Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chalkd95, Fowler28, Myersg71, Iapicc79, Singhs58
Hochgeladen von
api-19741990Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chalkd95, Fowler28, Myersg71, Iapicc79, Singhs58
Hochgeladen von
api-19741990Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Aerial Robotic Blimp
Jason Iapicco , Dan Chalk , Geoffrey Myers
1 1 1
Nick Folwer , Sukhbir Singh , Ali Daneshmand
1 1 1
Peter Renner , Will Weisnet
2 2
1
Department of Computer Science
2
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Email: [chalkd95, fowler28,myersg71, iapicc79, singhs58,
renner54, weisne46]@students.rown.edu , ali.daneshmand@gmail.com
Faculty Advisors: Dr. Adrian Rusu , Dr. Hong Zhang
1 2
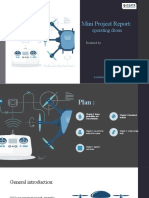
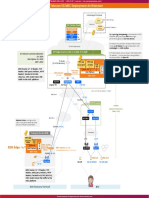
Maze layout that the blimp will
need to navigate Manual Control Window
Won a 2 Place Award at IARC 2006
nd
Abstract:
The main emphasis of this project is to create an
autonomously controlled Blimp to compete in the 2006
Indoor Aerial Robot Competition (IARC) at Drexel.
The Blimp needs to be able to find its way through a
maze and stay as long as it can in a circle with cross
wind from a fan. This Blimp includes three main
capabilities which when used together allows the Blimp
to move autonomously. First, computer vision (video
Each of the red circles recognition) determines which way the Blimp needs to
represents the location of a turn as well as keeping a running log of the turns.
Fiducial. The blimp uses Second, a Wireless Modem connection that allows the Maze Layout
these to decide which computer vision to communicate with the directional
direction to go. control on the Blimp. Last is the directional control
onboard the Blimp. It takes the data given to it from
computer vision and then determines which servo to
send a pulse width to for any directional changes or
vertical changes.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Confocal Scanning Optical Microscopy and Related Imaging SystemsVon EverandConfocal Scanning Optical Microscopy and Related Imaging SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autonomous Aerial Drone With Infrared Depth TrackingDokument8 SeitenAutonomous Aerial Drone With Infrared Depth TrackingHarry moesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 986 1059 PB PDFDokument6 Seiten986 1059 PB PDFmadan kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space MouseDokument33 SeitenSpace MouseVenkat KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DE6 Report - 1Dokument24 SeitenDE6 Report - 1Vishal ChudasamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Skeleton Tracking Based Human Recognition System Using Kinect and ArduinoDokument6 SeitenReal Time Skeleton Tracking Based Human Recognition System Using Kinect and ArduinoAdi TiawarmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vision-Based Obstacle Avoidance On Quadcopter: Kashif Khurshid Noori, Manish Kumar Mishra & Md. Zafaryab AbdullahDokument10 SeitenVision-Based Obstacle Avoidance On Quadcopter: Kashif Khurshid Noori, Manish Kumar Mishra & Md. Zafaryab AbdullahTJPRC PublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morphological Fire Fighting DroneDokument10 SeitenMorphological Fire Fighting DroneInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space Mouse (Pooja S)Dokument30 SeitenSpace Mouse (Pooja S)Pooja S100% (1)
- Landing Pad - 2Dokument6 SeitenLanding Pad - 2stealthcenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swarm Intelligence Based Fire Fighting RobotDokument6 SeitenSwarm Intelligence Based Fire Fighting RobotIJAERS JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2071 4258 1 SMDokument7 Seiten2071 4258 1 SMfauzanghozialayubiNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Gesture Recognition": A Final Report OnDokument49 Seiten"Gesture Recognition": A Final Report OnShruthi GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Guided Adhvik Humanoid RobotDokument4 SeitenSelf Guided Adhvik Humanoid RobotAshutosh ShrivastavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper TE-2Dokument8 SeitenPaper TE-2Sandro SiagianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arduino DroneDokument6 SeitenArduino Dronemahesh giteNoch keine Bewertungen
- FPGA Robot Arm Assistant: Final Project ReportDokument32 SeitenFPGA Robot Arm Assistant: Final Project Reporthassan angularNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlling Computer System Using Eye MovementDokument3 SeitenControlling Computer System Using Eye MovementPooja ChendakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Drone InformeDokument4 SeitenControl Drone InformeLaura PrietoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Short Review of The Drone Technology: August 2022Dokument17 SeitenA Short Review of The Drone Technology: August 2022rokomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Driving and Human Following TrolleyDokument41 SeitenSelf Driving and Human Following TrolleyOmm BhunyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Docsity Design of Optical Mouse Used For Oct Imaging Project 1 Report Ece 445Dokument24 SeitenDocsity Design of Optical Mouse Used For Oct Imaging Project 1 Report Ece 445Harika RavitlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Room Occupancy Sensing Mat: by Puri, Yohann Sethi, Aakarsh Wang, SteveDokument20 SeitenRoom Occupancy Sensing Mat: by Puri, Yohann Sethi, Aakarsh Wang, SteveNatinael AbrhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Short Review of The Drone Technology: August 2022Dokument17 SeitenA Short Review of The Drone Technology: August 2022sarthak ghimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Detection, Locking and Hitting A Fast Moving Aerial Object by Image Processing (Suitable For Guided Missile)Dokument10 SeitenAutomated Detection, Locking and Hitting A Fast Moving Aerial Object by Image Processing (Suitable For Guided Missile)mahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drone PresentationDokument31 SeitenDrone PresentationMed Rabeh100% (1)
