Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
7.6.4 Notes
Hochgeladen von
Me, Myself and I0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
26 Ansichten1 SeiteSome real world situations use both direct proportion and indirect proportion together. Direct proportion relates the product of two or more variables directly to a third. Joint variation mixes direct and indirect proportions together.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenSome real world situations use both direct proportion and indirect proportion together. Direct proportion relates the product of two or more variables directly to a third. Joint variation mixes direct and indirect proportions together.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
26 Ansichten1 Seite7.6.4 Notes
Hochgeladen von
Me, Myself and ISome real world situations use both direct proportion and indirect proportion together. Direct proportion relates the product of two or more variables directly to a third. Joint variation mixes direct and indirect proportions together.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
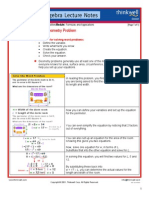
Joint and Combined Proportion
• Direct proportion is described by y = kx.
• Indirect proportion is described by y = k/x.
• Joint proportion relates the product of two or more variables directly to a third.
• Combined variation mixes direct and indirect proportions.
Some real world situations use both direct proportion and
indirect proportion together. One example is given here
relating the number of phone calls to the size of populations
and their distance apart.
Notice that all the elements for proportion are present. The
number of calls varies directly with the populations, so they
multiply with the constant. The number of calls varies
indirectly with the distance, so it divides into the constant.
This example applies the general proportion developed above
to a specific situation.
The first task is to use known information to determine the
value of k.
The numbers in the equation are “reduced” by dividing both
sides of the equation by 10,000 and by canceling 100 from
the fraction.
Then all the calculations are performed to determine k.
The final step is to use k. It is substituted into the proportion
equation with the populations and distance for the situation
in which the number of calls is desired.
Then the calculations are performed to determine how many
calls can be expected between these two cities.
www.thinkwell.com © Thinkwell Corp. 1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- 1.1 Sub Chapter NotesDokument2 Seiten1.1 Sub Chapter NotesMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Solving Dependent Systems: (Sample Problems)Dokument3 SeitenSolving Dependent Systems: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Using The Cartesian System S.P 3.1.1Dokument4 SeitenUsing The Cartesian System S.P 3.1.1Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Solving Systems With Two Equations: (Sample Problems)Dokument4 SeitenSolving Systems With Two Equations: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Solving Equations With Rational Exponents: (Sample Problems)Dokument4 SeitenSolving Equations With Rational Exponents: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Solving A System by Substitution: (Sample Problems)Dokument4 SeitenSolving A System by Substitution: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Solving Systems With Three Variables: (Sample Problems)Dokument4 SeitenSolving Systems With Three Variables: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Solving Inconsistent Systems: (Sample Problems)Dokument4 SeitenSolving Inconsistent Systems: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Scatterplots and Predictions: (Sample Problems)Dokument3 SeitenScatterplots and Predictions: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Sigh More 7.6.3 Inverse ProportionDokument2 SeitenSigh More 7.6.3 Inverse ProportionMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving A System by Elimination: (Sample Problems)Dokument4 SeitenSolving A System by Elimination: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Solving A System by Graphing S.P 5.1.2Dokument7 SeitenSolving A System by Graphing S.P 5.1.2Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Question X y InterceptsDokument1 SeiteQuestion X y InterceptsMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Questions On Mixture and Investment ProblemsDokument8 SeitenQuestions On Mixture and Investment ProblemsMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpreting Line Graphs: (Sample Problems)Dokument3 SeitenInterpreting Line Graphs: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Graphing The Solution Set of A System of Inequalities S.P 5.4.3Dokument4 SeitenGraphing The Solution Set of A System of Inequalities S.P 5.4.3Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Cost and Revenue: (Sample Problems)Dokument4 SeitenLinear Cost and Revenue: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Order of Operation (If Parentheses, Square Brackets, or Fraction Bars Are Present:)Dokument4 SeitenOrder of Operation (If Parentheses, Square Brackets, or Fraction Bars Are Present:)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Math Glossary Honors Algebra Cty Online CourseDokument6 SeitenMath Glossary Honors Algebra Cty Online CourseMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Investments: (Sample Problems)Dokument4 SeitenInvestments: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Review With SolutionsDokument13 SeitenFinal Review With SolutionsMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Graphing Linear and Nonlinear Inequalities: (Sample Problems)Dokument4 SeitenGraphing Linear and Nonlinear Inequalities: (Sample Problems)Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph PaperDokument1 SeiteGraph PaperMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Decoding