Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fungsi Eksponen Dan Logaritma
Hochgeladen von
Haanan GunnasagaranOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fungsi Eksponen Dan Logaritma
Hochgeladen von
Haanan GunnasagaranCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
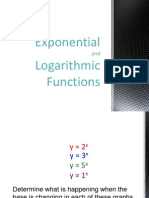
Exponential
and
Logarithmic
Functions
With your Graphing Calculator
graph each of the following
y = 2
x
y = 3
x
y = 5
x
y = 1
x
Determine what is happening when the
base is changing in each of these graphs.
y = 2
x
x y = 2
x
y = 3
x
-2 1/4 1/9
-1 1/3
0 1 1
1 2 3
2 4 9
3 8 27
y = 3
x
y = 2
x
x y = 5
x
y = 1
x
-2 1/25 1
-1 1/5 1
0 1 1
1 5 1
2 25 1
3 125 1
y = 3
x
y = 5
x
y = 1
x
y = 2
x
y = 3
x
y = 5
x
y = 1
x
Determine
where each of
the following
would lie?
y=10
x
y=4
x
y = (3/2)
x
y = 10
x
y = 4
x
y = (3/2)
x
f(x) = 2
x
f(x) = 2
x-3
f(x) = 2
x+2
-
3
f(x) = -(2)
x-4
2
Compound Interest
( )
nt
n
r
P A + = 1
You deposit $5000 into an account that pays 4.5 %
interest. What is the balance of the account after
10 years if the interest is compounded quarterly?
A = Final amount = unknown
P = Principal = $5000
r = rate of interest = .045
n = number of times compounded per year = 4
t = number of years compounded = 10
Compound Interest
( )
nt
n
r
P A + = 1
You deposit $5000 into an account that pays 4.5 %
interest. What is the balance of the account after
10 years if the interest is compounded quarterly?
A = unknown
P = $5000
r = .045
n = 4
( )
10 4
4
045 . 0
1 5000
+ = A
t = 10
88 . 7821 $ = A
Compound Interest
( )
nt
n
r
P A + = 1
You deposit $5000 into an account that pays 4.5 %
interest. What is the balance of the account after
10 years if the interest is compounded quarterly?
A = unknown
P = $5000
r = .045
n = 4
( )
10 52
52
045 . 0
1 5000
+ = A
t = 10
04 . 7840 $ = A
weekly?
52
With your Graphing Calculator
graph each of the following
y = 1
x
y = (1/2)
x
y = (1/3)
x
Determine what is happening when the
base is changing in each of these graphs.
y = 2
x
Jeff Bivin -- LZHS
x
y = ()
x
y = (1/3)
x
-2 4 9
-1 2 3
0 1 1
1 1/3
2 1/9
3 1/8 1/27
y = 3
x
y = 5
x
y = 1
x
y = (1/3)
x
y = ()
x
f(x) = 2
-x
= (1/2)
x
Jeff Bivin -- LZHS
f(x) = ()
x-3
- 2 = (2)
-x+3
- 2
A new Number
+ + + + + + =
! 5
1
! 4
1
! 3
1
! 2
1
! 1
1
! 0
1
e
We could use a spreadsheet to determine an approximation.
+ + + + + + =
120
1
24
1
6
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
e
=
0
!
1
n
e
A new Number
718 . 2
0
!
1
~ =
n
e
y = 2
x
x y = 2
x
y = 3
x
-2 1/9
-1 1/3
0 1 1
1 2 3
2 4 9
3 8 27
y = 3
x
y = e
x
Graph y = e
x
By Hendry P 2011
y = e
x
y = e
x+2
Graph:
y = e
x+2
x + 2 = 0
x = -2
By Hendry P 2011
Compound Interest-continuously
rt
Pe A =
You deposit $5000 into an account that pays 4.5 %
interest. What is the balance of the account after 10
years if the interest is compounded continuously?
A = Final amount = unknown
P = Principal = $5000
r = rate of interest = .045
t = number of years compounded = 10
By Hendry P 2011
Compound Interest-continuously
rt
Pe A =
You deposit $5000 into an account that pays 4.5 %
interest. What is the balance of the account after 10
years if the interest is compounded continuously?
