Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Structure of Indian Government
Hochgeladen von
Mayur PatelOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Structure of Indian Government
Hochgeladen von
Mayur PatelCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Structure of Indian Government
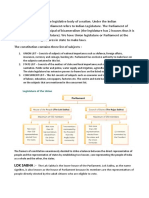
There are three different roles: 1. Legislature: Making laws 2. Executive: Implementing laws 3. Judiciary: Interpreting laws. Center, State, Local level has three roles (Legislature, Executive & Judiciary), the structure would be as follows. Central Government Legislature: Parliament: Contains MP's Executive : Prime Minister and his council of ministers Judiciary : supreme Court State Government Legislature: Vidhan Sabha(Legislative Assembly) : Consisting of MLA's Executive : Chief Minister and his council of ministers Judiciary : High Court Local Government Legislature: Municipal Council consisting of Councilors/corporators Executive : Municipal Commissioner and his team Judiciary : District courts and Lokadalats
The Structure of Zimbabwe's Government
Zimbabwe is a Semi-Presidential Republic. In the structure of the Zimbabwean Government separate power between the executive branch, the legislative branch and the judicial branch. The composition of each of these branches differs from the composition of the American branches of government. The Executive Branch The executive branch consists of two executives, the President and the Prime Minister. The President is the head of the state and is in charge of the Cabinet. The Prime Minister, on the other hand, is head of government and oversees the Council of Ministers. There are two vice presidents and two deputy prime ministers. The Legislative Branch Legislative power is vested in both government and parliament. The Cabinet and the Council of Ministers hold legislative power along with the elected Parliament. Parliament is divided between the Senate and the House of Assembly. The Judicial Branch The Zimbabwean judicial branch functions as the American judicial branch does. It consists of a Supreme Court and local court system. A Chief Justice is appointed by the president to direct the judicial system in Zimbabwe.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 1.basic Structure of Indian GovernmentDokument1 Seite1.basic Structure of Indian GovernmentmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Văn Hóa MDokument6 SeitenVăn Hóa MSunnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separation of PowersDokument8 SeitenSeparation of PowersM Vijay AbrajeedhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- System of Government in USADokument1 SeiteSystem of Government in USAvendapsendaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Salient Features of The ConstitutionDokument3 Seiten15 Salient Features of The Constitutionjohn ryan100% (1)
- 3 Branches of GovtDokument5 Seiten3 Branches of GovtLynne Led'z RNNoch keine Bewertungen
- GOVERNMENT-chapter 10Dokument16 SeitenGOVERNMENT-chapter 10Isaiah OumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5Dokument38 SeitenModule 5Swathy s LaijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Parliamentary and PresidentialDokument12 SeitenDifference Between Parliamentary and PresidentialCharmy Ann Gabinete100% (1)
- Members), and Heads of Independent Agencies. Here Are Some of The Things Those People DoDokument3 SeitenMembers), and Heads of Independent Agencies. Here Are Some of The Things Those People DoOr Terzulum lawrenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument24 SeitenUnit 2sachinyadavv13Noch keine Bewertungen
- President of IndiaDokument4 SeitenPresident of IndiaSrijib HalderNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Note 3602 Content Document 20230102055357PMDokument36 SeitenE-Note 3602 Content Document 20230102055357PMAshish ShankerNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Three Branches of GovernmentDokument21 SeitenThe Three Branches of Governmentlakshya mathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Indian ConstitutionDokument9 SeitenModule 3 Indian Constitutionajmalajupyk2424Noch keine Bewertungen
- National Government VocabDokument9 SeitenNational Government Vocabapi-262313031Noch keine Bewertungen
- Govt of IndiaDokument2 SeitenGovt of Indiadolecos850Noch keine Bewertungen
- Constitution Notes: You Will Be Writing Questions at Home Tonight. There Are 14 Slides of Information To Take Notes OnDokument16 SeitenConstitution Notes: You Will Be Writing Questions at Home Tonight. There Are 14 Slides of Information To Take Notes OnIuzi ValentinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branches of The U.S GovernmentDokument2 SeitenBranches of The U.S GovernmentHùng Nguyễn Viết0% (1)
- Chapter 8, Section 1: Goals and Principals of The ConstitutionDokument27 SeitenChapter 8, Section 1: Goals and Principals of The ConstitutionJames JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educ 201 Civics LessonDokument5 SeitenEduc 201 Civics Lessonapi-316820179Noch keine Bewertungen
- CL AssignmentDokument4 SeitenCL Assignmentwisalhilal03Noch keine Bewertungen
- United States ResumenDokument6 SeitenUnited States ResumenmiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Check and BalancesDokument11 SeitenCheck and Balancesapi-233206923Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session 10 - Skill Builders PowerpointDokument5 SeitenSession 10 - Skill Builders Powerpointapi-285720072Noch keine Bewertungen
