Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Genetics Practice Exam 2
Hochgeladen von
heyyyaleCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Genetics Practice Exam 2
Hochgeladen von
heyyyaleCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PCB3063 GENETICS FORM 1 EXAM1 Spring 2012
1. The intrepid scientist/explorer Ludwig Kenichi Tracey has come back from Stephanbugga Land with a new
life form. These critters make love in triplets. They are all triploids formed through the fusion of three
gametes, and gametic ratios are 1:1:1. The DNA from these critters is a
a. concatenation of amino acids.
b. methylated spiral.
c. triple helix.
d. double helix.
e. form of triangle with four sides.
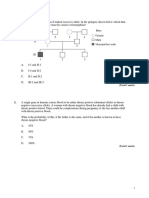
2. Pigeons may exhibit a checkered or plain color pattern. In a series of matings the following data were
obtained.
checkered X checkered 118 checkered
plain X plain 163 plain
checkered X plain 121 checkered F1 pigeons
F1checkered X F1 checkered 149 checkered and 53 plain
A reasonable hypothesis to explain this data is that
a. color is not inherited in pigeons.
b. color is a single locus, two allele (checkered dominant) system.
c. color is a single locus, two allele (plain dominant) system.
d. color is a single locus, two allele (checkered recessive) system.
e. color is a three locus system with a 9:3:3:1 expectation.
3. The meiotic explanation of Mendels Law of Segregation is that
a. the genetic material duplicates once and the cell divides twice.
b. the homologous chromosomes pair at metaphase I and then disjoin.
c. the homologous chromosomes may undergo crossing over.
d. nonhomologous chromosomes exchange p and q arms.
e. daughter cells are haploid.
4. The meiotic explanation of Mendels Law of Independent Assortment is that
a. daughter cells are diploid.
b. the homologous chromosomes pair at metaphase I and then disjoin.
c. the homologous chromosomes may undergo crossing over.
d. nonhomologous chromosomes align at random at metaphase 1.
e. nonhomologous chromosomes exchange p and q arms.
5. At metaphase 1 a chromosome contains ___ chromatids and ___ DNA double helices.
a. 2 , 2 b. 2, 4 c. 1 , 1 d. 3, 3 e. none of these is correct
6. After pairing at metaphase I chromosomes disjoin
a. without centromeric fission. b. with chromatids together.
c. into opposite daughter cells. d. a,b & c are all true.
7. If a pair of chromosomes at metaphase I contain the alleles M & M in one chromosome and m & m in the
other chromosome, the first daughter cells will contain
a. either m & m or M & M
b. either M & m or m & M
c. M & m and mm & M
d. MM Mm mM and mm
9. During replication a guanine is erroneously paired with an adenine on one of the new strands. At the
completion of meiosis the two haploids from this replication will be ____ and ____.
a. AT TA b. AG AT c. CG AT d. CG CA
10. In about 85 % of Europeans, known as secretors, antigen A or B is found in saliva and other bodily fluids
of people who are A, B or AB. Fifteen percent of Europeans who do produce red cell antigens do not secrete;
they are nonsecretors. A woman who is an A secretor marries another A secretor. Their first child is an A
nonsecretor. This result suggests that
a. secretor is dominant b. infidelity has occurred c. secretor is recessive d. the couple is sterile e. b & d are both
true
11. Professor Fromstazh has been collecting data from couples known to be carriers or heterozygotes for the
STR gene wiser. The data collected look like this
CHILDREN's PHENOTYPES
WW Ww ww
121 249 130 500
The expected number of heterzygotes is
a. 250 b. 400 c.125 d. 249 e. 15
12. Using his one locus two allele hypothesis the expected number of ww
homozygotes is
a. 18 b. 36 c. 41.25 d. 18.33 e. 125
13. and the expected number of WW homozygotes is
a. 125 b. 19 c. 13. d. 36.75 e. 18.33
14. The chi-square value for goodness of fit of this data is
[ Chi-square = SUM (obs-exp)
2
/exp ]
a. 0.0 b. 3.84 c. 0.32 d. 55 e. 0.001
PROBABILITY
df 0.95 0.90 0.50 0.25 0.05
1 .004 .016 .455 1.32 3.84
2 .103 .211 1.39 2.77 5.99
3 .352 .584 2.37 4.11 7.81
15. Professor Fromstazhs hypothesis
a. is consistent with this data.
b. should be rejected, because it does not fit the data.
c. is untestable. d. a. & c e. a & b
16. Another group of geneticists studying the wiser like loci identified carrier parents only when they had at
least one child who was homozygous for the recessive allele. Looking only at families with two children, what
fraction of heterozygous X heterozygous marriages would be missed?
a. 1/3 b. 2/3 c. 9/16 d. 7/16 e. 3/4
17. A biochemical event occurs while maternal and paternal genomes are separated and causes differential,
rather than equal, expression of the allele in the offspring. Mice who receive an IGF2, insulin like growth factor
2, allele from the paternal parent and a mutant nonfunctional allele from the maternal parent are normal.