A = unknown
P = $5000
r = .045
t = 10
10 045 . 0
5000
= e A
56 . 7841 $ = A
By Hendry P 2011
Bacteria Growth
kt
ne y =
You have 150 bacteria in a dish. It the constant of
growth is 1.567 when t is measured in hours. How
many bacteria will you have in 7 hours?
y = Final amount = unknown
n = initial amount = 150
k = constant of growth = 1.567
t = time = 7
By Hendry P 2011
Bacteria Growth
kt
ne y =
You have 150 bacteria in a dish. It the constant of
growth is 1.567 when t is measured in hours. How
many bacteria will you have in 7 hours?
y = unknown
n = 150
k = 1.567
t = 7
7 567 . 1
150
-
= e y
678 . 977 , 706 , 8 = y
bacteria 678 . 977 , 706 , 8
By Hendry P 2011
By Hendry P 2011
y = 2
x
x y
-2 1/4
-1
0 1
1 2
2 4
3 8
x y
1/4 -2
-1
1 0
2 1
4 2
8 3
x = 2
y
By Hendry P 2011
How do we
solve this
exponential
equation
for the variable y?
y = 2
x
x = 2
y
By Hendry P 2011
LOGARITHMS
exponential logarithmic
b > 0
A > 0
A b
m
= m A
b
= ) ( log
By Hendry P 2011
2 ) 9 ( log
3
=
9 3
2
=
exponential logarithmic
3 ) 125 ( log
5
=
125 5
3
=
( ) 3 log
8
1
2
=
8
1
3
2 =
5 ) 32 ( log
2
1
= ( ) 32
5
2
1
=
A b
m
= m A
b
= ) ( log
y
x 2 =
y x = ) ( log
2
By Hendry P 2011
u = ) 25 ( log
5
Evaluate
25 5 =
u
2
5 5 =
u
2 = u
2 ) 25 ( log
5
=
By Hendry P 2011
u = ) 81 ( log
3
Evaluate
81 3 =
u
4
3 3 =
u
4 = u
4 ) 81 ( log
3
=
By Hendry P 2011
( ) u =
32
1
2
log
Evaluate
32
1
2 =
u
5
2
1
2 =
u
5 = u
( ) 5 log
32
1
2
=
5
2 2
=
u
By Hendry P 2011
u = ) 7 ( log
7
Evaluate
7 7 =
u
1
7 7 =
u
1 = u
1 ) 7 ( log
7
=
By Hendry P 2011
u = ) 1 ( log
8
Evaluate
1 8 =
u
0
8 8 =
u
0 = u
0 ) 1 ( log
8
=
By Hendry P 2011
u n
n
= ) ( log
5
Evaluate
5
n n
u
=
5 = u
5 ) ( log
5
= n
n
By Hendry P 2011
y = 2
x
x y
-2 1/4
-1
0 1
1 2
2 4
3 8
x y
1/4 -2
-1
1 0
2 1
4 2
8 3
x = 2
y
y=log
2
x
By Hendry P 2011
x
y = log
2
x
1/4 -2
-1
1 0
2 1
4 2
8 3
y = log
2
x
y = log
3
x
y = log
5
x
x = 2
y
By Hendry P 2011
x
y = log
x
1/4 2
1
1 0
2 -1
4 -2
8 -3
y = log
x
x = ()
y
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
log
2
(x+5) = 4
2
4
= x + 5
16
= x + 5
11
= x
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
log
x
(32) = 5
x
5
= 32
x
5
= 2
5
x = 2
By Hendry P 2011
Evaluate
log
3
(25) = u
3
u
= 25
3
u
= 5
2
??????
