Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
For Mulaire 2
Hochgeladen von
jawadchefCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
For Mulaire 2
Hochgeladen von
jawadchefCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Formulaire du cours de propagation
( )
( ) 0 i RG
t
i
LG RC
t
i
LC
x
i
0 v RG
t
v
LG RC
t
v
LC
x
v
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
= +
= +
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
quations des tlgraphistes :
0
= 4t10
-7
H.m
-1
c
0
= 10
-9
/(36t) F.m
-1
1 8
0 0
. 10 . 3
1
~ = s m c
c
Rgime sinusodal
dt
dx
v
p
= =
|
e
0
r
2
c
t = | Vitesse de phase : et
( ) ( ) jC G jL R j + + = + = Constante de propagation :
c
c
2
2
2
V
x
V =
c
c
2
2
2
I
x
I =
quations en harmonique :
( ) ( )
x
r
x
i
x
r
x
i
e I e I x I e V e V x V + = + =
Solutions :
e
e
jC G
jL R
I
V
I
V
Zc
r
r
i
i
+
+
= = =
Impdance caractristique :
e
o
C
G
= tan
e
L
R
= tan
Tangentes de pertes :
|
.
|
\
|
+ = |
.
|
\
|
+ - = RcG
Rc
R
C
G
L
R
LC
2
1
2
1
e e
e o
Attnuation faibles pertes :
Ligne bifilaire
En HF
( ) m H
d
D
L /
2
ln
0
1
|
.
|
\
|
=
t
( ) m C G / ) tan( 2
1 2
1 1
O = o t e
( ) m F
d
D
C /
2
ln
1
|
.
|
\
|
=
tc
( ) m
D
d
d
f
R /
1
1
2
0
1
O
|
.
|
\
|
=
to
En BF
( ) m / H L L L
i HF 1
+ =
( ) m /
d
D 2
ln
tg f
2 G
1 2
1
O
|
.
|
\
|
o c
t = ( ) m / F
d
D 2
ln
C
1
|
.
|
\
|
tc
=
( ) m / ) 0 f ( R R
MHz 1 1
O = ~
Ligne coaxiale
( ) m H
d
d
L / ln
2
1
2 0
1 |
|
.
|
\
|
=
t
( ) m
d
d
tg f
G /
ln
4
1
1
2
2
1
O
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
o c
t ( ) m F
d
d
C /
ln
2
1
2
1
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
tc
( ) m
d d
f
R /
1 1
2 1
0
1
O
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
ot
Ligne ferme sur une charge
Zr
x y=l-x
v
x
i
x
Zc
Zi
ei
+
= =
x
x
x
x
x
i
i
v
v
R
Coefficient de rflexion
y 2 y 2
r
r
x
e e
V
V
R
+
= =
r
R
y th Z Z
y th Z Z
Z Zx
r c
c r
c
+
+
= Impdance ramene :
y jZ Z
y jZ Z
Z Zx
r c
c r
c
|
|
tan
tan
+
+
= sans pertes :
y j r
x x x
e
Zc
V
i v a
|
.
+
= + =
y j r
x x x
e
Zc
V
i v b
|
= = .
| |
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
2
1
2
1
.
