Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Jee 2014 Booklet5 HWT Halides
Hochgeladen von
varunkohliinOriginaltitel
Copyright
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Jee 2014 Booklet5 HWT Halides
Hochgeladen von
varunkohliinCopyright:
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 34 HWT/Chemistry
DATE : TIME : 45 Minutes MARKS : [ ___ /10] TEST CODE : ORG HL [1]
START TIME : END TIME : TIME TAKEN: PARENTS SIGNATURE :
This test contains a total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each question carries 1 mark. There is NO NEGATIVE marking.
Choose the correct alternative. Only one choice is correct.
1. The best method for the conversion of an alcohol into an alkyl chloride is the treating the alcohol with
(A) PCl
3
(B) PCl
5
(C) SOCl
2
in presence of pyridine (D) dry HCl in the presence of anhydrous ZnCl
2
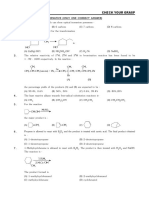
2.
The final product, is :
(A) (B) (C) (D)
3. Of the isomeric hexanes, the isomers that give the minimum and maximum number of monochloro derivatives are respectively.
(A) 3-methylpentane and 2, 3-dimethylbutane (B) 2, 3-dimethylbutane and n-hexane
(C) 2, 2-dimethylbutane and 2-methylpentane (D) 2, 3-dimethylbutane and 2-methylpentane
4. The catalyst used in the preparation of an alkyl chloride by the action of dry HCl on an alcohol is :
(A) anhy. AlCl
3
(B) FeCl
3
(C) anhy. ZnCl
2
(D) Cu
5. The alkyl halides that can be mace by free radical halogenation of alkanes are
(A) RCl and RBr but not RF or RI (B) RF, RCl and RBr but not RI
(C) RF, RCl, RBr, RI (D) RF, RCl and RI but not RBr
6. The molecular formula of diphenyl methane
is C
13
H
12
How many structural isomers are possible when one of the hydrogen is replaced by a chlorine atom?
(A) 6 (B) 4 (C) 8 (D) 7
7. Of the five isomeric hexanes, the isomer which can give two monochlorinated compound is :
(A) 2-methylpentane (B) 2, 2-dimethylbutane
(C) 2, 3-dimethylbutane (D) n-hexane
8. Tetiary butyl alcohol gives teritiary butyl chloride on treatment with :
(A) conc. HCl/anhy. ZnCl
2
(B) KCN
(C) NaOCl (D) Cl
2
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 35 HWT/Chemistry
9. In the following compound, least number of monochlorination is possible :
(A)
3 2 2 2 3
CH CH CH CH CH C (B)
3 2 3
3
CH CH CH CH
|
CH
(C)
3
3
3
CH
|
CH C H
|
CH
(D)
3
3 3
3
CH
|
CH C CH
|
CH
10. The number of possible enantiomeric pairs that can be produced during mono-chlorination of 2-methyl butane is :
(A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 1 (D) 2
11. On mixing a certain alkane with chlorine and irradiating it with ultraviolet light, forms only one monochloroalkane. This alkane
could be :
(A) propane (B) pentane (C) iso-pentane (D) neo-pentane
12. Following is the substitution reaction in which CN replaces Cl .
alcoholic
R Cl KCN RCN KCl
A
+ +
To obtain propanenitrile, R Cl should be :
(A) chloroethane (B) 1-chloropropane (C) chloromethane (D) 2-chloropropane
13. Which one of the following forms propane nitrile as the major product?
(A) Ethyl bromide + alcoholic KCN (B) Propyl bromide + alcoholic KCN
(C) Propyl bromide + alcoholic AgCN (D) Ethyl bromide + alcoholic AgCN
14. The product of reaction between alcoholic silver nitrite with ethyl bromide is :
(A) ethene (B) ethane (C) ethyl nitrile (D) nitro ethane
15. Which halide does not get hydrolysed by sodium hydroxide?
(A) Vinyl chloride (B) Methyl chloride (C) Ethyl chloride (D) Isopropyl chloride
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 36 HWT/Chemistry
DATE : TIME : 45 Minutes MARKS : [ ___ /10] TEST CODE : ORG HL [2]
START TIME : END TIME : TIME TAKEN: PARENTS SIGNATURE :
This test contains a total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each question carries 1 mark. There is NO NEGATIVE marking.
Choose the correct alternative. Only one choice is correct.
