Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Understanding Macronutrients Project
Hochgeladen von
api-253532759Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Understanding Macronutrients Project
Hochgeladen von
api-253532759Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
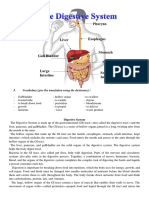
Carbohydrates The digestion and absorption of carbohydrates starts in the mouth where salivary amylase is secreted by the salivary
glands, which breaks down starch into shorter polysaccharides and maltose, which is a disaccharide. Then the food moves through the esophagus into the stomach where salivary amylase, is denatured by hydrochloric acid. At the same time, pancreatic amylase is secreted into the small intestine where it will come in contact with the chyme from the stomach. In the small intestine, pancreatic amylase which is produce by the pancreas continues to break down starch into maltose. It is digested by the enzyme maltase to produce glucose, which is absorbed by the enterocytes and enters the bloodstream. The enterocytes also absorb fructose and galactose to be absorbed in the bloodstream and thus to the liver, producing glucose to be used as energy. The undigested carbohydrates of fibers are partially digested by bacteria in the large intestine but most is excreted as waste. Fats The digestion and absorption of fats also start in the mouth with the salivary glands secreting salivary lipase when food is being mechanically digested by chewing. After food is swallowed, it reaches the stomach and is continued to be broken down into fat droplets by gastric lipase. Eating stimulates the gall bladder to release bile into the small intestine to be mixed with chyme from the stomach. Bile is produced in the liver and aids the process of fat digestion. Once the chyme enters the small intestine, the pancreas releases pancreatic lipase into the small intestine to separate the triglycerides into two free fatty acids and one monoglyceride. Monoglycerides are absorbed by the enterocytes and are absorbed by the bloodstream. The free fatty acids are transported by micelles, or spherical shaped molecules, to the mucosal cells for absorption. The lymph system is used in the digestion of fats because chylomicrons, which are
lipoproteins composed of fat-soluble vitamins, need to be removed of lipids so that they can be more easily absorbed to the bloodstream. Lipoprotein lipase further removes fats from chylomicrons and separates triglycerides so that it will be able to pass the cell membrane of muscle or adipose cells easily, where triglycerides are then reformed once inside the cell. Undigested food from the small intestine is transferred to the large intestine where water is absorbed and eventually excreted as waste. Proteins The first step in the digestion and absorption of proteins is the mechanical action of chewing in the mouth where food is moistened with saliva. When food enters the stomach, hydrochloric acid denaturizes or uncoils the strands of amino acids. The pepsin enzyme is also released in the stomach to hydrolize proteins into shorter polypeptide chains and single amino acids. When chyme enters the small intestine, the protease enzyme separates polypeptides into single amino acids so that they can be absorbed by mucosal cells to enter the bloodstream. The absorbed amino acids are transported to the liver which helps regulate them according to metabolism and other bodily needs. Undigested food from the small intestine is transferred to the large intestine where water is absorbed and eventually excreted as waste.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- All Therapy 200 RATOS 2010Dokument284 SeitenAll Therapy 200 RATOS 2010Bhargavi SunkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument8 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyDanielle V. Cercado100% (1)
- Chemistry Project File: Mannat GuptaDokument14 SeitenChemistry Project File: Mannat Gupta33 Samaksh 12 th BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bibliography SaulogDokument2 SeitenBibliography SaulogJedgar SaulogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 6 Case Study Pancreatic CancerDokument20 SeitenGroup 6 Case Study Pancreatic CancerMarcel TabucolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal TuberculosisDokument36 SeitenAbdominal TuberculosisImmanuel50% (2)
- KlatskinDokument24 SeitenKlatskinArian WawolumajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic PancreatitisDokument2 SeitenChronic PancreatitisIbraheem SairiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avian DigestionDokument18 SeitenAvian DigestionWilliam RobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growth Inhibition of Probiotics On The Growth of Streptococcus MutansDokument4 SeitenGrowth Inhibition of Probiotics On The Growth of Streptococcus MutansSi EllaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innovative Teaching Manuel: Poh-Imkv (XW BLM-C - Nsâ Cmk-Am-Ä - Ä A - ) - Z - Nsâ LSDokument5 SeitenInnovative Teaching Manuel: Poh-Imkv (XW BLM-C - Nsâ Cmk-Am-Ä - Ä A - ) - Z - Nsâ LSsandhyaaneesh2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Educational Brochure 12Dokument2 SeitenEducational Brochure 12Kourtney MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System Part 2Dokument56 SeitenDigestive System Part 2Raunak TimilsinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11th Zoology Ps Answer Key For Quarterly Exam 2019 Question Paper Shri Krishna English MediumDokument11 Seiten11th Zoology Ps Answer Key For Quarterly Exam 2019 Question Paper Shri Krishna English Mediumsri thamizhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Class-X CHAPTER-1, Life Processes A. Give Reasons, WhyDokument2 SeitenWorksheet Class-X CHAPTER-1, Life Processes A. Give Reasons, WhyHima ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 8Dokument44 SeitenThe Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 8SunnyReduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive SystemDokument25 SeitenDigestive Systembazaar9Noch keine Bewertungen
- LESSON PLAN Bsed 3bDokument12 SeitenLESSON PLAN Bsed 3bRjane CañeteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anorectal MalformationsDokument52 SeitenAnorectal MalformationsedrinsneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The Digestive System-NotesDokument78 SeitenAnatomy of The Digestive System-NotesDerrick njugunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver CirhosisDokument15 SeitenLiver CirhosisMoslem abd alzahra aziz AlsialwyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alimentary Tract-22073Dokument4 SeitenAlimentary Tract-22073daniel balteanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPC PancreatitisDokument67 SeitenCPC PancreatitisM. Baidar SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication - ALT-Template - Docusate SodiumDokument1 SeiteMedication - ALT-Template - Docusate SodiumNancyAmissahNoch keine Bewertungen
- JaundiceDokument5 SeitenJaundicemohamed mowafeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caj Baru Berperingkat Kos PembedahanDokument109 SeitenCaj Baru Berperingkat Kos PembedahanKhairul HaizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrectomy. (N.D.) - Retrieved From Encycopedia of Surgery:: Why Is A Partial Gastrectomy Performed?Dokument7 SeitenGastrectomy. (N.D.) - Retrieved From Encycopedia of Surgery:: Why Is A Partial Gastrectomy Performed?Angel Joy CATALAN (SHS)Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 - The Digestive SystemDokument21 Seiten3.1 - The Digestive SystemJavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- KJFP003 01 06Dokument17 SeitenKJFP003 01 06Mai Thiện NhânNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structures of The ForegutDokument13 SeitenStructures of The ForegutJatan KothariNoch keine Bewertungen