Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Che 90308 Typesofsolids
Hochgeladen von
api-2185117410 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten4 SeitenOriginaltitel
che 90308 typesofsolids
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten4 SeitenChe 90308 Typesofsolids
Hochgeladen von
api-218511741Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
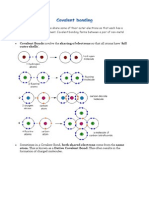
No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY
Molecular solids are made of
molecules. There are weak
intermolecular forces or van
der Waals forces (forces
BETWEEN molecules) holding
the molecules together, and
they require a small amount of
energy to be overcome. This
means the substances have
low melting and boiling points.
Since the weak van der Waals
forces allow the molecules to
be easily separated this makes
them soft or brittle - easy to
break the solid.
Non-polar molecules are usually
soluble in non-polar solvents such as
cyclohexane. Since both molecules
have similar weak intermolecular
forces, then weak forces can also
exist between the two different
molecules. (Like dissolves like).
Polar molecules are
usually soluble in
polar solvents such
as water. Since both
molecules have
similar weak
intermolecular
forces, then weak
forces can also exist
between the two
different molecules.
(Like dissolves like).
IMPORTANT
There are strong covalent
bonds between the atoms in
the molecules (intramolecular
forces) but it is NOT these that
are being broken when the
solids melts or the liquid boils.
Molecules may
be polar or non-
polar.
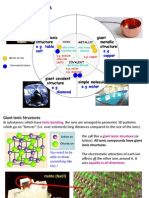
Molecular solids are made of molecules in which
the atoms are covalently bonded to each other.
They do not contain mobile charged particles (no
free electrons or mobile ions). Therefore molecular
substances cannot conduct in the solid or liquid
state.
MOLECULAR
Particles are
MOLECULES
No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY
Diamond is made of
carbon atoms. Each
carbon atom is covalently
bonded to 4 other C
atoms in a tetrahedral
arrangement, which forms
a covalent network solid.
The covalent bonds
between the carbon
atoms are very strong and
require a large amount of
energy explaining
diamonds strength and
high melting point.
Graphite consists of C atoms each
covalently bonded to 3 other C
atoms (in a trigonal planar shape) in
a 2D arrangement, forming layers
with weak van der Waals forces
between them. The weak
attractions between the layers of
atoms in graphite are easily broken.
Therefore, graphite is soft and
slippery and the layers can slide
over each other. This makes it
useful as a lubricant.
In order to melt covalent
network substances strong
covalent bonds between
atoms must be broken.
Because of their strength, a
lot of energy is required to
break these bonds and
separate atoms. Therefore
diamond, graphite and SiO
2
all have high melting points.
Silicon dioxide, SiO
2
, consists of
silicon and oxygen atoms held
together by covalent
bonds in a tetrahedral
arrangement, so that
a 3D network exists.
In graphite (solid) each carbon
atom is covalently bonded to 3
others. This leaves one
electron that is delocalised and
is free to move. Because this
electron is free to move, it
carries charge and so graphite
conducts electricity.
COVALENT
NETWORK
Particles are
ATOMS
No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY
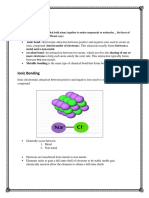
Solid ionic substances are a
3D lattice of ions held
together by strong ionic
bonds. These forces hold the
ions in a fixed position.
As the ions cannot move, the
solid will not conduct
electricity.
When melted (or dissolved in
water) the ions become free
to move, and this allows the
liquid to conduct electricity.
Ionic solids are made of positive ions
and negative ions, held together by
strong electrostatic attractions in a
3D lattice structure. As these
electrostatic attractions (ionic bonds)
are strong, they require a large
amount of energy to overcome them
so their melting points are high.
Ionic solids are soluble in
water as the ions are
separated from the lattice
due to attraction towards
the polar water molecules
which is sufficient to pull the
ions from the lattice.
Molecules of a nonpolar
solvent like cyclohexane are
not attracted towards the
ions and so ionic solids are
insoluble in these.
Particles in ionic
solids are IONS
Bonding in ionic
solids is IONIC
The bonds within ionic solids are directional so they
are not malleable or ductile. Instead they are brittle.
The oppositely charged ions are forced to shift
position and then like charges are lined up and repel,
causing the crystal to shatter.
