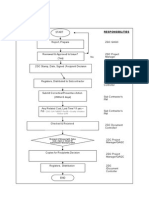
Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
QA Vs QC
Hochgeladen von
Ashutosh SinghOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
QA Vs QC
Hochgeladen von
Ashutosh SinghCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Improve this chart
Quality Assurance
QA is a set of activities for ensuring quality in the processes by which products are developed.
Quality Control
QC is a set of activities for ensuring quality in products. The activities focus on identifying defects in the actual products produced. QC aims to identify (and correct) defects in the finished product. Quality control, therefore, is a reactive process.
Definition:
Focus on:
QA aims to prevent defects with a focus on the process used to make the product. It is a proactive quality process. The goal of QA is to improve development and test processes so that defects do not arise when the product is being developed. Statistical Tools & Techniques can be applied in both QA & QC. When they are applied to processes (process inputs & operational parameters), they are called Statistical Process Control (SPC); & it becomes the part of QA. Prevention of quality problems through planned and systematic activities including documentation. Establish a good quality management system and the assessment of its adequacy & conformance audit of the operation system & the review of the system itself. Verification is an example of QA
Goal:
The goal of QC is to identify defects after a product is developed and before it's released.
Statistical Techniques:
When statistical tools & techniques are applied to finished products (process outputs), they are called as Statistical Quality Control (SQC) & comes under QC.
What:
The activities or techniques used to achieve and maintain the product quality, process and service. Finding & eliminating sources of quality problems through tools & equipment so that customer's requirements are continually met.
How:
Example:
Validation/Software Testing is an example of QC Quality control is usually the responsibility of a specific team that tests the product for defects.
Responsibility:
Everyone on the team involved in developing the product is responsible for quality assurance.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Difference Between QA and QCDokument6 SeitenDifference Between QA and QCGajendra Singh Raghav100% (1)
- Quality Assurance Process A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandQuality Assurance Process A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance Vs ControlDokument3 SeitenQuality Assurance Vs ControlYay B. GicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Chart-3. Internal NCRDokument1 SeiteFlow Chart-3. Internal NCRMubashir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Costs PDFDokument9 SeitenQuality Costs PDFYvonne Barton100% (1)
- Review Iso 9001 2015 PPMDokument27 SeitenReview Iso 9001 2015 PPMAFDHAL PASANoch keine Bewertungen
- QA/QC EngineersDokument1 SeiteQA/QC EngineersMahnooranjumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Project Quality Plan & QIP and Their Effective Implementation at Project SitesDokument35 SeitenImportance of Project Quality Plan & QIP and Their Effective Implementation at Project Sitesimran jamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- JD QAQC Engineer Mech 2016Dokument2 SeitenJD QAQC Engineer Mech 2016Sebastian Rajesh100% (1)
- Induction TrainingDokument6 SeitenInduction Trainingsowmiya245Noch keine Bewertungen
- Role of QA&QC in Manufacturing - PresentationDokument32 SeitenRole of QA&QC in Manufacturing - Presentationimran jamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Issues in QualityDokument19 SeitenIssues in QualityPappuRamaSubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Standards in The Workplace Book 1Dokument29 SeitenQuality Standards in The Workplace Book 1Annabelle Rigat de LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Monitoring and Reporting Quality ObjectivesDokument18 Seiten04 Monitoring and Reporting Quality ObjectivesSarahZachraNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA - QC Job Descriptions (Overview)Dokument4 SeitenQA - QC Job Descriptions (Overview)kannankriv100% (1)
- CPA Compliance ChecklistDokument25 SeitenCPA Compliance ChecklistFizz FirdausNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asq What Is A Quality PlanDokument3 SeitenAsq What Is A Quality PlanCloud RedfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Plan PresentationDokument16 SeitenQuality Plan Presentationel1980Noch keine Bewertungen
- QM-01-0001 Quality Manual Revision MDokument38 SeitenQM-01-0001 Quality Manual Revision MNader Shdeed100% (1)
- Quality Management: ©ian Sommerville 2000 Software Engineering, 6th Edition. Chapter 24 Slide 1Dokument55 SeitenQuality Management: ©ian Sommerville 2000 Software Engineering, 6th Edition. Chapter 24 Slide 1faroakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplier Name:: Manufacturing Process Plan (MPP)Dokument13 SeitenSupplier Name:: Manufacturing Process Plan (MPP)Nathan DrakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2Dokument18 SeitenCH 2suresh84123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Quality Management Job DescriptionDokument2 SeitenCorporate Quality Management Job DescriptionfiratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance & QUALITY CONTROldocDokument15 SeitenQuality Assurance & QUALITY CONTROldocapi-19786321Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance (QA) Management Procedures: SOP ListDokument9 SeitenQuality Assurance (QA) Management Procedures: SOP ListPranav UppadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 560-S27 QUALITY CONTROL PROGRAM Rev.4Dokument27 Seiten560-S27 QUALITY CONTROL PROGRAM Rev.4AbdelmuneimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 质量过程审核 Quality Process Audit: 修订履历 Revision HistoryDokument42 Seiten质量过程审核 Quality Process Audit: 修订履历 Revision HistoryphamtienkhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Requirements of ContractorsDokument15 SeitenQuality Requirements of ContractorsRoshin99Noch keine Bewertungen
- QA QC EngineerDokument1 SeiteQA QC EngineerTAHER AMMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) Submission AssessmentDokument15 SeitenProduction Part Approval Process (PPAP) Submission Assessmentffppxxzz100% (1)
