Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ATMega16 LCD Digital Clock
Hochgeladen von
jamban48Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ATMega16 LCD Digital Clock
Hochgeladen von
jamban48Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
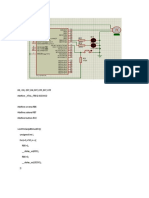
The figure below gives the circuit diagram for the ATmega16 LCD Digital Clock.
Important Note: In order for our digital clock to work correctly the internal oscillator of the
ATMega16 AVR microcontroller must be enabled and set to 4MHz.
ATMega16 LCD Digital Clock Software
Below is the AVR C implementation of the entire code for the ATMega16 based LCD digital
clock. The code was implemented and built using AVR Studio 5. Be reminded that the internal
clock of the ATMega16 microcontroller should be enabled and programmed to operate at 4MHz
for the AVR C code to operate correctly. A video of the LCD digital clock in operation is
presented at the end of this page.
/*
* LCD-Digital-Clock.c
*
* Written in AVR Studio 5
* Compiler: AVR GNU C Compiler (GCC)
*
* Created: 12/22/2011 6:34:36 PM
* Author: AVR Tutorials
* Website: www.AVR-Tutorials.com
*/
#define F_CPU 4000000UL
#include <avr/delay.h>
#include <avr/io.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <avr/interrupt.h>
/*Global Variables Declarations*/
unsigned char hours = 0;
unsigned char minutes = 0;
unsigned char seconds = 0;
char time[] = "00:00:00";
/*LCD function declarations */
void LCD_send_command(unsigned char cmnd);
void LCD_send_data(unsigned char data);
void LCD_init();
void LCD_goto(unsigned char y, unsigned char x);
void LCD_print(char *string);
void LCD_update_time(void);
/*Timer Counter 1 Compare Match A Interrupt Service Routine/Interrupt
Handler*/
ISR(TIMER1_COMPA_vect);
#define LCD_DATA_PORT PORTB
#define LCD_DATA_DDR DDRB
#define LCD_DATA_PIN PINB
#define LCD_CNTRL_PORT PORTC
#define LCD_CNTRL_DDR DDRC
#define LCD_CNTRL_PIN PINC
#define LCD_RS_PIN 5
#define LCD_RW_PIN 6
#define LCD_ENABLE_PIN 7
#define SET_HOUR 3
#define SET_MINUTE 4
int main(void)
{
unsigned char i;
LCD_init();
LCD_goto(1,2);
LCD_print("AVR-Tutorials");
LCD_goto(2,4);
LCD_print(time);
LCD_CNTRL_PORT = (1<<SET_HOUR | 1<<SET_MINUTE);
TCCR1B = (1<<CS12|1<<WGM12);
OCR1A = 15625-1;
TIMSK = 1<<OCIE1A;
sei();
while(1)
{
if(!(LCD_CNTRL_PIN & (1<<SET_HOUR)))
{
hours++;
if(hours > 23)
hours = 0;
}
if(!(LCD_CNTRL_PIN & (1<<SET_MINUTE)))
{
minutes++;
if(minutes > 59)
minutes = 0;
}
_delay_ms(250);
}
}
/* This function sends a command 'cmnd' to the LCD module*/
void LCD_send_command(unsigned char cmnd)
{
LCD_DATA_PORT = cmnd;
LCD_CNTRL_PORT &= ~(1<<LCD_RW_PIN);
LCD_CNTRL_PORT &= ~(1<<LCD_RS_PIN);
LCD_CNTRL_PORT |= (1<<LCD_ENABLE_PIN);
_delay_us(2);
LCD_CNTRL_PORT &= ~(1<<LCD_ENABLE_PIN);
_delay_us(100);
}
/* This function sends the data 'data' to the LCD module*/
void LCD_send_data(unsigned char data)
{
LCD_DATA_PORT = data;
LCD_CNTRL_PORT &= ~(1<<LCD_RW_PIN);
LCD_CNTRL_PORT |= (1<<LCD_RS_PIN);
LCD_CNTRL_PORT |= (1<<LCD_ENABLE_PIN);
_delay_us(2);
LCD_CNTRL_PORT &= ~(1<<LCD_ENABLE_PIN);
_delay_us(100);
}
void LCD_init()
{
LCD_CNTRL_DDR = 0xFF;
LCD_CNTRL_PORT = 0x00;
LCD_DATA_DDR = 0xFF;
LCD_DATA_PORT = 0x00;
_delay_ms(10);
LCD_send_command(0x38);
LCD_send_command(0x0C);
LCD_send_command(0x01);
_delay_ms(10);
LCD_send_command(0x06);
}
/* This function moves the cursor the line y column x on the LCD module*/
void LCD_goto(unsigned char y, unsigned char x)
{
unsigned char firstAddress[] = {0x80,0xC0,0x94,0xD4};
LCD_send_command(firstAddress[y-1] + x-1);
_delay_ms(10);
}
void LCD_print(char *string)
{
unsigned char i;
while(string[i]!=0)
{
LCD_send_data(string[i]);
i++;
}
}
void LCD_update_time()
{
unsigned char temp;
LCD_goto(2,4);
itoa(hours/10,temp,10);
LCD_print(temp);
itoa(hours%10,temp,10);