By Hendry P 2011
By Hendry P 2011
Change of Base Formula
a
x
x
a
10
10
log
log
log =
a
x
x
b
b
a
log
log
log =
By Hendry P 2011
Evaluate
log
3
(25)
= 2.930
3 log
25 log
10
10
=
By Hendry P 2011
Evaluate
log
5
(568)
= 3.941
5 log
568 log
10
10
=
By Hendry P 2011
Properties of Logarithms
Product Property
Quotient Property
Power Property
Property of Equality
By Hendry P 2011
Product Property
n m n m
a a a
+
=
) ( log ) ( log ) ( log n m n m
b b b
+ =
multiplication addition
multiplication addition
By Hendry P 2011
Product Property
) 4 ( log ) 16 ( log ) 4 16 ( log
2 2 2
+ =
) 2 ( log ) 2 ( log ) 2 2 ( log
2
2
4
2
2 4
2
+ =
2 4 ) 2 ( log
6
2
+ =
6 6 =
By Hendry P 2011
Quotient Property
n m
n
m
a
a
a
=
) ( log ) ( log ) ( log n m
b b
n
m
b
=
division subtraction
division subtraction
By Hendry P 2011
Quotient Property
( ) ) 4 ( log ) 32 ( log log
2 2
4
32
2
=
( ) ) 2 ( log ) 2 ( log 8 log
2
2
5
2 2
=
2 5 ) 2 ( log
3
2
=
3 3 =
By Hendry P 2011
Power Property
( )
n m
n
m
a a
=
log
b
(m
p
)
log
b
(m
p
) = plog
b
(m)
p
By Hendry P 2011
Power Property
( ) ) 2 ( log 7 2 log
2
7
2
=
1 7 7 =
7 7 =
By Hendry P 2011
Property of Equality
C A then =
) ( log ) ( log C A if
b b
=
By Hendry P 2011
) ( log
2 3
5
y x
Expand
) ( log ) ( log
2
5
3
5
y x +
) ( log 2 ) ( log 3
5 5
y x +
product property
power property
By Hendry P 2011
Expand
) ( log ) ( log
4
5
3 5
5
z y x
) ( log ) ( log ) ( log
4
5
3
5
5
5
z y x +
quotient property
product property
) ( log 4 ) ( log 3 ) ( log 5
5 5 5
z y x +
power property
( )
4
3 5
5
log
z
y x
By Hendry P 2011
( ) ) ( log ) ( log ) ( log
5
5
2
5
7
5
z y x +
) ( log ) ( log
5 2
5
7
5
z y x
Expand
quotient property
product property
) ( log 5 ) ( log 2 ) ( log 7
5 5 5
z y x
power property
( )
5 2
7
5
log
z y
x
) ( log ) ( log ) ( log
5
5
2
5
7
5
z y x
distributive property
By Hendry P 2011
z y x
3 3 3
log 2 log 6 log 5 +
Condense
power property
product property
2
3
6
3
5
3
log log log z y x +
( )
2
3
6 5
3
log log z y x
( )
2
6 5
3
log
z
y x
quotient property
By Hendry P 2011
4
10
2
10 10
log log log
2
1
z y x
z y x
10 10 10
2
1
log 4 log 2 log
Condense
group / factor
product property
( )
4
10
2
10 10
log log log
2
1
z y x +
( )
4 2
10 10
log log
2
1
z y x
|
.
|
\
|
4 2
2
1
10
log
z y
x
quotient property
Power property
( )
4 2
10
log
z y
x
=
By Hendry P 2011
4 5 2 3
log log log log w z y x
e e e e
+
( ) ( )
4 2 5 3
log log log log w y z x
e e e e
+ +
w z y x
e e e e
log 4 log 5 log 2 log 3 +
Condense
re-organize
group
4 2 5 3
log log log log w y z x
e e e e
+
( ) ( )
4 2 5 3
log log w y z x
e e
( )
4 2
5 3
log
w y
z x
e
product property
Power property
quotient property
By Hendry P 2011
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
3 9 3 + = x x
12 2 = x
6 = x
( ) ( ) 3 log 9 3 log
3 3
+ = x x
Property of
Equality
By Hendry P 2011
( ) ( ) 3 log 9 3 log
3 3
+ = x x
Solve for x
6 = x check
( ) ( ) 3 6 log 9 ) 6 ( 3 log
3 3
+ =
( ) ( ) 3 6 log 9 18 log
3 3
+ =
( ) ( ) 9 log 9 log
3 3
=
checks!