- Our GovernmentDokument5 SeitenOur Governmentapi-325337036Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class Lesson PPDokument5 SeitenClass Lesson PPapi-267591340Noch keine Bewertungen
- Belk, Jayme CivicsDokument5 SeitenBelk, Jayme Civicsapi-243107168Noch keine Bewertungen
- Our Government 1Dokument5 SeitenOur Government 1api-254136229Noch keine Bewertungen
- Duration of Governments 2Dokument18 SeitenDuration of Governments 2jamespaul8209Noch keine Bewertungen
- LESSONS 3 8 Political System and Process BlogDokument131 SeitenLESSONS 3 8 Political System and Process Blogdilrabosaidikramova4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Democratic Government of IndiaDokument4 SeitenDemocratic Government of IndiaDevesh chauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poliical Comparison On USA, India & UKDokument19 SeitenPoliical Comparison On USA, India & UKGaurav MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lok Sabha and Rajya SabhaDokument7 SeitenLok Sabha and Rajya SabhaYuvraj Gagare - VIII AmberNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Three Branches of The Federal GovernmentDokument4 SeitenThe Three Branches of The Federal Governmentvut267878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Essay UnderlinesDokument3 SeitenEssay Underlinesapi-385489563Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument43 SeitenUnit 2varun.nagar.cseds.2020Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Principles of The ConstitutionDokument29 SeitenThe Principles of The ConstitutionHabtamu AdimasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Political System USDokument4 SeitenPolitical System USIrina IonescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ssee Unit 02Dokument41 SeitenSsee Unit 02NayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systems of Government: The Czech RepublicDokument2 SeitenSystems of Government: The Czech RepublickorinekhovinekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject: Political Science Ii Teacher: Ms. Deepika Gahatraj Module: Ii, Wings of Government: Legislature LegislatureDokument3 SeitenSubject: Political Science Ii Teacher: Ms. Deepika Gahatraj Module: Ii, Wings of Government: Legislature LegislatureShahid AltamasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Government and Politics 3Dokument3 SeitenComparative Government and Politics 3ROsemarie JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 201 Skills 2 Session 10Dokument5 Seiten201 Skills 2 Session 10api-357055611Noch keine Bewertungen
- Civics LessonDokument5 SeitenCivics Lessonapi-264670798Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gcu 114 Zim Gov NewsletterDokument1 SeiteGcu 114 Zim Gov Newsletterapi-295561641Noch keine Bewertungen
- Our GovernmentDokument5 SeitenOur Governmentapi-299903651Noch keine Bewertungen
- Essay ExampleDokument1 SeiteEssay ExampleErika BaclorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civics LessonDokument5 SeitenCivics Lessonapi-284793905Noch keine Bewertungen
- Role of U.S Constitution: United States Government and Political System (Written Report)Dokument6 SeitenRole of U.S Constitution: United States Government and Political System (Written Report)MarimarjnhioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Law BKL1Dokument9 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Law BKL1Li Shuang ChooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powers and FuncDokument3 SeitenPowers and FuncSamiksha YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our GovernmentDokument5 SeitenOur Governmentapi-316725803Noch keine Bewertungen
- Slide - Session 6 - Organs of Government - Role of Legislature, Executive & JudiciaryDokument34 SeitenSlide - Session 6 - Organs of Government - Role of Legislature, Executive & JudiciaryAbdullah JayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- US State System: 1. Legislative BranchDokument5 SeitenUS State System: 1. Legislative BranchCоня ЧоловськаNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes For The Lesson State GovernmentDokument6 SeitenNotes For The Lesson State GovernmentAnandavana PpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our GovernmentDokument5 SeitenOur Governmentapi-315617352Noch keine Bewertungen
- Branches of Us GovernmentDokument21 SeitenBranches of Us Governmenthuyen dauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Politics of Zimbabwe PDFDokument7 SeitenPolitics of Zimbabwe PDFMayur PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pestel AnalysisDokument34 SeitenPestel AnalysisMayur Patel82% (11)
- Prootional ActivirtyDokument64 SeitenProotional ActivirtyMayur PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zimbabwe Briefing Issue 53Dokument4 SeitenZimbabwe Briefing Issue 53Mayur PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penting Potential ProbioticDokument22 SeitenPenting Potential Probioticamrihjoko9229Noch keine Bewertungen
- Milk Minigrant DraftDokument13 SeitenMilk Minigrant DraftMayur PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICICI Bank Was Set Up When The Process of Deregulation and Liberalization Had Just Begun in India and The Reserve Bank of IndiaDokument2 SeitenICICI Bank Was Set Up When The Process of Deregulation and Liberalization Had Just Begun in India and The Reserve Bank of IndiaMayur PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Close Up OverviewDokument6 SeitenClose Up OverviewMayur Patel0% (1)
- Print: Previous YearsDokument2 SeitenPrint: Previous YearsMayur PatelNoch keine Bewertungen