cannot Penetrate 21) What are the system integration functions of MAC management? Synchronization Power management Roaming Management information base (MIB) 22) What do you meant by roaming?. Moving between access point is called roaming. Even wireless networks may require
more than one access point to cover all rooms. In order to provide uninterrupted service, we require roaming when the user moves from one access point to another. 23) What is mobile routing? Even if the location of a terminal is known to the system, it still has to route the traffic through the network to the access point currently responsible for the wireless terminal. Each time a user moves to a new access point, the system must reroute traffic. This is known as mobile routing.
UNIT-4 1. What is mobile routing? Even if the location of a terminal is known to the system, it still has to route the traffic through the network to the access point currently responsible for the wireless terminal. Each time a user moves to a new access point, the system must reroute traffic. This is known as mobile routing. 2. What are the functions which support service and connection control? >Access point control function
>Call control and connection control function >Network security agent >Service control function >Mobility management function 3. What are the examples for service scenarios identified in WATM ? >Office environments >Universities, schools, training, centers >Industry >Hospitals >Home >Networked vehicles 4. What is BRAN? The broadband radio access networks(BRAN) which have been standardized by European Telecommunications Standard Institute(ETSI) are a possible choice for an RAL for WATM. Although BRAN has been standardized independently from WATM, there is co-operation between the two to concentrate the common efforts on one goal. The main motivation behind BRAN is the deregulation and privatization of the telecommunication sector in Europe. 5. What are the different network types of BRAN? >Hyperlan1 >Hyperlan2 >Hyper access >Hyperlink 6. What is the main problem for WATM during handover? The main problem for WATM during the handover is rerouting of all connections
and maintaining connection quality. 7. What are the different segments in ATM end-to-end connection? An ATM end-to-end connection is separated into different segments. >A fixed segment is a part of the connection that is not affected by the handover >Handover segment is affected by the handover and is located completely within a handover domain. 8. What is anchor point? The Anchor point is the boundary between a handover segment and a fixed segment. 9. What are different types of handover? >Hard handover >Terminal initiated >Network initiated >Network initiated, terminal assisted >Network controlled >Backward handover >Forward handover the extended TCP is called SCPS-transport protocols.(SCPS-TP). 10) What are Advantage and Disadvantage of MobileTCP? Advantages: i. M-TCP maintains the TCP end-to-end semantice. The SH does not send any ACK itself but forwards the ACKs from the MH. ii.If the MH is disconnected, M_TCP avoids useless retransmissions, slow starts or breaking connections by simply shrinking the senders window to 0; iii. Since M-TCP does not buffer data in the SH as I-TCP does, it is not necessary to
forward buffers to a new SH. Lost packets will be automatically retransmitted to the new SH. Disvantages: i. As the SH does not act as proxy as in I-TCP, packet loss on the wireless link due to bit errors is propagated to the sender. M-TCP assumes low bit error rates, which is not always a valid assumption. ii. A modified TCP on the wireless link not only requires modification to the MH protocol software but also new network elements like the bandwidth manager. 11) What is generic routing encapsulation? Generic routing encapsulation (GRE) is an encapsulation scheme which supports other network protocols in addition to IP. It allows the encapsulation of packets of one protocol suite into the payload portion of a packet of another protocol suite. 12) Define COA. The COA (care of address) defines the current location of the MN from an IP point of view. All IP packets sent to the MN are delivered to the COA, not directly to the IP address of the MN. Packet delivery toward the MN is done using the tunnel. 13) What is meant by Transparency? Mobility should remain invisible for many higher layer Protocols and applications. The only affects of mobility should be a higher delay and lower bandwidth which are natural in the case of mobile networks. 14)What is Binding Request? Any node that wants to know the current location of an MN can send a binding request to the HA. The HA can check if the MN has allowed dissemination of its current location. 15) What are the possibilities for the location of care-of-address (COA)?
The two possibilities for the location of care-of-address are: i.Foreign agent COA ii.Co-related COA 16) What are the requirements for the development of mobile IP standard? The requirements are: a.Compatibility b.Transparency c.Scalability and efficiency d.Security 17) What is Dynamic source Routing? Dynamic Source Routing eliminates all periodic routing updates. If a node needs to discover a route, it broadcast a route request with a unique identifier and the destination address as parameters. Any node that receivers a route request gives a list of addresses representing a possible path on its way toward the destination. 18) Why is need of routing? Routing is to find the path between source and destination and to forward the packets appropriately. 19) Define Mobile node: A mobile node is an end-system or router that can change its point of attachment to the Internet using mobile IP. The MN keeps its IP address and can continuously with any other system in the Internet as long as link layer connectivity is given.
