Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Graph Theory
Hochgeladen von
venki2490 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
80 Ansichten33 SeitenThis document defines and describes several key concepts in graph theory including graphs, subgraphs, paths, trees, co-trees, and different types of incidence matrices. Specifically, it defines a graph as the interconnection of all network elements, with a rank of N-1. It describes subgraphs, paths, trees which are connected oriented subgraphs without loops, and co-trees which are the complement of trees. It also lists several types of incidence matrices used to represent element-node, bus, branch-path, cutset, and loop relationships in a graph.
Originalbeschreibung:
graph thery
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document defines and describes several key concepts in graph theory including graphs, subgraphs, paths, trees, co-trees, and different types of incidence matrices. Specifically, it defines a graph as the interconnection of all network elements, with a rank of N-1. It describes subgraphs, paths, trees which are connected oriented subgraphs without loops, and co-trees which are the complement of trees. It also lists several types of incidence matrices used to represent element-node, bus, branch-path, cutset, and loop relationships in a graph.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
80 Ansichten33 SeitenGraph Theory
Hochgeladen von
venki249This document defines and describes several key concepts in graph theory including graphs, subgraphs, paths, trees, co-trees, and different types of incidence matrices. Specifically, it defines a graph as the interconnection of all network elements, with a rank of N-1. It describes subgraphs, paths, trees which are connected oriented subgraphs without loops, and co-trees which are the complement of trees. It also lists several types of incidence matrices used to represent element-node, bus, branch-path, cutset, and loop relationships in a graph.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 33
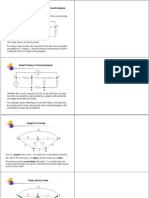
Graph : Graph is a interconnection of all elements of the network ,by replacing all
elements with a line segment
Rank : The rank of a graph is N-1
Sub graph : Any subset of elements of the graph is called a sub graph. A sub graph
is said to be proper if it is consists of strictly less than all the elements and nodes of
the graph
Path : A path is defined as a sub graph of connected elements such that not more
than two elements are connected to any one node.
Tree :A Tree is an oriented connected sub graph of an graph containing all the nodes
of the graph,but containing no loops .A tree has N-1 branches.The branches of a
tree are called twigs and remaining branches of the graph are called links/chords
Co Tree : The links forms a sub graph .Co Tree is the complement of tree .There is a
co-tree for every tree
b = n-1
No of links ,l=e-b
l = e-n+1
Incidence Matrices
Element node Incidence matrix
Bus incidence matrix
Branch path Incidence matrix
Basic cut set Incidence matrix
Augmented cutest Incidence matrix
Basic loop Incidence matrix
Augment loop Incidence matrix
Augmented cut-set Incidence matrix (B)
In the Basic cutest Incidence matrix ,the no of cutsets equal to the no of branches,The no of cutsets can be
made equal to the no of elements by introducing fictitious or imaginary cutsets called Tie-cuts.
