Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Receptors L1-Students 1
Hochgeladen von
api-2499729190 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
82 Ansichten26 SeitenOriginaltitel
receptors l1-students 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
82 Ansichten26 SeitenReceptors L1-Students 1
Hochgeladen von
api-249972919Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 26
University of Jordan 1
Receptors Functions and Signal
Transduction L1
Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
Introduction to Physiology (0501110) Spring 2014
Subject
Lecture
No.
Lecturer Pages in
the 12
th
edition
textbook
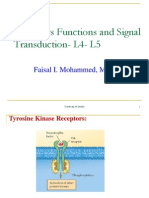
Receptors: types and adaptation
- Membrane or intracellular
- Ion channels
- G-protein
- Enzyme linked
- Intracellular
- Second messengers
- cAMP and cGMP, Phospholipid
- Calcium calmodulin and IRS
1-2 Dr. Faisal 886-891
Signal Transduction (Regulation of cellular machinery)
Extracellular regulators: nervous, endocrine, paracrine and
autocrine
3-4 Dr. Faisal 910-912
940-941
Steroids: Their Signal Transduction And Mechanism Of
Action
5 Dr. Faisal 926-927
931
Textbook: Guyton Medical Textbook of Physiology By: Guyton and Hall 12
th
edition
University of Jordan 3
Objectives
Define first messenger (Hormones)
List hormone types
Describe receptor types
Outline the hormone receptors interactions
Describe second messenger mechanism of action
List second messengers
University of Jordan 4
University of Jordan 5
University of Jordan 6
Intercellular Communication
Cell
Target Cell
Cell
Cell Target Cell
Target Cell Neuron
Hormone
Hormone
Hormone Hormone
Hormone
Hormone
Hormone
Endocrine
Paracrine
Autocrine
Blood
Neuroendocrine
Blood
Interstitial Fluid
Interstitial Fluid
University of Jordan 8
University of Jordan 9
GAS MOLECULE
University of Jordan 10
University of Jordan 11
University of Jordan 12
University of Jordan 13
Endocrine Glands and Hormones
Neurohormone:
Specialized neurons that secrete chemicals into the blood
rather than synaptic cleft.
Chemical secreted is called neurohormone.
Hormones:
Affect metabolism of target organs.
Help regulate total body metabolism, growth, and
reproduction.
University of Jordan 14
Peptide and Protein Hormones (amino acid
chain)
Steroid Hormones (derived from chlesterol)
Amine Hormones (derived from amino acid
e.g tyrosin)
Gas Nitric Oxide (NO)
Classes of Hormones
University of Jordan 15
Hormone types
Circulating circulate in blood throughout
body
Local hormones act locally
Paracrine act on neighboring cells
Autocrine act on the same cell that
secreted them
University of Jordan 16
University of Jordan 17
Chemical classes of hormones
Lipid-soluble hormones- use transport proteins in the
plasma
Steroid: Lipids derived from cholesterol.
Are lipophilic hormones.
Testosterone.
Estradiol.
Cortisol.
Progesterone.
Thyroid ( amine but lipid soluble)
Nitric oxide (NO)
University of Jordan 18
Chemical classes of hormones cont
Water-soluble circulate in free form in the plasma
Amines:
Hormones derived from tyrosine and tryptophan.
Polypeptides and proteins:
Polypeptides:
Chains of < 100 amino acids in length.
ADH.
Protein hormones:
Polypeptide chains with > 100 amino acids.
Growth hormone.
Eicosanoid (prostaglandins) derived from
arachidonic acid (20 carbon 4 double bonds)
University of Jordan 19
Chemical Classification of Hormones cont
Glycoproteins:
Long polypeptides (>100) bound to 1 or more carbohydrate
(CHO) groups.
FSH and LH, TSH and hCG (human chorionic
gonadotropin)
They have and subunits ( is common and is specific)
Hormones can also be divided into:
Polar:
H
2
0 soluble.
Nonpolar (lipophilic):
H
2
0 insoluble.
Can gain entry into target cells.
Steroid hormones and T
4
(thyroxine tetraiodothyronine))
University of Jordan 20
Prohormones and Prehormones
Prohormone:
Precursor is a longer chained polypeptide that is cut
and spliced together to make the hormone.
Proinsulin gives insulin
Preprohormone:
Prohormone derived from larger precursor molecule.
