Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Unit 1
Hochgeladen von
poo235Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Unit 1
Hochgeladen von
poo235Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Unit 1 1.
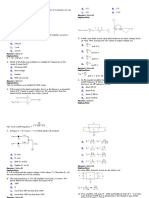
In common cathode seven segment LED display to display digit 1 the data input to segment is(Assume 0=Ground,1=+5V) A. a=1,b=0,c=0,d=0,e=0,f=0,g=0 B. a=0,b=1,c=1,d=0,e=0,f=0,g=0 C. a=1,b=0,c=0,d=1,e=1,f=1,g=1 D. a=0,b=0,c=0,d=0,e=1,f=1,g=0 Ans:- B 2. If the value of maximum power dissipation of zener diode is 1W with the zener voltage of 8V. The maximum value of zener current is A. 125mA B. 130mA C. 330mA D. 100mA Ans:- A 3. The cathode of zener diode in a voltage regulator is normally A. more positive than the anode B. more negative than the anode C. at +0.7V D. grounded Ans:- A 4. If a certain zener diode has a zener voltage of 3.6V, it operates in A. regulated breakdown B. zener breakdown C. forward conduction D. avalanche breakdown Ans:-B 5. For a certain 12V Zener diode, a 10mA change in zener current produces 0.1V change in Zener voltage. The Zener impedance is A. B. C. D. Ans:-C 6.Compared to a visible red LED, an infrared LED A. produces light with shorter wavelengths 1 Ohm 100 Ohm 10 Ohm 0.1 Ohm
B. produces light with all wavelengths C. produces only one color of light D. produces light with longer wavelengths Ans:-A 7. If you are checking a 60Hz full wave bridge rectifier and observe that the output has a 60Hz ripple A. the circuit is working properly B. there is an open diode C. the transformer secondary is shorted D. the filter capacitor is leaky Ans:-B 8. If the load resistance of capacitor filtered full wave rectifier is reduced, the ripple voltage A. increases B. decreases C. is not affected D. has a different frequency Ans:-A 9. A 60V peak full wave rectified voltage is applied to a capacitor input filter. If f=120Hz, RL=10K and C=10F, the ripple voltage is Vr=Vp/(RL*f*C) A. 0.6V B. 6mV C. 5V D. 2.88V Ans:-C 10. A certain power supply filter produces an output with a ripple of 100mV peak to peak and dc value of 20V. The ripple factor is A. 0.05 B. 0.005 C. 0.00005 D. 0.02 Ans:-B 11. When the peak output voltage is 100V, the PIV for each diode in a center tapped full wave rectifier is A. 100V
B. 200V C. 141V D. 50V Ans:- B 12When the peak output voltage is 100V, the PIV for each diode in a center tapped full wave rectifier is A. 100V B. 200V C. 141V D. 50V Ans:-B 13. When the rms output voltage of a bridge wave rectifier is 20V, the PIV across diode is 20V 40V 28.3V 56.6V Ans:-C 14. Reverse saturation current in silicon PN junction diode nearly doubles for every A. 20C rise in temperature B. 50C rise in temperature C. 60C rise in temperature D. 100C rise in temperature Ans:-D 15. GaAs, LED emits radiation in the A. UV region B. Blue color C. visible region D. infra-red region Ans:-D 16. The ripple factor of bridge rectifier is A. 0.482 B. 0.812 C. 1.11 D. 1.21 Ans:-A 17. The basic purpose of filter is to
A. minimize variations in a.c. input signal B. suppress harmonics in rectified output C. removes ripples from rectifier output D. stabilize dc output voltage Ans:-C 18. If Vm is the peak value of an applied voltage in half wave rectifier with a large capacitor across load, then PIV is A. Vm/2 B. Vm C. 2Vm D. 1.414Vm Ans:-B 19. if, by mistake ac source in a bridge rectifier is connected across the dc terminals it will burn out and hence short___________diodes A. One B. Two C. Three D. Four Ans:-D 20. if the input supply frequency is 50Hz, the output supply frequency of a bridge wave rectifier is_____________Hz A. 100 B. 75 C. 50 D. 25 Ans:-A 21. A silicon diode is in series with a 1K resistor and 5V battery. If the anode is connected to the positive battery terminal, the cathode voltage w.r.t. to the negative terminal of battery is A. 0.7V B. 0.3V C. 5.7V D. 4.3V Ans:-D 22. When the PN junction diode is forward biased A. the only current is hole current B. the only current is electron current
C. the only current is produced by majority carriers D. the current is produced by both holes and electrons Ans:-C 23. The average value of a half wave rectifier voltage with a peak value of 200V is A. 63.7V B. 127.3V C. 141V D. 0V Ans:-A 24. A voltage regulator is a circuit which A. Converts ac voltage to dc voltage B. Smoothens the ac variation in dc output voltage C. Maintain a constant dc output voltage inspite of the fluctuations in ac input voltage or load current D. None of above Ans:-C 25. A bridge wave rectifier is preferable to an ordinary two diode full wave rectifier because A. it need much smaller transformer for the same output B. it uses four diode C. its transformer does not require center tap D. All the above. Ans:-D 26. For 1N4736 Zener diode has Zz=3.5 . The datasheet gives Vzt=6.8V at Izt=37mA, What is voltage across zener terminals when the current is 50mA? A. 6.85V B. 7.85V C. 8.85V D. 9.95V Ans:-A 27. A Si PN junction has a reverse saturation current of I0=30nA at room temperature, the junction forward voltage required to produce current of 0.1mA is A. 0.42V B. 0.55V C. 0.80V D. 0.49V Ans:-A
28. If one of the diode in a Bridge wave rectifier is opens, the output is A. 0V B. one fourth of the amplitude of input voltage C. a half wave rectified voltage D. a 120Hz volage Ans:-C 29. If the load resistance of capacitor filtered full wave rectifier is reduced, the ripple voltage A. increases B. decreases C. is not affected D. has a different frequency Ans:-A 30. The peak value of the input to a half wave rectifier is 10V. the approximate peak value of output is A. 10V B. 3.18V C. 10.7V D. 9.3V Ans:-D 31. Which rectifier requires four diodes A. half wave voltage doubler B. full wave voltage doubler C. full wave bridge circuit D. voltage quadrupler Ans:-C 32. Junction breakdown of a PN junction occurs A. with forward bias B. with reverse bias C. because of manufacturing defect D. None of above Ans:-B 33. A PN junction diodes dynamic conductance is directly proportional to A. the applied voltage B. temperature
C. the current D. the thermal voltage Ans:-C 34. In a full wave rectifier, the current in each of the diodes flows for A. complete cycle of the input signal B. half cycle of the input signal C. less than half of the input signal D. None of above Ans:-A 35. the value of reverse bias resistance for an ideal diode is __________ A. infinity B. o C. one D. none of the above Ans:-A 36. device convert ac to dc is called _______________ A. transformer B. rectifier C. inverter D. none of the above Ans:-B 37. a capacitor offers ___________ reactance to dc A. infinite B. finite C. 50% D. None Ans:-A 38. semiconductor material have __________ temp. coefficient A. Positive B. Negative C. Both positive and negative D. None Ans:-B 39. A zener diode works on the principal of
A. tunneling of charge carriers across junction B. thermionic emission C. Diffusion of charge carriers across junction D. hopping of charge carriers across junction Ans:-C 40. a dot matrix is a ____________________ A. 2-dimensional array of dots B. 3-dimensional array of dots C. 4-dimensional array of dots D. 5-dimensional array of dots Ans:-A 41. The total secondary voltage of center-tapped full wave rectifier is 125Vrms. Neglecting the diode drop the rms output voltage is A. 125V B. 177V C. 100V D. 62.5V Ans:-D 42. the applied input ac power to a half wave rectifier is 100 watts. The d.c output power obtained is 40 watts. What is the rectification efficiency? A. 10% B. 20% C. 30% D. 40% Ans:-D 43. if the ac input to a half rectifier has an rms value of 400/2 volts, then diode PIV rating is A. 200V B. 400V C. 300V D. 200V Ans:-B 44. a half wave rectifier has an input voltage of 240 V r.m.s if the step down transformer has turnss ratio of 8:1, what is the load voltage? A. 27.5v B. 86.5v C. 30v
D. 42.5V Ans:-D 45. a crystal diode having internal resistance of 20 ohm is used for half wave rectification. If the applied voltage is 50sinwt and load resistance = 800 ohm, find the d.c. Output voltage? A. 15.52 V B. 10.52V C. 23.52V D. none Ans:-A 46. a power supply A delivers 10V dc with ripple of 0.5V r.m.s. While the power supply B delivers 25V dc with a ripple of 1 mV r.m.s which is better power supply? A. Supply A B. Supply B C. both same D. none Ans:-B 47. a crystal diode having internal resistance of 20 ohm is used for half wave rectification. If the applied voltage is 50sinwt and load resistance = 800 ohm,find the efficiency of rectification? A. 15.52 B. 10.52 C. 23.52 D. 39.5 Ans:-D 48. the value of reverse bias resistance for an ideal diode is __________ A. infinity B. o C. one D. none of the above Ans:-A 49. device convert ac to dc is called _______________ A. transformer B. rectifier C. inverter D. none of the above Ans:-B 50. semiconductor material have __________ temp. coefficient
A. Positive B. Negative C. Both positive and negative D. None Ans:-B 51. a dot matrix is a ____________________ A. 2-dimensional array of dots B. 3-dimensional array of dots C. 4-dimensional array of dots D. 5-dimensional array of dots Ans:-A 52. The cathode of zener diode in a voltage regulator is normally A. more positive than the anode B. more negative than the anode C. at +0.7V D. grounded Ans:-A 53. If a certain zener diode has a zener voltage of 3.6V, it operates in A. regulated breakdown B. zener breakdown C. forward conduction D. avalanche breakdown Ans:-B 54. For a certain 12V Zener diode, a 10mA change in zener current produces 0.1V change in Zener voltage. The Zener impedance is A. 1 B. 100 C. 10 D. 0.1 Ans:-C 55. The total secondary voltage of center-tapped fullwave rectifier is 125Vrms. Neglecting the diode drop the rms output voltage is A. 125V B. 177V C. 100V D. 62.5V Ans:-D
56. the applied input ac power to a half wave rectifier is 100 watts. The d.c output power obtained is 40 watts. What is the rectification efficiency? A. 10% B. 20% C. 30% D. 40% Ans:-D 57. Zener diodes are used primarily as A. Rectifier B. Votage regulator C. Oscillators D. Amplifiers Ans:-B 58. The electrical resistance of depletion layer is large because: A. it has no charge carriers B. it has large number of charge carriers C. it contains electrons as charge carriers D. it has holes as charge carriers Ans:-A 59. as temp. increases , reverse breakdown voltage A. increases B. decreases C. constant D. Both (a)&(b) Ans:-A 60. The process by which impurities are added to a pure semiconductor is A. Diffusing B. Drift C. Doping D. Mixing Ans:-C 61. The type of atomic bonding most common in semiconductor is A. Metallic B. Ionic C. Covalent
D. Chemical 62. Any semiconductor material has a valance of electrons A. 4 B. 6 C. 8 D. 12 Ans:-A 63. Semiconductor that is electrically neutral A. has no majority carriers B. has no minority carrier C. has no free charge carriers D. has equal amount of positive and negative carriers Ans:-D 64. Barrier potential for silicon diode A. B. C. D. Ans:-D 65. If an external dc voltage is applied in such a way that p- region terminal is connected to positive and n- region terminal is connected to negative, the biasing condition is called as A. Unbiased B. reverse biased C. forward biased D. none of the above Ans:-C 66. If an external dc voltage is applied in such a way that p- region terminal is connected to negative and n- region terminal is connected to positive, the biasing condition is called as A. Unbiased B. reverse biased C. forward biased D. none of the above Ans:-B 67.Due to forward bias voltage, width of Depletion region A. Enhances 0.3 V 0.4 V 0.1V 0.7 V
B. narrows C. remain same D. none of the above Ans:-B 68. Due to reverse bias voltage, width of Depletion region A. Enhances B. narrows C. remain same D. none of the above Ans:-A 69.Current of diode increases sharply w.r.to forward voltage A. Below the knee point B. at the origin C. above knee point D. none of the above Ans:-C 70. Reverse characteristic of diode is plotted in A. 1st Quadrant B. 2nd Quadrant C. 3rd Quadrant D. 4th Quadrant Ans:-C 71. Forward characteristic of diode is plotted in A. 1st Quadrant B. 2nd Quadrant C. 3rd Quadrant D. 4th Quadrant Ans:-A 72. Rectifier is used to convert A. ac to pure dc B. Unidirectional current to Bidirectional current C. dc to pure ac D. Bidirectional current to Unidirectional current Ans:-B 73. The amount of a.c. content in the output of rectifier is called A. form factor
B. peak factor C. ripple factor D. knee factor Ans:-C
74. Efficiency of half wave rectifier is A. 81.20% B. 40.60% C. 45.60% D. 82.10% Ans:-B 75. Ripple factor of half wave rectifier is A. 2.122 B. 1.112 C. 1.211 D. 2.11 Ans:-C 76. Efficiency of full wave rectifier is A. 81.20% B. 40.60% C. 45.60% D. 82.10% Ans:-A 77. Ripple factor of full wave rectifier is A. 0.122 B. 0.4 C. . 0.48 D. 0.05 Ans:-C 78. Efficiency of bridge rectifier is A. 81.20% B. 40.60% C. 45.60% D. 82.10% Ans:-A 79. Ripple factor of bridge rectifier is
A. 0.122 B. 0.4 C. 0.48 D. 0.05 Ans:-C 80. To minimize the ripple content in the circuit A. Diode circuit is used B. filter circuit is used C. bridge circuit is used D. none of the above Ans:-B 81. The zener diode as voltage regulater is generally operated in A. Forward breakdown region B. reverse breakdown region C. middle breakdown region D. all above Ans:-B 82. One of the application of zener diode is A. Amplifier B. Transmitter C. voltage regulator D. Receiver Ans:-C
83. A diode which emits light when forward biased is A. LCD B. LED C. TFT D. none of the above Ans:-B 84. Types of seven segment display are A. Common anode type B. common cathode type C. common gate type D. both A and B Ans:-D
85. Matrix display is used for A. Alphabets B. numeric characters C. information D. all above Ans:-D 86. Number of diodes used in half wave rectifier is A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Ans:- A 87. Number of diodes used in full wave rectifier with center tapped transformer is A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Ans:- B 1
88. Number of diodes used in bridge rectifier is A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Ans:- D 1
89. In an unbiased PN-junction, the junction current at equilibrium is A. due to diffusion of minority carriers only B. due to diffusion of majority carriers only C. zero, because equal but opposite carriers are crossing the junction D. zero, because no charges are crossing the junction Ans:-C 90. In a PN-junction diode, holes diffuse from the P region to the N region because A. the free electrons in the N region attract them B. they are swept across the junction by the potential difference C. there is greater concentration of holes in the P region as compared to N region D. . none of the above Ans:-C
91. In a PN-junction diode, if the junction current is zero, this means that A. the potential barrier has disappeared B. there are no carriers crossing the junction C. the number of majority carriers crossing the junction equals the number of minority carriers crossing the junction D. the number of holes diffusing from the P region equals the number of electrons diffusing from the N region Ans:-C 92. In a semiconductor diode, the barrier potential offers opposition to only A. majority carriers in both regions B. minority carriers in both regions C. free electrons in the N region D. holes in the P region Ans:-A 93. Avalanche breakdown in a semiconductor diode occurs when A. forward current exceeds a certain value B. reverse bias exceeds a certain value C. forward bias exceeds a certain value D. the potential barrier is reduced to zero Ans:-B 94. In a half-wave rectifier, the load current flows for A. the complete cycle of the input signal B. only for one half-cycle of the input signal C. less than half cycle of the input signal D. more than half cycle but less than the complete cycle of the input signal Ans:-B 95. In a full-wave rectifier, the current in each of the diodes flows for A. the complete cycle of the input signal B. half cycle of the input signal C. less than half cycle of the input signal D. zero time Ans:-B 96. In a half-wave rectifier, the peak value of the ac voltage across the secondary of the transformer is 202 V. If no filter circuit is used, the maximum dc voltage across the load will be A. 28.28 V
B. 14.14 V C. 20 V D. 9 V Ans:-D 97. If Vm is the peak voltage across the secondary of the transformer in a half-wave rectifier(without any filter circuit), then the maximum voltage on the reverse biased diode is A. B. C. D. Vm . Vm 2 Vm none of the above
98.If Vm is the peak voltage across the secondary of the transformer in a half-wave rectifier with a shunt capacitor filter circuit, then the maximum voltage on the reverse biased diode is A. Vm B. . Vm C. 2 Vm D. none of the above Ans:-A 99. In a centre-tap full-wave rectifier, Vm is the peak voltage between the centre-tap and one end of the secondary. The maximum voltage across the reverse biased diode is A. Vm B. . Vm C. 2 Vm D. none of the above Ans:-C 100. A zener diode A. has a high forward-voltage rating B. has a sharp breakdown at low reverse voltage C. is useful as an amplifier D. has a negative resistance Ans:-B 101. The light-emitting diode (LED) A. is usually made from silicon
B. used in reverse-biased condition C. gives a light output which increases with increase in temperature D. depends on the recombination of holes and electrons Ans:-D 102. A semiconductor has temperature coefficient of resistance. A. negative B. positive C. zero D. none of the above Ans:-A 103. When a pure semi-conductor is heated, its resistance. A. increases B. decreases C. Remains same D. none of the above Ans:-B 104. When a pentavalent impurity is added to a pure semi-conductor, it becomes semiconductor. A. intrinsic B. n-type C. p-type D. none of the above Ans:-B 105. A pentavalent impurity is called A. donor impurity B. acceptor impurity C. ionic impurity D. none of the above Ans:-A 106. A trivalent impurity has A. B. C. D. 3 valence electrons 5 valence electrons 6 valence electrons 4 valence electrons
Ans:-A 107. An ideal semiconductor diode has forward biased resistance of the order of . A. Ohm B. Mega Ohm C. Zero D. Infinity Ans:-C 108. An ideal semiconductor diode has reversed biased resistance of the order of . A. Ohm B. Mega Ohm C. Zero D. Infinity Ans:-D 109. The forward voltage drop across a practical silicon diode is about.. A. 2.5 V B. 3 V C. 0.7 V D. 10 V Ans:-C 110. A semiconductor diode is used as.. A. an amplifier B. a rectifier C. an oscillator D. a voltage regulator Ans:-B 111. An ideal semiconductor diode is one which behaves as a perfect when forward biased. A. conductor B. insulator C. resistance material D. none of the above Ans:-A
112. The leakage current in a semiconductor diode is due to. A. minority carriers B. majority carriers C. junction capacitance D. none of the above Ans:-A 113. If temperature of a semiconductor diode increases, leakage current A. remains the same B. decreases C. increases D. becomes zero Ans:-C 114. If the doping level of a semiconductor diode is increased, the breakdown voltage.. A. remains the same B. is decreased C. is increased D. none of the above Ans:-B 115. A semiconductor diode is a.. device. A. non-linear B. linear C. amplifying D. none of the above Ans:-A 116. The doping level in a zener diode is .. that of a semiconductor diode A. more than B. less than C. the same as D. none of the above Ans:-A 117. A pure semiconductor is often referred to as. A. extrinsic semiconductor B. intrinsic semiconductor
C. doped semiconductor D. none of the above Ans:-B 118. To forward bias a pn junction diode, A. the anode voltage must be positive with respect to its cathode B. the cathode voltage must be negative with respect to its anode C. the cathode voltage must be positive with respect to its anode D. either a or b Ans:-D 119. An ideal pn junction diode when reverse-biased, acts like.. A. closed switch B. open switch C. small resistance D. none of the above Ans:-B 120. When used as a voltage regulator, a zener diode is normally. A. forward-biased B. reverse- biased C. not biased D. none of the above Ans:-B 121. A p-type semiconductor is a semiconductor doped with.. A. trivalent impurity atoms B. impurity atoms whose electron valence is +4 C. pentavalent impurity atoms D. none of the above Ans:-A 122. To a first approximation, a forward-biased diode is treated like a A. open switch with infinite resistance B. closed switch with a voltage drop of 0V C. closed switch in series with a battery voltage of 0.7 V D. closed switch in series with a small resistance and a battery Ans:-B
123. What is the dc output voltage of an unfiltered half-wave rectifier whose peak output voltage is 9.8 V? A. 6.23 V B. 19.6 V C. 9.8 V D. 3.1 V Ans:-D 124. What is the frequency of the capacitor ripple voltage in a full-wave rectifier circuit if the frequency of mains supply voltage applied for rectification is 50 Hz? A. 60Hz B. 50 Hz C. 120 Hz D. 0 Hz Ans:-B 125. A 12 V zener diode has a 1W power rating. What is the maximum rated zener current? A. 120 mA B. 83.3 mA C. 46.1 mA D. 1A Ans:-B 126. In a loaded zener regulator, the series resistor has a current, Is of 120 mA. If the load current IL is 45 mA, how much is the zener current IZ? A. 45 mA B. 165 mA C. 75 mA D. 120 mA Ans:-C 127. The approximate voltage drop across a forward- biased LED is A. 0.3 V B. 0.7 V C. 5.6 V D. 2.0 V Ans:-D
128. The output from an unfiltered half-wave or full wave rectifier is.. A. a pulsating dc voltage B. steady dc voltage C. smooth dc voltage D. none of the above Ans:-A 129. What is the approximate dc output voltage of bridge rectifier with capacitor filter when amplitude of AC input voltage is 30V? A. 19.1 V B. 9.5 V C. 30 V D. none of the above Ans:-C 130. A half wave rectified sinusoidal waveform has a peak voltage of 12V. Its average value value of the output is given by A. 15/ V B. 20/ V C. 12/ V D. none of the above Ans:-C 131. The cut-in voltage of a Ge junction diode is nearly.. A. 0.7 V B. 0.2 V C. V D. 0.1V Ans:-D 132. The peak inverse voltage (PIV) is the maximum reverse voltage that can be applied to diode without A. burnout B. destruction C. forward breakdown D. reverse breakdown Ans:-D 133. In the forward region of its characteristic, an ideal diode appears as
A. open switch B. a high resistance C. a capacitor D. closed switch Ans:-D 134. The colour of light emitted by a LED depends on A. its forward bias B. its reverse bias C. the amount of forward current D. the type of semiconductor material used Ans:-D 135. Depletion region is a zone which contains A. Holes only B. Electrons only C. both electrons and holes D. ions only Ans:-D 136. Zener diode is mainly used for A. rectification B. amplification C. voltage stabilization D. current stabilization Ans:-C 137. If a pure Silicon crystal at a certain temperature has one million free electrons inside it, how many holes does it have at the same temperature? A. One million B. two million C. zero D. ten million Ans:-A 138. Assuming a barrier potential of 0.7 volts at an ambient temperature of 25 C, what is the barrier potential of a silicon diode when the junction temperature is 100 C? A. B. C. D. 0.7 V 0.55 V 0.9 V 1V
Ans:-B 139. Which of the following statement is true A. The width of depletion layer of a pn junction is independent of applied voltage. B. The width of depletion layer of a pn junction decreases with light dopin. C. The width of depletion layer of a pn junction increases under reverse bias. D. The width of depletion layer of a pn junction increases with heavy doping. Ans:-C 140. The merging of free electrons and holes is called A. lifetime B. covalent bonding C. recombination D. thermal energy Ans:-C 141. The voltage across diode during its non conducting period in a full wave rectifier with center tapped transformer having secondery voltage of peak value Vm , is A. Zero Volts B. Vm Volts C. 2Vm Volts D. 4Vm Volts Ans:-C 142. The no-load voltage in a full wave rectifier with Capacitor filter is A. 2Vm/ B. Vm/ C. Vm D. 3Vm/2 Ans:-A 143. How many valance electrons does a silicon atom have? A. 0 B. 8 C. 4 D. 16 Ans:-C 144. In an intrinsic semiconductor the number of holes
A. equals the number of free electrons B. is greater than the number of free electrons C. is less than the number of free electrons D. none of the above Ans:-A 145. At absolute zero temperature an intrinsic semiconductor has A. a few free electrons B. many holes C. many free electrons D. no holes or free electrons Ans:-D 146. The direction of flow of valance electrons to the right, means that holes are flowing to the A. left B. right C. either way D. none of the above Ans:-A 147. Trivalent atoms have how many valance electrons in it ? A. 1 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5 Ans:-B 148. Acceptor impurity atoms have how many valance electrons in it ? A. 3 B. 1 C. 4 D. 5 Ans:-A 149. If you wanted to produce an N type semiconductor which of these would you use? A. Acceptor atoms B. Donor atom C. Pentavalent impurity