Circle FormulasDokument1 SeiteDecoding Circle FormulasMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Sample ProblemsDokument101 SeitenChapter 10 Sample ProblemsMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Review Without SolutionsDokument11 SeitenFinal Review Without SolutionsMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 TestDokument6 SeitenChapter 10 TestMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Constructing A Linear Model From A Set of Data S.P 4.3.1Dokument4 SeitenConstructing A Linear Model From A Set of Data S.P 4.3.1Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Chapter 09 Test - Relations and Functions: y y X X 3Dokument3 SeitenChapter 09 Test - Relations and Functions: y y X X 3Me, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving A Quadratic Geometry Problem: Unit: Quadratic Equations and Inequalitiesmodule: Formulas and ApplicationsDokument5 SeitenSolving A Quadratic Geometry Problem: Unit: Quadratic Equations and Inequalitiesmodule: Formulas and ApplicationsMe, Myself and INoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 11 Physical Vapour DepositionDokument26 SeitenSession 11 Physical Vapour DepositionMurali DontuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus For Ntse Stage 1: Offline Test Series: MaharashtraDokument1 SeiteSyllabus For Ntse Stage 1: Offline Test Series: MaharashtraRamakant ChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Ideal GasesDokument32 SeitenProperties of Ideal GasesdvanupkleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sync 4Dokument41 SeitenSync 4Ankur SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torque On A CoilDokument24 SeitenTorque On A CoiledithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research PaperDokument18 SeitenResearch PaperRommel Dave Tejano100% (1)
- Quantitative Analysis of A Sulfate: I. RationaleDokument5 SeitenQuantitative Analysis of A Sulfate: I. RationaleBhupesh MulikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of The Concrete Based On Physical, Chemical, Technical Characteristics and ResistanceDokument21 SeitenClassification of The Concrete Based On Physical, Chemical, Technical Characteristics and ResistanceJOSE BERRU USHIÑAHUANoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 - Chapter 3 (Modeling in The Time Domain)Dokument57 SeitenLecture 3 - Chapter 3 (Modeling in The Time Domain)Jessiedee Mark GingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Env68 8 06 06 KCDokument1 SeiteEnv68 8 06 06 KCapi-367296283Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marksheet PDFDokument1 SeiteMarksheet PDFDurjoy DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHM260 Experiment 4Dokument11 SeitenCHM260 Experiment 4Muhammad Azri Haziq57% (7)
- Resistance of Concrete To Rapid Freezing and Thawing: Standard Test Method ForDokument6 SeitenResistance of Concrete To Rapid Freezing and Thawing: Standard Test Method FormaribelNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2014 (R) QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDokument28 SeitenJune 2014 (R) QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelArun MosesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Archangel Michael Becoming A World Server and Keeper of The Violet FlameDokument7 SeitenArchangel Michael Becoming A World Server and Keeper of The Violet FlameIAMINFINITELOVE100% (3)
- Home Assignment DC Motor Control1Dokument7 SeitenHome Assignment DC Motor Control1jegjegtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo General TeleH ESPDokument156 SeitenCatalogo General TeleH ESPAnonymous MbqTZHLNR9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Flow Simulation by Using A Mathematical Model Based OnDokument4 SeitenTraffic Flow Simulation by Using A Mathematical Model Based Onhkabir_juNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Systems Question Paper PDFDokument2 SeitenControl Systems Question Paper PDFsivaeinfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term PaperDokument6 SeitenTerm PaperNorshida CalibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heating Ventilation and Air ConditioningDokument68 SeitenHeating Ventilation and Air ConditioningchinnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy of Quantum Mechanics For EveryoneDokument14 SeitenPhilosophy of Quantum Mechanics For Everyonelo laNoch keine Bewertungen
- D2789Dokument7 SeitenD2789rimi7alNoch keine Bewertungen
- InterferenceDokument8 SeitenInterferencerajesh.v.v.kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hw3 Chap4 SolutionDokument13 SeitenHw3 Chap4 Solutioncoasterfan13100% (1)
- Medical Image Retrieval With Probabilistic Multi-Class Support Vector Machine Classifiers and Adaptive Similarity FusionDokument14 SeitenMedical Image Retrieval With Probabilistic Multi-Class Support Vector Machine Classifiers and Adaptive Similarity FusionDuraiPandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analyses of Car Model by CFD SoftwareDokument2 SeitenDesign and Analyses of Car Model by CFD SoftwareKrishan KamtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of Motion MCQs Sheet 1Dokument6 SeitenLaws of Motion MCQs Sheet 1eka123100% (1)
- Infer How Friction and Gravity Affect Movements of Different Objects S6Fe-Iiia-C-1Dokument17 SeitenInfer How Friction and Gravity Affect Movements of Different Objects S6Fe-Iiia-C-1Luisa Jamero Regalado100% (4)
- Asme II Part A (A 36) - 2010Dokument6 SeitenAsme II Part A (A 36) - 2010Nila GamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesVon EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2193)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceVon EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldVon EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (64)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingVon EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayVon EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (125)