LCD_print(temp);
LCD_print(":");
itoa(minutes/10,temp,10);
LCD_print(temp);
itoa((minutes%10),temp,10);
LCD_print(temp);
LCD_print(":");
itoa(seconds/10,temp,10);
LCD_print(temp);
itoa(seconds%10,temp,10);
LCD_print(temp);
}
/*Timer Counter 1 Compare Match A Interrupt Service Routine/Interrupt
Handler*/
ISR(TIMER1_COMPA_vect)
{
seconds++;
if(seconds == 60)
{
seconds = 0;
minutes++;
}
if(minutes == 60)
{
minutes = 0;
hours++;
}
if(hours > 23)
hours = 0;
LCD_update_time();
}
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCVon EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The MotherboardDokument3 SeitenThe Motherboardbryan ramosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing A Bootloader For The PIC16F87X: OperationDokument24 SeitenImplementing A Bootloader For The PIC16F87X: Operationboslim1580100% (1)
- Power On Self Test Beep CodesDokument5 SeitenPower On Self Test Beep CodesTilak AmarghdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BITS Pilani PresentationDokument20 SeitenBITS Pilani PresentationParag PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemd Cheat Sheet PDFDokument2 SeitenSystemd Cheat Sheet PDFPrayag InfosecNoch keine Bewertungen
- CANbedded CANopen Availability enDokument4 SeitenCANbedded CANopen Availability enAndres RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATMega16 AVR Microcontroller LCD Digital ClockDokument5 SeitenATMega16 AVR Microcontroller LCD Digital ClockAdrianMartinezMendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATMega16 Microcontroller Digital LM35 LCD ThermometerDokument4 SeitenATMega16 Microcontroller Digital LM35 LCD ThermometerAdrianMartinezMendez100% (3)
- LCD Code For AvrDokument4 SeitenLCD Code For AvrAadhya Suman100% (1)
- HX711Dokument9 SeitenHX711framqz100% (1)
- PIC18 Pulse Width ModulationDokument16 SeitenPIC18 Pulse Width ModulationAnoj Pahathkumbura100% (1)
- LCD Interface PGMDokument4 SeitenLCD Interface PGMNamrata Dhamal100% (1)
- Embedded C ProgramDokument7 SeitenEmbedded C ProgramLucifer100% (1)
- USB To RS232 Using Atmel ATtiny2313 or ATmega8Dokument4 SeitenUSB To RS232 Using Atmel ATtiny2313 or ATmega8Nugraha Indrawan100% (2)
- Brushless DC Electric Motor Control by CPLDDokument6 SeitenBrushless DC Electric Motor Control by CPLDIonela100% (3)
- Program LCDDokument2 SeitenProgram LCDAngga Wijaya Kusuma100% (1)
- Stepper Motor InterfacingDokument5 SeitenStepper Motor InterfacingShobanraj Letchumanan100% (1)
- How To Implement Icsp™ Using Pic16F8X Flash Mcus: Author: Rodger Richey Microchip Technology IncDokument8 SeitenHow To Implement Icsp™ Using Pic16F8X Flash Mcus: Author: Rodger Richey Microchip Technology Incadil100% (1)
- Basics of The Communication ProtocolDokument19 SeitenBasics of The Communication ProtocolNEETHU PRAKASH100% (1)
- Pic-Web Development Board Users Manual: Rev.A, July 2008Dokument14 SeitenPic-Web Development Board Users Manual: Rev.A, July 2008darazzi100% (1)
- AVR Microcontroller: Prepared By: Eng. Ashraf DarwishDokument19 SeitenAVR Microcontroller: Prepared By: Eng. Ashraf DarwishHectorLopez100% (2)
- Testing Pic Code For I2C Master - Slave CommunicationDokument15 SeitenTesting Pic Code For I2C Master - Slave CommunicationJavier Corimaya33% (3)
- What Is The Difference Between Microcontrollers and 8051Dokument6 SeitenWhat Is The Difference Between Microcontrollers and 8051Erandi Brito100% (1)
- CCP ModuleDokument11 SeitenCCP ModuleAltaaf Mulani100% (1)
- x64 AsmDokument4 Seitenx64 Asmasdmin100% (1)
- AVR Programming ExamplesDokument9 SeitenAVR Programming Examplesرضا میرزانیا100% (1)
- The Basics of Ethernet The Basics of Ethernet The Basics of Ethernet The Basics of EthernetDokument6 SeitenThe Basics of Ethernet The Basics of Ethernet The Basics of Ethernet The Basics of EthernetRupesh Kumar100% (1)