Each Tie cut set contains only one link of the connected graph
Augmented loop incidence matrix
The utility of these augmented incidence matrices will be seen when non
singular transformation method of obtaining network matrices
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Aph Theory PDFDokument27 SeitenAph Theory PDFjhansilaxman201367% (6)
- Network Topology: PPT By:-D V S RamanjaneyuluDokument25 SeitenNetwork Topology: PPT By:-D V S RamanjaneyuluRamanjaneyulu Anji YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit2 - NewDokument64 SeitenUnit2 - NewHarsha AnantwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture27Dokument24 SeitenLecture27Kethu SaikumarreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Theory-Unit1Dokument38 SeitenGraph Theory-Unit1Kranthi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit2 KCVDokument47 SeitenUnit2 KCVsanoopmkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topology Unit IIIDokument21 SeitenNetwork Topology Unit IIIMOHANDAS AUDIRALANoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit V - 1 - Graph TheoryDokument25 SeitenUnit V - 1 - Graph TheoryShirisha marasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Theory - GATE Study Material in PDFDokument9 SeitenGraph Theory - GATE Study Material in PDFTestbook Blog0% (1)
- Network Analysis VTU NotesDokument47 SeitenNetwork Analysis VTU NotesSagar S Poojary50% (2)
- Network Analysis - ECE - 3rd Sem - VTU - Unit 2 - Network Topology - Ramisuniverse, RamisuniverseDokument20 SeitenNetwork Analysis - ECE - 3rd Sem - VTU - Unit 2 - Network Topology - Ramisuniverse, Ramisuniverseramisuniverse71% (7)
- Netwrok Theory: Incidence Matrix (A)Dokument1 SeiteNetwrok Theory: Incidence Matrix (A)Amit RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2. Network TopologyDokument7 SeitenUnit 2. Network TopologySam AndersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network MatricesDokument65 SeitenNetwork MatricesMary Morse100% (2)
- Network TopologyDokument44 SeitenNetwork TopologyBrijesh B NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structure UNIT VDokument20 SeitenData Structure UNIT VMogili sivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NA Unit-IIIDokument26 SeitenNA Unit-IIIvijayalakshmiv VEMURINoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2Dokument14 SeitenTutorial 2rickyarya2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Theory in Electrical EngineeringDokument25 SeitenGraph Theory in Electrical EngineeringPappuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes: Power System AnalysisDokument97 SeitenLecture Notes: Power System AnalysisROHIT SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iare CMPS Lecture Notes PDFDokument98 SeitenIare CMPS Lecture Notes PDFjhon smithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psa PDFDokument182 SeitenPsa PDFPraveen Kumar pkNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCE 6237 Advanced Power System Analysis: Lecture One: Section ThreeDokument26 SeitenPCE 6237 Advanced Power System Analysis: Lecture One: Section ThreeBedasa ToleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Material II 23-Jul-2020 GraphBasics1Dokument33 SeitenReference Material II 23-Jul-2020 GraphBasics1Vaibhav GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To CTPSA QuestionBankDokument61 SeitenSolutions To CTPSA QuestionBankkrishna moorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph TheoryDokument8 SeitenGraph TheoryMoumouni SawadogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-1 Network TopologyDokument205 SeitenModule-1 Network Topologyabdul12rehamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologyDokument47 SeitenNetwork TopologySujeet Kumar100% (1)
- Lecture 27 StudentDokument6 SeitenLecture 27 StudentsharadbhupeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph TheoryDokument27 SeitenGraph TheoryYash SadbhaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication TopologyDokument6 SeitenCommunication TopologyKrishna ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE201 Matrix AnalysisDokument18 SeitenEE201 Matrix AnalysisAeshwrya PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Theory 1Dokument193 SeitenNetwork Theory 1Abhishek MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DM Unit 1Dokument31 SeitenDM Unit 1Rushikesh ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Analysis: Sharique Najam MuzaffarDokument32 SeitenNetwork Analysis: Sharique Najam Muzaffarmanzur_a_m100% (1)