1. Alkyl iodide reacts with NaCN to give alkyl cyanide and small amount of alkyl isocyanide. Formation of these two products is due
to the :
(A) ionic character of NaCN (B) nucleophilic character of CN
(C) ambidentate character of CN
(D) electrophilic character of CN
2. Grignard reagent is not prepared in aqueous medium but prepared in either medium, because :
(A) the reagent is highly reactive in ether (B) the reagent does not react with water
(C) the reagent becomes inactive in water (D) the reagent reacts with water
3. Which of the following compounds has the higher boiling point?
(A) CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
Cl (B) CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
Cl
(C) CH
3
CH(CH
3
)CH
2
Cl (D) (CH
3
)
3
CCl
4. 1, 2-dibromoethane reacts with alcoholic KOH to yield a product X. The hybridisation state of the carbons present in X
respectively, are:
(A) sp, sp (B) sp
3
, sp
3
(C) sp
3
, sp
2
(D) sp
3
, sp
2
5. Alkyl halides are less soluble in water because :
(A) they ionize in water (B) they do not form H-bonds with water
(C) they are highly viscous (D) they have very strong C X bond
6. Predict the product,
(A) (B) (C) (D)
7. In the reaction, 2A dry silver oxide ether 2Ag X
A
+ + A is a/an :
(A) primary alcohol (B) acid (C) alkyl halide (D) alcohol
8. An alkyl halide reacts with alcoholic ammonia in a sealed tube, the product formed will be :
(A) a primary amine (B) a secondary amine (C) a tertiary amine (D) a mixture of all the three
9. Maximum number of molecules of CH
3
I that can react with a molecule of CH
3
NH
2
are :
(A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 2 (D) 1
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 37 HWT/Chemistry
10. Match the following :
Reactants Products
[P] C
2
H
5
Cl, moist Ag
2
O 1. CH
3
CH
2
ONO
[Q] C
2
H
5
Cl, aqueous ethanolic AgCN 2. C
2
H
4
[R] C
2
H
5
Cl, aqueous ethanolic AgNO
2
3. CH
3
CH
2
OH
[S] C
2
H
5
Cl, ethanolic KOH 4. CH
3
CH
2
NC
The correct match is :
(A) P-III, Q-IV, R-II, S-I (B) P-I, Q-II, R-III, S-IV
(C) P-III, Q-IV, R-I, S-II (D) P-IV, Q-I, R-II, S-III
11. The conversion of ethyl chloride into diethyl ether takes place by :
(A) Williamsons synthesis (B) Perkins reaction
(C) Wurtz reaction (D) Grignard reaction
12. 1-chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives :
(A) but-1-ene (B) butan-1-ol (C) but-2-ene (D) butan-2-ol
13. In a group of isomeric alkyl halides, the order of boiling points is :
(A) primary < secondary < tertiary (B) primary > tertiary > secondary
(C) primary < secondary > tertiary (D) primary > secondary > tertiary
14.
3 3
CH Br Nu CH Nu Br
+ +
The decreasing order of the rate of the above reaction with nucleophiles (Nu )AtoD
is :
3
[Nu (A) PhO , (B) AcO , (C) HO , (D)CH O ]
=
(A) D > C > A < B (B) D > B > C > A (C) A > B > C > D (D) B > D > C > A
15. phX A phNC. + The reagent A is :
(A) AgCN (B) KCN (C) NaCN (D) Reaction not possible
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 38 HWT/Chemistry
DATE : TIME : 45 Minutes MARKS : [ ___ /10] TEST CODE : ORG HL [3]
START TIME : END TIME : TIME TAKEN: PARENTS SIGNATURE :
This test contains a total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each question carries 1 mark. There is NO NEGATIVE marking.
Choose the correct alternative. Only one choice is correct.
1. In the following sequence of reactions
2 5
AgCN Reduction
C H Br X Y. Y is :
(A) n-propyl amine (B) isopropylamine (C) ethylamine (D) ethylmethyl amine
2. The structure of the major product formed in the following reaction is :
(A) (B) (C) (D)
3. On treating a mixture of two alkyl halides with sodium metal in dry ether, 2-methyl propane was obtained. The alkyl halides are
(A) 2-chloropropane and chloromethane (B) 2-chloropropane and chloroethane
(C) chloromethane and chloroethane (D) chloromethane and 1-chloropropane
4.