Progeny of the reciprocal cross are runts. The normal IGF2 allele is _________ in the male parent.
a. methylated b. hydroylated c. epilated
d. esterified e. not methylated
18.The chi-square distribution relates
a. genetics to statistics b. deviation from theoretical value to probability
c. observed to expected d. metaphase to telophase
e. bases to sugars
19. In a cross of black-feathered Andalusian chickens with a strain having splashed-white feathers all the F
1
chicks were slate blue. { black X white blue F
1
s } When the F
1
s were intercrossed the chicks were 193
black, 409 blue and 198 white. Assuming that prior information had suggested single-locus codominance for
feather color, we would calculate _________ expected values. The total is 800 chicks.
a. 3:1 b. 1:1 c. 9:1 d. 1:2:1 e. 8:3
20. The expected number of blue chicks is
a. 600 b. 400 c. 198 d. 409 e. 193
21. The expected number of white chicks is
a. 600 b. 400 c. 200 d. 198 e. 193
22. The expected number of black chicks is
a. 600 b. 400 c. 200 d. 198 e. 193
23. The chi-square value for this test is
a. .47 b. 3.84 c. 9.74 d. 0.002 e. 9.4
-5-
Chi-square = SUM (obs-exp)
2
/exp
PROBABILITY
df 0.95 0.90 0.50 0.25 0.05
1 .004 .016 .455 1.32 3.84
2 .103 .211 1.39 2.77 5.99
3 .352 .584 2.37 4.11 7.81
24. The appropriate number of degrees of freedom for this test is
a. 1 b. 2 c. 1.5 d. 3 e. 0
25. The percentage of times one would expect to detect observed minus expected
discrepancies as large as these is
a. between 25 and 5 % b. less than 5% c. more than 95%
d. between 90 and 50% e. between 50 and 25%
26. In the Martin and Eaves study the data suggested that social attitudes were in large part inherited rather than
learned. This conclusion was based on
a. dominance effects at one locus.
b. greater resemblance between identical twins.
c. greater resemblance between identical twins.
d. 3:1 segragation ratio
e. cytoplasmic inheritance.
27. Alford and Hibbling subsequently found that approximately half of the variation in political attitudes was
genetically based, but _______ for party affiliation was found.
a. no genetic basis b. 50% genetic basis c. 40% genetic basis
d. imprinting e. complete genetic determination
GENETICS EXAM I 6 June 2001
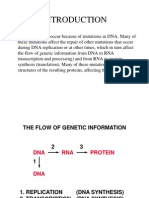
1. Chromosomes, colored bodies, are composed of proteins and DNA; so are chromatids. At metaphase I there are 46
chromosomes aligned in pairs along the human cells equatorial plate. At this stage there are______chromatids.
a. 23 b. 46 c. 92 d. 8 e.16
5. The gametic ratio for a heterozygote is roughly 1:1, 1/2 : 1/2 or whatever expression you like for equivalence. This
results from a. anaphase I disjunction b. mitotic crossingover c. Chi-square degrees of freedom d. telomeric sequences
e. all of the above
7. Knowing that the segregation ratios for a set of loci are all 1/2 : 1/2, we can predict the frequencies of all possible
gametic types by multiplying, if the loci are on different chromosomes and independent. For an AaBbCcDd four locus
heterozygote there are ______ possible gametes of equal frequency. a. 2 b. 4 c. 8 d. 16 e. 32
24. Arthur Beaudet identified a young girl with CF and short stature. Since CF is a recessive he was surprised to find that
she had no paternal chromosome 7 alleles, but all of the other chromosomes showed paternal as well as maternal alleles.