- Power System Analysis: Lecture NotesDokument12 SeitenPower System Analysis: Lecture NotesalfredzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit V: Trees (Refer T-1)Dokument28 SeitenUnit V: Trees (Refer T-1)Bum TumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formation of Power System Network MatrixDokument23 SeitenFormation of Power System Network MatrixMohammed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Binary TreeDokument35 SeitenBinary Treesrpaabinaya80529Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eee-Vii-computer Techniques in Power System Analysis (10ee71) - SolutionDokument106 SeitenEee-Vii-computer Techniques in Power System Analysis (10ee71) - Solutionanirudh.r.s.100% (3)
- Mod 2 (Aad)Dokument26 SeitenMod 2 (Aad)PonnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structures - MOD VDokument42 SeitenData Structures - MOD VManikandan SriramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Top Trees For Easy Programming of Tree AlgorithmsDokument12 SeitenUsing Top Trees For Easy Programming of Tree AlgorithmsnothardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjacency ListDokument5 SeitenAdjacency ListMinahel Noor FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prims AlgorithmsDokument3 SeitenPrims AlgorithmsnofeelingrahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Theory ModifiedDokument83 SeitenGraph Theory ModifiedKrishna Reddy Y.VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discret Math Unit 4-6Dokument8 SeitenDiscret Math Unit 4-6Erick InfanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Techniques in Power System AnalysisDokument144 SeitenComputer Techniques in Power System Analysismerebook100% (1)
- GraphDokument15 SeitenGraphmugiii321Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Nandi Branch:-Ee (2 Year) ROLL NO. - 31Dokument14 SeitenDeep Nandi Branch:-Ee (2 Year) ROLL NO. - 31DossDossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itt 05213Dokument12 SeitenItt 05213Genes GastoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics of GraphsDokument62 SeitenMathematics of GraphsBea Santos BarrozoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Standard 12 Chapter 2Dokument20 SeitenCambridge Standard 12 Chapter 2Raymond Zhu100% (1)
- Chapter - 12: Graph Matrices AND ApplicationsDokument24 SeitenChapter - 12: Graph Matrices AND ApplicationsPadmaja RakkisuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GraphsDokument39 SeitenGraphsjoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0009.Dokument17 SeitenWa0009.aayush waghereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises of Matrices and Linear AlgebraVon EverandExercises of Matrices and Linear AlgebraBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Ac DistributionDokument16 SeitenAc Distributionvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Power PlantDokument14 SeitenGas Power Plantvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Control System Questions and AnswersDokument10 SeitenControl System Questions and Answersvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- TariffsDokument49 SeitenTariffsvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Traveling Wave: Transient OvervoltagesDokument26 SeitenTraveling Wave: Transient Overvoltagesvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Substation ComponentsDokument44 SeitenSubstation Componentsvenki249100% (1)
- Lightning and Over Voltages ProtectionDokument24 SeitenLightning and Over Voltages Protectionvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- DistributionDokument29 SeitenDistributionvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Supply Systems: Viz., Transmission and Distribution. The PurposeDokument18 SeitenSupply Systems: Viz., Transmission and Distribution. The Purposevenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Power PlantDokument27 SeitenThermal Power Plantvenki249100% (1)
- Load Characteristics AND Load ForecastingDokument32 SeitenLoad Characteristics AND Load Forecastingvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Programming For EngineersDokument30 SeitenMatlab Programming For Engineersvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank Transmission and DistributionDokument7 SeitenQuestion Bank Transmission and Distributionvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power Flow Through TR LineDokument8 SeitenPower Flow Through TR Linevenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- ExamplesDokument32 SeitenExamplesvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab LoopsDokument30 SeitenMatlab Loopsvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alternating Current, Power Distribution, and Voltage SystemsDokument32 SeitenAlternating Current, Power Distribution, and Voltage Systemsvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab ProgrammingDokument312 SeitenMatlab Programmingwkpfckgw80% (5)
