Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Strong Vs Weak - Bottles
Hochgeladen von
api-2094028880 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
54 Ansichten11 SeitenOriginaltitel
strong vs weak - bottles
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
54 Ansichten11 SeitenStrong Vs Weak - Bottles
Hochgeladen von
api-209402888Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 11
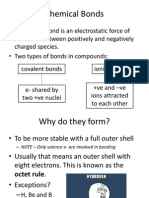
Strong vs.
Weak
Comparing strong and weak acids
2HCl + Mg MgCl2 + H2 is a much quicker reaction than
2CH3COOH + Mg (CH3COO)2Mg + H2
even if the acids have the same concentration. Why?
2H3O+(aq) + Mg(s) Mg2+(aq) + H2(g) + 2H2O(l)
Comparing strong and weak acids
Because the [H3O+] is much higher for HCl (the strong acid) than for the weak ethanoic acid. Because the ethanoic acid is only partially dissociated in solution
CH3COOH + H2O
CH COO + H O
3 3
HA
H+
A-
E.g.
HA
A-
H+
E.g.
Strong Acid
Weak Acid
Same concentration of acid
High
Very different [H3O+]
Low
1 mol L-1 HCl
pH = 0 [H3O+] = 1 mol L-1
1 mol L-1 CH3COOH
pH = 2 [H3O+] = 0.01 mol L-1
100 fold difference in [H3O+]
Strong and weak acids
Strong Acid completely dissociated
higher [H3O+] to react fast reaction
Weak Acid partially dissociated
lower [H3O+] to react slow reaction
2H3O+(aq) + Mg(s) Mg2+(aq) + H2(g) + 2H2O(l)
Strong and weak acids
Weak and strong acids of the same concentration and equal volume have the same amount of acid
Therefore they react to the same extent.
E.g. 1 mol of weak and strong acid will react with the same amount of Mg. The reaction will just take longer for a weak acid.
Strong and weak acids
You need to be very clear about the difference between strong and weak, and concentrated and dilute, in terms of acids (and bases). Strong and weak refer to extent of dissociation. Concentrated (and dilute) refers to the total amount added.
Properties of Strong and Weak Acids
Strong Acid Dissociation Ions Conductivity [H+] pH Reaction rates Completely Many ions High High Weak Acid Partially Few ions Low Low
Low
Fast
Higher
Slow
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Science Wairarapa Presentation On The EconomyDokument23 SeitenScience Wairarapa Presentation On The Economyapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Organics v1Dokument30 Seiten13 Organics v1api-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Preview: Hēki Mission To ISS: Betina Pavri, Senior Principal EngineerDokument27 SeitenPreview: Hēki Mission To ISS: Betina Pavri, Senior Principal Engineerapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Greg Briner Science Wairarapa Talk May 2023Dokument26 SeitenGreg Briner Science Wairarapa Talk May 2023api-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Min AnswerDokument3 Seiten10 Min Answerapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 7 - Equilibrium ConstantDokument35 SeitenLesson 7 - Equilibrium Constantapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Processing Conclusion Discussion and EvaluationDokument9 SeitenProcessing Conclusion Discussion and Evaluationapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ohms Law ExperimentDokument34 SeitenOhms Law Experimentapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Monohybrid Inheritance Punnet Squares and Pedigree ChartsDokument12 SeitenMonohybrid Inheritance Punnet Squares and Pedigree Chartsapi-209402888100% (1)
- Genetic VariationDokument13 SeitenGenetic Variationapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genes and AllesDokument4 SeitenGenes and Allesapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oxidation NumberDokument4 SeitenOxidation Numberapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geno and PhenoDokument8 SeitenGeno and Phenoapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonds and MoleculesDokument4 SeitenChemical Bonds and Moleculesapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oxidation-Reduction ReactionsDokument5 SeitenOxidation-Reduction Reactionsapi-209402888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)