Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Placement Schedule
Hochgeladen von
api-249704153Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Placement Schedule
Hochgeladen von
api-249704153Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
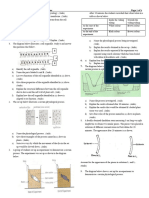
Mon Nov 18 Day 2
8:30 Gr 7 Science -intro to structures -cardboard boat intro -stability -centre of gravity 9:20 Gr 8 Science -what is a living thing? Jesses video -characteristics list -cell theory - work on word web and word wall (DUE tues) 10:35 Planning 11am Shelterhouse
Tues Nov 19 Day 3
9am Support workers in class No Gr 7 science class
Wed Nov 20 Day 4
8:30 Gr 7 history 9:20 Gr 8 science -yeast lab write-up (DUE Thursday) 10:35 planning 11:15 library (Lauren) -form groups for boat competition
Thurs Nov 21 Day 5
8:30 Gr 7 science -centre of gravity recap (write definition) -cardboard boat designs -structure classification 9:20 Gr 8 science -yeast lab write-up -cell components 10:35 gr 8 history 11:15 gym
Fri Nov 22 Day 1
8:30 planning 9:20 Gr 7 history
10:35 Gym 11:15 Gr 8 science -yeast experiment w/ diff water temps (variables independent, dependent, controlled) 1pm Language (Lauren) -independent read -point of view
10am movie depart (Hunger Games)
1pm Language (Lauren) -shared read
1pm Language (me) -independent read -read aloud (The table where rich people sit)
2pm Language(me) /music? -read aloud (five people you meet in heaven)
Mon Nov 25 Day 2
8:30 & 11:15 Gr 7 science -forces on a boat (internal, external) -egg crush experiment -start to plan boat design -conversions(weight/size) 9:20 Gr 8 science -cell components -animal vs. Plant cell 1pm Language (Lauren) -open response question - reading buddies?
Tues Nov 26 Day 3
8:30 planning 9:20 Grade 7 science -plan boat design -loads (static, dynamic)
Wed Nov 27 Day 4
8:30 Gr 7 history 9:20 Gr 8 Science -current news article -cell component story book 10:35 planning 11:15 Library -boat design research -answer questions 1pm Language (Lauren) -guided read
Thurs Nov 28 Day 5
8:30 Gr 7 Science -build cardboard boat
Fri Nov 29 Day 1
8:30 planning -formative evaluation 9:20 Gr 7 history 10:35 Gr 8 history
10:35 Gym 11:15 Gr 8 science -build a cell 1pm Language (Lauren) -Shared read -independent read
9:20 Gr 8 science -cell component story book 1pm Language (me) -independent read -read aloud
11:15 Gr 8 science -microscopes -article-how microscopes changed science 1pm Language (me) -read aloud (the story of stuff)
Mon Dec 2 Day 2
8:30 & 11:15 Gr 7 science - boat replica race -conversion to full-size boats -forces: magnitude, point/ plane of application 9:20 Gr 8 science -storybook presentations -microscopes: safe practises, draw cells 1pm Language (Lauren) -read aloud - reading buddies?
