Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
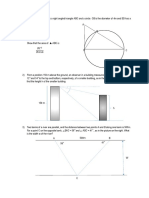
Trigonometry Q
Hochgeladen von
api-230427224Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Trigonometry Q
Hochgeladen von
api-230427224Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
3D applications of trigonometry HKCEE Paper 1 past paper sorted by topic
(1980 - 2009)
Vertical pole 1980 1981 1982 1983 1984 1985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 X
X X X X
Solid figures
Shadow
Paper folding
Inclined plane
NA
X X X X NA X X X X X NA X X Laser projection on vertical wall X X X X X X X X X
Page 1
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
Vertical pole on horizontal triangular plane 1980B9 P
h WEST C
NORTH EAST
x
A SOUTH 400
In the figure, PC represents a vertical object of height h metres. From a point A, south of C, the angle of elevation of P is . From a point B, 400 metres east of A, the angle of elevation of P is . AC and BC are x metres and y metres respectively. (a) (i) (ii) Express x in terms of h and . Express y in terms of h and . (4 marks) (b) If = 60 and = 30 , find the value of h correct to 3 significant figures. (6 marks)
Page 2
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1983B13
50 m
C
30
45
A P B SOUTH
EAST
In the figure, A, B and C are three points on the same horizontal ground. HC is a vertical tower 50 m high. A and B are respectively due east and due south of the tower. The angles of elevation of H observed from A and B are respectively 45 and 30 . (a) Find the distance between A and B. (6 marks) (b) P is a point on AB such that CP AB . (i) (ii) Find the distance between C and P to the nearest metre. Find the angle of elevation of H observed from P to the nearest degree. (6 marks)
Page 3
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1984B13
Page 4
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1985B8
Page 5
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1986B10
Page 6
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1990B10
Page 7
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1993B12
Page 8
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1994B14
Page 9
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
2002B14
Page 10
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
2008B15
Page 11
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
Solid figures 1982B8 B
y cm 9 cm
C x cm A x cm Figure not drawn to scale The figure represents the framework of a cuboid made of iron wire. It has a square base of side x cm and a height of y cm. The length of the diagonal AB is 9 cm. The total length of wire used for the framework (including the diagonal AB) is 69 cm. (a) Find all the values of x and y. (10 marks) (b) Hence calculate ABC to the nearest degree for the case in which y > x. (2 marks)
Page 12
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1987B11
Page 13
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
2005B14
Page 14
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
2007B16
Page 15
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
2009B17 The figure shows a geometric model fixed on the horizontal ground. The model consists of two thin triangular metal plates ABE and CDE, where D lies on AB and CE is perpendicular to the thin metal plate ABE. It is given that A, B, C and D lie on the horizontal ground. It is found that AC = 28 cm, BC = 25 cm, BD = 6 cm, BE = 24 cm and ABC = 57 . E
A D B (a) Find (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
the length of CD, BAC , the area of ABC , the shortest distance from E to the horizontal ground. (9 marks)
(b) A student claims that the angle between DE and the horizontal ground is CDE . Do you agree? Explain your answer. (2 marks)
Page 16
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
Plane object under sunshine and its shadow 1988B13
Page 17
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1989B10
Figure 3
Page 18
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1995B15
Page 19
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1998B17
Page 20
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
2003B14
Page 21
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
Paper Folding 1992B15
Figure 8a
Page 22
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
1999B18
Page 23
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
2001B16
Page 24
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
2006B17 In Figure 1, ABC is a triangular paper card. D is a point lying on AC such that BD is perpendicular to AC. It is known that AB = 40cm, BC = 60cm and AC = 90cm. B 60 cm C
40 cm D 90 cm
A Figure 1 (a) Find AD. (2 marks) (b) The triangular paper card in the figure is folded along BD such that AB and BC lie on a horizontal plane as shown in Figure 2. D
B C
A Figure 2 (i) Suppose DAC = 62 . (1) (2) (3) Find the distance between A and C on the horizontal plane. Using Herons formula, or otherwise, find the area of ABC on the horizontal plane. Find the height of the tetrahedron ABCD from the vertex D to the base ABC .
