Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
NSC 200 Cell Presentation
Hochgeladen von
api-2523422790 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten17 SeitenOriginaltitel
nsc 200 cell presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten17 SeitenNSC 200 Cell Presentation
Hochgeladen von
api-252342279Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 17
Cells
The building blocks of life
By Jessie Jones and Kayla
Hedin
Prokaryotic cells
2 different types
Bacteria
Archaea
No organized nucleolus
DNA is all just clumped in an area
No organelles, chloroplasts, or
mitochondria.
Very small
Eukaryotic cells
2 general types
Mitosis
Meiosis
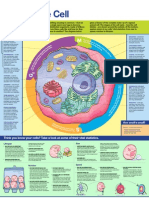
Classic Cell
Nucleus
Organelles
Extra
http://www.biology4kids.com/files/micro_eukar
yote.html
Cell Theory
All living things are made of cells
Unique Characteristics of
Plant Cells
Cell wall
Made of cellulose (a type of sugar)
Strong and rigid
Protects the cell
Large empty spaces in the cellulose make it
freely permeable
Plant Cells
Cell membrane
Against the cell wall
Made of protein and lipids
Selectively permeable
Controls the materials that come in and out
of the cell
Plant Cells
Cytoplasm
Jelly-like substance contained by the cell
membrane
Where chemical reactions take place
Organelles and granules are located here
Plant Cells
Chloroplast
Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment
Produce food
Traps light energy to make food (using
photosynthesis)
Plant and Animal Cells
Cell Membrane
Surrounds the cell, but has small holes to allow
things to come in and out
Cytoplasm
The fluid that fills a cell
Cell organelles are suspended in it
Has different molecules that keep the cell
working
It uses its enzymes to break down larger
molecules
Plant and Animal
Nucleus
Command center/ brain of the cell
Controls eating, movement, and
reproduction
In the middle of the cytoplasm
Chromosomes
Genetic information
Made up of DNA
Found in the nucleus
Plant and Animal
Centrioles
Two of them in animal cells
Made of microtubules
Move towards opposite ends of the nucleus
during cell division
Ribosomes
Protein builders/synthesizers
Can be found floating in the cytoplasm
Can be found on the endoplasmic
reticulum
Plant and Animal
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell
Digestive system
Take in nutrients, breaks them down, creates
energy
Process known as cellular respiration
Very small
Thousands can be found in some cells
Has two membranes-the outer membrane
covers ant contains the organelle, the inner
membrane folds many times to increase surface
area inside the organelle
Plant and Animal
Endoplasmic reticulum
Like the packaging system
Smooth ER-storage organelle, stores steroids
and ions
Rough ER-have ribosomes attached, help in the
process of protein synthesis and
packaging
Golgi
Another packaging cell like the ER
Gathers simple molecules and makes them
more complex by combining them
Then packages them in vesicles to store for later
use or send out of the cell
Plant and Animal
Vacuoles
Storage bubbles for nutrients or waste
products
Larger in plants
Microfilaments
Long, thin, stringy proteins
Everywhere in the cell
Help to form the structure of the cell
Help in moving the cell
Plant and Animal
Microtubules
Proteins that work with microfilaments
Thick, strong spirals
Part of centrioles and help the cell divide
Cilia and Flagella
Cilia-little hairs on the outside of some cells
that flap back and forth to help the cell
move
Flagella-long, thick tails that whip and twirl
to push the cell along
Plant and Animal
Lysosomes
In animal cells
Hold enzymes created by the cell
Their purpose is to digest things
Enzyme proteins created in the rough
ERpackaged in a vesicle and sent to the
GolgiGolgi creates the digestive enzyme
and pinches off a vesiclethe lysosome
Sources
http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_m
embrane.html
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Biomagnetic Pair Manual English PDFDokument79 SeitenBiomagnetic Pair Manual English PDFIra Ireland95% (21)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- A Plant Cell Is Like Walt Disney World!Dokument13 SeitenA Plant Cell Is Like Walt Disney World!Vinita Bhide PujariNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsDokument23 SeitenSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsEmer Perez50% (2)
- Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 3rd Edition Bauman Test BankDokument17 SeitenMicrobiology With Diseases by Body System 3rd Edition Bauman Test BankSerenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ssns SMK Za'Ba, Kuala Pilah, Negeri Sembilan Science Test 2 Form 1Dokument6 SeitenSsns SMK Za'Ba, Kuala Pilah, Negeri Sembilan Science Test 2 Form 1cimok85100% (1)
- Cell Structure FunctionDokument4 SeitenCell Structure FunctionLindley PareñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kami Export - Mya Bennett - Intro To Cells Recap by Amoeba SistersDokument2 SeitenKami Export - Mya Bennett - Intro To Cells Recap by Amoeba SistersMya BennettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacte Reviewer FinalDokument264 SeitenBacte Reviewer FinalRoselle Joyce Arce CalubanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Nature and Composition of Crops 124136Dokument79 SeitenChapter 4 Nature and Composition of Crops 124136S L A YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Test Cell StructureDokument7 SeitenBiology Test Cell Structuredee.aira29550% (1)
- Big Picture On The Cell PosterDokument1 SeiteBig Picture On The Cell PosterWellcome Trust100% (1)
- Cells Blackline Masters Discovery EducationDokument12 SeitenCells Blackline Masters Discovery EducationKari Kristine Hoskins BarreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1 NotesDokument4 SeitenGeneral Biology 1 NotesKrisha GatocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specialised CellsDokument1 SeiteSpecialised CellsMr. TigerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0653 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2025)Dokument134 Seiten0653 Scheme of Work (For Examination From 2025)Usha PerumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Fiitjee Chennai CentreDokument27 SeitenBiology Fiitjee Chennai CentreT SunderamalolanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note: The Lysosomes Are Oval and The Vacuoles Are More Rounded.Dokument6 SeitenNote: The Lysosomes Are Oval and The Vacuoles Are More Rounded.Bulan Santina100% (1)
- Cells, Tissues and OrgansDokument6 SeitenCells, Tissues and OrgansatheelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Wall and Cell Membrane 23rd AugustDokument7 SeitenCell Wall and Cell Membrane 23rd AugustRanjan SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and Function RDDokument18 SeitenCell Structure and Function RDapi-258400031Noch keine Bewertungen
- Buku Rujukan Biologi T4 KSSM FullDokument240 SeitenBuku Rujukan Biologi T4 KSSM Fullpooh86% (7)
- Lakshya 4.0 Test (Biology ) QuestionDokument19 SeitenLakshya 4.0 Test (Biology ) QuestionMonika RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant and AnimalDokument32 SeitenPlant and AnimalReynold GajusanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 9 BiologyDokument32 SeitenClass 9 BiologyAbinaya ParthasarathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Exposure To Cadmium On The Hippocampus in Adult Albino Rat and The Possible Role of L CarnitineDokument11 SeitenEffect of Exposure To Cadmium On The Hippocampus in Adult Albino Rat and The Possible Role of L CarnitineAYMAN AMERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Biology Worksheet 1Dokument5 SeitenGrade 8 Biology Worksheet 1YonasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1Dokument9 SeitenModule 1Ivan PaulinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCELPDokument9 SeitenSCIENCELPBhea GasparNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic CompondsDokument55 SeitenOrganic CompondsHappy Monamaladi Sibahle MoepyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytoplasmicmembranesystemschap8 130329081745 Phpapp01Dokument36 SeitenCytoplasmicmembranesystemschap8 130329081745 Phpapp01IzarreNoch keine Bewertungen