Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
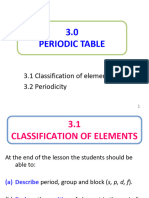
Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties PDF
Hochgeladen von
Vishal DaniOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties PDF
Hochgeladen von
Vishal DaniCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Mendeleevs periodic law:The properties of the elements are the periodic functions
of their atomic weights.
Modern periodic law:The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.
Modern periodic table: Horizontal rows: periods (7 periods) Vertical columns: groups (18 groups)
s-block elements: Group 1 (alkali metals) and 2 elements (alkaline earth metals) having ns1 and ns2 outermost electronic configuration respectively p-block elements: Elements belonging to Group 13 to 18; the outermost electronic configuration varies from ns2 np1 to ns2 np6 Elements of Group 16, 17, and 18 are called chalcogens, halogens, and noble gases respectively. d -block elements: Elements belonging to Group 3 to 12 The general electronic configuration is (n1) d 110ns02 .They are also called transition metals. f -block elements (Inner-transition metals): Lanthanoids and actinoids, with outermost electronic configuration (n-2) f 114(n1) d 01ns2 Metals, non-metals, and metalloids: 1. Metals are present on the left side of the periodic table and non-metals are located at the top right hand side of the periodic table. 2. The elements that exhibit properties of both metals and non-metals are called metalloids or semimetals.
Periodic trends:
Chemical reactivity: Oxides formed by the elements on the left of periodic table are basic and the oxides formed by the elements on the right are acidic in nature. The oxides of elements in the centre are amphoteric or neutral.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Name: Hazem Emam Ali Section: 2 I.D: 13P1082 Building Engineering Materials AssignmentDokument12 SeitenName: Hazem Emam Ali Section: 2 I.D: 13P1082 Building Engineering Materials AssignmentDolzMaGiCz100% (1)
- Assignment ChemistryDokument12 SeitenAssignment ChemistrySayyad Dawar100% (1)
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDokument2 SeitenClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesNirvana Adithya Visiobibliophobiatic GuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDokument2 SeitenClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Propertiesprince7890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1: Periodic PropertiesDokument8 SeitenUnit 1: Periodic PropertiesSkyblueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify The Demarcation of The Periodic TableDokument4 SeitenIdentify The Demarcation of The Periodic TableRana Irfan100% (1)
- Chemistry PPTNESDokument20 SeitenChemistry PPTNESTITLI SAHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic TableDokument8 SeitenPeriodic Tablechaitramallu.mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemis 8Dokument43 SeitenChemis 8hadassahhadidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Periodic TableDokument18 Seiten3.1 Periodic TablehaasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Division of Elements Into S, P, D and F BlocksDokument9 SeitenDivision of Elements Into S, P, D and F BlocksDASHRATH SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements PPT 1Dokument12 SeitenClassification of Elements PPT 1Krishiv RajkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Classification of Elements Xerox 2020Dokument7 SeitenPeriodic Classification of Elements Xerox 2020irehan.saiyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- EAMCET-QR-Chemistry-Jr Chem-2.Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDokument13 SeitenEAMCET-QR-Chemistry-Jr Chem-2.Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Propertiespvnchem100% (1)
- Classification of Elements - KPDokument4 SeitenClassification of Elements - KPKiran KiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry (PDF)Dokument9 SeitenClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry (PDF)Ankit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Properties-3Dokument17 SeitenPeriodic Properties-3qweerrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDokument4 SeitenClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesMAGU_MWENYEWENoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Chapter 3Dokument9 SeitenChemistry Chapter 3Ayush sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic PropertiesDokument19 SeitenPeriodic Propertiesnamannn555Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transition MetalsDokument13 SeitenTransition MetalsAaditya YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Class11Dokument20 SeitenChemistry Class11TITLI SAHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Class XI Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties NotesDokument5 SeitenClass XI Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties NoteseasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements AND Periodicity in Their PropertiesDokument23 SeitenClassification of Elements AND Periodicity in Their PropertiesmazharpunjabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Periodic TableDokument8 SeitenModern Periodic Tablemixing hubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Worksheets