- Signal-Slot in C++Dokument10 SeitenSignal-Slot in C++Don Camillo100% (1)
- I2C Interface To Serial EEPROMDokument8 SeitenI2C Interface To Serial EEPROMShri Kulkarni100% (1)
- Motor StepperDokument4 SeitenMotor Stepperfavour ukpai100% (1)
- Eeeb371 Pic Exp6newDokument7 SeitenEeeb371 Pic Exp6newSalemAbaad100% (2)
- AVR Microcontroller: Prepared By: Eng. Ashraf DarwishDokument28 SeitenAVR Microcontroller: Prepared By: Eng. Ashraf DarwishHectorLopez100% (2)
- Stepper Motor C CodeDokument4 SeitenStepper Motor C CodeJoël Mwabi100% (1)
- Introduction To Programming The PIC32Dokument17 SeitenIntroduction To Programming The PIC32Kim Breet100% (3)
- ICD2 Poster 51265hDokument1 SeiteICD2 Poster 51265hngt881100% (1)
- Using Internal EEPROM of PIC Microcontroller - MikroCDokument16 SeitenUsing Internal EEPROM of PIC Microcontroller - MikroCdevchandar100% (1)
- A Brief Tutorial On GCC Inline AsmDokument10 SeitenA Brief Tutorial On GCC Inline Asmxieyubo100% (3)
- In-Circuit Serial Programming - Picmicro Mid-Range Mcu Family PDFDokument14 SeitenIn-Circuit Serial Programming - Picmicro Mid-Range Mcu Family PDFMauro Vargas100% (2)
- LCD Basics McaDokument13 SeitenLCD Basics Mcaharshad lokhande100% (1)
- Ieee 802.11Dokument13 SeitenIeee 802.11jeffy100% (1)
- Isolated Power Supply 30wDokument43 SeitenIsolated Power Supply 30wchinnadurai20006034100% (1)
- Pic Usb - v2Dokument23 SeitenPic Usb - v2Andres Echeverry100% (1)
- YOG-Gigabit EthernetDokument50 SeitenYOG-Gigabit EthernetArya Man100% (1)
- DS Zadaci PDFDokument23 SeitenDS Zadaci PDFArnela Tatic100% (1)
- MB SM19116 ManualDokument2 SeitenMB SM19116 Manualmrjanus100% (1)
- Design of A Micro-Uart For Soc ApplicationDokument12 SeitenDesign of A Micro-Uart For Soc ApplicationUtkarsh Jain100% (1)
- Mobile Robot Chapter 4: C and 8051 (V4.a)Dokument10 SeitenMobile Robot Chapter 4: C and 8051 (V4.a)api-19786583Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8051 CDokument7 Seiten8051 CTrieu Do MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- E:/#0-2S2017/#1-TEC - SELDI/SAP-02 - Projeto Forno MCU/SELDI - SAP-02 MCU - FW/Forno - DSET-SAP01 - 137-V1.X/forno.hDokument7 SeitenE:/#0-2S2017/#1-TEC - SELDI/SAP-02 - Projeto Forno MCU/SELDI - SAP-02 MCU - FW/Forno - DSET-SAP01 - 137-V1.X/forno.hVinícius Lopes Sampaio100% (1)
- By Marl Us: Lighting The Right To TheDokument7 SeitenBy Marl Us: Lighting The Right To TheGiancarloRichardRivadeneyraMiranda100% (1)
- 8051 Password C Program - Embed4uDokument15 Seiten8051 Password C Program - Embed4uAnil D'SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.2 PWM 7 Mac 2017Dokument34 Seiten5.2 PWM 7 Mac 2017Elawarasi Nadarajan100% (1)
- LCD4Bit ModDokument5 SeitenLCD4Bit ModCleison Armando Manrique Aguirre100% (1)
- LCD 16x2Dokument6 SeitenLCD 16x2teguh iman100% (2)
- DC Motor Control Using CDokument6 SeitenDC Motor Control Using Cankitguptaims100% (2)
- LCD HandshakingDokument19 SeitenLCD HandshakingNvskinId100% (1)
- Writing DisassemblerDokument12 SeitenWriting DisassemblerGadjo Matto100% (1)
- LCD 16 X 2Dokument9 SeitenLCD 16 X 2Pradeev Balakrishnan100% (1)
- DIY Electronics (HK) LTD PO Box 88458, Sham Shui Po, Hong KongDokument17 SeitenDIY Electronics (HK) LTD PO Box 88458, Sham Shui Po, Hong Kongrajudp100% (1)
- HC SR04 PDFDokument3 SeitenHC SR04 PDFVipan Sharma100% (1)
- Hobby Servo Motor Control Via PIC Pulse Width Modulation: Nathan Markey April 4, 2003Dokument7 SeitenHobby Servo Motor Control Via PIC Pulse Width Modulation: Nathan Markey April 4, 2003Luciana Gutierrez Salazar100% (1)