Tues Dec 3 Day 3
8:30 planning 9:20 Grade 7 science -why structures fail
Wed Dec 4 Day 4
8:30 Gr 7 -Cardboard boat race
Thurs Dec 5 Day 5
8:30 Gr 7 Science -internal forces (tension, compression, torsion, shear)
Fri Dec 6 Day 1
8:30 planning 9:20 Gr 7 history 10:35 Gr 8 history
10:35 Gym 11:15 Gr 8 science -microscopes: prepare slides 1pm Language (Lauren) -Shared read -independent read
9:20 Gr 8 Science (supply) -unicellular vs. Multicellular organisms -review cell components
9:20 Gr 8 science -Kingfisher field trip
11:15 Gr 8 science -Kingfisher reflection -cell components & microscope TEST 1pm Language (me) -read aloud
1pm Language (me) -independent read -guided read
Mon Dec 9 Day 2
8:30 & 11:15 Gr 7 science -gingerbread houses -forces, loads -wrecking ball experiment 9:20 Gr 8 science --uni- vs. Multi-cellular organisms
Tues Dec 10 Day 3
8:30 planning 9:20 Grade 7 science -TEST (forces, loads) 10:35 Gym 11:15 Gr 8 science -plant tissues
Wed Dec 11 Day 4
8:30 Gr 7 history
Thurs Dec 12 Day 5
8:30 Gr 7 Science -solid, frame and shell classification 9:20 Gr 8 science - plant systems -animal systems
Fri Dec 13 Day 1
8:30 planning 9:20 Gr 7 history 10:35 Gr 8 history 11:15 Gr 8 science -animal systems
1pm Language (Lauren) -read aloud - reading buddies?
1pm Language (Lauren) -Shared read
9:20 Gr 8 Science -plant systems: adaptations -video (smarty plants the nature of things) 1pm Language (Lauren) -guided read -independent read
1pm Language (me) -read aloud -independent read
1pm Language (me) -shared read
Specific Expectations Grade 8 Science -- Understanding Life Systems: Cells
a. Cell identification, components 3.1 demonstrate an understanding of the postulates of the cell theory (e.g., the cell is the basic unit of life; all cells come from pre-existing cells; all living things are made up of one or more cells) 3.2 identify structures and organelles in cells, including the nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplasts, vacuole, mitochondria, and cytoplasm, and explain the basic functions of each (e.g., the nucleus holds all the information needed to make every cell in the body) 3.3 compare the structure and function of plant and animal cells 2.6 use a variety of forms (e.g., oral, written, graphic, multimedia) to communicate with different audiences and for a variety of purposes (e.g., using the conventions of science, make a labelled drawing of a cell; create a slide show to explain the results of investigations into the processes of osmosis and diffusion) b. Microscopes
1.1
assess the role of selected technologies (e.g., the development of the electron microscope, the ability to infuse dyes into cells, in vitro fertilization) in enhancing our understanding of cells and cellular processes
2.1 follow established safety procedures for handling apparatus and materials (e.g., wash hands after preparing materials for slides) and use microscopes correctly and safely (e.g., carry the microscope with both hands, place it near the centre of the desk, ensure that the sun cannot be directly focused through the instrument when sunlight is used for illumination, keep both eyes open when viewing to avoid eye strain) 2.2 use a microscope correctly and safely to find and observe components of plant and animal cells (e.g., using an onion slice or a prepared slide of a protist) and make accurate drawings of their observations 2.3 prepare dry- and wet-mount slides of a variety of objects for use with a microscope (e.g., a piece of newspaper, a hair)
c. Systems, multi-cellular organisms 3.5 identify unicellular organisms (e.g., amoebae) and multicellular organisms (e.g., invertebrates [worms], vertebrates [frogs]), and compare ways in which they meet their basic needs (e.g., nutrition, movement, gas exchange) 3.6 describe the organization of cells into tissues, organs, and systems (e.g., groups of cells with similar functions combine to make up tissues; groups of tissues with similar functions combine to make organs; groups of organs work together as organ systems) -------------- I think I will get to around here by the end of my placement (excluding animal systems for 3.6 above) 1.2 assess the potential that our understanding of cells and cell processes has for both beneficial and harmful effects on human health and the environment, taking different perspectives into account (e.g., the perspectives of farmers, pesticide manufacturers, people with life threatening illnesses) d. Osmosis, cell membranes 2.4 use scientific inquiry/experimentation skills to investigate the processes of osmosis and diffusion 3.4 explain the processes of diffusion and osmosis and their roles within a cell