By Hendry P 2011
( ) ( ) 3 log 9 3 log
3 3
+ = x x
Solve for x
3 9 3 + = x x
12 2 = x
6 = x
{ } 6
By Hendry P 2011
( ) ( ) ( ) n n 6 log 2 log 7 log
4 4 4
= +
Solve for n
n n 6 14 7 =
14 = n
( ) ( ) n n 6 log ) 2 ( 7 log
4 4
=
Condense
left side
Property of
Equality
By Hendry P 2011
( ) ( ) ( ) n n 6 log 2 log 7 log
4 4 4
= +
Solve for n
14 = n check
( ) ( ) ( ) ) 14 ( 6 log 2 14 log 7 log
4 4 4
= +
( ) ( ) ( ) 84 log 12 log 7 log
4 4 4
= +
( ) ( ) 84 log ) 12 ( 7 log
4 4
=
( ) ( ) 84 log 84 log
4 4
=
checks!
By Hendry P 2011
( ) ( ) n n 6 log ) 2 ( 7 log
4 4
=
( ) ( ) ( ) n n 6 log 2 log 7 log
4 4 4
= +
Solve for n
n n 6 14 7 =
14 = n
{ } 14
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
( ) ( ) 3 1 log 1 log
2 2
= + + x x
) 1 )( 1 ( 2
3
+ = x x
1 8
2
= x
2
9 x =
x = 3
( ) 3 ) 1 )( 1 ( log
2
= + x x
Condense
left side
Convert to
exponential
form
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
( ) ( ) 3 1 log 1 log
2 2
= + + x x
3 = x check 3 = x check
( ) ( ) 3 1 3 log 1 3 log
2 2
= + +
( ) ( ) 3 2 log 4 log
2 2
= +
3 1 2 = +
3 3 =
checks!
( ) ( ) 3 1 3 log 1 3 log
2 2
= + +
( ) ( ) 3 4 log 2 log
2 2
= +
fails
The argument
must be positive
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
( ) 3 ) 1 )( 1 ( log
2
= + x x
) 1 )( 1 ( 2
3
+ = x x
1 8
2
= x
2
9 x =
x = 3
{ } 3
( ) ( ) 3 1 log 1 log
2 2
= + + x x
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
3 3
2 2
+ + = x x
3 9
2
+ + = x x
6 0
2
+ = x x
) 2 )( 3 ( 0 + = x x
( ) 2 3 log
2
3
= + + x x
2 3 = = x or x
Convert to
exponential
form
By Hendry P 2011
( ) 2 3 log
2
3
= + + x x
Solve for x
3 = x check
checks!
( ) 2 3 ) 3 ( ) 3 ( log
2
3
= + +
( ) 2 3 3 9 log
3
= +
( ) 2 9 log
3
=
2 2 =
2 = x check
( ) 2 3 2 ) 2 ( log
2
3
= + +
( ) 2 3 2 4 log
3
= + +
( ) 2 9 log
3
=
2 2 =
checks!