UNIT V 1. What is Pervasive Computing? Pervasive Computing is a technology that pervades the users environment by making use of multiple independent information devices (both fixed and mobile, homogeneous or heterogeneous) interconnected seamlessly through wireless or wired computercommunication networks which are aimed to provide a class of computing / sensory /communication services to a class of users, preferably transparently and can provide personalized services while ensuring a fair degree of privacy / non-intrusiveness. 2. What should the Infrastructure provide? Pervasive Computing Infrastructure has to comprise of computing elements, communicating elements, sensors, actuators, and interface devices. 3. What are the basic aspects of a Pervasive Computing environment? Device Technology for Pervasive Computing include Power-provisioning technologies, Display technologies, Memory technologies, Communication technologies, Processor technologies, Interfacing technologies, Sensor Technologies and Authentication Technologies. 4. What are the different display device technologies available? Display-size,Display-shape,Display-resolution,Display-colour richness,Display viewing angles to be supported,Display power provisioning constraints,Display refresh rates etc.
5.What are the Interfacing Aspects and Technologies? Respective significance of Fitaly, Tegic T9, Octave methods of keyboards vis--vis traditional QWERTY layout based keyboards / keypads, in the context of mobile handheld devices: 6. What is Fitaly? Merit / Significance: Speeds up input of text, letters selected as per likely occurrence frequencies and ensuring minimization of inter-letter travel distance (to no more than 2 positions), supports 220 ANSI/ISO Latin- 1 character set, supports accents, available in on-screen as well as mechanical forms
Demerit: Specific to English languages estimated usage patterns, needs to be practiced for a while before use, needs to learn sliding for accents use etc. 7. What isTegic T9? Merit / Significance: Requires lesser number of keystrokes for textual input due to support for predictive text by combining use of dictionary and linguistic rules embedding, resolution of word-ambiguity is supported through prompts, available in on-screen as well as mechanical forms Demerit: Requires sizeable software support and computing resources (instruction cycles and memory) 8. What is Octave? Merit / Significance: Commands available to support multiple language dictionaries, available in on-screen as well as mechanical forms although second form is more popular, gesture-based iconic support for certain insertions, word-recognition supported by dictionary, ability to resolve stroke-ambiguity with the help of dictionary Demerit: Requires sizeable software support and computing resources (instruction cycles and memory) 9. What is Traditional QWERTY? Merit / Significance: Simplicity in design and use, available in on-screen as well as mechanical forms Demerit: Requires more space and may be difficult in use in case of devices with very small form-factor 10. what are the Major Interfacing technologies? Navigation technologies Haptic interfacing technologies On-screen / Touch-panel technologies Voice interfacing technologies Video-interfacing technologies Handwriting-based interfacing technologies Hybrid interfacing technologies)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cs2402-Mobile Pervasive ComputingDokument26 SeitenCs2402-Mobile Pervasive ComputingAnand KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesVon EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Cs2402 - Mobile and Pervasive Computing Unit 1: Ans: AdvantagesDokument4 SeitenCs2402 - Mobile and Pervasive Computing Unit 1: Ans: AdvantagesSakthivel VelusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communications Interview Questions and AnswersDokument7 SeitenCommunications Interview Questions and Answersshiv389Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GVon EverandIndoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- ECE Interview Questions With AnswersDokument7 SeitenECE Interview Questions With AnswersRohit Xavier100% (1)
- 2 Marks Cellular & Mobile CommunicationDokument38 Seiten2 Marks Cellular & Mobile CommunicationVishnu PriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grand Viva Question For Ece StudentDokument17 SeitenGrand Viva Question For Ece Studentapi-35904739086% (7)
- Mobile Computing Sample Ques AnsDokument6 SeitenMobile Computing Sample Ques AnsAmirtharaj SelvamohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece QuestionsDokument6 SeitenEce QuestionsArockia RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument184 SeitenUntitledKathiravan ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information About CDMADokument8 SeitenInformation About CDMANishabh ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Communication 2-MARK Questions and AnswersDokument16 SeitenMobile Communication 2-MARK Questions and Answersnoblelion92% (12)
- Mobile Computing Viva Voce QuestionsDokument10 SeitenMobile Computing Viva Voce QuestionsMohamed Rafi100% (1)
- Mobile CommunicationDokument16 SeitenMobile CommunicationArun SampathNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6042 Module 2-Satellite CommunicationDokument12 Seiten6042 Module 2-Satellite CommunicationAlenNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCC Probable QNS PDFDokument21 SeitenMCC Probable QNS PDFAbhijeet ShitoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By:: Reshma.D & Sravani.BDokument18 SeitenPresented By:: Reshma.D & Sravani.Bsrinu0887Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1-15ec81Dokument24 SeitenModule 1-15ec81Asha JNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACN Unit2Dokument10 SeitenACN Unit2Smit prajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CST64Dokument16 SeitenCST64Thiagu RajivNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1-15ec81Dokument25 SeitenModule 1-15ec81PRANEETH DpvNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is OFDMDokument39 SeitenWhat Is OFDMRenu PareekNoch keine Bewertungen