Grade 7 Science Understanding structures and mechanisms: Form and function
a. Structural stability 2.3 investigate the factors that determine the ability of a structure to support a load (e.g., the weight of the structure itself; the magnitude of the external loads it will need to support; the strength of the materials used to build it) 3.1 classify structures as solid structures (e.g., dams), frame structures (e.g., goal posts), or shell structures (e.g., airplane wings) 3.2 describe ways in which the centre of gravity of a structure (e.g., a childs high chair, a tower) affects the structures stability
b. Forces 2.2 design, construct, and use physical models to investigate the effects of various forces on structures (e.g., the struts of a roof experience compression forces from shingles; the support cables of a suspension bridge are in tension; a twisted ruler has torsion forces; the pin that holds the two parts of a pair of scissors together has shear forces acting on it) 2.4 use technological problem-solving skills to determine the most efficient way for a structure (e.g., a chair, a shelf, a bridge) to support a given load 3.3 identify the magnitude, direction, point of application, and plane of application of the forces applied to a structure 3.4 distinguish between external forces (e.g., wind, gravity, earthquakes) and internal forces (tension, compression, shear, and torsion) acting on a structure c. Design 2.6 use appropriate science and technology vocabulary, including truss, beam, ergonomics, shear, and torsion), in oral and written communication 2.7 use a variety of forms (e.g., oral, written, graphic, multimedia) to communicate with different audiences and for a variety of purposes (e.g., use a graphic organizer to show the steps taken in designing and making a product) 3.5 describe the role of symmetry in structures (e.g., aesthetic appeal, structural stability) 3.6 identify and describe factors that can cause a structure to fail (e.g., bad design, faulty construction, foundation failure, extraordinary loads) ---------------- I will try get to here by the end of my placement d. Social aspects of structure and design 1.1 evaluate the importance for individuals, society, the economy, and the environment of factors that should be considered in designing and building structures and devices to meet specific needs (e.g., function; efficiency; ease of use; user preferences; aesthetics; cost; intended lifespan; effect on the environment; safety, health, legal requirements)
1.2 evaluate the impact of ergonomic design on the safety and efficiency of workplaces, tools, and everyday objects (e.g., furniture, computer equipment, home tools and equipment), and describe changes that could be made in personal spaces and activities on the basis of this information (e.g., use computer keyboards and mice that are ergonomically designed; use kitchen tools such as knives with ergonomic handles; use equipment for household jobs that is designed to ease strain on the body, such as ergonomically designed snow shovels and garden tools) 2.5 investigate methods used by engineers to ensure structural safety (e.g., incorporating sensors in structures to detect unusual stresses and give early warning of failure; designing structures to carry much heavier loads than they will actually have to bear) 3.7 identify the factors (e.g., properties of the material as they relate to the product, availability, costs of shipping, aesthetic appeal, disposal) that determine the suitability of materials for use in manufacturing a product (e.g., a running shoe)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Practicum Week 3 Self AssessmentDokument2 SeitenPracticum Week 3 Self Assessmentapi-249704153Noch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Philosophy of EducationDokument10 SeitenPersonal Philosophy of Educationapi-249704153Noch keine Bewertungen
- Renewable Nonrenewable Resources Lesson PlanDokument9 SeitenRenewable Nonrenewable Resources Lesson Planapi-249704153Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practicum ReflectionDokument5 SeitenPracticum Reflectionapi-249704153Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lisa Hanlon - Teaching Resume March 2014Dokument2 SeitenLisa Hanlon - Teaching Resume March 2014api-249704153Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hanlon Lisa - Ed4260 - Why Science AssignmentDokument4 SeitenHanlon Lisa - Ed4260 - Why Science Assignmentapi-249704153Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Nota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 3Dokument12 SeitenNota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 3Firas Muhammad50% (4)
