Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Blood Brain Barrier
Hochgeladen von
Chicilia Windia T. WOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Blood Brain Barrier
Hochgeladen von
Chicilia Windia T. WCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Blood Brain Barrier
Unit 8 / Week 2
Prof. Lammers
R.E.B, 4MedStudents.com, 2003
What is Blood Brain Barrier?
The BBB is formed by the single layer of
endothelial cells that line the inner surfaces of
capillaries in the brain.
It is a semi-permeable capillary membrane;
that is, it allows some materials to cross, but
prevents others from crossing. In most parts of
the body the capillaries, are lined with
endothelial cells. The endothelial tissue has
small spaces between each individual cell so
substances can move readily between the
inside and the outside of the vessel. However,
in the brain, the endothelial cells fit tightly
together and substances cannot pass out of the
bloodstream. (Some molecules, such as
glucose, are transported out of the blood by
special methods such as active transport.)
Functions and Properties of the
BBB
The BBB has several important functions:
1. Protects the brain from "foreign substances" in the
blood that may injure the brain.
2. Protects the brain from hormones and
neurotransmitters in the rest of the body.
3. Maintains a constant environment for the brain.
Functions and Properties of the
BBB
General Properties of the BBB
1. Large molecules do not pass through the BBB easily.
2. Low lipid (fat) soluble molecules do not penetrate into the brain.
However, lipid soluble molecules rapidly cross the BBB into the
brain.
3. Molecules that have a high electrical charge to them are slowed.
Therefore:
The BBB is selectively permeable to :Oxygen, Carbon dioxide and
glucose
The BBB is not permeable to
hydrogen ions
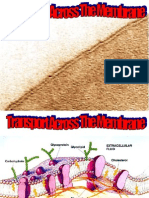
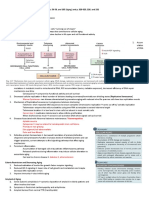
Transport at the BBB
There are five basic mechanisms by which
solute molecules move across membranes:
1. simple diffusion
2. facilitated diffusion
3. simple diffusion through an aqueous channel
4. active transport through a protein carrier
5. Endocytosis
Transport mechanisms at the BBB. 1 = paracellular diffusion , 2 = transcellular diffusion , 3 = ion channel 4 = ion-symport
channel 5 = ion-antiport channel 6 = facilitated diffusion , 7 = active efflux pump 8 = active-antiport transport , 9 =
receptor mediated endocytosis
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Wjarr 2023 1265Dokument6 SeitenWjarr 2023 1265shubham shendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wjarr 2023 1265Dokument7 SeitenWjarr 2023 1265Delavemia RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy LecDokument6 SeitenAnaphy LecfilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane Interactive Note Sheet-Updated Spring 2022Dokument4 SeitenCell Membrane Interactive Note Sheet-Updated Spring 2022Chandler BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Structure and Membrane TransportDokument7 SeitenCellular Structure and Membrane TransportKANT JAMES D. MAHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Module 7Dokument16 SeitenBiology - Module 7gangcheng1972Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mosaic Model NotesDokument4 SeitenFluid Mosaic Model NotesanzalnaamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelecture Questions 2Dokument7 SeitenPrelecture Questions 2kaslana kianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles 1Dokument17 SeitenCell Organelles 1James IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I Cell Physiology Purpose of Study: Kripa's Notes.Dokument29 SeitenUnit I Cell Physiology Purpose of Study: Kripa's Notes.Kripa NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nanoparticle Transport Across The Blood Brain BarrierDokument18 SeitenNanoparticle Transport Across The Blood Brain Barriersouvik maitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Binding and Transport ProcessesDokument7 SeitenMolecular Binding and Transport ProcessesWolfgang Amadeus MozartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviews: The Blood-Brain Barrier As An Endocrine TissueDokument12 SeitenReviews: The Blood-Brain Barrier As An Endocrine TissueCony GSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells:: Chapter-5Dokument4 SeitenCells:: Chapter-5MadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell MembranesDokument5 SeitenCell MembranesJANET ANNE BORROMEONoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell StructureDokument10 SeitenCell StructureJane NadalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Brain Barrier BBBDokument10 SeitenBlood Brain Barrier BBBaamnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Share Cell Structure and FunctionsDokument47 SeitenShare Cell Structure and FunctionszzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane Transport and Cell SizeDokument105 SeitenCell Membrane Transport and Cell SizeTitliMaopussyNoch keine Bewertungen