- Construction Quality AssuranceDokument8 SeitenConstruction Quality AssuranceMalek AlhussienNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 13485:2016 Quality Systems Manual: Document No. QMD-001Dokument11 SeitenISO 13485:2016 Quality Systems Manual: Document No. QMD-001Roslan.Affandi2351100% (1)
- Quality Control DepartmentDokument5 SeitenQuality Control DepartmentRonnel MatampaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- As 3904.4-1994 Quality Management and Quality System Elements Guidelines For Quality ImprovementDokument9 SeitenAs 3904.4-1994 Quality Management and Quality System Elements Guidelines For Quality ImprovementSAI Global - APACNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Management Quality Assurance Quality ControlDokument22 SeitenQuality Management Quality Assurance Quality ControljennyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance Job DescriptionDokument1 SeiteQuality Assurance Job DescriptionSWPriestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance and Quality ControlDokument23 SeitenQuality Assurance and Quality Controlamitywave1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guidance For Preparing Standard Operating Procedures (Sops) : Epa Qa/G-6Dokument60 SeitenGuidance For Preparing Standard Operating Procedures (Sops) : Epa Qa/G-6rai_khan_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management Review Wasit-1Dokument7 SeitenManagement Review Wasit-1SANUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplier Audits and SurveysDokument13 SeitenSupplier Audits and SurveysBighneswar PatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMF-project Quality ManagementDokument41 SeitenPMF-project Quality Managementabdella.whateverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monitoring and Assessment Quality Objectives - Form - Admin.2Dokument3 SeitenMonitoring and Assessment Quality Objectives - Form - Admin.2Vanny Joyce BaluyutNoch keine Bewertungen
- COPQDokument8 SeitenCOPQJocelyn Garcia100% (1)
- Job Responsibilities of Quality ManagerDokument3 SeitenJob Responsibilities of Quality Managersok daraNoch keine Bewertungen
- QSV 2 Product Release Procedure EN 01Dokument6 SeitenQSV 2 Product Release Procedure EN 01prashanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control of Monitoring and Measuring EquipmentDokument18 SeitenControl of Monitoring and Measuring EquipmentFranklyn OnyeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionVon EverandQuality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOP QualiityDokument28 SeitenSOP QualiityUttam KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document Control ProcedureDokument3 SeitenDocument Control ProcedureHeny Kusumawati100% (1)
- Quality PlanDokument9 SeitenQuality PlanSuresh Pahadia100% (2)
- Supplier Auditpak 2000Dokument52 SeitenSupplier Auditpak 2000Adrian AustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gaurav Pathak CV Opex 20.11.2022Dokument2 SeitenGaurav Pathak CV Opex 20.11.2022Abhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Manual: M. Barbisotti & Sons LTDDokument20 SeitenQuality Manual: M. Barbisotti & Sons LTDengsam777100% (1)
- StorageDokument31 SeitenStoragesandy cyborgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance ManagerDokument2 SeitenQuality Assurance Managermounirs719883Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Engineer-CAD ManagerDokument2 SeitenDesign Engineer-CAD ManagerIvan DerežićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Manual RS QMS 002Dokument11 SeitenQuality Manual RS QMS 002WayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raw Material Inspection ProcedureDokument5 SeitenRaw Material Inspection ProcedureAli RazuNoch keine Bewertungen
- QC SupervisorDokument2 SeitenQC SupervisorAnnisa Citra SetiacahyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coal India Sample Question Paper MT 2012Dokument9 SeitenCoal India Sample Question Paper MT 2012Ashutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 2473-1975 - Norma Furos de CentroDokument8 SeitenIs 2473-1975 - Norma Furos de CentroEduardo Lopes100% (1)
- NSEZ Unit Details - 310516Dokument45 SeitenNSEZ Unit Details - 310516Anonymous 9AnxnHaW3D0% (1)
- Gantt Chart Template STDFDokument1 SeiteGantt Chart Template STDFAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardness Conversion ChartDokument10 SeitenHardness Conversion ChartAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Gantt v4Dokument14 SeitenExcel Gantt v4PMPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lear-75-GM Quality System Basics Audit FormDokument12 SeitenLear-75-GM Quality System Basics Audit FormalexrferreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Digestive System: by Seth and RobinDokument9 SeitenThe Digestive System: by Seth and RobinAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- JD FormatDokument4 SeitenJD FormatAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5480 2Dokument40 Seiten5480 2Ashutosh Singh80% (10)
- Technical Skill Matrix EnggDokument19 SeitenTechnical Skill Matrix EnggAshutosh Singh100% (1)
- Spline Program Ver 1.1Dokument6 SeitenSpline Program Ver 1.1Ashutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE (Advanced) Physics Syllabus: The Syllabus Is Same As Previous IIT JEE SyllabusDokument7 SeitenJEE (Advanced) Physics Syllabus: The Syllabus Is Same As Previous IIT JEE SyllabusAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spline Program Ver 1.1Dokument6 SeitenSpline Program Ver 1.1Ashutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Forging OperationsDokument6 SeitenTypes of Forging OperationsAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Date: 25.08.2014 HR Manager XXX: XXXXXXXXDokument1 SeiteTo Date: 25.08.2014 HR Manager XXX: XXXXXXXXAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Digestive System: by Seth and RobinDokument9 SeitenThe Digestive System: by Seth and RobinAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Eng Induction Heating GeneratorDokument9 Seiten2 Eng Induction Heating GeneratorAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardness Conversion ChartDokument34 SeitenHardness Conversion ChartAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Books For IES Mechanical EngineeringDokument1 SeiteBooks For IES Mechanical EngineeringAshutosh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen