Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
DIP Meter Log (Well Logging)
Hochgeladen von
Aleena SaeedOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DIP Meter Log (Well Logging)
Hochgeladen von
Aleena SaeedCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dip meter Log: Dip meter log provide a continuous record of formation dip and direction of dip.
Uses of dip meter log: Generally--------Dip of the formations In Structural Geology Structural dip Unconformities Faults, Folds Dip correlation with seismic section dips
In Sedimentary Geology Facies Information Paleocurrent direction Bed orientation Working: Dip meter toll measures dip by comparing the micro resistivities curves from opposing sides of borehole wall. 4 or 6 micro resistivities pads are used to measure resistivity. Limited to water based muds and blade scratchers are used to attach with well walls. For oil based mud specially designed oil based dip meter tool used. HDT---High resolution dip meter tool (older technology used in normal well conditions) SHDT--- Staratigraphic high resolution dip meter tool (2.5mm samples and gives high resolution) OBDT--- Oil based dip meter tool (when there is oil based mud in well) Processing: Data processing is an important step in dip meter log interpretation. processing is required to find dip direction and dip amount from micro resistivity curves. There are 2 principle methods used for data processing Fixed interval correlation(Dip is produced by selection of entire selected interval and used frequently) Feature recognition (By correlation of features, can involve human error)
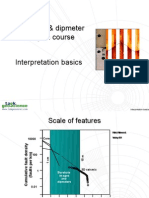
Processed log presentation: Tadpole is standard presentation for processed dip meter log. Depth is plotted on vertical scale and both dip parameters(Dip amount and dip direction) plotted along horizontal scale. 0-90 Dip is plotted as a large black dot (Tadpole head) The azimuth is given by a small straight line plotted from center of dot. Dip=10 Azimuth=SE 130 Good quality data= Lower quality data= Noise dips produced due to Borehole quality Rotation of toll Washouts/mud cake(due to Increase/decrease factors of well diameter) Processing quality
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reservoir Geomechanics MOOC HW1 2020Dokument2 SeitenReservoir Geomechanics MOOC HW1 2020Delano100% (1)
- Mesa Expert Training Manual Expert PDFDokument95 SeitenMesa Expert Training Manual Expert PDFBambang Trenggono MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 DipmeterDokument175 Seiten8 DipmeterStart BackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Open Hole LoggingDokument277 SeitenIntroduction To Open Hole LoggingKean PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formation Evaluation: Dr. Adel M. Al-MataryDokument22 SeitenFormation Evaluation: Dr. Adel M. Al-Mataryكهلان البريهيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Porosity ModelingDokument5 SeitenPorosity Modelinganima1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Elements and Importance of Site InvestigationDokument12 SeitenThe Elements and Importance of Site InvestigationArun KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lithologic Analysis of Rock VolumeDokument9 SeitenLithologic Analysis of Rock VolumeKaiysse YoukéNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRIGGERFISH Tech Overview March 2013Dokument27 SeitenTRIGGERFISH Tech Overview March 2013Ndomadu100% (1)
- Din 48204Dokument3 SeitenDin 48204Thanh Dang100% (4)
- BS en 50216-6 2002Dokument18 SeitenBS en 50216-6 2002Jeff Anderson Collins100% (3)
- 3D Seismic Survey Design - KhalidDokument68 Seiten3D Seismic Survey Design - KhalidUmairKhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Techlog 3D Petrophysics For High and Low Angle Well EvaluationDokument19 SeitenTechlog 3D Petrophysics For High and Low Angle Well EvaluationSamir DharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistivity 1 PDFDokument43 SeitenResistivity 1 PDFAnonymous lbhVwnGzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthetic Trace: L 7 - Well-Seismic 1 Courtesy of ExxonmobilDokument19 SeitenSynthetic Trace: L 7 - Well-Seismic 1 Courtesy of ExxonmobilAna Cristina Coelho100% (1)
- 3d Far Field Middle East CsDokument2 Seiten3d Far Field Middle East CslakhanmukhtiarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D FinalDokument82 Seiten3D Finalkhan_69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ecoscope: Multifunction LWD ServiceDokument3 SeitenEcoscope: Multifunction LWD ServiceAli ChouayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Interpretation BasicsDokument16 Seiten2 - Interpretation BasicsMohammed Al SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dip LogDokument12 SeitenDip LogSoma Sankar100% (1)
- Seismic SurveyDokument7 SeitenSeismic SurveyShadab Hashmi wihcjPkRcrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vp/Vs Ratio and Poisson's Ratioo: Porosity - Lithology Case HistoryDokument5 SeitenVp/Vs Ratio and Poisson's Ratioo: Porosity - Lithology Case HistoryHcene Hcen100% (1)