- Reloj Digital Con Atmega16Dokument6 SeitenReloj Digital Con Atmega16OmarRosasRiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reloj Digital Con Atmega16Dokument6 SeitenReloj Digital Con Atmega16Isaac Noyola ManzanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 10Dokument9 SeitenLab 10ubaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- TechlineDokument2 SeitenTechlineKashif AdeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- RaidDokument43 SeitenRaidnishasaiyed2304Noch keine Bewertungen
- Slide-5 (8086 Maximum Mode)Dokument13 SeitenSlide-5 (8086 Maximum Mode)Hafsaa Binte HarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arduino and Bluetooth HC-05 Connecting Easily - All As PDFDokument9 SeitenArduino and Bluetooth HC-05 Connecting Easily - All As PDFEnnio AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Iphone Repair Shop in LondonDokument7 SeitenBest Iphone Repair Shop in LondonElectroclinicNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8051 InterruptDokument21 Seiten8051 InterruptarunvittoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debug 1214Dokument3 SeitenDebug 1214Fariz DzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Navigation: How To Enable VT On PC To Support Android EmulatorDokument1 SeiteQuick Navigation: How To Enable VT On PC To Support Android Emulatorjose SaavedraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied CADokument2 SeitenApplied CAEdouard Mvogo BilegueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Quarter Activities Ict 10 Regular CurriculumDokument4 Seiten4th Quarter Activities Ict 10 Regular Curriculumfangelg05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Linux Forensics: Dr. Phil Polstra @ppolstra PHD, Cissp, CehDokument7 SeitenLinux Forensics: Dr. Phil Polstra @ppolstra PHD, Cissp, CehscrapyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResumenLocal 2018Dokument1.456 SeitenResumenLocal 2018JUAN CARLOS ZABARBURU VENTURANoch keine Bewertungen
- Intel Microprocessor: Robert Jason D. Ramos 4-Bsece Computer System OrganizationDokument5 SeitenIntel Microprocessor: Robert Jason D. Ramos 4-Bsece Computer System OrganizationRobert Jason RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATMELAVRDokument45 SeitenATMELAVRTani DaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCem .9 ReadmeDokument12 SeitenPCem .9 ReadmeTroy FullwoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmel 42153 8 Bit AVR XMEGA AT03160 Migrating Bootloader From ATxmega128A1 To Other XMEGA Devices Application NoteDokument16 SeitenAtmel 42153 8 Bit AVR XMEGA AT03160 Migrating Bootloader From ATxmega128A1 To Other XMEGA Devices Application NotemachintrucNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOS Interrupt Call: Help Us Improve Wikipedia by Supporting It FinanciallyDokument5 SeitenBIOS Interrupt Call: Help Us Improve Wikipedia by Supporting It FinanciallyMuhammad RdiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document From SUHASDokument37 SeitenDocument From SUHASsuhassomnathreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systick and Watchdog TimerDokument31 SeitenSystick and Watchdog Timerxa yNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISA Bus Pins SVGDokument3 SeitenISA Bus Pins SVGEmin KültürelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8051 Flash Magic ManualDokument4 Seiten8051 Flash Magic ManualNarendra JadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Rak AblamDokument131 SeitenData Rak AblamRiswan AprilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Manual To Accompany Pic Microcontroller and Embedded Systems 1st Edition 0131194046Dokument6 SeitenSolutions Manual To Accompany Pic Microcontroller and Embedded Systems 1st Edition 0131194046crabbyscatter0lb1iNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between MiniDokument2 SeitenDifference Between MiniShreesh BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Franca Rezende 2021Dokument146 SeitenFranca Rezende 2021joao.soares.diNoch keine Bewertungen