Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Amino Acids
Hochgeladen von
denerys2507986Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Amino Acids
Hochgeladen von
denerys2507986Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
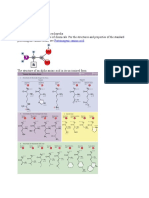
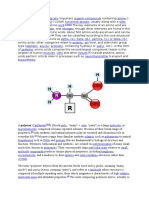
Amino acids (/mino/, /mano/, or /mno/) are biologically important organic compounds composed
of amine (-NH
2
) and carboxylic acid (-COOH) functional groups, along with a side-chain specific to each
amino acid. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, though other
elements are found in the side-chains of certain amino acids. About 500 amino acids are known
[1]
and can be
classified in many ways. They can be classified according to the core structural functional groups' locations
as alpha- (-), beta- (-), gamma- (-) or delta- (-) amino acids; other categories relate topolarity, pH level, and
side-chain group type (aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form ofproteins,
amino acids comprise the second-largest component (water is the largest) of human muscles, cells and
other tissues.
[2]
Outside proteins, amino acids perform critical roles in processes such
as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Polypeptide: A Is An Unbranched Chain of Amino AcidsDokument4 SeitenPolypeptide: A Is An Unbranched Chain of Amino AcidsJerlindassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino AcidDokument69 SeitenAmino AcidTasmih Rob MowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino AcidDokument17 SeitenAmino AcidAnonymous E4Rbo2sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino AcidDokument6 SeitenAmino AcidheiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acid: Navigation SearchDokument11 SeitenAmino Acid: Navigation SearchSamiuddin YezdaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acid and PolymerDokument2 SeitenAmino Acid and PolymerFrederickDionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino AcidDokument5 SeitenAmino AcidRobin TimkangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Biochemistry - 3rd Year Chem - Protein Structure and Function - Chapter-3Dokument21 Seiten3 - Biochemistry - 3rd Year Chem - Protein Structure and Function - Chapter-3MD. SAJID GHUFRANNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Mi No AcidsDokument38 SeitenA Mi No AcidspavanavulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of Amino Acids - ProteinsDokument81 SeitenChemistry of Amino Acids - ProteinsgurmroadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 Proteins and Amino Acids 1Dokument29 SeitenLecture 3 Proteins and Amino Acids 1Caamir Dek HaybeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proteins: Amino AcidsDokument14 SeitenProteins: Amino AcidsShivam KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acid 22Dokument12 SeitenAmino Acid 22Ansh SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Title of ExperimentDokument14 SeitenA. Title of ExperimentPutri SalsabilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acid and Protein Chemistry - Part 1Dokument15 SeitenAmino Acid and Protein Chemistry - Part 1historymonday10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chem ProjectDokument9 SeitenChem Projectguptaom9839Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Chapter 4Dokument17 SeitenBiochemistry Chapter 4Jayson AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino AcidsDokument1 SeiteAmino AcidsSoorya SureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein and Amino Acid Chemistry: What Are PROTEINS?Dokument7 SeitenProtein and Amino Acid Chemistry: What Are PROTEINS?Jayson AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein UoP 22-23Dokument35 SeitenProtein UoP 22-23Maryam AyazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constitution of Sovereignty: The Summary: Submitted By: Kervy Jay T. AgraviadorDokument7 SeitenConstitution of Sovereignty: The Summary: Submitted By: Kervy Jay T. AgraviadorKervy Jay AgraviadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acid: Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine HistidineDokument16 SeitenAmino Acid: Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine HistidineCrystal GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Biochemistry 2023-2024Dokument26 SeitenLecture 1 Biochemistry 2023-2024fatimakareem0623Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bpo C Chapter 23Dokument72 SeitenBpo C Chapter 23Josiah JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Titration of Amino Acids and PeptidesDokument2 SeitenTitration of Amino Acids and PeptidesAbi Diciembre Briones100% (1)
- Amino Acids: M. Sc. Ist SemDokument17 SeitenAmino Acids: M. Sc. Ist SemGaming StuffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Chapter 4Dokument16 SeitenBiochemistry Chapter 4Jayson AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids: ChemistryDokument6 SeitenAmino Acids: ChemistryCarlosSchlozJuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND PROPERTIES OF AMINO ACIDSDokument8 SeitenLecture 2 STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND PROPERTIES OF AMINO ACIDSSafura IjazNoch keine Bewertungen
- ContentsDokument5 SeitenContentsVasile CuprianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acid and ProtienDokument25 SeitenAmino Acid and ProtienAli SeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProteinsDokument3 SeitenProteinsJun Hong TeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sir Julius Amino AcidsDokument30 SeitenSir Julius Amino AcidsApril Marie AlcazarenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids PropertiesDokument15 SeitenAmino Acids PropertiesNadia HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCHM 201 Amino AcidDokument28 SeitenBCHM 201 Amino AcidHabila OniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grey and Pink Scientific Project Presentation - 20240128 - 204009 - 0000Dokument13 SeitenGrey and Pink Scientific Project Presentation - 20240128 - 204009 - 0000Regha PrayogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids: UNIT - 14 BiomoleculesDokument12 SeitenAmino Acids: UNIT - 14 BiomoleculesG.V.GokulakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids: UNIT - 14 BiomoleculesDokument12 SeitenAmino Acids: UNIT - 14 BiomoleculesPREJAN RAJANoch keine Bewertungen