IONIC
No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY
Metal atoms are held
together in a 3D lattice
by metallic bonding, in
which valence electrons
are attracted to the nuclei
of neighbouring atoms.
The valence electrons are
free to move throughout
the structure in both the
solid and liquid state.
This is why metals are
good conductors of
electricity (and heat).
Many metals are hard and
strong, and have high
melting and boiling points as
there is a strong attraction to
overcome between the
valence electrons and the
nuclei of neighbouring
atoms.
Metals are not
soluble in water, as
the metallic bonds
are too strong to be
broken by the
attraction to the
water molecules.
The attraction of the metal atoms for the
valence electrons is not in any particular
direction (a non-directional force),
therefore metal atoms can move past one
another (without breaking the metallic
bond and disrupting the structure and
breaking the metal), and so metals are both
malleable and ductile.
Particles in metals
ATOMS
Bonding in
metals
METALLIC
METALS
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.Von EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Covalent and Metallic BondingDokument8 SeitenNotes On Covalent and Metallic Bondingselma samadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding and Properties of SubstancesDokument3 SeitenBonding and Properties of Substancesdan964Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 2: Quarter 3: Module 2Dokument5 SeitenChemistry 2: Quarter 3: Module 2Ann Lorraine Montealto SadoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDokument10 SeitenCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding and Structure: Group: Hammad Rashid Luqman Arshad Moeed AliDokument11 SeitenBonding and Structure: Group: Hammad Rashid Luqman Arshad Moeed AliPro IdiotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms CombiningDokument12 SeitenAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Study Notes Igcse EdexcelDokument34 SeitenChemistry Study Notes Igcse EdexcelAhmed KhalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2 Properties of Solids StudentDokument7 Seiten3.2 Properties of Solids StudentZachary Daniel UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond NotesDokument8 SeitenGiant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond Notesnihan.8558Noch keine Bewertungen
- Covalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileDokument17 SeitenCovalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileMahi QuaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesDokument16 SeitenIGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesChemistryKlipz100% (6)
- Csec Chemistry Notes 5Dokument3 SeitenCsec Chemistry Notes 5debestieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements, Compounds and AtomsDokument12 SeitenElements, Compounds and Atomsananya.arumugarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Privacy Statement Site Map Contact Us: GcseDokument8 SeitenPrivacy Statement Site Map Contact Us: GcsetashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding NotesDokument6 SeitenChemical Bonding NotesAyesha Awan100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding Board NotesDokument19 SeitenChemical Bonding Board NotesEmaan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 10.2 The Solid StateDokument14 SeitenLesson 10.2 The Solid StatefitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Dokument11 SeitenCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding in Solids Definition: Solid State ChemistryDokument9 SeitenBonding in Solids Definition: Solid State Chemistryhaimanot yibeltalNoch keine Bewertungen
- BondsDokument24 SeitenBondsPavithran Kamaleswari Year 10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODokument6 SeitenChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 ANSWERS SummaryDokument1 Seite06 ANSWERS SummaryJean AlmiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 3, ChemDokument6 SeitenCH 3, ChemAbdullah SalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giant Ionic and Giant CovalentDokument8 SeitenGiant Ionic and Giant CovalentSamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDokument6 SeitenDescribe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent Compoundsmadhuri pawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFDokument6 SeitenLesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFMia ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument3 SeitenChemistryMohammad Ammar GanatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covalent BondingDokument5 SeitenCovalent BondingNicola NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metallic Ionic and Covalent BondingDokument3 SeitenMetallic Ionic and Covalent BondinglesarouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their Properties PDFDokument13 SeitenIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their Properties PDFpieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic and Covalent BondingDokument39 SeitenIonic and Covalent Bondingchickuwa pawawawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEN CHEM 2 LESSON 3 Intermolecular Forces of Solids and Their Properties1.1Dokument27 SeitenGEN CHEM 2 LESSON 3 Intermolecular Forces of Solids and Their Properties1.1Loraine Castro0% (1)