(ii) Describe how the volume of the tetrahedron ABCD varies when ADC increases from 30 to 150 . Explain your answer. (9 marks)
Page 25 May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
Rectangular inclined plane 1996B15
Page 26
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
2004B17
Page 27
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
The golden proportion for distinction
http://hk.myblog.yahoo.com/vinci_mak
Laser projection 2000B17
Page 28
May2009 edition vinci_mak@hotmail.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Guess Paper - 2012 Class - IX Subject - : MathematicsDokument4 SeitenGuess Paper - 2012 Class - IX Subject - : MathematicsGursimar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigDokument5 SeitenTrigDaniel KwokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometrical Construction 9Dokument6 SeitenGeometrical Construction 9Darwin ManoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry RevisionDokument2 SeitenTrigonometry RevisionZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC Geometry2Dokument3 SeitenMC Geometry2biswajit karNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Exercises - Express and SpecialDokument26 SeitenExtra Exercises - Express and Specialdmal88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Revision WorksheetDokument4 SeitenMathematics Revision WorksheetLiciaMcNoch keine Bewertungen
- pr14 EsDokument31 Seitenpr14 EsMohamed Fouad KorraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearings, Sine Rule & Cosine Rule Worksheet MathsMeterDokument2 SeitenBearings, Sine Rule & Cosine Rule Worksheet MathsMeterKatherine Williams83% (6)
- AB 11 CM, AO 8 CM, OD 6 CM.: 32) AB Is Parallel To CD. The Lines AD and BC Intersect at Point ODokument3 SeitenAB 11 CM, AO 8 CM, OD 6 CM.: 32) AB Is Parallel To CD. The Lines AD and BC Intersect at Point OAnonymous EmjOwXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths - 9Dokument5 SeitenMaths - 9Gitanjali NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ws - Lines and AnglesDokument4 SeitenWs - Lines and AnglesManya Elhance100% (1)
- HKCEE Maths 2002 Paper 1Dokument33 SeitenHKCEE Maths 2002 Paper 1auau1997100% (1)
- Eton - KS - MathsBPaper - 2010Dokument4 SeitenEton - KS - MathsBPaper - 2010kabirNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.3 Holiday Work (Technical Drawing) Attempt All QuestionsDokument3 SeitenS.3 Holiday Work (Technical Drawing) Attempt All QuestionsAthiyo MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Texas Geometry Staar DiagnosticDokument29 SeitenTexas Geometry Staar DiagnosticJason MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Basic TrigonometryDokument7 Seiten14 Basic TrigonometryAda LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper For Maths (Class 8)Dokument4 SeitenQuestion Paper For Maths (Class 8)Saniat Ahmed ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry - Straight Lines - Voronoy Diagrams - Basic Concepts of FunctionsDokument6 SeitenTrigonometry - Straight Lines - Voronoy Diagrams - Basic Concepts of FunctionselenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS1 - VectorsDokument3 SeitenWS1 - VectorsElaine BonaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (S3) Test-Midterm 20230315Dokument10 Seiten(S3) Test-Midterm 20230315gurnoorkaur sandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1 Isometric Drawings - Sample ProblemsDokument14 Seiten5.1 Isometric Drawings - Sample ProblemsMurugarajan AngamuthuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triangles: Office: 606, 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road Ranchi 1 PH: 0651-2562526,9835508812,8507613968Dokument7 SeitenTriangles: Office: 606, 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road Ranchi 1 PH: 0651-2562526,9835508812,8507613968QSQFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Italy ITAMO 2012 92Dokument1 SeiteItaly ITAMO 2012 92Aldo MateosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv Ex 07 Trigonometry II (Application)Dokument12 SeitenAdv Ex 07 Trigonometry II (Application)Leroy ChengNoch keine Bewertungen
- KS Papers 2010 - Maths BDokument4 SeitenKS Papers 2010 - Maths BakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Sa1 Maths Sample Paper1Dokument22 Seiten9 Sa1 Maths Sample Paper1empty_shake5319Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1701832667764.QP PS CB IX Math CirclesDokument7 Seiten1701832667764.QP PS CB IX Math Circleskabbur.anushkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co Ordinate GeometryDokument1 SeiteCo Ordinate GeometryDevansh AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CXC Mathematics June 07 P2Dokument15 SeitenCXC Mathematics June 07 P2Lueshen WellingtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths ExerciseDokument4 SeitenMaths ExercisechenziuleiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry Revision ExerciseDokument5 SeitenTrigonometry Revision ExerciselinnbrownieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triangles: Objective Type QuestionsDokument3 SeitenTriangles: Objective Type QuestionsNikhil DeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Mathematics Part IIDokument5 Seiten02 Mathematics Part IIAtul JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Lines and AnglesDokument9 SeitenChapter 6 Lines and Anglessanjaykr4991Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7th Maths Final Exampaper 2023-24Dokument8 Seiten7th Maths Final Exampaper 2023-24alexanjali213Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Add Math Form 5 Chapter 4 VectorDokument6 SeitenSPM Add Math Form 5 Chapter 4 VectorRuban RubanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Add Math Form 5 Chapter 4 VectorDokument6 SeitenSPM Add Math Form 5 Chapter 4 VectorschorynerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 28-Trigonometry Paper 2Dokument6 Seiten28-Trigonometry Paper 2iyaad MubarakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Form 1Dokument5 SeitenPhysics Form 1Sand FossohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Value of (256) X (256) Is (A) 4 (B) 16 (C) 64 (D) 256.25 2. Form of 0.1 Is (A) (B) (C) (D) None of TheseDokument11 SeitenValue of (256) X (256) Is (A) 4 (B) 16 (C) 64 (D) 256.25 2. Form of 0.1 Is (A) (B) (C) (D) None of TheseAkshita KambojNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Geometry Problems: Contributors: Djmathman, Abishek99, CaptainflintDokument8 Seiten100 Geometry Problems: Contributors: Djmathman, Abishek99, CaptainflintAllan Añavisa Ostique Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Angles Summary: 1. (I) The Space Enclosed Between The Lines AB and BC Is Referred To As An AngleDokument49 SeitenAngles Summary: 1. (I) The Space Enclosed Between The Lines AB and BC Is Referred To As An Anglekaziba stephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icse Maths Sample Paper (2005)Dokument5 SeitenIcse Maths Sample Paper (2005)Rittik DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry and Quadratic Kvpy PYQDokument6 SeitenTrigonometry and Quadratic Kvpy PYQTanay AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constructions PDFDokument6 SeitenConstructions PDFRajesh Kumar GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ix Visto-2 M.T-1 23-24Dokument7 SeitenIx Visto-2 M.T-1 23-24pranavsugan31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 9 Maths PE II PaperDokument5 SeitenClass 9 Maths PE II PaperPrince PrasannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xiii Geometrical Olympiad in Honour of I.F.Sharygin The Correspondence Round. SolutionsDokument13 SeitenXiii Geometrical Olympiad in Honour of I.F.Sharygin The Correspondence Round. Solutions89a12 Nguyễn Lã Trọng NguyênNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sec3 TrigonometryDokument10 SeitenSec3 TrigonometryCharles PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sine Law - ProblemsDokument2 SeitenSine Law - ProblemsSyed Shuja HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- BGW ElemgeoDokument10 SeitenBGW ElemgeosreedharbharathNoch keine Bewertungen
- W s-6 Thales TheoremDokument3 SeitenW s-6 Thales Theoremapi-253679034Noch keine Bewertungen
- GeolemmasDokument10 SeitenGeolemmasddkillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 3 Final Exam Paper 2Dokument8 SeitenForm 3 Final Exam Paper 2hoi ching wongNoch keine Bewertungen
- EGMO Chap2Dokument18 SeitenEGMO Chap2helo08976Noch keine Bewertungen
- bk9 12Dokument18 Seitenbk9 12Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Iii: Similar Triangles: Two Line Segments AB and CD Are Propotional To ADokument14 SeitenChapter Iii: Similar Triangles: Two Line Segments AB and CD Are Propotional To ADuong QuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Maths MsDokument16 Seiten2015 Maths Msapi-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- SQL WorkshopDokument105 SeitenSQL Workshopapi-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sqlii Workshop NotesDokument3 SeitenSqlii Workshop Notesapi-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Websams Training Staff 2014Dokument68 SeitenWebsams Training Staff 2014api-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonmetry 3DDokument3 SeitenTrigonmetry 3Dapi-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Hkdse 2014 Paper1 Question EngDokument24 SeitenMaths Hkdse 2014 Paper1 Question Engapi-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Hkdse 2014 Paper2 Question EngDokument15 SeitenMaths Hkdse 2014 Paper2 Question Engapi-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Test ch-11Dokument4 SeitenMaths Test ch-11api-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- English-Speaking-Day-Schedule 2014-15 Non English Teacher DutyDokument2 SeitenEnglish-Speaking-Day-Schedule 2014-15 Non English Teacher Dutyapi-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Synchronize School CalednarDokument2 SeitenSynchronize School Calednarapi-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Morning AssemblyDokument1 SeiteMorning Assemblyapi-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 ADokument10 SeitenUnit 4 AChetan p ShirahattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decs vs. San DiegoDokument7 SeitenDecs vs. San Diegochini17100% (2)