Reduction
3
Na C H OH
2 5
CH Br KCN (alc.) X Y
+
+
What is Y in the series?
(A) CH
3
CN (B) C
2
H
5
CN (C) C
2
H
5
NH
2
(D) CH
3
NH
2
5. Elimination of bromine from 2-bromobutane results in the formation of
(A) predominantly 2-butyne (B) predominantly 1-butene
(C) predominantly 2-butene (D) predominantly 2-butene
6. Ethyl chloride on heating with AgCN forms a compound X. The functional isomer of X is :
(A) C
2
H
5
NC (B) C
2
H
5
NH
2
(C) C
2
H
5
CN (D) None of these
7. When 32.25 g of ethyl chloride is subjected to dehydrohalogenation reaction the yield of the alkene formed is 50%. The mass of the
product formed is (atomic mass of chlorine is 35.5)
(A) 14 g (B) 28 g (C) 7 g (D) 56 g
8. Compound A react with alcoholic KOH to yield compound B which on ozonolysis followed by reaction with Zn/H
2
O gives
methanal and propanal. Compound A is :
(A) 1-propanol (B) 1-butanol (C) 1-chlorobutane (D) 2-chlorobutane
9. Identify A and B in the following reactions :
Aq. NaOH AgOH
2 5
A C H OH B
A
(A) A = C
2
H
2
, B = C
2
H
6
(B) A = C
2
H
5
Cl, B = C
2
H
4
(C) A = C
2
H
4
, B = C
2
H
5
Cl (D) A = C
2
H
5
Cl, B = C
2
H
5
Cl
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 39 HWT/Chemistry
10. Which of the following applies in the reaction,
Alc. KOH
3 2 3
CH CHBrCH CH
I. CH
3
CH = CHCH
3
(major product) II. CH
2
= CHCH
2
CH
3
(minor product)
(A) Markownikoffs rule (B) Saytzeffs rule (C) Kharasch effect rule (D) Hoffmanns rule
11. Identify X and Y in the following sequence
X Y
2 5 3 7 2
C H Br product C H NH
(A) X = KCN, Y = LiAlH
4
(B) X = KCN, Y = H
3
O
+
(C) X = CH
3
NH
2
, Y = AlCl
3
/HCl (D) X = CH
3
NH
2
, Y = HNO
2
12. The order of reactivities of methyl halides in the formation of Grignard reagent is :
(A) CH
3
I > CH
3
Br > CH
3
Cl (B) CH
3
Cl > CH
3
Br > CH
3
I
(C) CH
3
Br > CH
3
Cl > CH
3
I (D) CH
3
Br > H
3
I > CH
3
Cl
13. A bromoalkane X reacts with magnesium in dry ether to form compound Y. The reaction of Y with methanal followed by
hydrolysis yield an alcohol having molecular formula C
4
H
10
O. The compound X is :
I bromoethane II bromomethane III 1-bromopropane IV 2-bromopropane
The correct option is :
(A) I, III (B) IV (C) III (D) III, IV
14. Identify A and B in the following reaction
A B
2 5 2 5 2 5 2 5
C H Cl C H OH C H O C H
(A) A = aqueous KOH; B = AgOH (B) A = alcoholic KOH/ ; B aqueous NaOH A =
(C) A = aqueous NaOH; B = H
3
O
+
(D) A = AgNO
2
; B = KNO
2
15. In the reaction sequence,
C H OH H O
2 5 3
2 5
C H Cl KCN X Y
A
+
What is the molecular formula of Y?
(A) C
3
H
6
O
2
(B) C
3
H
5
N (C) C
2
H
4
O
2
(D) C
2
H
6
O
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 40 HWT/Chemistry
DATE : TIME : 45 Minutes MARKS : [ ___ /10] TEST CODE : ORG HL [4]
START TIME : END TIME : TIME TAKEN: PARENTS SIGNATURE :
This test contains a total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each question carries 1 mark. There is NO NEGATIVE marking.
Choose the correct alternative. Only one choice is correct.