The two CF alleles were both maternal. Engel in an 1980 issue of the American Journal of Medical Genetics described
this as _________________.
a. interchromosomal methylation b. meiotic arrest c. uniparental disomy d. semiconservative e. flibbertigibbitt
25. A biochemical event occurs while maternal and paternal genomes are separated and causes differential, rather than
equal, expression of the alleles in the offspring. Mice who receive an IGF2, insulin like growth factor 2, allele from the
paternal parent and a mutant nonfunctional allele from the maternal parent are growth-deficient. Progeny of the reciprocal
cross are normal. The normal IGF2 allele is _________ in the male parent.
a. somnubalated b. hydroylated c. epilated d. esterified e. methylated
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Pyridine Nucleotide CoenzymesVon EverandThe Pyridine Nucleotide CoenzymesJohannes EverseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics WorkbookDokument57 SeitenGenetics WorkbookLauren WinnettNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Texas BIO 325 ExamDokument6 SeitenUniversity of Texas BIO 325 ExamGeetika InstaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics problems solved with Punnett squaresDokument2 SeitenGenetics problems solved with Punnett squaresnaomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patterns of Inheritance in Plants and AnimalsDokument8 SeitenPatterns of Inheritance in Plants and Animalsmzunl25476Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics QPDokument79 SeitenGenetics QPTimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Pedigree AnalysisDokument48 Seiten4 Pedigree AnalysisBiologistAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Problems AnimalGeneticsDokument21 SeitenSolving Problems AnimalGeneticsrksudheer9768100% (1)
- Polytene and Lampbrush ChromosomesDokument3 SeitenPolytene and Lampbrush Chromosomesneeru.bhagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Questions To PrepareDokument6 SeitenGenetics Questions To PrepareJohn Osborne100% (1)
- Genetics, Lecture 11 (Lecture Notes)Dokument16 SeitenGenetics, Lecture 11 (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-QudsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linkage, Crossing-Over, & GeneDokument13 SeitenLinkage, Crossing-Over, & GeneAbel ClaireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Notes Bio 2C03Dokument29 SeitenGenetics Notes Bio 2C03Wayne FangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 Past Exam MC QuestionsDokument14 SeitenTopic 3 Past Exam MC QuestionsAhmad FarhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gene RegulationDokument30 SeitenGene Regulationprehealthhelp67% (3)
- SY12202 Variation in Chromosome Number StructureDokument49 SeitenSY12202 Variation in Chromosome Number StructureMasni Shah NingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Practice ProblemsDokument6 SeitenGenetics Practice ProblemsCatalinaCardenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Profiling & Paternity TestingDokument7 SeitenDNA Profiling & Paternity TestingizabelssonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Molecular Biology: Marla Grace CostesDokument58 SeitenIntroduction To Molecular Biology: Marla Grace Costesschstg100% (2)
- Genetics QuestionsDokument14 SeitenGenetics QuestionsKwang Jun KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single-Nucleotide PolymorphismDokument21 SeitenSingle-Nucleotide PolymorphismdearbhupiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacterial Gene AnnotationDokument12 SeitenBacterial Gene AnnotationAndrew Steele100% (1)
- Genetics Chapter 2 QuestionsDokument9 SeitenGenetics Chapter 2 QuestionslifecostNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Genetic PrinciplesDokument37 SeitenBasic Genetic PrinciplesShaira Reyes0% (1)
- Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDokument42 SeitenChapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cyclesimma haznaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3Dokument18 SeitenUnit 3harshbharatdesai_783Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic Basis of Oral DiseasesDokument23 SeitenGenetic Basis of Oral Diseasesshanima sherinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 Semifinal Exam QuestionsDokument42 Seiten2011 Semifinal Exam Questionsmartynapet100% (1)
- Examn of Molecular BiologyDokument11 SeitenExamn of Molecular BiologycegfracNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of MutationsDokument64 SeitenTypes of MutationsI'm Cracked100% (1)
- Genome Annotation and ToolsDokument20 SeitenGenome Annotation and ToolsKumar KunalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quizlet GeneticsDokument4 SeitenQuizlet GeneticsMa Cecilia SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stem Cell Plasticity-Building The Brain of Dreams: by Sally TempleDokument22 SeitenStem Cell Plasticity-Building The Brain of Dreams: by Sally TempleGagan KarwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis QuestionsDokument10 SeitenMitosis QuestionscapremaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDokument12 SeitenCell Cycle and Cell DivisionMajid Al-hachami100% (1)