- Month Puzzle Two VariableDokument6 SeitenMonth Puzzle Two VariableNayan KaithwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRESS HealthDokument40 SeitenSTRESS HealthHajra KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding PumpDokument113 SeitenUnderstanding Pumpnyr1981_942955963100% (5)
- Being Agile. Staying Resilient.: ANNUAL REPORT 2021-22Dokument296 SeitenBeing Agile. Staying Resilient.: ANNUAL REPORT 2021-22PrabhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemisah ZirconDokument10 SeitenPemisah ZirconLorie Banka100% (1)
- 2012 Karshaniya YavaguDokument4 Seiten2012 Karshaniya YavaguRANJEET SAWANTNoch keine Bewertungen
- FBDokument27 SeitenFBBenjaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 1 HRM in PandemicDokument2 SeitenCase Study 1 HRM in PandemicKristine Dana LabaguisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions For Tutorial Exercises Association Rule Mining.: Exercise 1. AprioriDokument5 SeitenSolutions For Tutorial Exercises Association Rule Mining.: Exercise 1. AprioriMarkib Singh AdawitahkNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Technical Report ON Centre of Pressure ONA Plane Surface ExperimentDokument13 SeitenA Technical Report ON Centre of Pressure ONA Plane Surface ExperimentVictor OwolekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. N. Kumarappan IE (I) Council Candidate - Electrical DivisionDokument1 SeiteDr. N. Kumarappan IE (I) Council Candidate - Electrical Divisionshanmugasundaram32Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adel Lock ManualDokument1 SeiteAdel Lock Manual24245677843Noch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanic SoilsDokument14 SeitenVolcanic SoilsVictor Hugo BarbosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charging Station For E-Vehicle Using Solar With IOTDokument6 SeitenCharging Station For E-Vehicle Using Solar With IOTjakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bach Polonaise G Min BWV 119 A4Dokument1 SeiteBach Polonaise G Min BWV 119 A4vincenzovaiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christine Remembered That Today Is The Birthday of Her BossDokument1 SeiteChristine Remembered That Today Is The Birthday of Her BossA.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Turning The Mind Into An AllyDokument244 SeitenTurning The Mind Into An AllyNic Sosa67% (3)
- Beyond The Breech Trial. Maggie BanksDokument4 SeitenBeyond The Breech Trial. Maggie Bankspurpleanvil100% (2)
- TRUMPF Marking Laser BrochureDokument48 SeitenTRUMPF Marking Laser BrochureKKM SBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menu Planning in HospitalDokument4 SeitenMenu Planning in HospitalERva Soelkarnaen100% (1)
- Operations Management Stevenson 11th Edition Test BankDokument10 SeitenOperations Management Stevenson 11th Edition Test BankAries Gonzales Caragan50% (2)
- Contemplation (Murāqaba) and Spiritual Focus/attention (Tawajjuh) in The Pre-Mujaddidi Naqshibandi OrderDokument5 SeitenContemplation (Murāqaba) and Spiritual Focus/attention (Tawajjuh) in The Pre-Mujaddidi Naqshibandi OrderShahmir ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 Interview Question Code Galatta - HandbookDokument16 Seiten50 Interview Question Code Galatta - HandbookSai DhanushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring Newsletter 2014-LockedDokument4 SeitenSpring Newsletter 2014-Lockedapi-244488788Noch keine Bewertungen
- Web Programming: GET / HTTP/1.1 ..Dokument16 SeitenWeb Programming: GET / HTTP/1.1 ..Alecu IlieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philips fwt9200Dokument37 SeitenPhilips fwt9200Alex BrazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet TBJ SBW13009-KDokument5 SeitenDatasheet TBJ SBW13009-KMarquinhosCostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membrane and TransportDokument25 SeitenMembrane and TransportHafsa JalisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- House Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetVon EverandHouse Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crochet Creatures of Myth and Legend: 19 Designs Easy Cute Critters to Legendary BeastsVon EverandCrochet Creatures of Myth and Legend: 19 Designs Easy Cute Critters to Legendary BeastsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (10)
- The Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingVon EverandThe Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (11)