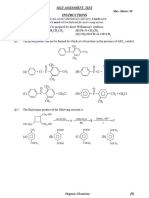
1. In the chemical reactions,
the compound A and B respectively are :
(A) nitrobenzene and chlorobenzene (B) phenol and benzene
(C) benzene diazonium chloride and fluorobenzene (D) nitrobenzene and fluorobenzene
2. In the preparation of chlorobenzene from aniline, the most suitable reagent is :
(A) chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light (B) chlorine in the presence of AlCl
3
(C) nitrous acid followed by heating with Cu
2
Cl
2
(D) HCl and Cu
2
Cl
2
3. Among the following which one has weakest carbon-halogen bond?
(A) Benzyl bromide (B) Bromobenzene (C) Vinyl bromide (D) Benzyl chloride
4. Which one of the following chlorohydrocarbons readily undergoes solvolysis?
(A) CH
2
= CHCl (B) (C) (D)
5. The reaction of toluene with Cl
2
in presence of FeCl
3
gives predominantly :
(A) benzoyl chloride (B) benzyl chloride (C) o-and p-chlorotoluene (D) m-chlorotoluene
6. The compound formed on heating chlorobenzene with chloral in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid is :
(A) gammexane (B) DDT (C) freon (D) hexachloroethane
7.
AgNO
3
HNO
3
X Yellow or white ppt.
Which of the following can be X?
I. II. (CH
3
)
2
CHCl III. IV.
The correct choice is :
(A) I, II (B) II, III (C) II, III, IV (D) III, IV
8. Fluorobenzene (C
6
H
5
F) can be synthesized in the laboratory :
(A) by heating phenol with HF and KF
(B) from aniline by diazotization followed by heating the diazonium salt with HBF
4
(C) by direct fluorination of benzene with F
2
gas
(D) by reacting bromobenzene with NaF solution
9. Which of the following statements about benzyl chloride is incorrect?
(A) It gives a white precipitate with alcoholic silver nitrate
(B) It can be oxidised to benzaldehyde by boiling with copper nitrate solution
(C) It is a lachrymatory liquid and answers Beilsteins test
(D) It is less reactive than alkyl halides
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 41 HWT/Chemistry
10. Chlorobenzene gives aniline with :
(A) NH
3
/Cu
2
O, A (B) NH
3
/H
2
SO
4
, A (C) NH
3
/EtOH (D) None of the above
11. Chlorination of Toluene in presence of light and heat followed by treatement with aqueous NaOH gives :
(A) o-cresol (B) p-cresol
(C) mixture of o-cresol and p-cresol (D) benzoic acid
12. p-nitrobromobenzene can be converted to p-nitroaniline by using NaNH
2
. The reaction proceeds through the intermediate named :
(A) carbocation (B) carbanion (C) benzyne (D) dianion
13.
Compound A is :
(A) (B) (C) (D)
14. For the preparation of p-nitroiodobenzene form p-nitroaniline, the best method is :
(A) NaNO
2
/HCl followed by KI (B) NaNO
2
/HCl followed by CuCN
(C) LiAiH
4
followed by I
2
(D) NaBH
4
followed by I
2
15. Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding benzyl chloride?
(A) It gives white precipitate with alcoholic AgNO
3
(B) It is an aromatic compound with substitution in the side chain
(C) It is oxidised to give benzaldehyde (D) It is less reactive than vinyl chloride
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 42 HWT/Chemistry
DATE : TIME : 45 Minutes MARKS : [ ___ /10] TEST CODE : ORG HL [5]
START TIME : END TIME : TIME TAKEN: PARENTS SIGNATURE :
This test contains a total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each question carries 1 mark. There is NO NEGATIVE marking.
Choose the correct alternative. Only one choice is correct.
1. In the reaction :
The major product A is :
(A) (B) (C) (D) A can't be formed.
2. Which one of the following possess highest M.P?
(A) Chlorobenzene (B) o-dichlorobenzene (C) m-dichlorobenzene (D) p-dichlorobenzene
3. Which one of the following compound reacts with chlorobenzene to produce DDT?
(A) Acetaldehyde (B) Nitrobenzene
(C) m-chloroacetaldehyde (D) Trichloroacetaldehyde
4. Bottles containing C
6
H
5
I and C
6
H
5
CH
2
I lost their original labels. They were labelled A and B for testing. A and B were separately
taken in a test tube and boiled with NaOH solution. The end solution in each tube was made acidic with dilute HNO
3
and then some
AgNO
3
solution was added. Substance B gave a yellow precipitate. Which one of the following statements is true for this
experiment?