- Bonding and Structure: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyDokument17 SeitenBonding and Structure: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyKhemou DjvickzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding Summary NotesDokument17 SeitenBonding Summary NotesaleenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Crystal Structure and Properties of Ionic CompoundsDokument2 SeitenThe Crystal Structure and Properties of Ionic CompoundskushanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Dokument3 SeitenComparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Fatima Ahmed-VeriterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and BondingDokument3 SeitenStructure and Bondingjordangrierson12Noch keine Bewertungen
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDokument16 SeitenO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Chemistry Week 8 Lesson 1Dokument5 SeitenGrade 10 Chemistry Week 8 Lesson 1Nikoli MajorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd QTR - Notes 3 - Chemical StructuresDokument7 Seiten3rd QTR - Notes 3 - Chemical StructuresDolor GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 Chemical BondingDokument10 SeitenGrade 9 Chemical BondingAmonique DaveyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - Chemical BondingDokument3 SeitenChemistry - Chemical BondingMegan TaylorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Solids: Cations AnionsDokument2 SeitenIonic Solids: Cations AnionsMyrna Getuaban SidonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding Structure..Dokument6 SeitenChemical Bonding Structure..rachelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding & Structure NotesDokument11 SeitenBonding & Structure NotesKamran TajbakhshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Dokument25 SeitenInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?lianghoo94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Is of Immense Significance To Us in Both Its Elemental Form and in The Combined FormDokument2 SeitenCarbon Is of Immense Significance To Us in Both Its Elemental Form and in The Combined FormkalloliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesDokument3 SeitenSummary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesAnonymous L7ZuSkR100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsDokument7 SeitenIGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsdanielmahsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical BondingDokument6 SeitenChemical BondingNoongju AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding A Level NotesDokument5 SeitenBonding A Level NotesWashington NyakaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquids and SolidsDokument107 SeitenLiquids and SolidsMorgan BowersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and BondingDokument18 SeitenCsec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and Bondingchelsea AlexandriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding and Naming CompoundsDokument10 SeitenBonding and Naming CompoundsDaniel BerryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry GSCE NotesDokument16 SeitenChemistry GSCE NotesMariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical BondingDokument8 SeitenChemical BondingAhmed AbdelghanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding IIDokument7 SeitenChemical Bonding IIdanielmahsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covalent Bonds Involve The Sharing of Electrons So That All Atoms Have 'Full Outer Shells'Dokument3 SeitenCovalent Bonds Involve The Sharing of Electrons So That All Atoms Have 'Full Outer Shells'love2read1Noch keine Bewertungen
- EnergyDokument12 SeitenEnergyapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Timetable 2019Dokument1 SeiteExam Timetable 2019api-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science As 90944 OverviewDokument2 SeitenScience As 90944 Overviewapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry AssessmentDokument7 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Assessmentapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Research TaskDokument4 SeitenChemistry Research Taskapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Student Handout 2017Dokument4 SeitenStudent Handout 2017api-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answers Hess and P-R QuestionsDokument7 SeitenAnswers Hess and P-R Questionsapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry AssessmentDokument6 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Assessmentapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Student Handout 2016 DraftDokument3 SeitenStudent Handout 2016 Draftapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eslwriting Video Worksheet CosmeticsDokument5 SeitenEslwriting Video Worksheet Cosmeticsapi-2185117410% (1)
- 2 5 Marking ScheduleDokument6 Seiten2 5 Marking Scheduleapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Compare and Contrast QuestionsDokument4 SeitenCompare and Contrast Questionsapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Painkillers WorksheetDokument2 SeitenPainkillers Worksheetapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- IUPAC HandoutDokument9 SeitenIUPAC HandoutjanellamaikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level 2 Basic Facts WorksheetDokument8 SeitenLevel 2 Basic Facts Worksheetapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- First Spontaneous Reactions WorksheetDokument2 SeitenFirst Spontaneous Reactions Worksheetapi-2185117410% (1)