a
a
b
b
S
Ondes de
puissance :
Rflexion sur la charge :
Zc Zr
Zc Zr
R
r
+
=
linaire dB
o o - = 686 . 8
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Correction TD Capteur Actionneur 22042020 PDFDokument4 SeitenCorrection TD Capteur Actionneur 22042020 PDFAmdouni AmeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SN041a-Conception Et Calcul Des Assemblages de Jarret de PortiquesDokument24 SeitenSN041a-Conception Et Calcul Des Assemblages de Jarret de PortiquesWissem TaktakNoch keine Bewertungen
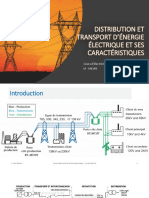
- Chapitre 1 Distribution Et Transport D'énergie ÉlectriqueDokument40 SeitenChapitre 1 Distribution Et Transport D'énergie Électriquezazar100% (1)
- Memento FormulaireDokument26 SeitenMemento FormulaireMaria AlielhadjiabdouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Support Cours Khodja PDFDokument77 SeitenSupport Cours Khodja PDFEmmad Abdelkarim100% (1)
- Cour CIRCUIT MAGNETIQUEDokument8 SeitenCour CIRCUIT MAGNETIQUERahal karim100% (2)
- Colonnes Montantes - Calcul Canalisation Collective - Dérivations IndividuellesDokument3 SeitenColonnes Montantes - Calcul Canalisation Collective - Dérivations IndividuellestiklitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Analyse VibratoireDokument11 Seiten1 Analyse VibratoireAnonymous LfeGI2hM50% (2)
- Épistémologie de L'interdisciplinarité Et Représentations Sociales. ... - Garnier & Robert (2003)Dokument14 SeitenÉpistémologie de L'interdisciplinarité Et Représentations Sociales. ... - Garnier & Robert (2003)Eduardo Aguirre DávilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modelisation PDFDokument10 SeitenModelisation PDFAppia CekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devoir de Synthèse N°1 - Sciences Physiques - Bac Informatique (2012-2013) MR Abdmouleh NabilDokument6 SeitenDevoir de Synthèse N°1 - Sciences Physiques - Bac Informatique (2012-2013) MR Abdmouleh NabilMrDOMONoch keine Bewertungen
- BAEP2 CompoBP2014Dokument2 SeitenBAEP2 CompoBP2014Nacer Assam0% (1)
- CCNDL 1ere C Maths 2011 2012 Composition de Fin Du 1er TrimDokument2 SeitenCCNDL 1ere C Maths 2011 2012 Composition de Fin Du 1er Trimfreyter freyter417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tuyere de LavalDokument4 SeitenTuyere de LavalSilvia JaimesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rapport TP 1 Et 2Dokument31 SeitenRapport TP 1 Et 2treda79% (39)
- CNC Corrige 2000 2008Dokument339 SeitenCNC Corrige 2000 2008Ouma imaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cour FDTD - 102518Dokument38 SeitenCour FDTD - 102518EL MESSAOUDI MariemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canevas 7Dokument58 SeitenCanevas 7Mosko RioNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRPS en 12390-7 (2008)Dokument16 SeitenSRPS en 12390-7 (2008)Boško JanjuševićNoch keine Bewertungen
- P4 3 Dipole MagnetiqueDokument9 SeitenP4 3 Dipole MagnetiquesevemasseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 6 OXYDO REDUCTIONDokument11 SeitenChap 6 OXYDO REDUCTIONMoustapha SallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pendule de FoucaultDokument12 SeitenPendule de FoucaultMichel LL.Noch keine Bewertungen
- RESUME Moteur AsynchroneDokument2 SeitenRESUME Moteur Asynchronebasma100% (4)
- Modélisation ThermodynamiqueDokument22 SeitenModélisation ThermodynamiqueAmine Aitali100% (1)
- Partie: Physique Mouvement Plan Exercice N°1: JEU DU BOULETDokument25 SeitenPartie: Physique Mouvement Plan Exercice N°1: JEU DU BOULETtamersamira80Noch keine Bewertungen
- La GéophysiqueDokument29 SeitenLa GéophysiquetinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qcm-Correct - Atomistique - 2022 CopieDokument4 SeitenQcm-Correct - Atomistique - 2022 CopieloxlloydNoch keine Bewertungen
- TD1Dokument3 SeitenTD1Aaouine AbderrazzakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cours Transfert-ThermiqueDokument78 SeitenCours Transfert-ThermiqueDounia AniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controle 1 - 2 S1 PC 1bac FRDokument2 SeitenControle 1 - 2 S1 PC 1bac FRElmahdi BenhNoch keine Bewertungen