(A) A was C
6
H
5
I (B) A was C
6
H
5
CH
2
I (C) B was C
6
H
5
I (D) Addition of HNO
2
was
unnecessary
5. Which of the following compound is not formed in iodoform reaction of acetone?
(A) CH
3
COCH
2
I (B) ICH
2
COCH
2
I (C) CH
3
COCHI
2
(D) I
3
C CO CH
3
6. Which of the compounds when brominated turns to meso 2, 3-dibromobutane?
(A) Cis-2-butene (B) Iso-butane (C) Butane (D) Trans-2- butene
7. Which of the following does not answer iodoform test?
(A) n-butyl alcohol (B) Acetophenone (C) Acetaldehyde (D) Ethylmethyl ketone
8. Which of the following will not respond to iodoform test?
(A) Ethyl alcohol (B) Propanol-2 (C) Propanol-1 (D) Ethanal
9. Ethyl ortho formate is obtained by heating..with sodium ethoxide.
(A) CHCl
3
(B) C
2
H
5
OH (C) HCOOH (D) CH
3
CHO
10. lodoform test is not given by.
(A) 2-pentanone (B) ethanol (C) ethanal (D) 3-petnanone
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 43 HWT/Chemistry
11. What happens if CCl
4
is treated with AgNO
3
?
(A) A white ppt. of AgCl will form (B) NO
2
will be evolved
(C) CCl
4
will dissolve in AgNO
3
(D) Nothing will happen
12. Which one of the following does not give iodoform?
(A) (B) CH
3
OH
(C) CH
3
CH
2
OH (D)
3 3
CH CH CH
|
OH
13. Choroform gives a trichloro derivative of an alcohol on reaction with :
(A) conc. Nitric acid (B) aq. alkali
(C) acetone and alkali (D) a primary amine and an alkali
14. Which of the following ketones will not respond to iodoform test?
(A) Methyl isopropyl ketone (B) Ethyl isopropyl ketone
(C) Dimethyl ketone (D) 2-hexanone
15. , )
2 2
2
CaOCl H O Ca OH X + +
3
X CH CHO Y +
2 3
Y Ca(OH) CHCl +
What is Y ?
(A) CH
3
CH(OH)
2
(B) CH
2
Cl
2
(C) CCl
3
CHO (D) CCl
3
COCH
3
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 44 HWT/Chemistry
DATE : TIME : 45 Minutes MARKS : [ ___ /10] TEST CODE : ORG HL [6]
START TIME : END TIME : TIME TAKEN: PARENTS SIGNATURE :
This test contains a total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each question carries 1 mark. There is NO NEGATIVE marking.
Choose the correct alternative. Only one choice is correct.
1. Chloropicrin is obtained by the reaction of
(A) steam on carbon tetrachloride (B) nitric acid on chlorobenzene
(C) chlorine on picric acid (D) nitric acid on chloroform
2. Among the following the one that gives positive iodoform test upon reaction with I
2
and NaOH is :
(A) CH
3
CH
2
CH(OH)CH
2
CH
3
(B) C
6
H
5
CH
2
CH
2
OH
(C)
3 2
3
CH O CH CH OH
|
CH
(D) PhCHOHCH
3
3. What is the product A in the following?
(A) (B)
(C) Both (A) and (B) (D) None of the above
4. Ethyl alcohol is used as a preservative for chloroform because it :
(A) prevents aerial oxidation of chloroform
(B) prevents decomposition of chloroform
(C) decomposes phosgene by converting it to ethyl carbonate
(D) removes phosgene by converting it to ethyl carbonate
5. Chloroform, when kept open, is oxidised to :
(A) CO
2
(B) COCl
2
(C) CO
2
, Cl
2
(D) None of these
6. The reaction in which phenol differs from isopropyl alcohol is :
(A) it undergoes esterification with carboxylic acid (B) it reacts with ammonia
(C) it forms yellow crystals of iodoform (D) it liberates H
2
with Na metal
7. In the reaction sequence
3
2
3 2 4
CCl
|
Cl CHO
FeCl H SO
X Y DDT. Compound X is :
(A) chlorobenzene (B) benzene (C) toluene (D) biphenyl methane
8. Which one of the following compounds when heated with KOH and a primary amine gives carbylamine test?
(A) CHCl
3
(B) CH
3
Cl (C) CH
3
OH (D) CH
3
CN
9. Which of the following compounds gives trichloromethane on distilling with bleaching powder?
(A) Methanal (B) Phenol (C) Ethanol (D) Methanol
10. The chemical formula of tear gas is :
(A) COCl
2
(B) CO
2
(C) Cl
2
(D) CCl
3
NO
2
Vidyamandir Classes
VMC/Halogen Containing Organic Compounds 45 HWT/Chemistry
11. 1, 2-dibromo cyclohexane on dehydrohalogenation gives :