- Resistivity LoggingDokument33 SeitenResistivity LoggingUmarDhillonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Science: Majeed Abimbola, Faisal Khan, Nima Khakzad, Stephen ButtDokument12 SeitenSafety Science: Majeed Abimbola, Faisal Khan, Nima Khakzad, Stephen ButtMomha Jean-AlainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Band Limited Impedance Inversion of Blackfoot Field, Alberta, CanadaDokument6 SeitenBand Limited Impedance Inversion of Blackfoot Field, Alberta, CanadaSatya PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Import Sidetracks To PetrelDokument6 SeitenImport Sidetracks To PetrelMuhamad Afiq RosnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 - Initial Data Analysis - 2010Dokument9 Seiten04 - Initial Data Analysis - 2010Marcelo Saez100% (1)
- Summary Report PertaminaPBMSJ BTJ-206 HendrikSahertian 4August-13August2013Dokument17 SeitenSummary Report PertaminaPBMSJ BTJ-206 HendrikSahertian 4August-13August2013Menly TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theleadingedge201306 DL PDFDokument136 SeitenTheleadingedge201306 DL PDFKristyo AdhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ion To 3D Seismic Survey Design ProblemDokument25 SeitenIon To 3D Seismic Survey Design ProblemParth SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- KheremDokument46 SeitenKherembhupender100% (1)
- 2d3d Land Data Acquisition1Dokument53 Seiten2d3d Land Data Acquisition1Pallav KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic Data Processing and InterpretationDokument15 SeitenSeismic Data Processing and InterpretationmustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dipmeter Image Repair Notes ADokument30 SeitenDipmeter Image Repair Notes ARosa K Chang HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Resistivity Tomography Using Wenner BDokument7 SeitenElectrical Resistivity Tomography Using Wenner BKamel HebbacheNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpendTect User Documentation Version 4Dokument29 SeitenOpendTect User Documentation Version 4Olaoluwa OlatonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Techlog-Technical Brochure 2007Dokument20 SeitenTechlog-Technical Brochure 2007ari_si75% (4)
- Predicting Pore Pressure and Porosity From VSP DataDokument4 SeitenPredicting Pore Pressure and Porosity From VSP DataAna Karen Patraca MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dipole Sonic Imager LOGDokument7 SeitenDipole Sonic Imager LOGdtriamindo100% (1)
- Matlab - Spectral Decomposition of Correlation MatrixDokument1 SeiteMatlab - Spectral Decomposition of Correlation Matrixapi-378442975% (4)
- Lab 4-Measurement of Plastic Viscosity of Different Mud Samples by Viscometer.Dokument20 SeitenLab 4-Measurement of Plastic Viscosity of Different Mud Samples by Viscometer.Sunny BbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petrophysics Logging ToolsDokument61 SeitenPetrophysics Logging ToolsMuhammad Ramdhan QodriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airgun ArraysDokument21 SeitenAirgun ArraysGianni PavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Shots On A 3d Seismic SurveyDokument3 SeitenMoving Shots On A 3d Seismic SurveyRodrigo Silva100% (1)
- Useful Formulas in Seismic Survey DesignDokument2 SeitenUseful Formulas in Seismic Survey DesignDanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout Processing 1Dokument39 SeitenHandout Processing 1MordekhaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENM200 Reservoir Rock Properties - NotesDokument14 SeitenENM200 Reservoir Rock Properties - NotescssdNoch keine Bewertungen
- PetroMod2013 Manual CompletoDokument23 SeitenPetroMod2013 Manual CompletoDaniel PreciadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic ReflectionDokument26 SeitenSeismic ReflectionJeevan BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- KINGDOM Glossary: NumericsDokument39 SeitenKINGDOM Glossary: NumericsSarfraz KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic Interpretation Report GuidelinesDokument3 SeitenSeismic Interpretation Report Guidelinesn_shekar100% (2)
- Estimation of Oil & Gas: by DR Anil KumarDokument40 SeitenEstimation of Oil & Gas: by DR Anil KumarHemant Srivastava100% (1)