- Grupo de Asistencia Técnica S.R.LDokument2 SeitenGrupo de Asistencia Técnica S.R.LLeandro BecerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sam0le of Laboratory ManualDokument40 SeitenSam0le of Laboratory ManualCJ DaodaoenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sow Combined Science Year 9 (2+3 Programme) v2 - 3 YearsDokument56 SeitenSow Combined Science Year 9 (2+3 Programme) v2 - 3 YearsYenny Tiga100% (2)
- 02 - Colligative PropertiesDokument46 Seiten02 - Colligative PropertiesamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 The Cell Gayagoy Rosalino JR. S PDFDokument12 SeitenExperiment 1 The Cell Gayagoy Rosalino JR. S PDFMingNoch keine Bewertungen
- REVERSE OSMOSIS TECHNOLOGY FOR WATER TREATMENTDokument73 SeitenREVERSE OSMOSIS TECHNOLOGY FOR WATER TREATMENTAkhil ShrivastavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell PhysiologyDokument4 SeitenCell PhysiologyVernon100% (1)
- Salinity and It's Effect On The Germination Rates of Radishes - Ranier KnowlesDokument8 SeitenSalinity and It's Effect On The Germination Rates of Radishes - Ranier KnowlesRanierNoch keine Bewertungen
- August 2022 Report For Dennis T MuzilaDokument11 SeitenAugust 2022 Report For Dennis T MuzilaDennis MuzilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Water Purifier DesignDokument3 SeitenSolar Water Purifier DesignretechNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB Chapter3Dokument14 SeitenTB Chapter3Senthereng MoaisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis Cell EquilibriumDokument3 SeitenOsmosis Cell EquilibriumGalex YeveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane Coloring WorksheetDokument6 SeitenCell Membrane Coloring WorksheetArleenaAmnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Production Based On Osmotic Pressure.: Øystein S. Skråmestø, Stein Erik Skilhagen, Werner Kofod NielsenDokument10 SeitenPower Production Based On Osmotic Pressure.: Øystein S. Skråmestø, Stein Erik Skilhagen, Werner Kofod NielsenShrishti ChaurasiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fresh Water Geberator and Osmosis ProcessesDokument62 SeitenFresh Water Geberator and Osmosis ProcessesSuhas KassaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of RO Membrane & Its CharacterizationDokument27 SeitenDevelopment of RO Membrane & Its CharacterizationZohaib SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permeability of Portland Cement PasteDokument19 SeitenPermeability of Portland Cement PasteQuoc Tri PhungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salting Curing MixturesDokument2 SeitenSalting Curing MixturesAsia VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDokument3 SeitenPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsNabila Ulfiah YasminNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 PSPM Kedah Biology 123 W AnsDokument93 Seiten2010 PSPM Kedah Biology 123 W Ansjee2kk100% (1)
- BIOL1408 Introductory Biology Name Lab Unit 6/7: Diffusion & Osmosis Date Dr. Flo OxleyDokument10 SeitenBIOL1408 Introductory Biology Name Lab Unit 6/7: Diffusion & Osmosis Date Dr. Flo OxleyJavier E. Dubon0% (1)
- Chapter 3 Egg OsmosisDokument4 SeitenChapter 3 Egg OsmosisYma FeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Chem 2 Q2 Module 10 PDFDokument19 SeitenGen Chem 2 Q2 Module 10 PDFMike LarguezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Report - Reverse Osmosis FIXDokument39 SeitenFull Report - Reverse Osmosis FIXendang dian lestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potatoe Lab ReportDokument5 SeitenPotatoe Lab Reportapi-309561913Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Midterms 2021Dokument13 SeitenBiology Midterms 2021Keano GelmoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Human Physiology 16th Edition Stuart Fox Krista RompolskiDokument30 SeitenTest Bank For Human Physiology 16th Edition Stuart Fox Krista Rompolskisamanthadayphdamdzkyirej100% (26)
- General Biology: Transport Mechanism That Contributes To The Survival of The CellDokument16 SeitenGeneral Biology: Transport Mechanism That Contributes To The Survival of The Cell할에이필Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Lab Prelim ReviewerDokument5 SeitenBiochem Lab Prelim Revieweramethys manuelNoch keine Bewertungen