(A) (B) (C) (D) None of these
12. Which of the following is not inflammable?
(A) CHCl
3
(B) Benzene (C) Toluene (D) Carbon tetrachloride
13. In the dichlorination reaction of propane, mixture of products are obtained. How many isomers the mixture contains?
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5
14. The product of Vinyl chloride and HCl is a :
(A) gem chloride (B) ethylidene chloride (C) 1, 1 dichloroethane (D) All are correct
15. Chloroform is slowly oxidised by air in the presence of light and air to form :
(A) formly chloride (B) trichloro methanol (C) phosgene (D) formaldehyde
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Halogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQDokument11 SeitenHalogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQParshantKumarBajaj92% (13)
- Garlic - Toxic and A Brain Synchronization DestroyerDokument6 SeitenGarlic - Toxic and A Brain Synchronization Destroyerxreader0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesDokument10 SeitenAlkanes Alkenes AlkynesPanda Boy100% (2)
- HELIUMDokument2 SeitenHELIUMEleojan ContayosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X XDokument14 SeitenSection-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X XPriyansh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Test-1-Aldehydes & Ketones - PreparationDokument5 SeitenClass Test-1-Aldehydes & Ketones - PreparationSarthak VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Unit 2Dokument12 SeitenChemistry Unit 2kelon scottNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes, Alkenes & Cyclic HydrocarbonsDokument17 SeitenAlkanes, Alkenes & Cyclic HydrocarbonsEllaŠtrbac100% (1)
- Organization of Genes and Chromosomes CompleteDokument13 SeitenOrganization of Genes and Chromosomes Completebiotecnika_testNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aromatic CompoundsDokument16 SeitenAromatic CompoundsadityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09-Final With SolutionsDokument27 Seiten09-Final With SolutionsDanielle Wood100% (2)
- Aldehydes & Ketones (Booklet-2Dokument15 SeitenAldehydes & Ketones (Booklet-2kraken monsterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohol & EtherDokument217 SeitenAlcohol & EtherAmitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Subsea Pipeline Cathodic Protection SurveyDokument38 SeitenGuidelines For Subsea Pipeline Cathodic Protection SurveyjavadNoch keine Bewertungen
- (J. D. Coyle) Introduction To Organic Photochemist (BookFi)Dokument94 Seiten(J. D. Coyle) Introduction To Organic Photochemist (BookFi)AlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ On Molecular BiologyDokument12 SeitenMCQ On Molecular Biologyronojoysengupta0% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Cable NomenclatureDokument5 SeitenCable NomenclatureSushantGore100% (1)
- BS en 10136-2019Dokument16 SeitenBS en 10136-2019Martijn GrootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotary Kiln BurnerDokument5 SeitenRotary Kiln BurnerAllen de Guzman100% (1)
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Oxygen Containing Organic Compounds IIDokument10 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Oxygen Containing Organic Compounds IIvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- HC Docx1Dokument13 SeitenHC Docx1ayushsekhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenesDokument27 SeitenMCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenessarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questions: Question Bank Class: Xii, Chemistry Unit 4: Haloalknaes & HaloarenesDokument27 SeitenMultiple Choice Questions: Question Bank Class: Xii, Chemistry Unit 4: Haloalknaes & HaloarenesAkshita BoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resonance Chemistry DPP 6 (Advanced)Dokument11 SeitenResonance Chemistry DPP 6 (Advanced)Anurag1210701067% (6)
- Iit Questions On Carbonyl Compounds & Carboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeDokument12 SeitenIit Questions On Carbonyl Compounds & Carboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Chemistry Test HydrocarbonsDokument9 SeitenClass 11 Chemistry Test HydrocarbonsSRINANDAN R BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question BankDokument16 SeitenHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Question BankBrown HustlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl CompoundDokument197 SeitenCarbonyl CompoundAmitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Reactions and MechanismsDokument160 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Reactions and MechanismsRohit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Halo Alkane Halo Arene Part 1 PDFDokument10 SeitenHalo Alkane Halo Arene Part 1 PDFEkansh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic chemistry practice questionsDokument29 SeitenOrganic chemistry practice questionsHet PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HODokument7 SeitenExercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HOChesta MalhotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl Compounds SheetDokument133 SeitenCarbonyl Compounds Sheetadityavaish739Noch keine Bewertungen
- Halogen Containing CompoundsDokument67 SeitenHalogen Containing Compoundsonline_mktg100% (6)