Class 11 On Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Set 1Dokument2 SeitenChemistry Worksheets Class 11 On Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Set 1Devesh chauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 ClassificationDokument11 Seiten2021 ClassificationSora RoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- C3 PERIODIC TABLE Sem I 202223Dokument76 SeitenC3 PERIODIC TABLE Sem I 202223a200812Noch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic ClassificationDokument7 SeitenPeriodic ClassificationTHE ASSAM GAMER NILAV 01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Periodic TableDokument14 SeitenChapter 3 Periodic Tableapi-361318565Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Periodic TableDokument14 SeitenChapter 3 Periodic Tableapi-361302099Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Periodic TableDokument14 SeitenChapter 3 Periodic Tableapi-361298866Noch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Periodic TableDokument8 SeitenModern Periodic TableSabbir HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDokument148 SeitenChapter 2 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesSajag GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Properties Class 1Dokument33 SeitenPeriodic Properties Class 1akshat.sh2021Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chem-1, Chap-3, S, P, D&F Blocks & Periodic PropertyDokument35 SeitenChem-1, Chap-3, S, P, D&F Blocks & Periodic PropertyAfroze NigarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science BookletDokument91 SeitenScience Bookletmarc.habib2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.0 Periodic TableDokument88 Seiten3.0 Periodic TableTasya KassimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties Dobereiner Classification of ElementsDokument5 SeitenClassification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties Dobereiner Classification of ElementsVigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Periodic Class11Dokument6 SeitenChem Periodic Class11vrajmenon6260Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Periodic TableDokument11 SeitenChemistry Periodic Tablesubhadeepdey85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDokument58 SeitenPeriodic Classification of ElementsNevin ShajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of Transition and Inner Transition Elements+.Dokument60 SeitenChemistry of Transition and Inner Transition Elements+.Nidhi Singh75% (4)
- Periodic ClassificationDokument44 SeitenPeriodic ClassificationJitendra PaliwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements and PeriodicityDokument4 SeitenClassification of Elements and PeriodicityminimataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of ElementsDokument4 SeitenClassification of ElementsSatyam MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDokument8 SeitenClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertieskeerthanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- XI-Chemistry-DOE Support Material 2019-20 - 3Dokument18 SeitenXI-Chemistry-DOE Support Material 2019-20 - 3Samik RaghavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements-NotesDokument8 SeitenClassification of Elements-NotesSuprathik VineeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Classification If ElementsDokument19 Seiten3.1 Classification If ElementsSharon RamaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements-2019-20Dokument13 SeitenClassification of Elements-2019-20ritvikpradeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of ElementsDokument17 SeitenClassification of Elementsaaranyaka shobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimia 1. Apakah Sistem Periodik Unsur Itu?Dokument35 SeitenKimia 1. Apakah Sistem Periodik Unsur Itu?Tolchah MansurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDokument24 SeitenClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesMadhan chakravarthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic ClassificationDokument55 SeitenPeriodic ClassificationHarshtej Singh MakkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument23 SeitenLecture 1Az-zahraa'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classificationof Elements Lecture Notes 20-21Dokument11 SeitenClassificationof Elements Lecture Notes 20-21SHAJIYA ANoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4 - Periodic TableDokument37 SeitenCH 4 - Periodic Tableahmad yasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideVon EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Smithells Metals Reference BookVon EverandSmithells Metals Reference BookE A BrandesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refractory Transition Metal Compounds: High Temperature CermetsVon EverandRefractory Transition Metal Compounds: High Temperature CermetsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zone Areas AhmedabadDokument4 SeitenZone Areas AhmedabadVishal DaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- No Input in Question 1a. Screenshot of OUTPUT of Question 1aDokument2 SeitenNo Input in Question 1a. Screenshot of OUTPUT of Question 1aVishal DaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 What Is Routing?Dokument15 Seiten1.1 What Is Routing?Vishal DaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- So Much Depends On The Authority of A Reality To Guide Me in A Logic of CircumstanceDokument1 SeiteSo Much Depends On The Authority of A Reality To Guide Me in A Logic of CircumstanceVishal DaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers: TEST - 1 (Paper-I)Dokument10 SeitenAnswers: TEST - 1 (Paper-I)Vishal DaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen PDFDokument5 SeitenHydrogen PDFVishal DaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic:: Prepared By: Standard: Roll No.Dokument1 SeiteTopic:: Prepared By: Standard: Roll No.Vishal DaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARSONDokument4 SeitenARSONangelica naquitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Fixation, Decalcification & DehydrationDokument3 Seiten2 Fixation, Decalcification & DehydrationNur-Reza MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5Dokument158 SeitenModule 5Ashritha SureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 12952 6 2021Dokument38 SeitenIso 12952 6 2021Jim FrenkenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicios Resueltos: Ingenieria de MaterialesDokument3 SeitenEjercicios Resueltos: Ingenieria de MaterialesNicole AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebaco Indoor Rubber FlooringDokument3 SeitenEbaco Indoor Rubber FlooringRushabh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swelling Index Test Results of Pellets - PP3 - 14th Mar 2022Dokument2 SeitenSwelling Index Test Results of Pellets - PP3 - 14th Mar 2022रविकान्त सागरNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Analysis of Drugs of Abuse in Biologic SamplesDokument6 SeitenHigh-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Analysis of Drugs of Abuse in Biologic SamplesPutra SpNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9701 Chemistry Data Booklet 2016Dokument20 Seiten9701 Chemistry Data Booklet 20168q74ndhrhxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Watson - 1931 - Prediction of Critical Temperatures and Heats of VDokument5 SeitenWatson - 1931 - Prediction of Critical Temperatures and Heats of VMartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Introduction To Forensic ChemistryDokument6 SeitenModule 1 Introduction To Forensic ChemistryRacky Jones MontealtoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in Blood and Tissue FluidsDokument22 SeitenTransport of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in Blood and Tissue FluidsmutialailaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Heat EffectsDokument41 SeitenModule 3 Heat EffectsJatskinesisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental 2 Cylinder Horizontal Valveless Steam Engine. (B 30Mmxs 30Mm) General Arrangement, Notes and Bill of MaterialDokument3 SeitenExperimental 2 Cylinder Horizontal Valveless Steam Engine. (B 30Mmxs 30Mm) General Arrangement, Notes and Bill of MaterialOscar OsornoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base Worksheet 2Dokument2 SeitenAcid Base Worksheet 2Tutor Academy100% (1)
- Insumos de PerfuraçãoDokument626 SeitenInsumos de PerfuraçãoyariosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromatography: 1 Biochemistry of MedicsDokument44 SeitenChromatography: 1 Biochemistry of MedicsAlkallain Brands CompanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irrigation Beyond of The Smear LayerDokument19 SeitenIrrigation Beyond of The Smear LayerOscar ManjarresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bộ Đề Thi Thử 2019 Tiếng Anh Lovebook - Đề Số 34.Dokument17 SeitenBộ Đề Thi Thử 2019 Tiếng Anh Lovebook - Đề Số 34.vvctriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Spectroscopy Notes PDFDokument59 SeitenUnit 3 Spectroscopy Notes PDF7nx58s9dyhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verder PH Controller With PumpDokument8 SeitenVerder PH Controller With Pumpprabal rayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science7 q1 Mod6 Solutions 1-19Dokument19 SeitenScience7 q1 Mod6 Solutions 1-19api-114144039Noch keine Bewertungen
- All Pyq Classification of ElementsDokument26 SeitenAll Pyq Classification of Elementssaurabh shuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Experimental Investigationof Material Removal Rateon EDMof Cold Work Tool Steel D2Dokument6 SeitenAn Experimental Investigationof Material Removal Rateon EDMof Cold Work Tool Steel D2ANKITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDokument6 SeitenPhysical and Chemical Properties of MatterRampotz Ü EchizenNoch keine Bewertungen
- USP-NF Acepromazine Maleate InjectionDokument2 SeitenUSP-NF Acepromazine Maleate InjectionStalin VacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FenAMI - Deltacon Power - LowDokument2 SeitenFenAMI - Deltacon Power - Lowanh NGUYENNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbidimetry and Nephelometry: March 2012Dokument7 SeitenTurbidimetry and Nephelometry: March 2012Jafar MohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrophobic Films and Their Efficiency Against Moisture Transfer. 1. in Uence of The Film Preparation TechniqueDokument7 SeitenHydrophobic Films and Their Efficiency Against Moisture Transfer. 1. in Uence of The Film Preparation TechniqueAdam Yoga GinanjarNoch keine Bewertungen