By Hendry P 2011
( ) 2 3 log
2
3
= + + x x
Solve for x
3 3
2 2
+ + = x x
3 9
2
+ + = x x
6 0
2
+ = x x
) 2 )( 3 ( 0 + = x x
2 3 = = x or x
{ } 2 , 3
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
) 19 log( ) 5 log( ) 7 3 ( = x
) 19 log( ) 5 log( 7 ) 5 log( 3 = x
) 5 log( 7 ) 19 log( ) 5 log( 3 + = x
( )
( ) ) 5 log( 3
) 5 log( 7 ) 19 log( +
= x
943 . 2 = x
( ) ( ) 19 log 5 log
7 3
=
x
) 5 log( 3 ) 5 log( 3
By Hendry P 2011
( ) ( )
2 4
7 log 5 log =
x
Solve for x
) 7 log( ) 2 ( ) 5 log( ) 4 ( = x
( )
( ) ) 5 log( 4
) 7 log( 2
= x
605 . 0 = x
) 5 log( 4 ) 5 log( 4
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
) 9 log( ) 5 ( ) 11 log( ) 1 2 ( = + x x
) 9 log( 5 ) 11 log( 1 ) 11 log( 2 x x = +
) 11 log( ) 9 log( 5 ) 11 log( 2 = x x
( ) ) 11 log( ) 9 log( 5 ) 11 log( 2 = x
( ) ) 9 log( 5 ) 11 log( 2
) 11 log(
= x
387 . 0 = x
( ) ( )
x x 5 1 2
9 log 11 log =
+
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
) 5 log( ) 1 ( ) 3 log( ) 2 ( + = + x x
) 5 log( 1 ) 5 log( ) 3 log( 2 ) 3 log( + = + x x
) 3 log( 2 ) 5 log( ) 5 log( ) 3 log( = x x
( ) ) 3 log( 2 ) 5 log( ) 5 log( ) 3 log( = x
( )
( ) ) 5 log( ) 3 log(
) 3 log( 2 ) 5 log(
= x
( ) ( )
1 2
5 log 3 log
+ +
=
x x
151 . 1 = x
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
) 3 log( ) 8 9 ( ) 7 log( ) 2 3 ( = x x
) 3 log( 8 ) 3 log( 9 ) 7 log( 2 ) 7 log( 3 = x x
) 3 log( 8 ) 7 log( 2 ) 3 log( 9 ) 7 log( 3 = x x
( ) ) 3 log( 8 ) 7 log( 2 ) 3 log( 9 ) 7 log( 3 = x
( )
( ) ) 3 log( 9 ) 7 log( 3
) 3 log( 8 ) 7 log( 2
= x
209 . 1 = x
( ) ( )
8 9 2 3
3 log 7 log
=
x x
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
) ln( ) 2 3 ( ) 15 ln( e x =
2 3 ) 15 ln( = x
x 3 2 ) 15 ln( = +
x =
+
3
2 ) 15 ln(
x = 569 . 1
( ) ( )
2 3
ln 15 ln
=
x
e
1
By Hendry P 2011
Solve for x
) ln( ) 6 5 ( ) ln(
3
7
e x + =
6 5 ) ln(
3
7
+ = x
x 5 6 ) ln(
3
7
=
x =
5
6 ) ln(
3
7
x = 031 . 1
1
6 5
3 7
+
=
x
e
( ) ( )
6 5
3
7
ln ln
+
=
x
e
By Hendry P 2011
) 2 log( ) 1 3 ( ) log(
7
5
= x
Solve for x
) 2 log( 3 ) 2 log( ) log(
7
5
x = +
( )
( )
x =
+
) 2 log( 3
) 2 log( ) log(
7
5
x = 172 . 0
1 3
2 7 5
=
x
( ) ( )
1 3
7
5
2 log log
=
x
) 2 log( 1 ) 2 log( 3 ) log(
7
5
= x
By Hendry P 2011
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsVon EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Fungsi Eksponen Dan LogaritmaDokument83 SeitenFungsi Eksponen Dan LogaritmaMutia ZaharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exponential and LogDokument91 SeitenExponential and Loghappygirl833Noch keine Bewertungen
- NJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsDokument10 SeitenNJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exponential Logarithmic Functions: By: Jeffrey Bivin Lake Zurich High SchoolDokument83 SeitenExponential Logarithmic Functions: By: Jeffrey Bivin Lake Zurich High Schoolhappygirl833Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dhs h2 Math p1 SolutionDokument11 SeitenDhs h2 Math p1 SolutionjimmytanlimlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIEEE 2011 Mathematics Question PaperDokument12 SeitenAIEEE 2011 Mathematics Question Papermohit24031986Noch keine Bewertungen
- PJC h2 Math p1 SolutionsDokument13 SeitenPJC h2 Math p1 SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- ROOT FINDINGDokument3 SeitenROOT FINDINGyana22Noch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB FormulasDokument3 SeitenMATLAB FormulasRoberto Alessandro IonescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 SOLUTIONSDokument15 SeitenH2 MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 SOLUTIONSnej200695Noch keine Bewertungen
- 104 Pracexam 2Dokument3 Seiten104 Pracexam 2ladyjacket42Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dhs h2 Math p2 SolutionDokument14 SeitenDhs h2 Math p2 SolutionjimmytanlimlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsDokument11 Seiten2013 - 2014 H2 Maths JJC Promo SolnsLionel Torres LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summation Notation ExplainedDokument12 SeitenSummation Notation ExplainedCélj Filmund GamayNoch keine Bewertungen