- CD MaDokument21 SeitenCD Mashashwat2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument5 Seiten1sandeshwari yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Communications Interview Questions & AnswersDokument8 SeitenElectronic Communications Interview Questions & AnswerssmydyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCS Midterm 1 - PreviousDokument9 SeitenMCS Midterm 1 - PreviouspfmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Communication NotesDokument17 SeitenSatellite Communication NotesAkhil RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPCDokument17 SeitenMPCBoova RagavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1Dokument26 SeitenModule 1Varshini NNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Communication SystemDokument18 Seiten1.1 Communication SystemMohammed AlShibanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Is A Digital Cellular Technology Used For Mobile Communication. CDMA Is The Base On Which Access Methods SuchDokument25 SeitenCode Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Is A Digital Cellular Technology Used For Mobile Communication. CDMA Is The Base On Which Access Methods SuchChristopher AiyapiNoch keine Bewertungen
- It1402 Mobile Computing (2 Marks & 16marks) ModelDokument33 SeitenIt1402 Mobile Computing (2 Marks & 16marks) ModelDinesh CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Topics in MIMO-OFDM SystemsDokument7 SeitenAdvanced Topics in MIMO-OFDM SystemsThành PhạmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthogonal Frequency-Division MultiplexingDokument12 SeitenOrthogonal Frequency-Division MultiplexingfiraszekiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDMADokument59 SeitenCDMAAmit NainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Marks WCDokument6 SeitenTwo Marks WCbaby yodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Ofdm PPT 3Dokument36 SeitenFinal Ofdm PPT 3Pankaj AroteNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC505Dokument87 SeitenEC505kashi13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Communication: Unit-I Two Marks Q&ADokument20 SeitenMobile Communication: Unit-I Two Marks Q&AKarthika NarasimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ofdm Basics For Wirless Communications: AbstractDokument11 SeitenOfdm Basics For Wirless Communications: AbstractRaji SharmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of TechnologyDokument33 SeitenSns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of TechnologyakttripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument20 SeitenAbstractaman_tanvirNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDMA - Quick Guide - TutorialspointDokument32 SeitenCDMA - Quick Guide - Tutorialspointhadeer.hNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT1402 Nov Dec+2009Dokument20 SeitenIT1402 Nov Dec+2009piccoloashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks Assignment-2: Topic-Working of Physical Layer in 1G, 2G, 3G and 4G NetworksDokument12 SeitenComputer Networks Assignment-2: Topic-Working of Physical Layer in 1G, 2G, 3G and 4G NetworksPunit KyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled DocumentDokument9 SeitenUntitled Document121Anik sahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code-Division Multiple AccessDokument11 SeitenCode-Division Multiple AccessMr. Akhil WaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Umts Quick GuideDokument52 SeitenUmts Quick GuideSreeram SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cnce 010103Dokument6 SeitenCnce 010103kiaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer NetworkDokument36 SeitenComputer Network121Anik sahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDMADokument41 SeitenCDMAdasdawtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orthogonal Frequency Division MultiplexingDokument49 SeitenOrthogonal Frequency Division MultiplexingAndrew SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 MC Solved Final AjayaDokument12 SeitenUnit 2 MC Solved Final AjayaMario MonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Project Report On "Pilot Based OFDM Channel Estimation"Dokument57 SeitenA Project Report On "Pilot Based OFDM Channel Estimation"Omkar ChogaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless and CELLULAR COMMUNICATION (18EC81) Module-4Dokument37 SeitenWireless and CELLULAR COMMUNICATION (18EC81) Module-4Vishwanath DesaigoudarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCS - Cheat Sheet - T1Dokument10 SeitenMCS - Cheat Sheet - T1Katta Revanth ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tdma, FdmaDokument26 SeitenTdma, Fdmasarab1111Noch keine Bewertungen
- VS20 Full Manual V11 ENGDokument81 SeitenVS20 Full Manual V11 ENGIonut BujorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tej2O Unit 2 Eportfolio - NetworkingDokument4 SeitenTej2O Unit 2 Eportfolio - Networkingapi-480356496Noch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring TSM BA Client Option and Client System FilesDokument6 SeitenConfiguring TSM BA Client Option and Client System Filesanon_326668689Noch keine Bewertungen