- An Autonomous Firefighting Robot: Abstract: The Field of Firefighting Has Long Been ADokument6 SeitenAn Autonomous Firefighting Robot: Abstract: The Field of Firefighting Has Long Been Apooja madhurkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadcopter - Obstacle Detection and Collision Avoidance: Prathamesh Salaskar, Saee Paranjpe, Jagdish Reddy, Arish ShahDokument4 SeitenQuadcopter - Obstacle Detection and Collision Avoidance: Prathamesh Salaskar, Saee Paranjpe, Jagdish Reddy, Arish ShahRyan FebrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Vehicle Detection and Speed Measurement in Video Sequence IJERTV2IS100920Dokument4 SeitenMoving Vehicle Detection and Speed Measurement in Video Sequence IJERTV2IS100920aniket wadheNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF - Object Detection and Person Tracking Using UavDokument11 SeitenPDF - Object Detection and Person Tracking Using UavVj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kangunde2021 Article AReviewOnDronesControlledInReaDokument16 SeitenKangunde2021 Article AReviewOnDronesControlledInReahawicha AbomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection of Components With The Support of The DronesDokument6 SeitenInspection of Components With The Support of The DronesF. GiacobbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion Detection and Its ApplicationsDokument6 SeitenMotion Detection and Its ApplicationsIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Drone PresentationDokument15 SeitenFinal Drone PresentationAtharva ZagadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arm 2103Dokument78 SeitenArm 2103nikhilvishwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELB1502 MajorTest2 S1-2023Dokument2 SeitenELB1502 MajorTest2 S1-2023Siphamandla CokaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drone ProjectDokument27 SeitenDrone ProjectNirmal Raj BaskaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space Mouse: Seminar Report OnDokument30 SeitenSpace Mouse: Seminar Report OnWaitingforu MyGrlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Face Recognition On UAV AI DroneDokument6 SeitenFace Recognition On UAV AI DroneInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Mouse Hack by ShivDokument6 SeitenOptical Mouse Hack by ShivShiv KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors 21 05293Dokument14 SeitenSensors 21 05293MIGUEL ANGEL VICENTE CANAVIRINoch keine Bewertungen
- Supervisors: Dr. Jan Carlo Barca & Dr. Hoam Chung: Brian Ramirez EspinosaDokument1 SeiteSupervisors: Dr. Jan Carlo Barca & Dr. Hoam Chung: Brian Ramirez Espinosahbhbhb hbhbhbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Remote Controlled POV DisplayDokument7 SeitenWireless Remote Controlled POV DisplayDNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Project Report ON: Mobile Robot ARMDokument18 SeitenA Project Report ON: Mobile Robot ARMVivek WaykoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Space Mouse": Electronics and Communication EngineeringDokument28 Seiten"Space Mouse": Electronics and Communication EngineeringBismi ĹLaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report "Nayan Drishti": A Revolutionary Navigation/Visual Aid For The Visually ImpairedDokument68 SeitenProject Report "Nayan Drishti": A Revolutionary Navigation/Visual Aid For The Visually Impairedyogesh naikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amorphous Computing and Swarm IntelligenceDokument35 SeitenAmorphous Computing and Swarm IntelligenceAnkur PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jmse 10 01716Dokument23 SeitenJmse 10 0171620EUMT037 MAHADEER MOHAMED YNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOT Mid ProjectDokument4 SeitenIOT Mid Projectsai krishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijetae 1214 100Dokument5 SeitenIjetae 1214 100akula pranathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yolo Vs RCNNDokument5 SeitenYolo Vs RCNNsrinidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hds Report PrintDokument32 SeitenHds Report PrintVikas SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Object Identification Using Ann: Members of Project Team 1. 2Dokument4 SeitenMoving Object Identification Using Ann: Members of Project Team 1. 2Sujith Kumar ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engr2105 ProjectDokument6 SeitenEngr2105 ProjectSUPER AMAZINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spinoff2015 PDFDokument219 SeitenSpinoff2015 PDFBrad MogrovejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Wisp - Capstone Final Report - Nathan Warren-AcordDokument40 SeitenProject Wisp - Capstone Final Report - Nathan Warren-Acordapi-428315790Noch keine Bewertungen
