Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
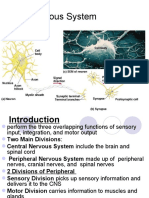
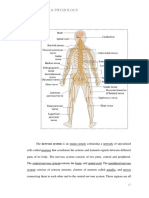
The Nervous System
Hochgeladen von
katebelikovcullen0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
83 Ansichten2 SeitenThe Nervous System
Originaltitel
The Nervous System.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe Nervous System
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
83 Ansichten2 SeitenThe Nervous System
Hochgeladen von
katebelikovcullenThe Nervous System
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
The Nervous System
The Nervous System:
- The master controlling and communicating system of the body
- Cells communicate via electrical and chemical signals
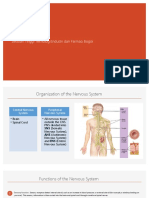
Functions of the Nervous System:
Sensory System:
- Information is gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external
changes.
Integration:
- Process and interprets sensory input.
Motor Input:
- Activation of effector organs.
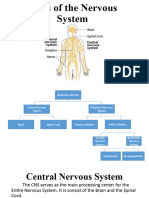
The Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Made up of the brain and spinal cord
- Integrative and control centres
- Interprets sensory input and then dictates motor output.
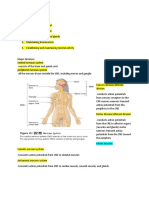
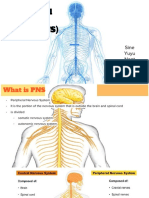
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- The portion outside the CNS
- Consists of mainly nerves
- Spinal nerves to a from the spinal cord
- Cranial nerves to and from the brain
The two functional divisions:
- Sensory (afferent) Division is made up of:
Somatic sensory fibers impulses from skin, skeletal muscles
and joints to the CNS
Visceral sensory fibers impulses from visceral organs to the
CNS
- Motor (efferent) division transmits impulses from the CNS to effector organs
- And is made up of the:
Somatic Nervous system: Conscious control of skeletal muscles
and voluntary nervous system
Autonomic nervous system: Visceral motor nerve fibers,
regulates smooth muscles, glands and cardiac muscle,
involuntary nervous system,
Further Sub-divisions of the Motor System:
- Sympathetic: Fight or flight response, modilises the body during activity and
extreme situations
- Parasympathetic: Rest and digest, performs maintenance activities and
preserves energy
- Counterbalance each other
-
Histology of Nervous Tissue
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- GBSDokument33 SeitenGBSbungadielaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Neuron Diseases: by Dr. Deepti Patil Dept. of DravyagunaDokument36 SeitenMotor Neuron Diseases: by Dr. Deepti Patil Dept. of DravyagunaDrVikas100% (1)
- S.C.E.N.A.R.: Self-Controlled Energetic Neuro-Adaptive RegulatorDokument41 SeitenS.C.E.N.A.R.: Self-Controlled Energetic Neuro-Adaptive RegulatorHoracio CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahDokument24 SeitenThe Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahAzhar MehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.autonomic NS - P1-dlvrdDokument8 Seiten5.autonomic NS - P1-dlvrdArooj FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument26 SeitenNervous SystemAe-jay CacalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology ReviewDokument65 SeitenPhysiology ReviewNandita KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organization of The Nervous System (Student)Dokument4 SeitenOrganization of The Nervous System (Student)raquel_kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inter Neurons-To Connect Sensory and Motor Neurons Sensory Neurons - AreDokument4 SeitenInter Neurons-To Connect Sensory and Motor Neurons Sensory Neurons - AreMilie Milie VanilieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System 2023Dokument31 SeitenNervous System 2023Rayjie G RuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinDokument43 SeitenPertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinErsha PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science - The Nervous SystemDokument4 SeitenScience - The Nervous SystemsudasinghesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Nervous SystemDokument4 SeitenHuman Nervous SystemHandi Wahyu RamadhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented by G3Dokument23 SeitenPresented by G3Bernadette GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSM 1Dokument1 SeiteTSM 1tigizetayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - Biological Psychology The NSDokument25 SeitenUnit 2 - Biological Psychology The NSJad KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System 2Dokument23 SeitenNervous System 2TinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument27 SeitenNervous SystemNARESH JANDIALNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.nervous SystemDokument25 Seiten2.nervous SystemEka PuspitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Nervous System: Autonomic DrugsDokument52 SeitenAutomatic Nervous System: Autonomic DrugslalitrajindoliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System: Sekolah Tinggi Teknologi Industri Dan Farmasi BogorDokument7 SeitenNervous System: Sekolah Tinggi Teknologi Industri Dan Farmasi Bogorrizal bohalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterDokument25 SeitenNervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterRegin BaguioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System ToDokument12 SeitenNervous System Togianexp123Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Nervous System - Overview: (A) Topographical DivisionsDokument2 SeitenThe Nervous System - Overview: (A) Topographical DivisionsOjambo FlaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument10 SeitenNervous SystemPogi BearNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motoneuron Output Is Conduction of Signals From TheDokument5 SeitenMotoneuron Output Is Conduction of Signals From TheTanvir AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDokument39 SeitenPeripheral Nervous SystemHengky HanggaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Nervous SystemDokument3 SeitenWhat Is The Nervous SystemSittie Asleah SandiganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuctional Organization and Basic Functions of The Nervous SystemDokument48 SeitenFuctional Organization and Basic Functions of The Nervous SystemQairul AzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomic Nervous System: Dr. Lawrence A. OlatunjiDokument122 SeitenAutonomic Nervous System: Dr. Lawrence A. OlatunjiSasikala MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Through The: Control of Body System Nervous SystemDokument33 SeitenThrough The: Control of Body System Nervous SystemPo GiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and NeurotransmittersDokument3 SeitenOrganization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters22 - Fernandez, Lyza Mae D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument2 SeitenNervous SystemEMMA SLAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain BeeDokument2 SeitenBrain BeeYe Rim Won100% (1)
- Autonomic N.S 1 - DentistryDokument22 SeitenAutonomic N.S 1 - DentistryMustafa SaßerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System of HumanDokument12 SeitenNervous System of Humanibnulwaqt97% (33)
- Deepak PPT 1Dokument15 SeitenDeepak PPT 1Røbiñ ĢuđNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument1 SeiteNervous Systemcarla lizondraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous Systems, Cardiovascular, BloodDokument43 SeitenNervous Systems, Cardiovascular, BloodArianne Jen GenotivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peripheral NervousDokument22 SeitenPeripheral Nervousroselhyn SottoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organisation of Nervous SystemDokument3 SeitenOrganisation of Nervous SystemHDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 3RD QuarterDokument3 SeitenScience 3RD QuarterG03 Bonavente, Mickaela Vhey M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Terms DefDokument3 SeitenBio Terms Defapi-31355470Noch keine Bewertungen
- V. Anatomy & PhysiologyDokument5 SeitenV. Anatomy & PhysiologyAbigael Patricia GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)Dokument7 SeitenChapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)tomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nervous System: Chapter 25 Section 1Dokument34 SeitenThe Nervous System: Chapter 25 Section 1thegedusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec2 Sem2 Cnsweek1 20110630Dokument10 SeitenLec2 Sem2 Cnsweek1 20110630arhamsalahuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peripheral Nervous System - NervesDokument48 SeitenPeripheral Nervous System - NervesOpheliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Dokument24 SeitenGroup 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Tara DolotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument46 SeitenNervous Systemrabia khalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE - ResearchDokument9 SeitenSCIENCE - Researchmarealyn.hermida.camachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument13 SeitenNervous SystemAnn SerratoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ??????? ?????? H. Idris N. Macmod A. Mangondato M. OmarDokument70 Seiten??????? ?????? H. Idris N. Macmod A. Mangondato M. OmarHestia GreyertNoch keine Bewertungen