D. Silicon Ans:- B 150. Electrons are the minority carriers in which type of semiconductor? A. extrinsic B. intrinsic C. N type D. P type Ans:-D 151. Holes are the minority carriers in which type of semiconductor? A. extrinsic B. intrinsic C. N type D. P type Ans:-B 152. Electrons are the mejority carriers in which type of semiconductor? A. extrinsic B. intrinsic C. N type D. P type Ans:-C 153. Holes are the mejority carriers in which type of semiconductor? A. extrinsic B. intrinsic C. N type D. P type Ans:-D 154. The process of adding an impurity to an intrinsic semiconductor is called A. doping B. recombination C. atomic modification D. ionization Ans:-A 155. A trivalent impurity is added to silicon to create A. germanium
B. a P type semiconductor C. an N type semiconductor D. a depletion region Ans:-B 156. A pentavalent impurity is added to silicon to create A. germanium B. a P type semiconductor C. an N type semiconductor D. a depletion region Ans:-C 157. To forward bias a diode A. an external voltage is applied that is positive at the anode and negative at the cathode B. an external voltage is applied that is negative at the anode and positive at the cathode C. an external voltage is applied that is positive at the p-region and negative at the n-region D. answers A and C Ans:-D 158. When a diode is forward-biased A. the only current is hole current B. the only current is electron current C. the only current is produced by majority carriers D. the current is produced by both holes and electrons Ans:-D 159. Although forward current is blocked in reverse bias A. there is some current due to majority carriers B. there is a very small current due to minority carriers C. there is an avalanche current D. none of the above Ans:-B 160. When a voltmeter is placed across a reverse biased diode, it will read a voltage approximately equal to A. B. C. D. the bias battery voltage 0V the diode barrier potential the total circuit voltage
Ans:-A 161. A silicon diode is connected in series a 5V battery. If the anode is connected to the positive terminal and a 1K resister is connected in between cathode and negative battery terminal. The voltage at cathode with respect to the negative battery terminal is A. 0.7V B. 0.3 V C. 5.7 V D. 4.3 V Ans:-D 162. The positive lead of an ohmmeter is connected to the anode of a diode and negative lead is connected to the cathode. The diode is A. reverse biased B. open C. forward biased D. faulty Ans:-C 163. The average value of a half wave rectified voltage with a peak value of 200V is A. 63.7V B. 127.3 V C. 141V D. 0V Ans:-A 164. When a 50 Hz sinusoidal voltage is applied to the input of a half wave rectifier, the output frequency is A. 100 Hz B. 100 Hz C. 50 Hz D. 0 Hz Ans:-C
165. The peak value of the input to a half wave rectifier is 10V. the approximate peak value of the output is A. 10 V B. 3.18 V
C. 10.7 V D. 9.3 V Ans:-A 166. The average value of full wave rectified voltage with a peak value of 75V, is A. 53 V B. 47.8 V C. 37.5 V D. 23.9 V Ans:-B 167. When a 50 Hz sinusoidal voltage is applied to the input of a full wave rectifier, the output frequency is A. 100 Hz B. 25 Hz C. 50 Hz D. 0 Hz Ans:-A 168. The total secondary voltage in a centre tapped full wave rectifier is 125 V rms. Neglecting the diode drop, the rms output voltage is A. 125V B. 177 V C. 100 V D. 62.5 V Ans:-D 169. When the peak output voltage is 100V, the PIV for each diode in a centre- tapped full wave rectifier is( neglecting the diode drop) A. 100 V B. 200 V C. 141 V D. 50V Ans:-B 170. When the rms output voltage of a bridge full-wave rectifier is 20V, the peak inverse voltage across the diodes is ( neglecting the diode drop) A. 20V
B. 40 V C. 28.3 V D. 56.6 V Ans:-C 171. In ideal conditions dc output voltage of a capacitor input filter is equal to A. the peak value of the rectified voltage B. the average value of the rectified voltage C. the rms value of the rectified voltage D. none of the above Ans:-A 172. A certain power supply filter produces an output with a ripple of 100 mV peak-to-peak and dc value of 20V. the ripple factor is A. 0.05 B. 0.005 C. 0.00005 D. 0.02 Ans:-B 173. A 60 V peak full wave rectified voltage is applied to a capacitor input filter. If f=120 Hz, RL =10KW and C= 10 F, the ripple voltage is A. 0.6 V B. 6 mV C. 5 V D. 2.88 V Ans:-C 174. If the load resistance of capacitor filtered full wave rectifier is reduced , the ripple voltage A. increases B. decreases C. not affected D. has a different frequency Ans:-B 175. If one of the diodes in a bridge full wave rectifier opens, the output is A. 0V
B. one-fourth the amplitude of the input voltage C. a half wave rectified voltage D. a 100Hz voltage Ans:-C 176. If you are checking a 50 Hz full wave bridge rectifier and observe that the output has 50Hz ripple A. the circuit is working properly B. there is an open diode C. the transformer secondary is shorted D. the filter capacitor is leaky Ans:-B 177. For a certain 12 V Zener diode, a 10 mA change in zener current produces a 0.1 V changes in Zener voltage. The Zener impedance for this current range is A. 1 B. 100 C. 10 D. 0.1 Ans:-C 178. The data sheet for a particular zener gives Vz = 10 V at I ZT = 500 mA. ZZ for these conditions is A. B. C. D. Ans:-B 179. An LED A. emits light when reverse biased B. senses light when reverse biased C. emits light when forward biased D. acts as a variable resistance Ans:-C 180. The current of a photodiode 50 20 10 unknown
A. increases with light intensity when reverse biased B. decreases with light intensity when reverse biased C. increases with light intensity when forward biased D. decreases with light intensity when forward biased Ans:-A 181. In a silicon diode the reverse current is usually A. very small B. very large C. zero D. in the breakdown region Ans:-A 182. When the reverse voltage decreases, the depletion layer A. becomes smaller B. becomes larger C. is unaffected D. breaks down Ans:-A 183. When a diode is forward biased, the recombination of free electrons and holes may produce A. heat B. light C. radiation D. all of the above Ans:-D 184. A reverse voltage of 10 V is across a diode. What is the voltage across the depletion layer? 0 V 0.7 V A. 10 V B. none of the above Ans:-C 185. If the load resistance increases in a Zener regulator, the Zener current A. B. C. D. decreases stays the same increases equals the source voltage divided by the series resistance