- Signal Transduction: Desak Made WihandaniDokument56 SeitenSignal Transduction: Desak Made WihandaniMaha Satya Dwi Palguna100% (1)
- CH 10 Gene ExpressionDokument23 SeitenCH 10 Gene ExpressionerichaasNoch keine Bewertungen
- t2 Bio Revision Ex 1 Answer SchemeDokument15 Seitent2 Bio Revision Ex 1 Answer SchemeNicholas OwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology Practice 2 Questions and AnswersDokument15 SeitenCell Biology Practice 2 Questions and AnswersNgMinhHaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modes of InheritanceDokument47 SeitenModes of Inheritancesudhir_narang_3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heredity and VariationDokument25 SeitenHeredity and VariationDre ParkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChromosomesDokument4 SeitenChromosomesعامر جدونNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Genetic Disorders ExplainedDokument6 SeitenClassification of Genetic Disorders ExplainedshobhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1A - Exploring Ncbi: Bioinformatic Methods I Lab 1Dokument22 SeitenLab 1A - Exploring Ncbi: Bioinformatic Methods I Lab 1Ariadna Andrade AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Practice Problems PDFDokument9 SeitenGenetics Practice Problems PDFanaphade5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics 1Dokument24 SeitenGenetics 1api-237826806Noch keine Bewertungen
- H-W Practice Prob+keyDokument2 SeitenH-W Practice Prob+keysalewaity100% (2)
- Mendelian Genetics in Humans: Mutaz AminDokument32 SeitenMendelian Genetics in Humans: Mutaz AminMustafa Khalid MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bi 341 Chapter 1 The Genetic Code of Genes and Genomes & Introduction - KBDokument76 SeitenBi 341 Chapter 1 The Genetic Code of Genes and Genomes & Introduction - KBMATHIXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gene MutationDokument20 SeitenGene Mutationdheeresh aggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 - Chromosome & GenomeDokument64 SeitenLecture 1 - Chromosome & GenomeFriendlyGoodGirlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics of Common DiseasesDokument57 SeitenGenetics of Common Diseaseskholoud220Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chromosomes: Sardar Hussain Asst - Prof.biotechnology GSC, CtaDokument127 SeitenChromosomes: Sardar Hussain Asst - Prof.biotechnology GSC, CtaAshikuzzaman AntorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction Notes Biol1008 ANUDokument14 SeitenReproduction Notes Biol1008 ANUAbby FaureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Alberts Test BankDokument10 SeitenMolecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Alberts Test Bankqocax0% (1)
- Approval Sheet: Name: Andi Nurlaeli Reg - No: 071404159 Group: IV (Fourth)Dokument12 SeitenApproval Sheet: Name: Andi Nurlaeli Reg - No: 071404159 Group: IV (Fourth)Lhely Andi NurlaeliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Semifinal Exam PartAandB QuestionsDokument39 Seiten2012 Semifinal Exam PartAandB Questionsmartynapet100% (3)
- Dna Genes Chromosomes 2011Dokument65 SeitenDna Genes Chromosomes 2011Suliman GarallehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Problems and SolutionsDokument18 SeitenGenetics Problems and SolutionsDeblina JanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prac Ex 01Dokument11 SeitenPrac Ex 01Jinal PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNTITLED2 Answer Key Test with Quadrant III and x-axis QuestionsDokument2 SeitenUNTITLED2 Answer Key Test with Quadrant III and x-axis QuestionsheyyyaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.3-1.4 Test Review: Convert Each Degree Measure Into Radians and Each Radian Measure Into DegreesDokument2 Seiten1.3-1.4 Test Review: Convert Each Degree Measure Into Radians and Each Radian Measure Into DegreesheyyyaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 13 Outcomes SlideDokument1 SeiteLecture 13 Outcomes SlideheyyyaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic FieldDokument37 SeitenChapter 28 Sources of Magnetic FieldheyyyaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiochemistryDokument2 SeitenBiochemistryheyyyaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions for Selected End of Chapter 6 ProblemsDokument6 SeitenSolutions for Selected End of Chapter 6 Problemsheyyyale100% (1)