- Enthalpy Level 2 RevisionDokument1 SeiteEnthalpy Level 2 Revisionapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- On WorksheetDokument2 SeitenOn Worksheetapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Chem Notes BDokument22 SeitenQuantitative Chem Notes Bapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Chem Notes Titrations OnlyDokument18 SeitenQuantitative Chem Notes Titrations Onlyapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Level 2 Basic Facts Worksheet AnswersDokument9 SeitenLevel 2 Basic Facts Worksheet Answersapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iron - Thiocyanate EquilibriumDokument7 SeitenIron - Thiocyanate Equilibriumapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Astronomy Starter (Literacy)Dokument7 SeitenAstronomy Starter (Literacy)api-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Entropy Notes and Exam QuestionsDokument3 SeitenEntropy Notes and Exam Questionsapi-218511741100% (1)
- 3 Exams For Benchmark Revision AnswersDokument14 Seiten3 Exams For Benchmark Revision Answersapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility AnswersDokument2 SeitenSolubility Answersapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physical PropertiesDokument1 SeitePhysical Propertiesapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Esterification ExperimentDokument2 SeitenEsterification Experimentapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fats and Oils NotesDokument1 SeiteFats and Oils Notesapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reflux, Distillation and SeparationDokument2 SeitenReflux, Distillation and Separationapi-218511741Noch keine Bewertungen
- Distance Between WeldsDokument2 SeitenDistance Between Weldshendraox3996100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics - Solutions PDFDokument56 SeitenFluid Mechanics - Solutions PDFJuba W Allen100% (1)
- JMBEC D31 JMB Environmental Consulting Pty LTD Company ProfileDokument11 SeitenJMBEC D31 JMB Environmental Consulting Pty LTD Company Profilevikas2504Noch keine Bewertungen
- GIR Courses For First Year-1 2019-2020 NIT TrichyDokument23 SeitenGIR Courses For First Year-1 2019-2020 NIT TrichyGirish ThiyagarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Element Cube Project: Side #1 - Symbol and NameDokument2 SeitenElement Cube Project: Side #1 - Symbol and NameMary Ann OrsuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gypsum ProductsDokument53 SeitenGypsum ProductsKiran KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAO 2000-12 - Schedule of Fees For RA 6969 (Chemical Substances and Hazardous Wastes)Dokument3 SeitenDAO 2000-12 - Schedule of Fees For RA 6969 (Chemical Substances and Hazardous Wastes)Pacific SpectrumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4HB0 01 Que 20140108Dokument32 Seiten4HB0 01 Que 20140108Lalith77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Paper Battery PresentationDokument16 SeitenSeminar Paper Battery Presentationrishabh dixit100% (1)
- 0819492485Dokument405 Seiten0819492485arulmurugu100% (1)
- Albida EP2Dokument2 SeitenAlbida EP2dassoumennNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry-Week 3 - QuizizzDokument2 SeitenGeneral Chemistry-Week 3 - QuizizzAmanda NauraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HCL PDFDokument13 SeitenHCL PDFjoycepeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timeline of Atomic NatureDokument19 SeitenTimeline of Atomic NatureLesly Justin FuntechaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2.3 FormativeDokument2 SeitenTopic 2.3 Formativeishaan50% (2)
- Virgo Evs Valve BrochureDokument4 SeitenVirgo Evs Valve Brochureshashikanth79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 8 States of MatterDokument9 SeitenUnit 8 States of Mattersyaifulzubir1986100% (1)
- LC NMR LectureDokument18 SeitenLC NMR LectureGeetha Anjali100% (1)
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Adefovir DipivDokument6 SeitenSpectrophotometric Determination of Adefovir DipivEbruÇetinkayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element Analysis of Composite Pressure Vessels With A Load Sharing Metallic LinerDokument9 SeitenFinite Element Analysis of Composite Pressure Vessels With A Load Sharing Metallic Linervsraju2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Is SP 23 1982 PDFDokument151 SeitenIs SP 23 1982 PDFMano MaddulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Questions - NDDCDokument2 SeitenSample Questions - NDDCKelvin ChuksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 Task 1 Lesson Plan PPDokument9 SeitenModule 3 Task 1 Lesson Plan PPapi-380746081Noch keine Bewertungen
- EQMS Consulting Limited (Testing Laboratory)Dokument2 SeitenEQMS Consulting Limited (Testing Laboratory)Afrin NadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmometry ElectrochemistryDokument25 SeitenOsmometry ElectrochemistryMohamed MidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix 7.: Nutritional Goals For Age-Sex Groups Based On Dietary Reference Intakes &Dokument2 SeitenAppendix 7.: Nutritional Goals For Age-Sex Groups Based On Dietary Reference Intakes &GloryJaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM213A Win22 HW2Dokument4 SeitenCHEM213A Win22 HW2attiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rubric HM FR FR MotultechDokument2 SeitenRubric HM FR FR MotultechNiang Abdoul malickNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITA 2012 Sir Alan Muir Wood LectureDokument10 SeitenITA 2012 Sir Alan Muir Wood LectureFlaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHHW Grade 11 SCDokument20 SeitenWHHW Grade 11 SCssssNoch keine Bewertungen