- 34 Alcohols & Ethers - Problems For Practice - Level 1Dokument14 Seiten34 Alcohols & Ethers - Problems For Practice - Level 1Abuturab MohammadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Questions 1Dokument3 SeitenOrganic Questions 1SABARI SRINIVAS ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Aromatic Compounds (13th)Dokument24 SeitenAromatic Compounds (13th)Raju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2-Chemistry Unit 5 Sample PaperDokument22 SeitenA2-Chemistry Unit 5 Sample PaperDimuthu SandaruwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Alcohols and Alkyl Halides: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanDokument13 SeitenChapter 4 Alcohols and Alkyl Halides: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanCeseley HaynesNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDokument8 SeitenThis Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl Compounds 12thDokument24 SeitenCarbonyl Compounds 12thRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS QDokument20 Seiten12TH CBSE DPP 37. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ ASSERTION REASON CS Q123Noch keine Bewertungen
- A (2e, 4e) B (2Z, 4Z) C (2Z, 4e) D (2e, 4Z)Dokument1 SeiteA (2e, 4e) B (2Z, 4Z) C (2Z, 4e) D (2e, 4Z)Agatha chilesheNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Alkanepdf DLDokument8 SeitenPDF Alkanepdf DLGeraldineNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET - Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Practice PaperDokument3 SeitenNEET - Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Practice PaperGanga DharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry-JeeDokument33 SeitenOrganic Chemistry-JeeRamesh Babu GarlapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocarbon 4Dokument35 SeitenHydrocarbon 4AjayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Class 12 WorksheetDokument8 SeitenChem Class 12 WorksheetBHAVYA KUSHWAHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocarbon and Isomerism TestDokument6 SeitenHydrocarbon and Isomerism TestveerlocusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument21 SeitenQuestion Bank Class Xii (Chemistry) Unit 5: Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers Multiple Choice QuestionsSahilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alka NetDokument13 SeitenAlka Netjonida88Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH-12 - MCQS Ald, Ket & Car - AcidsDokument3 SeitenCH-12 - MCQS Ald, Ket & Car - AcidsPranav ShankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Option Correct Type (+4/-1)Dokument5 SeitenMultiple Option Correct Type (+4/-1)Vinod AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 10 Paper 1Dokument30 SeitenTopic 10 Paper 1RawanMazen SharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkyl HalideDokument8 SeitenAlkyl HalideMegh Raj BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch12org MetalicoDokument21 SeitenCh12org MetaliconicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 11. Aldehydes - Ketones Tatva (NM)Dokument48 SeitenCH 11. Aldehydes - Ketones Tatva (NM)chandan mallikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes - Alkenes - Alkynes - DPP 3Dokument3 SeitenAlkanes - Alkenes - Alkynes - DPP 3Vishal_93100% (1)
- Hydrocarbon - Practice SheetDokument3 SeitenHydrocarbon - Practice SheetAbhishek PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkyl and Aryl Halides Test Level 1 Friday 29 April, 2016: SP SP SP SPDokument10 SeitenAlkyl and Aryl Halides Test Level 1 Friday 29 April, 2016: SP SP SP SPSuryansh SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Organic 1Dokument6 SeitenQuiz Organic 1ronakgupta332005Noch keine Bewertungen
- DPP - Alcohols (Biswajit Sir) (NPS)Dokument2 SeitenDPP - Alcohols (Biswajit Sir) (NPS)Kuleen SinkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocar SHEET3Dokument4 SeitenHydrocar SHEET3Aayush SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Mid ExamDokument4 SeitenChemistry Mid ExamKidu GideyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 Promo 1Dokument15 Seiten2008 Promo 1shinkir0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 14 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 14 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 15 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 15 - Solutionsvarunkohliin100% (2)
- Mock JEE Mains - 13 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 13 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moke JEE Mains - 2 - SolutionsDokument10 SeitenMoke JEE Mains - 2 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 11 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 11 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 7 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 7 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 9 - SolutionsDokument8 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 9 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 10 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 10 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 7 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 7 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 12 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 12 - Solutionsvarunkohliin0% (1)
- Mock JEE Mains - 8 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 8 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 9 - SolutionsDokument8 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 9 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 6 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 6 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 1 - SolutionsDokument10 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 1 - Solutionsvarunkohliin100% (2)