Ans:-C 186. If the load resistance increases in a Zener regulator, the Zener current A. decreases B. stays the same C. increases D. equals the source voltage divided by the series resistance Ans:-A 187. When the source voltage increases in a Zener regulator, which of these current remain approximately constant? A. series current B. Zener current C. load current D. total current Ans:-C 188. As compared to a silicon rectifier diode, an LED has a A. lower forward voltage and lower breakdown voltage B. lower forward voltage and higher breakdown voltage C. higher forward voltage and lower breakdown voltage D. higher forward voltage and higher breakdown voltage Ans:-C 189. To display the digit 0 in a LED seven segment Display, A. only C segment must be off B. only G segment must be off C. only F segment must be on D. all segments must be lighted Ans:-B 190. For a half wave rectifier, load current flows for . of input wave. A. 0 B. 90 C. 180 D. 360 Ans:-.C 191. For a full wave rectifier, load current flows for . of input wave.
A. 0 B. 90 C. 180 D. 360 Ans:-.D 192. What is the peak load voltage in a full wave rectifier if the secondary voltage is 20 V rms? A. 0 V B. 0.7 V C. 14.1 V D. 28.3 V Ans:-C 193. We want a peak load voltage of 40 V out of a bridge rectifier. What is the approximate rms value of secondary voltage? A. 0 V B. 14.4 V C. 28.3 V D. 56.6 V Ans:-C 194. With the same secondary voltage and filter, which of the following has the most ripple? A. half wave rectifier B. full wave rectifier C. bridge rectifier D. none of the above Ans:-A 195. With the same secondary voltage and filter, which of the following has the most ripple? A. half wave rectifier B. full wave rectifier C. bridge rectifier D. none of the above Ans:-A 196. With the same secondary voltage and filter which of the following produces the least load voltage? A. half wave rectifier B. full wave rectifier C. bridge rectifier
D. none of the above Ans:-C 197. Semiconductor material have... temp. coefficient. A. positive B. negative C. can be positive and negative D. none of the above. Ans:-B 198. As compared to a full wave rectifier using two diodes, the four diode bridge rectifier has the dominant advantage of A. higher current carrying capacity B. low peak inverse voltage requirement C. lower ripple factor D. higher efficiency Ans:-B 199. Which of the following statement(s) is true for the silicon diode? A. The p-type material of the diode is the cathode and the n-type the anode. B. The diode is reverse-biased if the potential on the n-type material is more negative than the potential on the p-type material. C. The barrier potential of the diode is 0.3V. D. The p-n junction must be forward-biased to operate properly Ans:-D 200. A p-n junction that radiates energy as light instead of as heat is called A. LED B. Photo-diode C. Photo cell D. Zener-diode Ans:-A 201. What is the peak voltage of a sine wave that measures 220 VAC rms? A. 155V B. 169V C. 311V D. 440V Ans:-C
202. Which of the following is one of the functions performed by a diode? A. filter B. amplifier C. rectifier D. inverter Ans:-C
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Von EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Polarization CurveDokument9 SeitenPolarization Curvefreeuser3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Chemistry MCQ (MSSBTE)Dokument18 SeitenBasic Chemistry MCQ (MSSBTE)Hackr Dee100% (2)
- A Selection of Micro:bit ProjectsDokument12 SeitenA Selection of Micro:bit ProjectsBuzatu GianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Integrated Circuit Questions and AnswersDokument22 SeitenLinear Integrated Circuit Questions and Answerselakya79% (24)
- Review of Pulsed Power For Efficient Hydrogen ProductionDokument16 SeitenReview of Pulsed Power For Efficient Hydrogen ProductionMiguel Arango100% (1)
- Optical Fibre Communications JOHN.M.seniORDokument575 SeitenOptical Fibre Communications JOHN.M.seniORnavneetk_865% (26)
- Analog ElectronicsDokument482 SeitenAnalog ElectronicsCristina TungpalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redox and Electrochem Review Multiple Choice Eboard AnswersDokument4 SeitenRedox and Electrochem Review Multiple Choice Eboard AnswersKhaledEl-MaghallawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. B. C. D.: Answer: Option B ExplanationDokument10 SeitenA. B. C. D.: Answer: Option B ExplanationKuya KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCH4U - Unit 4 - Version CDokument45 SeitenSCH4U - Unit 4 - Version CMr. SharpnNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Chap 6Dokument16 SeitenMCQ Chap 6Ariel Paulo G. TabangayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sybase CommandsDokument1 SeiteSybase Commandspoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- DEVO 10 User Manual PDFDokument84 SeitenDEVO 10 User Manual PDFThái ThiênNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power ElectronicsDokument16 SeitenPower ElectronicsPradeep AmmasaikuttiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectifier & Filters MCQDokument12 SeitenRectifier & Filters MCQKshitij SalaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lithium Batteries Science and TechnologyDokument766 SeitenLithium Batteries Science and Technologymarchelo_cheloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Electronics Objective QuestionDokument77 SeitenAnalog Electronics Objective QuestionYOGESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Von EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Analog ElectronicsDokument361 SeitenAnalog ElectronicsVia Marie MesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dendera Lights ReduxDokument29 SeitenDendera Lights ReduxOsiadan Khnum PtahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Electronics PDFDokument9 SeitenAnalog Electronics PDFDoan BaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Elex Sec.1Dokument26 SeitenPower Elex Sec.1Kuya KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument23 SeitenUnit 2poo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 3 With SoluDokument7 SeitenSheet 3 With SoluAmr HatemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diode ApplicationsDokument22 SeitenDiode ApplicationsAnonymous eWMnRr70qNoch keine Bewertungen