- General BiologyDokument23 SeitenGeneral BiologyPereyra Faith AngeliqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Blood-Brain Barrier: Structure, Function and Impact on Drug DeliveryDokument37 SeitenThe Blood-Brain Barrier: Structure, Function and Impact on Drug DeliveryAkilandeshwari AlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDokument16 SeitenOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and FunctionDokument2 SeitenCell Structure and FunctionRoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument50 SeitenUntitledMichael DeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Life ScienceDokument30 SeitenEarth and Life ScienceChristian VitalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure & FunctionsDokument70 SeitenCell Structure & FunctionsEDLYN BRAZILNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIF101 Handouts PDF FULL BOOK UPDATED 2022 BY STUDENT INFO 5-1-1Dokument205 SeitenBIF101 Handouts PDF FULL BOOK UPDATED 2022 BY STUDENT INFO 5-1-1Alishba khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology NoteDokument6 SeitenBiology NoteGUO JIAYI 22S203Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 9THDokument54 SeitenClass 9THzargarfaisal690Noch keine Bewertungen
- Education NotesDokument5 SeitenEducation NotesRwynn MemoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELL STRUCTURE AND PHYSIOLOGYDokument37 SeitenCELL STRUCTURE AND PHYSIOLOGYAliyu Aisha100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology DefinitionsDokument48 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology Definitionscyrus kirwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and Function 1Dokument4 SeitenCell Structure and Function 1Dianne LarozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MisconceptionDokument2 SeitenMisconceptionNurl AinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneDokument15 SeitenCell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneMariane CarandangNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGYFINALanswers (1stedition)Dokument61 SeitenBIOLOGYFINALanswers (1stedition)Abhinav VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of The CELLDokument14 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of The CELLlorelie asisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Ultrastructure: Tissues of The Body ModuleDokument38 SeitenCell Ultrastructure: Tissues of The Body ModuleQasmNoch keine Bewertungen
- m2 DraftDokument4 Seitenm2 DraftMae lea AndoloyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Le1Dokument14 SeitenCell Le1eng.raghdah98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 11 Biology Module 1 2023 NotesDokument55 SeitenYear 11 Biology Module 1 2023 NotesLNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - A&P The CellDokument23 Seiten5 - A&P The CellsabrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 7, Anatomy and Physiogy (ABEGAIL C. RELUNIA)Dokument4 SeitenModule 7, Anatomy and Physiogy (ABEGAIL C. RELUNIA)Abegail ReluniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weeks 1-3 Module: Learning Content: Basic Unit of Life. Protection and SupportDokument8 SeitenWeeks 1-3 Module: Learning Content: Basic Unit of Life. Protection and SupportShana AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument10 SeitenLecture 2manaln.2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 8 - Cell MembraneDokument26 SeitenLesson 8 - Cell MembraneArvin Jay LamberteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholesterol Is A Type of Steroid Which Is Helpful in Regulating Molecules Entering and ExitingDokument2 SeitenCholesterol Is A Type of Steroid Which Is Helpful in Regulating Molecules Entering and ExitingAce RafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physiology Cell Membrane: By: Dr. Hamza Al-TradDokument21 SeitenGeneral Physiology Cell Membrane: By: Dr. Hamza Al-TradibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Brain Barrier: By: Eman N. QaroutiDokument4 SeitenBlood Brain Barrier: By: Eman N. QaroutiLuigi AndradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Unit of Life: CellDokument14 SeitenFundamental Unit of Life: CellSHASHI BHUSHAN SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology-9 (U1 Tutorial) 2020-21Dokument10 SeitenBiology-9 (U1 Tutorial) 2020-21fahad darNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular StructureDokument6 SeitenCellular StructureVela STEM Naron, Claire KylaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDokument6 SeitenProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsJam MoralejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - kh201295 kh201295Dokument11 Seiten2 - kh201295 kh201295murtada gubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch10 Kitabcd Class 8 MSBHSE Science NotesDokument14 SeitenCh10 Kitabcd Class 8 MSBHSE Science NotesONE CLICK COMPUTERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cornell Notes 1Dokument2 SeitenCornell Notes 1api-333316198100% (1)