- 100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiVon Everand100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Edward's Menagerie New Edition: Over 50 easy-to-make soft toy animal crochet patternsVon EverandEdward's Menagerie New Edition: Over 50 easy-to-make soft toy animal crochet patternsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swatch This, 3000+ Color Palettes for Success: Perfect for Artists, Designers, MakersVon EverandSwatch This, 3000+ Color Palettes for Success: Perfect for Artists, Designers, MakersBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Crochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!Von EverandCrochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (10)
- Little Happy Circus: 12 Amigurumi Crochet Toy Patterns for Your Favourite Circus PerformersVon EverandLittle Happy Circus: 12 Amigurumi Crochet Toy Patterns for Your Favourite Circus PerformersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Crochet Zodiac Dolls: Stitch the horoscope with astrological amigurumiVon EverandCrochet Zodiac Dolls: Stitch the horoscope with astrological amigurumiBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Edward's Menagerie: Dogs: 50 canine crochet patternsVon EverandEdward's Menagerie: Dogs: 50 canine crochet patternsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (5)
- Amigurumi Cats: Crochet Sweet Kitties the Japanese Way (24 Projects of Cats to Crochet)Von EverandAmigurumi Cats: Crochet Sweet Kitties the Japanese Way (24 Projects of Cats to Crochet)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Crochet Style: 15 Colourful Crochet Patterns For You and Your HomeVon EverandModern Crochet Style: 15 Colourful Crochet Patterns For You and Your HomeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Treasure Bookmaking: Crafting Handmade Sustainable JournalsVon EverandTreasure Bookmaking: Crafting Handmade Sustainable JournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crochet in a Weekend: 29 Quick-to-Stitch Sweaters, Tops, Shawls & MoreVon EverandCrochet in a Weekend: 29 Quick-to-Stitch Sweaters, Tops, Shawls & MoreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- 100 Crochet Tiles: Charts and patterns for crochet motifs inspired by decorative tilesVon Everand100 Crochet Tiles: Charts and patterns for crochet motifs inspired by decorative tilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Embroidery: A Book of Stitches to Unleash CreativityVon EverandModern Embroidery: A Book of Stitches to Unleash CreativityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crochet Iconic Women: Amigurumi Patterns for 15 Women Who Changed the WorldVon EverandCrochet Iconic Women: Amigurumi Patterns for 15 Women Who Changed the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (30)
- Textiles Transformed: Thread and thrift with reclaimed textilesVon EverandTextiles Transformed: Thread and thrift with reclaimed textilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Funny Amigurumi: 16 Creatures & Their Accessories to CrochetVon EverandFunny Amigurumi: 16 Creatures & Their Accessories to CrochetBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Fairytale Blankets to Crochet: 10 Fantasy-Themed Children's Blankets for Storytime CuddlesVon EverandFairytale Blankets to Crochet: 10 Fantasy-Themed Children's Blankets for Storytime CuddlesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Shetland Fine Lace Knitting: Recreating Patterns from the Past.Von EverandShetland Fine Lace Knitting: Recreating Patterns from the Past.Bewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- How to Embroider Almost Everything: A Sourcebook of 500+ Modern Motifs & Easy Stitch TutorialsVon EverandHow to Embroider Almost Everything: A Sourcebook of 500+ Modern Motifs & Easy Stitch TutorialsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Modern Crochet Sweaters: 20 Chic Designs for Everyday WearVon EverandModern Crochet Sweaters: 20 Chic Designs for Everyday WearBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Crochet Cute Dolls with Mix-and-Match Outfits: 66 Adorable Amigurumi PatternsVon EverandCrochet Cute Dolls with Mix-and-Match Outfits: 66 Adorable Amigurumi PatternsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Upcycling: 20 Creative Projects Made from Reclaimed MaterialsVon EverandUpcycling: 20 Creative Projects Made from Reclaimed MaterialsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edward's Crochet Doll Emporium: Flip the mix-and-match patterns to make and dress your favourite peopleVon EverandEdward's Crochet Doll Emporium: Flip the mix-and-match patterns to make and dress your favourite peopleBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Art Journals & Creative Healing: Restoring the Spirit through Self-ExpressionVon EverandArt Journals & Creative Healing: Restoring the Spirit through Self-ExpressionBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (7)
- Supersize Crochet Animals: 20 Adorable Amigurumi Sized to SnuggleVon EverandSupersize Crochet Animals: 20 Adorable Amigurumi Sized to SnuggleBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Fellowship of the Knits: Lord of the Rings: The Unofficial Knitting BookVon EverandThe Fellowship of the Knits: Lord of the Rings: The Unofficial Knitting BookBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)