- Mock JEE Mains - 4 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 4 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock JEE Mains - 3 - SolutionsDokument9 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 3 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Magnetic Effects of CurrentDokument10 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Magnetic Effects of Currentvarunkohliin100% (1)
- Mock JEE Mains - 5 - SolutionsDokument8 SeitenMock JEE Mains - 5 - SolutionsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Solutions 3d GeometryDokument3 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Solutions 3d GeometryvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Solutions ProbabilityDokument12 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Solutions ProbabilityvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Magnetism & MatterDokument12 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Magnetism & MattervarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Electromagnetic InductionDokument12 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Electromagnetic InductionvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT ProbabilityDokument14 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Probabilityvarunkohliin100% (1)
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Oxygen Containing Organic Compounds IDokument10 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Oxygen Containing Organic Compounds IvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Nitrogen Containing Organic CompoundsDokument8 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Nitrogen Containing Organic CompoundsvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Oxygen Cont Organic Compounds IIIDokument6 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT Oxygen Cont Organic Compounds IIIvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee 2014 Booklet7 HWT AnswersDokument6 SeitenJee 2014 Booklet7 HWT AnswersvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Test Contains A Total of 10 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDokument13 SeitenThis Test Contains A Total of 10 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE Markingvarunkohliin100% (1)
- This Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDokument8 SeitenThis Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingvarunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetrahedral and octahedral void sizes in close packingDokument7 SeitenTetrahedral and octahedral void sizes in close packingPrachi Agarwal100% (1)
- 10 Chapter 4Dokument52 Seiten10 Chapter 4CuriosityShop100% (1)
- FEECO Complete OfferingsDokument8 SeitenFEECO Complete OfferingsawfahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Temperature on Chemical and Physical WeatheringDokument4 SeitenEffect of Temperature on Chemical and Physical WeatheringAshlynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emulsion LectureDokument30 SeitenEmulsion LectureRay YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Present Situation of The Old Shoes Recycling ADokument7 SeitenThe Present Situation of The Old Shoes Recycling AEvan GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi Refined Paraffin Wax - 1-3%Dokument2 SeitenSemi Refined Paraffin Wax - 1-3%miketyson11Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry II Module on Intermolecular ForcesDokument5 SeitenGeneral Chemistry II Module on Intermolecular ForcesJerry De Leon TaayNoch keine Bewertungen
- API SN 5w 30 MsdsDokument5 SeitenAPI SN 5w 30 MsdsahmetNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Szirmay RókusDokument3 SeitenDR - Szirmay RókusDR.Szirmay Rókus Phd.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Repair and Reinforcing Techniques for Steel ComponentsDokument108 SeitenRepair and Reinforcing Techniques for Steel ComponentsValy CoulibalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ht-Discharge Pipes and Fittings (PPS) : KunststoffeDokument35 SeitenHt-Discharge Pipes and Fittings (PPS) : Kunststoffeluis eduardo ramos rebataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquatherm NA 2015-1 PDFDokument143 SeitenAquatherm NA 2015-1 PDFdaniyalahmad119Noch keine Bewertungen
- E-Waste Management: A Case Study of Bangalore, IndiaDokument5 SeitenE-Waste Management: A Case Study of Bangalore, IndiaJatindra Kumar PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biofar 3Dokument11 SeitenBiofar 3dediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D178Dokument9 SeitenAstm D178Rodrigo Escárate BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muntingia Calabura A Review of Its Traditional Uses Chemical Properties and Pharmacological ObservationsDokument27 SeitenMuntingia Calabura A Review of Its Traditional Uses Chemical Properties and Pharmacological ObservationsDharmastuti Fatmarahmi100% (1)
- Inspection & Test Plans PDFDokument85 SeitenInspection & Test Plans PDFshareyhouNoch keine Bewertungen
- CARBOXYLIC ACID Derivatives - Salts and ReactionsDokument6 SeitenCARBOXYLIC ACID Derivatives - Salts and ReactionsmarcelompassosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation Tool For Waste Disposal in Municipal Solid Waste Incinerators MSWI For Ecoinvent v2.1 (2008)Dokument129 SeitenCalculation Tool For Waste Disposal in Municipal Solid Waste Incinerators MSWI For Ecoinvent v2.1 (2008)JKKNoch keine Bewertungen