- m41993 OMAF Overview 20171210 d06Dokument105 Seitenm41993 OMAF Overview 20171210 d06Kirill PokutnyyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petromod 1D WorkflowDokument9 SeitenPetromod 1D WorkflowIsmail A. IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module - Well Planning: Horizontal Well Options Adding Many Vertical WellsDokument7 SeitenModule - Well Planning: Horizontal Well Options Adding Many Vertical WellsTarek HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolytic Tiltmeter Basics: Jewell Electrolytic Sensor Technical NoteDokument2 SeitenElectrolytic Tiltmeter Basics: Jewell Electrolytic Sensor Technical NoteSamudera Dandi ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 6 Upscaling PDFDokument17 SeitenPart 6 Upscaling PDFTrần Hoàng ChươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigating Slope Failures Using Electrical Resistivity Case StudiesDokument10 SeitenInvestigating Slope Failures Using Electrical Resistivity Case StudiesZamzuri ZaidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 3Dokument73 SeitenDay 3tonystark8052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling of Resistivity and Acoustic Borehole Logging Measurements Using Finite Element MethodsVon EverandModeling of Resistivity and Acoustic Borehole Logging Measurements Using Finite Element MethodsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pushpalata Boro - MWD ReportDokument30 SeitenPushpalata Boro - MWD ReportHamid MasoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Scanning of River BedDokument18 Seiten3D Scanning of River Bedindra kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Max9924 Max9927Dokument23 SeitenMax9924 Max9927someone elseNoch keine Bewertungen
- IJISRT23JUL645Dokument11 SeitenIJISRT23JUL645International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EceDokument75 SeitenEcevignesh16vlsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oss Kpi SummaryDokument7 SeitenOss Kpi SummaryMohd FaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Introduction: 1.1 What Is Manufacturing (MFG) ?Dokument19 SeitenGeneral Introduction: 1.1 What Is Manufacturing (MFG) ?Mohammed AbushammalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre K Kindergarten Alphabet Letter TracingDokument28 SeitenPre K Kindergarten Alphabet Letter TracingNeha RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blackstone The Dash Model #1610 Owner's ManualDokument53 SeitenBlackstone The Dash Model #1610 Owner's ManualSydney Adam SteeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- B205A TMA Project Spring 2021 - UpdatedDokument6 SeitenB205A TMA Project Spring 2021 - UpdatedIoan 23Noch keine Bewertungen
- BS EN 50483-6-2009 EnglishDokument27 SeitenBS EN 50483-6-2009 EnglishДмитро Денис100% (2)
- Ebook Computer Forensics Principles and Practices 1St Edition Volonino Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument29 SeitenEbook Computer Forensics Principles and Practices 1St Edition Volonino Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmundifycoucheefnhgl100% (10)
- " Suratgarh Super Thermal Power Station": Submitted ToDokument58 Seiten" Suratgarh Super Thermal Power Station": Submitted ToSahuManishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clevite Bearing Book EB-40-07Dokument104 SeitenClevite Bearing Book EB-40-07lowelowelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tournament Rules and MechanicsDokument2 SeitenTournament Rules and MechanicsMarkAllenPascualNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mathematics SS3 2ND Term SchemeDokument2 SeitenGeneral Mathematics SS3 2ND Term Schemesam kaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- 103-Article Text-514-1-10-20190329Dokument11 Seiten103-Article Text-514-1-10-20190329Elok KurniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Ways To Make A USB BootableDokument6 Seiten5 Ways To Make A USB Bootableconnect.rohit85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Birth Trauma and Post Traumatic Stress Disorder The Importance of Risk and ResilienceDokument5 SeitenBirth Trauma and Post Traumatic Stress Disorder The Importance of Risk and ResilienceMsRockPhantomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arte PoveraDokument13 SeitenArte PoveraSohini MaitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument15 SeitenCase StudyChaitali moreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disbursement VoucherDokument7 SeitenDisbursement VoucherDan MarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schematic Circuits: Section C - ElectricsDokument1 SeiteSchematic Circuits: Section C - ElectricsIonut GrozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Cheat Sheet-1Dokument8 SeitenPython Cheat Sheet-1RevathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BypassGoldManual PDFDokument6 SeitenBypassGoldManual PDFBrad FrancNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes - Introduction To Big DataDokument8 SeitenLecture Notes - Introduction To Big Datasakshi kureley0% (1)
- 3D Tetris Cake Evening 2Dokument13 Seiten3D Tetris Cake Evening 2Subham KarmakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bhagwan Mahavir College of Architecture: Topic: Lacing, Batteneing, BracingDokument14 SeitenBhagwan Mahavir College of Architecture: Topic: Lacing, Batteneing, BracingJai MenDparaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIDTERM Exam - Programming 2 - 2SEM 2020Dokument3 SeitenMIDTERM Exam - Programming 2 - 2SEM 2020Bab bidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOM - Rampa Hidráulica - Blue GiantDokument32 SeitenIOM - Rampa Hidráulica - Blue GiantPATRICIA HERNANDEZNoch keine Bewertungen