- Topics For Reporting GenbioDokument20 SeitenTopics For Reporting GenbioDel Enriquez RiboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3, Cells and How They WorkDokument14 SeitenModule 3, Cells and How They WorkMARIA CORAZON CONTANTENoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition and Sources of DrugsDokument29 SeitenDefinition and Sources of DrugsSAHILA SHEIKHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characterization of Aerobic Spore Forming Bacteria - Lucking Et Al 2013Dokument10 SeitenCharacterization of Aerobic Spore Forming Bacteria - Lucking Et Al 2013AlexisLopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSI Polymerase Chain Reaction Lab ManualDokument6 SeitenCSI Polymerase Chain Reaction Lab ManualDank MoviesNoch keine Bewertungen
- QTR 2 Module 5 InteractionsDokument18 SeitenQTR 2 Module 5 InteractionsNick BantoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Which Came First, The Feather or The BirdDokument10 SeitenWhich Came First, The Feather or The BirdPabloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gizmo Handout Paramecium HomeostasisDokument4 SeitenGizmo Handout Paramecium HomeostasisJimena Somoano0% (2)
- IBO 2005 Pract Part 4Dokument14 SeitenIBO 2005 Pract Part 4pdbiocompNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patentstorm: Cellulase Compositions and Methods of UseDokument39 SeitenPatentstorm: Cellulase Compositions and Methods of UseRAVIBIOTEC2008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Synaptic IntegrationDokument3 SeitenSynaptic IntegrationOmar AlemánNoch keine Bewertungen
- Receptors and EffectorsDokument29 SeitenReceptors and EffectorscmabdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Actinomycetes As Potential BiofungicidesDokument5 SeitenSoil Actinomycetes As Potential Biofungicideskopeal100% (3)
- The Kingdom Protoctista (Protista)Dokument4 SeitenThe Kingdom Protoctista (Protista)MSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDokument23 SeitenSexual Reproduction in PlantsStephen AreriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Transport Practice TestDokument4 SeitenCell Transport Practice TestLavander Blush100% (2)
- Praktikum FisiologiDokument49 SeitenPraktikum FisiologiNurul Fadhilah Taniyo100% (1)
- CAPE Biology Unit 2 ProjectDokument13 SeitenCAPE Biology Unit 2 ProjectAudi Sweetangel0% (1)
- The Weekly Time Table For Year I Semester II of 2016 - 2017 FinalDokument26 SeitenThe Weekly Time Table For Year I Semester II of 2016 - 2017 FinalsoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inner Visions - Iridology - Discovering The Whole You (PDFDrive)Dokument137 SeitenInner Visions - Iridology - Discovering The Whole You (PDFDrive)Gursewak Singh100% (1)
- Hybrid Rice Breeding Seed ProductionDokument41 SeitenHybrid Rice Breeding Seed ProductionGENIUS1507Noch keine Bewertungen
- Liv.52 TabletsDokument2 SeitenLiv.52 TabletsSYED MUSTAFANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDokument11 SeitenChapter 4 Tissues, Glands, and MembranesMaria Angela Del Gallego100% (2)
- Christian EthicsDokument36 SeitenChristian EthicsJoseph FordNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology - q2 - Week 4Dokument33 SeitenGeneral Biology - q2 - Week 4Renard JaenNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Biology - Chapter 29 Discussion AnswersDokument3 SeitenAP Biology - Chapter 29 Discussion Answersangel91me6371100% (1)
- RFLP Teaching KitDokument5 SeitenRFLP Teaching Kitkuldip.biotechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Chapter on ReproductionDokument4 SeitenScience Chapter on ReproductionAnita GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- APP Ch.3 OutlineDokument5 SeitenAPP Ch.3 OutlineAlliePalmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robbins Notes: Aging, Radiation, and Inflammation Self StudyDokument44 SeitenRobbins Notes: Aging, Radiation, and Inflammation Self StudyJustine HungNoch keine Bewertungen
- MrsaDokument10 SeitenMrsaNurul FaizaahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pest ManagementDokument5 SeitenPest Managementkiran100% (1)