- Asteria RulebookDokument31 SeitenAsteria RulebookSudeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- AI Facial Recognition SystemDokument54 SeitenAI Facial Recognition SystemcontactchrisyellenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identitas JurnalDokument15 SeitenIdentitas JurnalihsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Range Security System For Vehicle Navigation: M. URA ofDokument6 SeitenRange Security System For Vehicle Navigation: M. URA ofmkollamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sponsored By: "A Picture Is Worth A Thousand Words"Dokument75 SeitenSponsored By: "A Picture Is Worth A Thousand Words"api-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- TestBeamESA EPAC06Dokument1 SeiteTestBeamESA EPAC06api-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- WorkshopposterDokument1 SeiteWorkshopposterapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Across The World: International Poster CompetitionDokument11 SeitenPhysics Across The World: International Poster Competitionapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Poster 2Dokument1 SeitePoster 2api-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- MSC Project - Poster PresentationsDokument22 SeitenMSC Project - Poster Presentationsapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- University of Maryland School of Medicine September 27/28, 2005 MSTF AtriumDokument12 SeitenUniversity of Maryland School of Medicine September 27/28, 2005 MSTF Atriumapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gogeoposter 2Dokument1 SeiteGogeoposter 2api-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Creating Effective Poster Presentations: Stuart Boon Centre For Academic Practice & Learning EnhancementDokument20 SeitenCreating Effective Poster Presentations: Stuart Boon Centre For Academic Practice & Learning Enhancementapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Making The Most of Your Conference Poster: DR Krystyna Haq Graduate Education Officer Graduate Research SchoolDokument19 SeitenMaking The Most of Your Conference Poster: DR Krystyna Haq Graduate Education Officer Graduate Research Schoolapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kaushal Issgc05 PosterDokument1 SeiteKaushal Issgc05 Posterapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- IST2001 PosterDokument1 SeiteIST2001 Posterapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- IeMRC PosterDokument1 SeiteIeMRC Posterapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- HEA MiniProjectv3Dokument1 SeiteHEA MiniProjectv3api-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- GHGT-9 Poster TemplateDokument1 SeiteGHGT-9 Poster Templateapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eng Design A1 PortraitDokument1 SeiteEng Design A1 Portraitapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eng Design A1 LandscapeDokument1 SeiteEng Design A1 Landscapeapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Polarization-Independent Techniques For Optical Signal ProcessingDokument52 SeitenPolarization-Independent Techniques For Optical Signal Processingapi-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2mrad RobAppleby EPAC06Dokument1 Seite2mrad RobAppleby EPAC06api-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Casa Postertemplate08Dokument1 SeiteCasa Postertemplate08api-19741990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shenzhen Gooky Technology Co.,Ltd.: Laptop Price ListDokument31 SeitenShenzhen Gooky Technology Co.,Ltd.: Laptop Price ListFanta KeitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7755 PDFDokument2 Seiten7755 PDFIbrahim JaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msha Text Pager ApprovalDokument6 SeitenMsha Text Pager ApprovalJosh GreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Khon Kaen University Department of Electrical Engineering CM - 03: Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Frequency Modulation Preliminary DiscussionDokument23 SeitenKhon Kaen University Department of Electrical Engineering CM - 03: Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Frequency Modulation Preliminary DiscussionMichelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.4.pcm Numericals and Line CodesDokument25 Seiten3.4.pcm Numericals and Line CodesA47Sahil Rahate100% (1)
- Data Communications Instructor: Engr. Dominic P. BolimaDokument4 SeitenData Communications Instructor: Engr. Dominic P. BolimaErica May ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellphone Network Jammer Circuit Using NE555 Timer: Olayiwola Joy Oluwabukola & Aliu Olaniyi HabibDokument8 SeitenCellphone Network Jammer Circuit Using NE555 Timer: Olayiwola Joy Oluwabukola & Aliu Olaniyi Habibmrunofficial000Noch keine Bewertungen
- United States Patent: CA (US) Shouri Chatterjee, New 2733272 g1 2588 (1) Beige 341/59Dokument14 SeitenUnited States Patent: CA (US) Shouri Chatterjee, New 2733272 g1 2588 (1) Beige 341/59arupNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Tourism: Concept and Evolution: Iulian CondratovDokument4 SeitenE-Tourism: Concept and Evolution: Iulian CondratovAndra AndreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced View of Projects Raspberry Pi List - Raspberry PI ProjectsDokument189 SeitenAdvanced View of Projects Raspberry Pi List - Raspberry PI ProjectsBilal AfzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- M-8PGH-M65-16T212-TD (MRV 2600M)Dokument4 SeitenM-8PGH-M65-16T212-TD (MRV 2600M)jaager1985Noch keine Bewertungen