- AREA UNDER CURVEDokument13 SeitenAREA UNDER CURVEAnita Yun Chu PengNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006 AJC H2 MY SolnDokument9 Seiten2006 AJC H2 MY Solnjunie9201Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mi h2 Math Solutions p1Dokument10 SeitenMi h2 Math Solutions p1jimmytanlimlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Misrimal Navajee Munoth Jain Engineering College, Chennai - 97Dokument26 SeitenMisrimal Navajee Munoth Jain Engineering College, Chennai - 97bhagyagr8Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math SolnDokument15 Seiten2012 ACJC Prelim H2 Math Solnckhowh_23284524667% (3)
- HCI 2008 Promo W SolutionDokument12 SeitenHCI 2008 Promo W SolutionMichael CheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 Set B Mock Paper 1 SolutionsDokument15 Seiten2011 Set B Mock Paper 1 SolutionsJordan TiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet On IndicesDokument9 SeitenWorksheet On Indicesmathsman9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Part2 DifferentiationDokument10 SeitenPart2 Differentiationjjs144Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Arithmetic - Ercegovac & Lang 2004 Chapter 7: Solutions To ExercisesDokument6 SeitenDigital Arithmetic - Ercegovac & Lang 2004 Chapter 7: Solutions To Exercisesarunkorath6663Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Sequence & Series HWT - 1Dokument7 SeitenSolutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Sequence & Series HWT - 1varunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practise Exam-MemoDokument13 SeitenPractise Exam-Memoruthie_gundaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid IDokument11 SeitenMid IpassmefoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAT112 WEEK 7 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONSDokument10 SeitenMAT112 WEEK 7 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONSolasunmboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet Algebra 2 TrigDokument4 SeitenFormula Sheet Algebra 2 TrigfrancescoabcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics SolutionsDokument16 SeitenAdvanced Engineering Mathematics SolutionsPooja JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Diploma Programe Standard Level Course Companion Worked Solution Chapter 1Dokument13 SeitenIB Diploma Programe Standard Level Course Companion Worked Solution Chapter 1DeeganasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions Its OperationsDokument58 SeitenFunctions Its OperationsGame AccountNoch keine Bewertungen
- K 0 P LVJ Ox VPT ZX Anzheyrn HF7 Es J1 BR 0 X MMSH Rba 3Dokument33 SeitenK 0 P LVJ Ox VPT ZX Anzheyrn HF7 Es J1 BR 0 X MMSH Rba 3Jatin YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- AJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1Dokument12 SeitenAJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2011 Mid Year Exam Solutions Paper 1jimmytanlimlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChristianDokument7 SeitenChristianJohnny JanulgueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADokument5 SeitenAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul 5 Indices LogarithmsDokument14 SeitenModul 5 Indices Logarithmsysheng98Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - HPW 13 Ism 04 Ii PDFDokument14 Seiten10 - HPW 13 Ism 04 Ii PDF蔥蔥Noch keine Bewertungen
- HCI H2 Math Prelim Paper 1 SolutionsDokument12 SeitenHCI H2 Math Prelim Paper 1 Solutionsnej200695Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answers Paper AIEEEDokument17 SeitenAnswers Paper AIEEESuyash ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nyjc h2 Math p2 SolutionDokument11 SeitenNyjc h2 Math p2 SolutionjimmytanlimlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- JC2 Math Mid-Year Exam SolutionsDokument14 SeitenJC2 Math Mid-Year Exam SolutionsjimmytanlimlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Tryout MTK Ips PDFDokument10 SeitenSoal Tryout MTK Ips PDFmufnzlvrzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermediate Maths II A Guess Papers SolutionsDokument31 SeitenIntermediate Maths II A Guess Papers SolutionsSandeep BandaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMA Quantitative Techniques Exam SolvedDokument6 SeitenCMA Quantitative Techniques Exam SolvedArafatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADokument6 SeitenAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating integrals and solving economics problemsDokument4 SeitenCalculating integrals and solving economics problemsÐhammaþriyaKamßleNoch keine Bewertungen