- One OhmDokument4 SeitenOne OhmMayyank GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog ElectronicsDokument10 SeitenAnalog ElectronicsRaj PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ QuestDokument17 SeitenMCQ Questshankusaran99999100% (1)
- Unitwise Objective Question With AnswerDokument19 SeitenUnitwise Objective Question With AnswerKutty ShivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Mastery 4Dokument5 SeitenElectronics Mastery 4Jonas ParreñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- WAPDA Hydel Test Electrical 2018 PDFDokument13 SeitenWAPDA Hydel Test Electrical 2018 PDFSaad Shamshad AwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compilations of Problems by Thomas FloydDokument4 SeitenCompilations of Problems by Thomas FloydmgoldiieeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elecs Circuits Semi-Final Exam SetCDokument7 SeitenElecs Circuits Semi-Final Exam SetCEruditeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage RegulatorDokument23 SeitenVoltage RegulatorJulio Gabriel AseronNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1519292487one Indian Girl by Chetan BhagatDokument32 Seiten1519292487one Indian Girl by Chetan Bhagatabhishek kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Exam MCQsDokument12 SeitenLab Exam MCQsShivansh LaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Ecp 483L1 2015Dokument4 SeitenFinal Exam Ecp 483L1 2015Ronn Albert GabucayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dsaaasdg FgdsDokument6 SeitenDsaaasdg Fgdstetimo mekutoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BXE U1 (MCQS) 31-05Dokument27 SeitenBXE U1 (MCQS) 31-05soham pawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE - Diodes QuestDokument10 SeitenECE - Diodes QuestSathyanatha PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ-EC 302 (101 Question)Dokument17 SeitenMCQ-EC 302 (101 Question)alokesh1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- D. Maintain A Constant Voltage Under Varying LoadsDokument4 SeitenD. Maintain A Constant Voltage Under Varying LoadsRonn Albert GabucayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Supply - BoylestadDokument9 SeitenPower Supply - BoylestadoddonekunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank BEEE FinalDokument183 SeitenQuestion Bank BEEE Finalgadepranjali04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Objective Questions Set 01Dokument19 SeitenObjective Questions Set 01GAURAV GUPTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank - Unit - 1 Part - A (Each Question Carries 1 Mark)Dokument8 SeitenQuestion Bank - Unit - 1 Part - A (Each Question Carries 1 Mark)Nithya SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Set ADokument10 SeitenElectronics Set ADenisse Torizo OlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Past ExamDokument11 SeitenFinal Past ExamMotasem MrwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOC Question Bank - 2017 Subject:-Basic Electronics Engineering Class: - (FE) Name of Unit: - Diode Circuits (Unit-I) (Mark1) Ans:-A) 63.7 VDokument22 SeitenMOC Question Bank - 2017 Subject:-Basic Electronics Engineering Class: - (FE) Name of Unit: - Diode Circuits (Unit-I) (Mark1) Ans:-A) 63.7 VGilt RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Solved MCQs (Set-2)Dokument5 SeitenElectronic Devices and Circuits Solved MCQs (Set-2)yashraj netke. 56.1kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Circuits-1 Exit Exam ModifiedDokument17 SeitenElectronics Circuits-1 Exit Exam ModifiedZerihun BekeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 10 ResistorDokument2 SeitenA 10 ResistorRajeev RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEC MCQ For LABDokument4 SeitenAEC MCQ For LABManas Ranjan MantriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Synthesis Model ExitDokument10 SeitenNetwork Synthesis Model ExitERMIAS AmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Sample Problems 09Dokument6 SeitenElectronics Sample Problems 09Genesis PinedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.determine The Value of The Voltage Measured by The Meter: SSC JE Electrical Important MCQ Part 30Dokument10 Seiten1.determine The Value of The Voltage Measured by The Meter: SSC JE Electrical Important MCQ Part 30Pankaj KaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ice Elecs 8 QueDokument4 SeitenIce Elecs 8 QueJojo TakatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam ECP483L1 1415 Set A ANSWERDokument4 SeitenFinal Exam ECP483L1 1415 Set A ANSWERRonn Albert GabucayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test and AnswerDokument9 SeitenTest and AnswerKristiqn KolevNoch keine Bewertungen
- False: True True True TrueDokument2 SeitenFalse: True True True TrueSuubi brianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malvino PrintDokument6 SeitenMalvino Printmary_nailynNoch keine Bewertungen
- NA Unit 1 - MCQ - 1515601861294Dokument50 SeitenNA Unit 1 - MCQ - 1515601861294पंकज काळेNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE 50 MCQsDokument9 SeitenPE 50 MCQsSudhakar MarojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.A. Gate Question 28Dokument9 SeitenS.A. Gate Question 28premalathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ObjectiveDokument20 SeitenObjectiveAnonymous sBvtnZQNoch keine Bewertungen
- HomeworkAssignment03 SolutionDokument14 SeitenHomeworkAssignment03 Solutionmk07 natNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 ProblemsDokument3 Seiten10 ProblemsGlennNacarGanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malvino MCQ in Power AmplifiersDokument7 SeitenMalvino MCQ in Power Amplifiersআশিক পালোয়ানNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boost Converter DesignDokument10 SeitenBoost Converter Designpoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tech Feast 2014-2015Dokument4 SeitenTech Feast 2014-2015poo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Statement Syllogism Questions: Question Statement: Question StatementDokument48 Seiten2-Statement Syllogism Questions: Question Statement: Question Statementpoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of Frequency Reconfigurable Microstrip Patch Antenna For WLAN ApplicationsDokument6 SeitenDesign and Analysis of Frequency Reconfigurable Microstrip Patch Antenna For WLAN Applicationspoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ec Paper - I:: Ies 2010 Objective PaperanswersDokument6 SeitenEc Paper - I:: Ies 2010 Objective Paperanswerspoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial EconomicsDokument1 SeiteManagerial Economicspoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spartan3 Tutorial PDFDokument30 SeitenSpartan3 Tutorial PDFHossein Mamaghanian100% (4)