- AOS-CX Simulator Lab - PIM-SM Troubleshooting Lab GuideDokument13 SeitenAOS-CX Simulator Lab - PIM-SM Troubleshooting Lab Guidetest testNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intellian Installation Manuali9w - ManualDokument73 SeitenIntellian Installation Manuali9w - ManualRay GeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet RPIV R4 8Dokument8 SeitenDatasheet RPIV R4 8Aldenir Jose BatistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 Ec 421Dokument3 Seiten18 Ec 421Srujana PurohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- C 75 Dual Radio Dual Concurrent Wave 1 Access Point AmtDokument8 SeitenC 75 Dual Radio Dual Concurrent Wave 1 Access Point Amtsantoimam112Noch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual Taiga Tracker - enDokument23 SeitenUser Manual Taiga Tracker - enAldo RahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 10 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) in PIC18F452 ObjectiveDokument10 SeitenExperiment 10 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) in PIC18F452 Objectivehira Nawaz100% (1)
- Hot Dialer Instructions: (Unit # 103-049)Dokument1 SeiteHot Dialer Instructions: (Unit # 103-049)Payphone.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Versio IngestDokument2 SeitenVersio IngestdfdfNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Low-Power Single Sideband Circuits: Philips SemiconductorsDokument10 SeitenNew Low-Power Single Sideband Circuits: Philips SemiconductorsEne AlexandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Get Started - Public DNS - Google DevelopersDokument3 SeitenGet Started - Public DNS - Google DevelopersparirNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Interview Questions & Answers - Network KingsDokument22 SeitenCCNA Interview Questions & Answers - Network KingsRaghunandan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFID vs. Barcode (ICA Assignment) - Muddasir Ali Soomro: Bar CodeDokument4 SeitenRFID vs. Barcode (ICA Assignment) - Muddasir Ali Soomro: Bar CodeSalman KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st & 2nd CN PracticalDokument10 Seiten1st & 2nd CN PracticalVishal GorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei NGN System OverviewDokument26 SeitenHuawei NGN System OverviewRonald SimamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Koreasat 5 & Palapa D at 113.0°E - LyngSatDokument5 SeitenKoreasat 5 & Palapa D at 113.0°E - LyngSatHaiqal MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ManualDokument82 SeitenLab ManualSafa MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dhi-Nvr4108/4116Hs-8P-4Ks2: 8/16 Channel Compact 1U 8poe 4K&H.265 Lite Network Video RecorderDokument3 SeitenDhi-Nvr4108/4116Hs-8P-4Ks2: 8/16 Channel Compact 1U 8poe 4K&H.265 Lite Network Video RecorderJimmy Andres Arias TrujilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- B2C Edge: SK Telecom 5G MEC Deployment ArchitectureDokument1 SeiteB2C Edge: SK Telecom 5G MEC Deployment ArchitectureAshish GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewVon EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Cyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItVon EverandCyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (66)
- Chaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyVon EverandChaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (111)
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldVon EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (55)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsVon EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (722)
- The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andVon EverandThe E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (709)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldVon EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyVon EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (51)
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyVon EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootVon EverandSystem Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreVon EverandMini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (76)
- AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderVon EverandAI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (399)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumVon EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (12)
- Excel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceVon EverandExcel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeVon EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (69)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindVon EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Von EverandLearn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (34)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveVon EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Some SMS Verification Services and Virtual Credit Cards Services for Online Accounts VerificationsVon EverandEvaluation of Some SMS Verification Services and Virtual Credit Cards Services for Online Accounts VerificationsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldVon EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (107)
- Solutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesVon EverandSolutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Bitcoin Standard: The Decentralized Alternative to Central BankingVon EverandThe Bitcoin Standard: The Decentralized Alternative to Central BankingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (41)
- 100M Offers Made Easy: Create Your Own Irresistible Offers by Turning ChatGPT into Alex HormoziVon Everand100M Offers Made Easy: Create Your Own Irresistible Offers by Turning ChatGPT into Alex HormoziNoch keine Bewertungen