- Smartmax M2M HSPA Smart Modem - Maxon SolutionsDokument2 SeitenSmartmax M2M HSPA Smart Modem - Maxon SolutionsAdvanced Telemetry Product ManufacturersNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 LIFT电梯助手产品介绍Dokument3 Seiten5 LIFT电梯助手产品介绍Rebecca DangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generated by JDSU 5800Dokument15 SeitenGenerated by JDSU 5800Barathkumar ThangavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 156-315.80 Exam - Questions Answer Discussion From Exam TopicsDokument200 Seiten156-315.80 Exam - Questions Answer Discussion From Exam TopicsAonymousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Test Css g12Dokument30 SeitenChapter Test Css g12flash driveNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual: Melag FTP ServerDokument16 SeitenUser Manual: Melag FTP ServerМаксим ШульгаNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Sync Howto: Using Jpilot To Sync Your Palmos Device To Your Desktop Across A Wireless (802.11B) NetworkDokument9 SeitenWireless Sync Howto: Using Jpilot To Sync Your Palmos Device To Your Desktop Across A Wireless (802.11B) Networka.gNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dasan Zhone MXK F219 Spec SheetDokument1 SeiteDasan Zhone MXK F219 Spec SheetHernan3571Noch keine Bewertungen
- FOS 8.2.2b ReleaseNotes 03082023041114Dokument66 SeitenFOS 8.2.2b ReleaseNotes 03082023041114Sagar A.MNoch keine Bewertungen
- InnGate 3 Administrator Manual r1.01Dokument164 SeitenInnGate 3 Administrator Manual r1.01Min Thein HtikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MWEB Business: HackedDokument13 SeitenMWEB Business: HackedBirte ReiterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 DM - TS3301 - E01 WDM and OTN Common Alarm Analysis 62PDokument62 Seiten07 DM - TS3301 - E01 WDM and OTN Common Alarm Analysis 62PhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Pci Express V.92 56K Data Fax Modem - Pcie Dial Up ModemDokument3 SeitenInternal Pci Express V.92 56K Data Fax Modem - Pcie Dial Up Modemsorin_ncsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Hardening GuideDokument21 SeitenSecurity Hardening GuideDeepak ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rouing ConceptsDokument211 SeitenRouing ConceptsmntesnotNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Microsoft - Certshared.az-305.exam - Question.2023-Jun-18.by - Jerome.177q.vceDokument13 Seiten03 Microsoft - Certshared.az-305.exam - Question.2023-Jun-18.by - Jerome.177q.vceendinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei Train4sure H12-261 v2021-04-28 by Liuwei 164qDokument83 SeitenHuawei Train4sure H12-261 v2021-04-28 by Liuwei 164qhoussemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.layered UVM Sequences PDFDokument19 Seiten6.layered UVM Sequences PDFmanchuricoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei SD Wan TechnologiesDokument30 SeitenHuawei SD Wan TechnologiesaxmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integritas Industrial Battery Charger: Application Industries FeaturesDokument4 SeitenIntegritas Industrial Battery Charger: Application Industries Featurescelimo0710Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Office Sharepoint Server 2007 Integration GuideDokument49 SeitenMicrosoft Office Sharepoint Server 2007 Integration GuideIan VianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solaris 11 Cheat Sheet 1556378 PDFDokument7 SeitenSolaris 11 Cheat Sheet 1556378 PDFlacoste123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hyper Transport TechnologyDokument23 SeitenHyper Transport Technologyshaheen sayyad 463Noch keine Bewertungen
- MIPL - AMC Support Escalation Matrix - Ver-1.0Dokument8 SeitenMIPL - AMC Support Escalation Matrix - Ver-1.0Ajay AryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Corning HX 709C006801 PDFDokument46 SeitenManual Corning HX 709C006801 PDFtomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate - Skills MeasuredDokument4 SeitenMicrosoft Certified: Azure Security Engineer Associate - Skills MeasuredAldo SENoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6 - Reading5 - InternetSecurityDokument7 SeitenModule 6 - Reading5 - InternetSecurityChristopher AdvinculaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsVon EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsVon EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksVon EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNVon EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Von EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Unlock Any Roku Device: Watch Shows, TV, & Download AppsVon EverandUnlock Any Roku Device: Watch Shows, TV, & Download AppsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZVon EverandPHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsVon EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing and Building Security Operations CenterVon EverandDesigning and Building Security Operations CenterBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (3)
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamVon EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Mastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionVon EverandMastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionVon EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityVon EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (13)
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachVon EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)Von EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)Noch keine Bewertungen
- FTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationVon EverandFTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamVon EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical TCP/IP and Ethernet Networking for IndustryVon EverandPractical TCP/IP and Ethernet Networking for IndustryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- ITIL 4: Direct, plan and improve: Reference and study guideVon EverandITIL 4: Direct, plan and improve: Reference and study guideNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideVon EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)