- Solutions to Selected End of Chapter 5 ProblemsDokument3 SeitenSolutions to Selected End of Chapter 5 ProblemsheyyyaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna & RnaDokument43 SeitenDna & RnaheyyyaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resource Competition: Intra and InterspecificDokument4 SeitenResource Competition: Intra and InterspecificheyyyaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharma Companies by StateDokument8 SeitenPharma Companies by StateMuhammad Farhan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Obat PharmacyDokument7 SeitenDaftar Obat PharmacyparulianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAFC Biosciences - Technical Bulletin - BIOEAZE Bags - Ethyl Vinyl Acetate (EVA) FilmDokument4 SeitenSAFC Biosciences - Technical Bulletin - BIOEAZE Bags - Ethyl Vinyl Acetate (EVA) FilmSAFC-Global100% (1)
- Aplied Biosystems Step One Plus TR PCR Manual UtilizareDokument320 SeitenAplied Biosystems Step One Plus TR PCR Manual UtilizareFlorea RodicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIP Cycle Development ISPEDokument9 SeitenCIP Cycle Development ISPEvijayns_250355172Noch keine Bewertungen
- ArticuloDokument7 SeitenArticuloCarlosGuevaraPáezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orbital Shaker For Co2 IncubatorDokument2 SeitenOrbital Shaker For Co2 Incubatororbitalshakerforco2iNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthetic Antibodies Methods and Protocols (Methods in Molecular Biology)Dokument420 SeitenSynthetic Antibodies Methods and Protocols (Methods in Molecular Biology)phyaraviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nab™ Spin Columns, 0.2 ML For Antibody Purification: InstructionsDokument3 SeitenNab™ Spin Columns, 0.2 ML For Antibody Purification: InstructionsHiro MurayamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO5TEC Timetable 2019 Rev 2Dokument1 SeiteBIO5TEC Timetable 2019 Rev 2James BondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioactive Lipid Mediators - (2015)Dokument424 SeitenBioactive Lipid Mediators - (2015)MohammedAjebliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqua Maris nasal sprays and solutionsDokument110 SeitenAqua Maris nasal sprays and solutionsCornelia Lia0% (1)
- Case 1: Bristol-Myers Squibb's Growth Through Addition, Subtraction, and SharingDokument2 SeitenCase 1: Bristol-Myers Squibb's Growth Through Addition, Subtraction, and SharingJanine BouwerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Biotech in Medical - Projects in BiopharmaceuticalDokument2 SeitenApplications of Biotech in Medical - Projects in BiopharmaceuticalParveen DagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Electric Fields (PEF) For Food Processing TechnologyDokument15 SeitenPulse Electric Fields (PEF) For Food Processing TechnologyPraful BhosaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOL10521 Sem1 1516 Questions PDFDokument12 SeitenBIOL10521 Sem1 1516 Questions PDFPetr BrožNoch keine Bewertungen
- IFT Expert Report On Biotechnology and FoodsDokument56 SeitenIFT Expert Report On Biotechnology and FoodsdnukhetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time and ConcentrationDokument2 SeitenTime and ConcentrationikrimakhaerunnisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoikiometri Reaksi Dan Neraca MassaDokument4 SeitenStoikiometri Reaksi Dan Neraca Massaandari yuta palwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Danaher Annual Report 2018Dokument154 SeitenDanaher Annual Report 2018Robert Sunho LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Plasmid Vectors Using Replication Origin, Selection Marker and Promoter As Criteria. WWW - Picb.ac - CNDokument5 SeitenClassification of Plasmid Vectors Using Replication Origin, Selection Marker and Promoter As Criteria. WWW - Picb.ac - CNAhmad SolikinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rumen MicrobiologyDokument15 SeitenRumen MicrobiologyJ Jesus Bustamante GroNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 26 Annual Biosciences Quiz BeeDokument3 SeitenThe 26 Annual Biosciences Quiz BeeMatthew Rei De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To DownstreamprocessingDokument24 SeitenIntro To DownstreamprocessingmluluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting The Ethanol Productivity of Yeast in MolassesDokument4 SeitenFactors Affecting The Ethanol Productivity of Yeast in Molassesakash sawarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE HELPLINE Bioprocess Engineering MCQ IDokument4 SeitenGATE HELPLINE Bioprocess Engineering MCQ ISanthosh Kalash100% (8)
- Lab Act 1Dokument8 SeitenLab Act 1KarenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Ekstrak Jeruk Nipis Dan Ampas KopiDokument6 SeitenJurnal Ekstrak Jeruk Nipis Dan Ampas KopiAD RizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Inheritance N Variation PDFDokument4 SeitenPrinciples of Inheritance N Variation PDFshodhan shettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmaco GeneticsDokument8 SeitenPharmaco GeneticsArti Tyagita KusumawardhaniNoch keine Bewertungen