- HWDokument41 SeitenHWjhdmssNoch keine Bewertungen
- JETIR1907J51Dokument13 SeitenJETIR1907J51Debayanbasu.juNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inverse Functions Small Group 2 2017Dokument2 SeitenInverse Functions Small Group 2 2017api-304977850Noch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 4: Benjamin StahlDokument9 SeitenHomework 4: Benjamin StahlReza AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secondary 3 Additional Mathematics Chapter 2 PracticeDokument10 SeitenSecondary 3 Additional Mathematics Chapter 2 PracticesqhaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2007 YJC Paper 1solDokument12 Seiten2007 YJC Paper 1solYudi KhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Revision Questions SolutionsDokument17 SeitenAdditional Revision Questions SolutionsNicholas TehNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 HCI C1 Block Test H2 Mathematics Revision Package SolutionsDokument80 Seiten2013 HCI C1 Block Test H2 Mathematics Revision Package SolutionsGabriel Francis ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cover BM 2 Buku 1Dokument5 SeitenCover BM 2 Buku 1Haanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 1Dokument3 SeitenMathematics 1Haanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ewrf E4j DiagnosticDokument5 SeitenEwrf E4j DiagnosticHaanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- E4J Name List SJK LDG HenrietaaDokument1 SeiteE4J Name List SJK LDG HenrietaaHaanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Bina Insan Guru Fasa 6: Program Ijazah Sarjana Muda Perguruan (Pismp) SEMESTER 6, 2014Dokument2 SeitenLaporan Bina Insan Guru Fasa 6: Program Ijazah Sarjana Muda Perguruan (Pismp) SEMESTER 6, 2014Haanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 4Dokument15 SeitenRPT Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 4Haanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jsu Bi Paper 1 T4Dokument2 SeitenJsu Bi Paper 1 T4Haanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSV DS T3 Shared by Ravindran SjktpangkorDokument24 SeitenDSV DS T3 Shared by Ravindran SjktpangkorChia Wen LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan Ujian Akhir Tahun Bi T5-Paper 1Dokument13 SeitenSoalan Ujian Akhir Tahun Bi T5-Paper 1firdausbasrolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ahad 31.7Dokument2 SeitenAhad 31.7Haanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti DadahDokument2 SeitenAnti DadahHaanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix Operations and Linear EquationsDokument2 SeitenMatrix Operations and Linear EquationsHaanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name List SJKT Henrietta 1 HaananDokument1 SeiteName List SJKT Henrietta 1 HaananHaanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centre Report (E4J)Dokument1 SeiteCentre Report (E4J)Haanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Teacher Guidebook Year 2Dokument330 SeitenEnglish Teacher Guidebook Year 2Azlan Ahmad100% (2)
- Activity 1 BattleshipDokument4 SeitenActivity 1 BattleshipHaanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Questioning 1Dokument22 SeitenEffective Questioning 1Haanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bill PDFDokument4 SeitenBill PDFHaanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exponential Logarithmic FunctionsDokument17 SeitenExponential Logarithmic FunctionsHaanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Tasks: ELE 3102: Principles of English Language TeachingDokument3 SeitenTutorial Tasks: ELE 3102: Principles of English Language TeachingHaanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 1Dokument1 SeiteQuestion 1Haanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom ManagementDokument48 SeitenClassroom ManagementHaanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lamp IranDokument3 SeitenLamp IranHaanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ajk Tertinggi Program Bina Insan Guru 4 Pismp 2013Dokument1 SeiteAjk Tertinggi Program Bina Insan Guru 4 Pismp 2013Haanan GunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of ReportDokument2 SeitenExample of ReporthgunnasagaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - Baltazar