- NS and ESDokument23 SeitenNS and ESDesiree FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument2 SeitenNervous SystemSoha MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System Intro NERVESDokument22 SeitenNervous System Intro NERVESJoshdave cuambotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Types of Nervous SystemDokument1 SeiteTwo Types of Nervous SystemRandomly SelectedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wonders of Nervous SystemDokument2 SeitenWonders of Nervous SystemMa Victoria Shainee GaliciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organs and DivisionsDokument56 SeitenOrgans and DivisionsArpana KelothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiological Bases of BehaviorDokument31 SeitenPhysiological Bases of BehaviorjrbajaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) : Sine Yuyu Nont Noey KhingDokument6 SeitenPeripheral Nervous System (PNS) : Sine Yuyu Nont Noey Khingapi-358413758Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Nervous System - PsychologyDokument17 SeitenThe Nervous System - Psychologyjanet100% (2)
- Nervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesVon EverandNervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expanding and FactorisingDokument1 SeiteExpanding and FactorisingkatebelikovcullenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology NotesDokument8 SeitenBiology NoteskatebelikovcullenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em C Am B5: Why Fight This Pointless WarDokument3 SeitenEm C Am B5: Why Fight This Pointless WarkatebelikovcullenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Legal Studies Key TermsDokument3 SeitenUnit 4 Legal Studies Key TermskatebelikovcullenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neural MobilizationDokument12 SeitenNeural Mobilizationmanthan pandyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory and Motor Nerve EndingsDokument42 SeitenSensory and Motor Nerve EndingsMark GanirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Investigatory Project Ageing: Submitted By:-Jayashri CBSE Roll No.Dokument35 SeitenBiology Investigatory Project Ageing: Submitted By:-Jayashri CBSE Roll No.Anonymous ImSMU2BqNSNoch keine Bewertungen
- GanglionDokument10 SeitenGanglionPraveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System Review Answer KeyDokument18 SeitenNervous System Review Answer Keydanieljohnarboleda67% (3)
- (H.a.) Chapter 15 - Neurologic SystemDokument9 Seiten(H.a.) Chapter 15 - Neurologic SystemLevi Sebastian T. CabiguinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Img 20240111 0002Dokument11 SeitenImg 20240111 00029E EYAD AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs by Jahaan Opal Biology ICSE Class 10Dokument4 SeitenMCQs by Jahaan Opal Biology ICSE Class 10Jahaan OpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - Nervous System RP PDFDokument105 SeitenChapter 8 - Nervous System RP PDFpizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charcot - MarieDokument4 SeitenCharcot - MarieAlexandra MardareNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Spinal Cord InjuryDokument20 SeitenWhat Is Spinal Cord Injurymizah100% (1)
- Major Divisions and PartsDokument16 SeitenMajor Divisions and PartsManu MicosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental NerveDokument5 SeitenMental NerveAyitiYonLotImajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transes Nervous SystemDokument13 SeitenTranses Nervous SystemAlther LorenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Celestial Being or Terrestrial Being (1) 2Dokument23 SeitenCelestial Being or Terrestrial Being (1) 2sean lee96% (23)
- Brain Facts Book PDFDokument96 SeitenBrain Facts Book PDFjlangseth100% (1)
- The Constant Direct Current Electrotherapy PhysiotherapyDokument39 SeitenThe Constant Direct Current Electrotherapy Physiotherapyismail100% (15)
- CNS MCQSDokument24 SeitenCNS MCQSSTEVEN OKURUT100% (2)
- Biomedical InstrumentationDokument16 SeitenBiomedical Instrumentationshaswatece100% (6)
- Lec.14.Stress and Health MC 2018Dokument26 SeitenLec.14.Stress and Health MC 2018sofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 1st Edition Saladin Solutions Manual 1Dokument5 SeitenEssentials of Anatomy and Physiology 1st Edition Saladin Solutions Manual 1karen100% (33)
- Janus FacesDokument8 SeitenJanus FacesAurelio Sartori100% (1)
- Sensation, Perception, and CognitionDokument55 SeitenSensation, Perception, and CognitionRikha ParamittaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guyton, Receptoret Dhe Qarqet NeuronaleDokument13 SeitenGuyton, Receptoret Dhe Qarqet Neuronalegjin kushnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical NeurodynamicsDokument41 SeitenClinical Neurodynamicsramesh2007-mptNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro Part 1 NotesDokument3 SeitenNeuro Part 1 NotesMarc JasminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of ReceptorsDokument24 SeitenTypes of Receptorsmaham1085Noch keine Bewertungen