- Distribution Automation NewDokument21 SeitenDistribution Automation Newvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Substation Components and Bus SchemesDokument32 SeitenSubstation Components and Bus Schemesvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psoc 2015 NewDokument20 SeitenPsoc 2015 Newvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- PLC FinalDokument70 SeitenPLC Finalvenki249Noch keine Bewertungen
- International Standard: Iso/Iec 7816-2Dokument16 SeitenInternational Standard: Iso/Iec 7816-2Anwar MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Minutes of MeetingDokument3 SeitenSample Minutes of MeetingMohamad AzmeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tawjihi 7Dokument55 SeitenTawjihi 7api-3806314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Management Systems and Strategies by Dipak Kumar BhattacharyyaDokument385 SeitenPerformance Management Systems and Strategies by Dipak Kumar Bhattacharyyasayal96amrit100% (3)
- FM Assignment 17-M-518 MMM - Eicher MotorDokument33 SeitenFM Assignment 17-M-518 MMM - Eicher MotorTrilokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Geosynthetics in Pavement DesignDokument7 SeitenApplication of Geosynthetics in Pavement DesignAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022+ACCF+111+Class+test+2 Moderated+versionDokument8 Seiten2022+ACCF+111+Class+test+2 Moderated+versionLucas LuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Sniffing - Telegraph+Dokument9 SeitenGSM Sniffing - Telegraph+Sridhar PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5 Flight of Projectile, Air Resistance Neglected: OverviewDokument7 SeitenLesson 5 Flight of Projectile, Air Resistance Neglected: OverviewNadjer C. AdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- GE2410 Student Booklet (UpdatedDec27)Dokument88 SeitenGE2410 Student Booklet (UpdatedDec27)markhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic V Mangotara DigestDokument3 SeitenRepublic V Mangotara DigestMickey Ortega100% (1)
- Case For Overhead and DistributionDokument2 SeitenCase For Overhead and DistributionBhargav D.S.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reducing Motor Vehicle Crashes in B.C.Dokument260 SeitenReducing Motor Vehicle Crashes in B.C.Jeff NagelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serie10 ElecDokument75 SeitenSerie10 Elecmealier severineNoch keine Bewertungen
- PA SystemDokument4 SeitenPA SystemSnehal DambhareNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB PROGRAMMING An Engineering PerspectiveDokument129 SeitenMATLAB PROGRAMMING An Engineering PerspectivelolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nickel 200 201 PDFDokument20 SeitenNickel 200 201 PDFwdavid81Noch keine Bewertungen
- EmbOS GenericDokument324 SeitenEmbOS Genericbogd33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iecex Bas 13.0069XDokument4 SeitenIecex Bas 13.0069XFrancesco_CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dede - (2010) - Comparing Frameworks For 21st Century Skills PDFDokument16 SeitenDede - (2010) - Comparing Frameworks For 21st Century Skills PDFNaing Lynn HtunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Audit, Compliance& Ethics and Risk Management: Section 1) 1.1)Dokument6 SeitenInternal Audit, Compliance& Ethics and Risk Management: Section 1) 1.1)Noora Al ShehhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TreatmentDokument14 SeitenHeat TreatmentAkhilesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mrs. Saba Khan 15 Shahbad Diwan Khana, Bareilly, City, Bareilly, Bareilly, Utt AR PRADESH, 243003,9219172265Dokument28 SeitenMrs. Saba Khan 15 Shahbad Diwan Khana, Bareilly, City, Bareilly, Bareilly, Utt AR PRADESH, 243003,9219172265amitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reconductoring Using HTLS Conductors. Case Study For A 220 KV Double Circuit Transmission LINE in RomaniaDokument7 SeitenReconductoring Using HTLS Conductors. Case Study For A 220 KV Double Circuit Transmission LINE in RomaniaJose ValdiviesoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dinengdeng RecipeDokument1 SeiteDinengdeng RecipeFuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Would You Like Eddy Current, Video & Strip Chart in One Portable Case?Dokument2 SeitenWould You Like Eddy Current, Video & Strip Chart in One Portable Case?Daniel Jimenez MerayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure Mastertile TilingDokument48 SeitenBrochure Mastertile TilingMaha Mufleh100% (1)
- Case Study-BPPVDokument97 SeitenCase Study-BPPVArbie Jacinto83% (6)
- 3 - RA-Erecting and Dismantling of Scaffolds (WAH) (Recovered)Dokument6 Seiten3 - RA-Erecting and Dismantling of Scaffolds (WAH) (Recovered)hsem Al EimaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prishusingh Blogspot Com 2024 03 Digital-Marketing-Course HTMLDokument12 SeitenPrishusingh Blogspot Com 2024 03 Digital-Marketing-Course HTMLsudharaj86038Noch keine Bewertungen