Preproinsulin.
Prehormone:
Molecules secreted by endocrine glands that are
inactive until changed into hormones by target cells.
T
4
converted to T
3
(tri-iodothyronin).
University of Jordan 21
Hypothalamus
Anterior pituitary
Posterior pituitary
Thyroid
Pancreas
Liver
Parathyroid
TRH, GnRH, CRH
GHRH, Somatostatin,
ACTH, TSH, FSH, LH,
PRL, GH
Oxytocin, ADH
Calcitonin
Insulin,Glucagon,
Somatostatin
Somatomedin C (IGF-1)
PTH
Placenta
Kidney
Heart
G.I. tract
Adipocyte
Adrenal medulla
HCG, HCS or HPL
Renin
ANP
Gastrin, CCK,
Secretin, GIP,
Somatostatin
Leptin
Norepinephrine,
epinephrine
Gland/Tissue Hormones Gland/Tissue Hormones
Peptide & Protein Hormones
University of Jordan 22
Synthesis and secretion of peptide hormones
University of Jordan 23
Amine Hormones
Hypothalamus
Thyroid
Adrenal medulla
Dopamine
T
3
, T
4
Epinephrine and
Norepinephrine
(NE, EPI)
Gland/Tissue Hormones
Tyrosine
L-Dopa
Dopamine
tyrosine
hydroxylase
Norepinephrine
dopa decarboxylase
dopamine -
hydroxylase
Dopaminergic
Neurons
Thyroid Hormones
Adrenergic
Neurons
Epinephrine
phenylethanolamine-
N-methyltransferase
Thyroid Gland
Adrenal Glands
Synthesis of Amine Hormones
University of Jordan 25
Adrenal Cortex
Testes
Ovaries
Corpus Luteum
Placenta
Kidney
Cortisol, Aldosterone,
Androgens
Testosterone
Estrogens, Progesterone
Estrogens, Progesterone
Estrogens, Progesterone
1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
(calcitriol)
Gland/Tissue
Hormones
Steroid Hormones
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- MediastinumDokument24 SeitenMediastinumapi-249972919100% (1)
- Endocrine - Dr. Allam 2021Dokument69 SeitenEndocrine - Dr. Allam 2021Alokh Saha RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 LAS Quarter 3Dokument89 SeitenScience 10 LAS Quarter 3Christopher John Natividad100% (3)
- Lecture Quiz On Integumentary SystemDokument2 SeitenLecture Quiz On Integumentary SystemCeline Miller100% (1)
- Ovarian New GrowthDokument1 SeiteOvarian New GrowthLouie Cedrick Camposano Tria50% (2)
- General Arrangement of The Abdominal VisceraDokument30 SeitenGeneral Arrangement of The Abdominal Visceraapi-249972919100% (2)
- Thyroid Disorders Guide: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentsDokument81 SeitenThyroid Disorders Guide: Causes, Symptoms & Treatmentschetankumarbhumireddy50% (2)
- Lecture 3 - PHDokument26 SeitenLecture 3 - PHapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 - Buffers IDokument26 SeitenLecture 4 - Buffers Iapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - WaterDokument27 SeitenLecture 2 - Waterapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 - Buffers II 1Dokument14 SeitenLecture 5 - Buffers II 1api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo 5Dokument17 SeitenEmbryo 5api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo Edited 2ed LectureDokument17 SeitenEmbryo Edited 2ed Lectureapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Receptors L3-StudentsDokument30 SeitenReceptors L3-Studentsapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Receptors L4-StudentsDokument40 SeitenReceptors L4-Studentsapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo 3Dokument31 SeitenEmbryo 3api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 - Acid BaseDokument32 SeitenLecture 1 - Acid Baseapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo 4Dokument33 SeitenEmbryo 4api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Receptors L2-Students 1Dokument27 SeitenReceptors L2-Students 1api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 11 1Dokument5 SeitenLec 11 1api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Abdomen RepairedDokument14 SeitenThe Abdomen Repairedapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- HeartDokument35 SeitenHeartapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 7Dokument11 SeitenLec 7api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Accessory OrgansDokument20 SeitenAccessory Organsapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction System-Students-FDokument29 SeitenConduction System-Students-Fapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo 2Dokument22 SeitenEmbryo 2api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomic Nervous System AnsDokument23 SeitenAutonomic Nervous System Ansapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- DR Mohtaseb Slide 16 Embryology 7Dokument32 SeitenDR Mohtaseb Slide 16 Embryology 7api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- First and Second Week of DevelopmentDokument18 SeitenFirst and Second Week of Developmentapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Muscle Physiology - StudentsDokument25 SeitenCardiac Muscle Physiology - Studentsapi-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 10Dokument9 SeitenLec 10api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 12Dokument17 SeitenLec 12api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 6Dokument11 SeitenLec 6api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 5Dokument13 SeitenLec 5api-249972919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of The Thyroid Gland Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19eDokument21 SeitenDisorders of The Thyroid Gland Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 19ePeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salma (Sameer)Dokument16 SeitenSalma (Sameer)Sahil HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proiect de Absolvire: Şcoala Postliceală Sanitară Carol Davila" BucurestiDokument34 SeitenProiect de Absolvire: Şcoala Postliceală Sanitară Carol Davila" BucurestiValentin StefanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Neuroendocrine Control of Testicular FunctionDokument15 Seiten12 Neuroendocrine Control of Testicular FunctionKOTAMRAJUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aging-Reversing Effects of TRH in MiceDokument31 SeitenAging-Reversing Effects of TRH in MiceFelipe Hernan Herrera Salinas100% (2)
- Megaloblastic Anemia Case in Addison's Disease PatientDokument4 SeitenMegaloblastic Anemia Case in Addison's Disease PatientIzzan Ferdi AndrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- (1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) MANAGEMENT of ENDOCRINE DISEASE - Hypothyroidism-Associated Hyponatremia - Mechanisms, Implications and TreatmentDokument6 Seiten(1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) MANAGEMENT of ENDOCRINE DISEASE - Hypothyroidism-Associated Hyponatremia - Mechanisms, Implications and TreatmentZamrina AdilafatmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organs SystemDokument4 SeitenOrgans SystemJan Paul SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 PDFDokument12 SeitenUnit 4 PDFJack TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-7 BaileysDokument7 Seiten1-7 BaileysAura NirwanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine NotesDokument9 SeitenEndocrine NotesLucky GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Test: Scrotal Sac, Bladder, Epididymis, Prostate Gland. (9 Marks)Dokument5 SeitenClass Test: Scrotal Sac, Bladder, Epididymis, Prostate Gland. (9 Marks)Kamleshwar BoodhooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menstrual cycle, hormones, and female reproductive systemDokument3 SeitenMenstrual cycle, hormones, and female reproductive systemKHRISTINE KAYE SALUDESNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Male Reproductive SystemDokument5 SeitenThe Male Reproductive SystemTamie P. GalindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grave's Disease2.Dokument42 SeitenGrave's Disease2.safeer kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive System (Midterm)Dokument57 SeitenReproductive System (Midterm)Jaden GilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Result of Hyperthyroidism: Sumber: Mayo ClinicDokument9 SeitenResult of Hyperthyroidism: Sumber: Mayo ClinicChrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mpharm Year 2 Gastrointes Nal Tract Example MCQ'SDokument8 SeitenMpharm Year 2 Gastrointes Nal Tract Example MCQ'SManish JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- H H H H H M M M M M: Ormone Ormone Ormone Ormone Ormone ET ET ET ET Etabolism Abolism Abolism Abolism AbolismDokument28 SeitenH H H H H M M M M M: Ormone Ormone Ormone Ormone Ormone ET ET ET ET Etabolism Abolism Abolism Abolism AbolismHoth HothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Gland 111Dokument28 SeitenAdrenal Gland 111Renz OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 08 Ristic RDokument13 Seiten7 08 Ristic RsucrooNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Read A Medical ReportDokument3 SeitenHow To Read A Medical ReportpinkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autoimmune Polyglandular SyndromesDokument76 SeitenAutoimmune Polyglandular SyndromesSenoAriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sankha Jee Medical Receipt-18.08.2022Dokument12 SeitenSankha Jee Medical Receipt-18.08.2022saajnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS NURSING: REPRODUCTIVE DEVELOPMENTDokument9 SeitenBS NURSING: REPRODUCTIVE DEVELOPMENTJerica Mae VenoyaNoch keine Bewertungen