Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Acer
Hochgeladen von
Clark InovejasOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Acer
Hochgeladen von
Clark InovejasCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Terms
Definitions
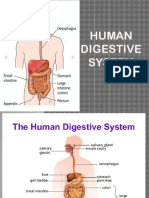
salivary glands saliva
in the oral cavity produce saliva; very thick watery and slick fluid allows food to be swallowed with less danger of choking chewed food that is ready to swallow digestive enzyme that begins the digestion of carbohydrates parotid, submandibular and sublingual
bolus amylase three pairs of salivary glands parotid glands submandibular and sublingual liver
in front of the ears in the floor of the mouth
large organ that processed nutrients absorbed by the intestins, detoxifying hamrful substances in the body and produce bile breaks up large fat globules into smaller droplets; produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder the process of bile breaking down fat globules making them easier to digest in the watery environment inside the intestines small organ located just under the liver; releases bile into the duodenum leads from the liver to the common bile duct; transports bile leads from the gallbladder to the common bile duct, carries bile carries bile to the duodenum where it is able to emulsify the fat in chyme
bile
emulsification
gallbladder
hepatic duct cystic duct common bile duct
pancreas
connected to the duodenum; produces two imporant secretions for digestion; also an endocrine gland that produces the hormones insulin and glucagon, which play a role in regulating the level of glucose in the blood neutralize acidic chyme that has just left the stomach chemically digest carbohydrates, fats and proteins
buffers pancreatic enzymes two secretions of the pancreas
buffers and pancreatic enzymes
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Leaky Gut Syndrome Stop!: A Complete Guide To Leaky Gut Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & A Holistic System To Eliminate LGS Naturally & PermanentlyVon EverandLeaky Gut Syndrome Stop!: A Complete Guide To Leaky Gut Syndrome Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & A Holistic System To Eliminate LGS Naturally & PermanentlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System and Parts Function: 12STEM-1 General Biology 2Dokument4 SeitenDigestive System and Parts Function: 12STEM-1 General Biology 2hazel lagaticNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On The Digestive SystemDokument48 SeitenPresentation On The Digestive SystemOsman Saidu Sesay0% (1)
- Digestive System: Is It Outdated? Or...... Adapted?Dokument9 SeitenDigestive System: Is It Outdated? Or...... Adapted?Monojit DharNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Digestive SystemDokument5 SeitenThe Digestive Systemvidur_talrejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food DigestionDokument36 SeitenFood Digestionthiruchelvam1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System ScriptDokument4 SeitenDigestive System ScriptNEPERESM TALCEY BORCESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument45 SeitenPresentation 1Ashish UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Digestive SystemDokument5 SeitenThe Human Digestive SystemnitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive SystemDokument35 SeitenDigestive SystemNYL BRIAN BUISERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition: What Is Malnutrition?Dokument43 SeitenNutrition: What Is Malnutrition?Starpril_88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition in Human BeingsDokument8 SeitenNutrition in Human Beingsparashakthi PRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adi DigestiveSystemStructuresDokument4 SeitenAdi DigestiveSystemStructuresnkpatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion Is The Breakdown of Large, Insoluble Food Molecules Into Small, Water-Soluble Molecules Using Mechanical and Chemical ProcessesDokument14 SeitenDigestion Is The Breakdown of Large, Insoluble Food Molecules Into Small, Water-Soluble Molecules Using Mechanical and Chemical ProcessesMuhammad AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Really Final Discussion of Group 6Dokument16 SeitenReally Final Discussion of Group 6Nicole Hershley RequieroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Processes (Digestion)Dokument1 SeiteLife Processes (Digestion)Farid AhemadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY EditedDokument3 SeitenANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY EditedBSN 2 - Sasis, Rusmaryte C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Digestive System: Prepares Food For Use by All Body CellsDokument44 SeitenThe Digestive System: Prepares Food For Use by All Body CellstryhtrtgerfgNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGY (Second Term)Dokument55 SeitenBIOLOGY (Second Term)carlaplana2008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Human Digestion PresentationDokument35 SeitenHuman Digestion PresentationYamyang Galay-BañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System ReviewDokument2 SeitenDigestive System ReviewSherriena LeangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion and AbsorptionDokument4 SeitenDigestion and AbsorptionMin NimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alimentary System (Gi Tract)Dokument6 SeitenAlimentary System (Gi Tract)Victoria JoubertNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Ăm'ə-Lāce ) or Ptyalin (Tī'ə-Lĭn) Is The Digestive Enzyme Found in Saliva. ItDokument5 Seiten(Ăm'ə-Lāce ) or Ptyalin (Tī'ə-Lĭn) Is The Digestive Enzyme Found in Saliva. ItKyle Keen TaerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaDokument37 SeitenUman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaBishal Khaidem0% (1)
- Digestive SystemDokument80 SeitenDigestive SystemElla Shaine BeceraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology NotesDokument11 SeitenBiology NotesKarina Gonzalez100% (1)
- Essay # 4. DigeDokument9 SeitenEssay # 4. DigeAbdul Karim BurkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 35.1 - The Digestive SystemDokument16 Seiten35.1 - The Digestive SystemMostafa Galal El Din100% (1)