vs. Lingayen Gulf Electric PowerDokument17 Seiten10 - Baltazar vs. Lingayen Gulf Electric PowerJeanne CalalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loan Receivable Measurement and ImpairmentDokument10 SeitenLoan Receivable Measurement and Impairmentjustine cabanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPD-I (Paper-I) MCQ - Analysis and Interpretation of Financial StatementsDokument9 SeitenCPD-I (Paper-I) MCQ - Analysis and Interpretation of Financial Statementsravi yadavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pag-Ibig Salary Loan Form PDFDokument3 SeitenPag-Ibig Salary Loan Form PDFtandangmark75% (52)
- Virginia Henry BillieBMO Harris Bank StatementDokument4 SeitenVirginia Henry BillieBMO Harris Bank StatementQuân NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Reserve Policy To Control InflationDokument8 SeitenFederal Reserve Policy To Control InflationSunny YaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BancomundialpaperDokument32 SeitenBancomundialpaperpaulo.bessa.antunesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Account Statement 101021 090122Dokument31 SeitenAccount Statement 101021 090122Mohammed jawedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commission Agent SystemDokument7 SeitenCommission Agent Systemiqra akramNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Report: Ibs, GurgaonDokument16 SeitenA Report: Ibs, GurgaonKunal PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- General insurance phone binding loan detailsDokument3 SeitenGeneral insurance phone binding loan detailsKrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MACROECONOMICS EXAM REVIEW KEY TERMSDokument38 SeitenMACROECONOMICS EXAM REVIEW KEY TERMSTawhid QurisheNoch keine Bewertungen
- F6mys 2007 Dec PPQDokument19 SeitenF6mys 2007 Dec PPQAnslem TayNoch keine Bewertungen
- C10 - PAS 7 Statement of Cash FlowsDokument15 SeitenC10 - PAS 7 Statement of Cash FlowsAllaine Elfa100% (2)
- USDC Doc# 45-1 Through 45-15 Declaration of Paolo Bruckner ISO Request For Entry of Default W-ExhibitsDokument157 SeitenUSDC Doc# 45-1 Through 45-15 Declaration of Paolo Bruckner ISO Request For Entry of Default W-ExhibitsSYCR ServiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 The Investment Industry A Top Down ViewDokument21 Seiten1 The Investment Industry A Top Down ViewhimanshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GOHLAS V.2 2013 - Housing Loan SchemeDokument14 SeitenGOHLAS V.2 2013 - Housing Loan Schemebreatrice.sscNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Moneybanking and Financial Markets Cecchetti Schoenholtz 4th EditionDokument11 SeitenSolution Manual For Moneybanking and Financial Markets Cecchetti Schoenholtz 4th Editionsugarysestine.fllo5z100% (48)
- No Co Maker Application Form TSL v.052623Dokument2 SeitenNo Co Maker Application Form TSL v.052623Rio A. EbueNoch keine Bewertungen
- BAB 5 - Consumer Behaviour Consumer BankingDokument67 SeitenBAB 5 - Consumer Behaviour Consumer BankingSyai GenjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Casio Fx-9860GIIDokument412 SeitenManual Casio Fx-9860GIISantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management - Midterm Exam - 1st DraftDokument5 SeitenFinancial Management - Midterm Exam - 1st DraftRenalyn Paras100% (2)
- Plastic Money Market & Future GrowthDokument57 SeitenPlastic Money Market & Future Growthअंजनी श्रीवास्तवNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved RBI Grade B 17 NOV 2002 Paper With SolutionsDokument94 SeitenSolved RBI Grade B 17 NOV 2002 Paper With SolutionsAniruddha ShidhayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes PayableDokument38 SeitenNotes PayableNadira AristyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules on Bancassurance and Variable Life InsuranceDokument24 SeitenRules on Bancassurance and Variable Life Insurancelancekim21Noch keine Bewertungen
- GRI G4 FinancialServicesSectorDisclosuresDokument48 SeitenGRI G4 FinancialServicesSectorDisclosuresStephanie ClarestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes History of Economic ThoughtDokument42 SeitenNotes History of Economic Thoughtblubibub100% (5)
- SPT PPH BDN 2009 English OrtaxDokument39 SeitenSPT PPH BDN 2009 English Ortaxanon_265770590Noch keine Bewertungen