- Universal College of Engineering & Research, Pune: Class Time Table - Te E&Tc (Sem-Ii)Dokument4 SeitenUniversal College of Engineering & Research, Pune: Class Time Table - Te E&Tc (Sem-Ii)poo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- SCR Circuit OperationDokument20 SeitenSCR Circuit Operationpoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pune UniversitycollegesDokument10 SeitenPune Universitycollegespoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Paper1 Pooja LambaDokument10 SeitenPaper1 Pooja Lambapoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- VK's MGT MemoirsDokument5 SeitenVK's MGT Memoirspoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)Dokument32 SeitenBasic Concepts of Computer (1.25 MB)poo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Six Letter Password Security SystemDokument46 SeitenSix Letter Password Security Systempoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- BCH AlgorithmDokument5 SeitenBCH Algorithmpoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Universal College of Engineering & Research, Pune: Class Time Table - Te E&Tc (Sem-V)Dokument24 SeitenUniversal College of Engineering & Research, Pune: Class Time Table - Te E&Tc (Sem-V)poo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument39 SeitenUnit 1poo2350% (1)
- Unit 6Dokument12 SeitenUnit 6poo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ - First YearDokument1 SeiteMCQ - First Yearpoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- Six Letter Password Security SystemDokument46 SeitenSix Letter Password Security Systempoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- VHDL Mem - Type Dual PortDokument7 SeitenVHDL Mem - Type Dual Portpoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- All Cats Are DogsDokument42 SeitenAll Cats Are Dogspoo235Noch keine Bewertungen
- SAIL Electronics and Electrical Engineering Objective Type Questions With Answers For PracticeDokument49 SeitenSAIL Electronics and Electrical Engineering Objective Type Questions With Answers For Practicepoo235100% (1)
- FILELISTDokument7 SeitenFILELISTjamesearl_cubillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosion Lecture KineticsDokument43 SeitenCorrosion Lecture KineticsBaso Rahmat TarmiziNoch keine Bewertungen
- E16 Determination of The Specific Charge of Electron Using MagnetronDokument2 SeitenE16 Determination of The Specific Charge of Electron Using MagnetronAnik ManojNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrochemistry - by WWW - LearnEngineering.inDokument24 SeitenElectrochemistry - by WWW - LearnEngineering.inhi sirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Energy Materials - 2020 - Hirsh - Sodium Ion Batteries Paving The Way For Grid Energy StorageDokument8 SeitenAdvanced Energy Materials - 2020 - Hirsh - Sodium Ion Batteries Paving The Way For Grid Energy StorageSantiago EdingerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Dokument12 SeitenCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42ZubairHassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - Electron Charge-To-Mass Ratio.v1.4-10-06Dokument12 Seiten10 - Electron Charge-To-Mass Ratio.v1.4-10-06koolfreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary of Metallurgical TermsDokument226 SeitenGlossary of Metallurgical Termsanon_558662375Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solid-State Li-Ion Batteries Using Fast, Stable, Glassy Nanocomposite Electrolytes For Good Safety and Long Cycle-LifeDokument11 SeitenSolid-State Li-Ion Batteries Using Fast, Stable, Glassy Nanocomposite Electrolytes For Good Safety and Long Cycle-LifeMDRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brady Solution Chapter 20Dokument31 SeitenBrady Solution Chapter 20NurrahmisrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode - Ray - Oscilloscop First Year 1Dokument7 SeitenCathode - Ray - Oscilloscop First Year 1Tangent ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics of Fuel Cells: 2.2.1 Electrochemical AspectsDokument13 SeitenThermodynamics of Fuel Cells: 2.2.1 Electrochemical AspectsKemas FarosiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathelco ICCP For ShipDokument12 SeitenCathelco ICCP For ShipLê Anh ChiếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steffel Materials CatalogueDokument150 SeitenSteffel Materials CatalogueAlvaro AguinagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrochromism A Fascinating Branch of Electrochemistry PDFDokument18 SeitenElectrochromism A Fascinating Branch of Electrochemistry PDFOnime No IchinoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of The Slurry Mixing Process On The Structural Properties of The Anode and The Resulting Fast-Charging Performance of The Lithium-Ion Battery CellDokument14 SeitenEffect of The Slurry Mixing Process On The Structural Properties of The Anode and The Resulting Fast-Charging Performance of The Lithium-Ion Battery CellTeddy KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnodicProtectionofDigestersTAPPI2003 PDFDokument26 SeitenAnodicProtectionofDigestersTAPPI2003 PDFabdur sufaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D5462 PDFDokument6 SeitenD5462 PDFZamir Danilo Morera ForeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolytic ProcessesDokument9 SeitenElectrolytic ProcessesIshitha ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolarographyDokument5 SeitenPolarographyPATHAN SOHAILNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008-02 - ICAF Installation Manual CWC 1.0 EngDokument30 Seiten2008-02 - ICAF Installation Manual CWC 1.0 EnggennaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- CK138 Single-Door Controller User Manual (Ver 2.5) : Product DescriptionDokument2 SeitenCK138 Single-Door Controller User Manual (Ver 2.5) : Product DescriptionChathurike NelugollaNoch keine Bewertungen