- Foods and Nutrition Paper OneDokument119 SeitenFoods and Nutrition Paper OneNaduku EridadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Biochemistry Aminoacids & Proteins-1Dokument22 SeitenUnit 1 Biochemistry Aminoacids & Proteins-1kamsjain6802Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lif101 6Dokument34 SeitenLif101 6Shubham MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids, Essential Amino Acids, Isoelectric Point, ZwitterionsDokument10 SeitenAmino Acids, Essential Amino Acids, Isoelectric Point, ZwitterionsZafar IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview PDFDokument160 SeitenOverview PDFJoy Mazo FaderagaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Week 7 - ProteinsDokument6 SeitenBiochemistry Week 7 - ProteinsMicah JadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Amino AcidsDokument3 SeitenEssential Amino AcidsNurshamimi JaafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec. 1Dokument8 SeitenLec. 1Dr. Mohamed ShamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids: Amino Acids: Are Organic Molecules That Are The Building Block ofDokument69 SeitenAmino Acids: Amino Acids: Are Organic Molecules That Are The Building Block ofjkc collegeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioquímica 1: Bioelementos Y Biomoléculas 1. Bioelementos O Elementos Biogenésicos 1.2. SecundariosDokument9 SeitenBioquímica 1: Bioelementos Y Biomoléculas 1. Bioelementos O Elementos Biogenésicos 1.2. SecundariosBRITALDO CAMPOS HUAMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Word Protein Was Suggested (Coined) byDokument2 SeitenThe Word Protein Was Suggested (Coined) byBalaji Prasanna KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mikrobiologi: Karakteristik, Peran MolekulDokument28 SeitenMikrobiologi: Karakteristik, Peran MolekulMuhammad Dorojatun KarimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proteins For NursingDokument7 SeitenProteins For Nursingroshanpakistan712Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids Peptides and ProteinsDokument27 SeitenAmino Acids Peptides and ProteinsabctutorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino AcidsDokument29 SeitenAmino AcidsSangay ChodenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio-Chemical Engineering: CHE-422 Date: 08/03/2018Dokument33 SeitenBio-Chemical Engineering: CHE-422 Date: 08/03/2018Atif MehfoozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry ProteinDokument71 SeitenBiochemistry Proteinurooj ilyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Midterm ReviewerDokument19 SeitenBiochem Midterm ReviewerERIKA ROSE ALEJONoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical Engineering: Lect. 2Dokument43 SeitenBiochemical Engineering: Lect. 2Mohamed AbdelaalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids and ProteinDokument44 SeitenAmino Acids and ProteinAliyu MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Peptides: Volume II Synthesis, Occurrence, and Action of Biologically Active PolypeptidesVon EverandThe Peptides: Volume II Synthesis, Occurrence, and Action of Biologically Active PolypeptidesNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Unicellular OrganismDokument1 SeiteA Unicellular Organismdenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Animals Phylum /P Ɒ Rɪfərə/ Mesohyl Cells Nervous Digestive Circulatory SystemsDokument1 SeiteAnimals Phylum /P Ɒ Rɪfərə/ Mesohyl Cells Nervous Digestive Circulatory Systemsdenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Subatomic Electric Charge Elementary Charge Nucleus Atom Neutrons Nucleons Atomic Number Element Ernest RutherfordDokument1 SeiteSubatomic Electric Charge Elementary Charge Nucleus Atom Neutrons Nucleons Atomic Number Element Ernest Rutherforddenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- BacteriaDokument1 SeiteBacteriadenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protoplasm Is The Living Contents of ADokument1 SeiteProtoplasm Is The Living Contents of Adenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon (From: Greatly Upgraded DatabaseDokument1 SeiteCarbon (From: Greatly Upgraded Databasedenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Myst and MythDokument3 SeitenMyst and Mythdenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Common Collocations With Hunting-HunterDokument2 SeitenCommon Collocations With Hunting-Hunterdenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- ED - A Narrow Fellow in The GrassDokument3 SeitenED - A Narrow Fellow in The Grassdenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Literacy. The Book Addressed Some Topics That I Thought Were ReallyDokument11 SeitenLiteracy. The Book Addressed Some Topics That I Thought Were Reallydenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emily Dickinsons Poems Theme of Nature2Dokument17 SeitenEmily Dickinsons Poems Theme of Nature2denerys2507986100% (1)
- A Narrative of The Life of Frederick DouglassDokument10 SeitenA Narrative of The Life of Frederick Douglassdenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- CommentaryDokument529 SeitenCommentarydenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- What To The Slave Is The Fourth of July-NarrativeDokument9 SeitenWhat To The Slave Is The Fourth of July-Narrativedenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- E. Dickinson-Theme of LoveDokument9 SeitenE. Dickinson-Theme of Lovedenerys2507986Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Narrative of Life of Frederick Douglass-Criticism of SlaveryDokument10 SeitenA Narrative of Life of Frederick Douglass-Criticism of Slaverydenerys2507986100% (1)