- DigestiveDokument74 SeitenDigestiveLeah Magbago RemolisanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Digestive SystemDokument48 SeitenHuman Digestive SystemSharifah NurainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition in Human Beings Class 6Dokument5 SeitenNutrition in Human Beings Class 6Sarada KasyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System NewDokument49 SeitenDigestive System NewPHAMAE JOY MEMBREVENoch keine Bewertungen
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: Anam FarzandDokument25 SeitenUman Digestive System Structure and Function: Anam FarzandTahir AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive-System-2 Grade 8Dokument39 SeitenDigestive-System-2 Grade 8Joshua Muego100% (2)
- Digestion and AbsorptionDokument11 SeitenDigestion and Absorption2023541012tnauNoch keine Bewertungen
- DigestiveDokument26 SeitenDigestiveshairaorquetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q4 Week 3 Human Digestive System - PPTX 4thDokument47 SeitenQ4 Week 3 Human Digestive System - PPTX 4thdenveralbarico143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System - MCAT ReviewDokument5 SeitenDigestive System - MCAT ReviewMano JayaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGY ReviewerDokument8 SeitenBIOLOGY ReviewerandreamrieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Chapter 6 (6.4)Dokument34 SeitenBiology Chapter 6 (6.4)Shirmei WangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive SystemDokument2 SeitenDigestive SystemDrexel DalaygonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Digestive SystemDokument39 SeitenHuman Digestive SystemSha KhinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Diet & NUTRITIONDokument30 SeitenModule 1 Diet & NUTRITIONarzooNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 DigestionDokument49 Seiten9 DigestionUsama MumtazNoch keine Bewertungen
- LN Digestive SystemDokument6 SeitenLN Digestive SystemCasey Dkaye MorrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion and Absorption of Nutrients: Dr. Sooad Al-Daihan Biochemistry DepartmentDokument11 SeitenDigestion and Absorption of Nutrients: Dr. Sooad Al-Daihan Biochemistry DepartmentNyasha RumhezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MouthDokument1 SeiteMouthJean CabingatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Digestive System ProcessDokument7 SeitenHuman Digestive System ProcessdatoysybilrussmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion: The Digestive SystemDokument66 SeitenDigestion: The Digestive SystemTonique Gordon100% (1)
- Digestive System HandoutDokument7 SeitenDigestive System Handouttheodore_estradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Nutrition: The MouthDokument7 SeitenAnimal Nutrition: The Moutheugene_970418755Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System and Process of DigestionDokument4 SeitenDigestive System and Process of DigestionSid QNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Digestive SystemDokument11 SeitenHuman Digestive SystemSyeda NafeezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Digestive SystemDokument11 SeitenHuman Digestive SystemSyeda NafeezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DigestiveDokument17 SeitenDigestiveDayan EsparteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- COOKERY - Module 1Dokument117 SeitenCOOKERY - Module 1Clark Inovejas50% (4)
- Seno Vs MangubatDokument5 SeitenSeno Vs MangubatClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Sickle Is A HandDokument11 SeitenA Sickle Is A HandClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence Case DigestDokument48 SeitenEvidence Case DigestClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hanopol Cannot Have A Better Right Than Appellee Pilapil Who, According To The Trial Court, "Was Not Shown To Be A Purchaser in Bad Faith"Dokument2 SeitenHanopol Cannot Have A Better Right Than Appellee Pilapil Who, According To The Trial Court, "Was Not Shown To Be A Purchaser in Bad Faith"Clark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seno Vs MangubatDokument5 SeitenSeno Vs MangubatClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Success Story As A TeacherDokument21 SeitenA Success Story As A TeacherClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing TheoryDokument1 SeiteNursing TheoryClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- QUALITY POLICY: The Mariano Marcos Memorial Hospital & Medical Center Shall Ensure The Highest Standard ofDokument1 SeiteQUALITY POLICY: The Mariano Marcos Memorial Hospital & Medical Center Shall Ensure The Highest Standard ofClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States Clearing House: Mercantile (Or Commercial) Agencies, Is The Name Given inDokument1 SeiteUnited States Clearing House: Mercantile (Or Commercial) Agencies, Is The Name Given inClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing TheoryDokument1 SeiteNursing TheoryClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Great Wall of ChinaDokument1 SeiteGreat Wall of ChinaClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuguid Vs Nuguid 1Dokument2 SeitenNuguid Vs Nuguid 1Clark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clemente Reyes and Anselmo NadresDokument2 SeitenClemente Reyes and Anselmo NadresClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfield PhilippinesDokument1 SeiteTransfield PhilippinesClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPR Case 1 Soriano vs. DizonDokument7 SeitenCPR Case 1 Soriano vs. DizonClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strike: Dextral SinistralDokument1 SeiteStrike: Dextral SinistralClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clemente Reyes and Anselmo NadresDokument2 SeitenClemente Reyes and Anselmo NadresClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 Bar Exams ResultsDokument22 Seiten2008 Bar Exams ResultsClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adoption Table Form 2Dokument4 SeitenAdoption Table Form 2Clark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 Bar Exams ResultsDokument22 Seiten2008 Bar Exams ResultsClark InovejasNoch keine Bewertungen