Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Rocket Types: EGR 4347 Analysis and Design of Propulsion Systems
Hochgeladen von
John Roy0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
51 Ansichten28 SeitenSlide show on rocket types
Originaltitel
Lesson 38 Rocket Types
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenSlide show on rocket types
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
51 Ansichten28 SeitenRocket Types: EGR 4347 Analysis and Design of Propulsion Systems
Hochgeladen von
John RoySlide show on rocket types
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 28
Rocket Types
EGR 4347 Analysis
and Design of
Propulsion Systems
Rocket Propulsion
Ideal Rocket Thrust
Specific Impulse
e a e
c
e e
i
A P P
g
V m
F
.
c
o
sp
g m
Fg
w
F
I
. .
Rocket
Propulsion
Rocket Propulsion
Rocket Propulsion Elements Sutton and Biblarz
Rocket Propulsion
Rocket Propulsion Elements Sutton and Biblarz
Rocket Propulsion
Chemical Rockets
Liquid typical O
2
and H
2
Solid
Scientific American March 2000
Liquid Rockets
Scientific American March 2000
Solid Rockets
Scientific American March 2000
Solid Rockets
Rocket Performance Mars Mission
Thrust force 1 N lb
f
Exhaust Speed Measure of fuel efficiency
Sample Burn Time How long the rocket must fire to
accelerate a 25-ton payload from low earth orbit to
escape velocity. The time is inversely related to the
thrust.
Sample fuel ratio fraction of the total spacecraft
mass taken up by propellant. The amount of fuel is
exponentially related to the exhaust speed.
Scientific American March 2000
Rocket Performance
Type Thrust (N) Exhaust Speed
(km/s)
Burn Time Fuel ratio (%)
Chemical 110K 4.5 21 min 55
Nuclear Rockets
Tested in 1960s
Hydrogen heated to
2,500 deg C
Reactors can generate
electricity
Public opposition
Scientific American March 2000
Rocket Performance
Type Thrust (N) Exhaust Speed
(km/s)
Burn Time Fuel ratio (%)
Chemical 110,000 4.5 21 min 55
Nuclear 67,000 9.0 27 min 32
ION
1950s
Electrical fields
accelerate particles
Scientific American March 2000
Fuel cesium or xenon
Cathode dumps
electrons into flow at exit
Grids get in the way
ION
Rocket Propulsion Elements Sutton and Biblarz
Rocket Performance
Type Thrust (N) Exhaust Speed
(km/s)
Burn Time Fuel ratio (%)
Chemical 110,000 4.5 21 min 55
Nuclear 67,000 9 27 min 32
Ion 30 30 79 days 22
Hall Effect
1970s Russia
Radial Magnetic Field
Xenon
No grids
Scientific American March 2000
Hall Effect
Rocket Propulsion Elements Sutton and Biblarz
Rocket Performance
Type Thrust (N) Exhaust Speed
(km/s)
Burn Time Fuel ratio (%)
Chemical 110,000 4.5 21 min 55
Nuclear 67,000 9 27 min 32
Ion 30 30 79 days 22
Hall Effect 30 15 90 days 38
Magnetoplasmadynamic (MPD)
Scientific American March 2000
Magnetic acceleration
Magnetic field electrically generated
Rocket Performance
Type Thrust (N) Exhaust Speed
(km/s)
Burn Time Fuel ratio (%)
Chemical 110,000 4.5 21 min 55
Nuclear 67,000 9 27 min 32
Ion 30 30 79 days 22
Hall Effect 30 15 90 days 38
MPD 100 20 - 100 21-25
days
6.7 - 31
Pulsed Inductive Thruster (PIT)
Argon Fuel
Radial Magnetic Field
200 times a second
No electrodes
Scientific American March 2000
Rocket Performance
Type Thrust (N) Exhaust Speed
(km/s)
Burn Time Fuel ratio (%)
Chemical 110,000 4.5 21 min 55
Nuclear 67,000 9 27 min 32
Ion 30 30 79 days 22
Hall Effect 30 15 90 days 38
MPD 100 20 - 100 21-25
days
6.7 - 31
PIT 20 50 110 days 14
VASIMR
Variable Specific
Impulse Magnetoplasma
Rocket
Radio waves heat fuel
Ionized propellant
(Hydrogen)
Magnetic fields
Scientific American March 2000
VASIMR
Rocket Performance
Type Thrust (N) Exhaust Speed
(km/s)
Burn Time Fuel ratio (%)
Chemical 110,000 4.5 21 min 55
Nuclear 67,000 9 27 min 32
Ion 30 30 79 days 22
Hall Effect 30 15 90 days 38
MPD 100 20 - 100 21-25 days 6.7 - 31
PIT 20 50 110 days 14
VASIMR H 40 300 53 days 2.4
VASIMR L
1,200 10 2.1 days 46
Solar Sails
Scientific American March 2000
9 N per square km
Large fragile structure
NASA working on Magnetic sail to catch sun
particles
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Satellite Design Course Spacecraft Configuration Structural Design Preliminary Design MethodsDokument85 SeitenSatellite Design Course Spacecraft Configuration Structural Design Preliminary Design Methodsmegustalazorra100% (1)
- TRW Pintle EngineDokument23 SeitenTRW Pintle EngineMuhammad Azeem AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starfish PrimeDokument31 SeitenStarfish PrimeonatbrossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysVon EverandMaterials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- PV Installer Program-Participant GuideDokument238 SeitenPV Installer Program-Participant Guidekatzgons100% (1)
- Artemis I - Press KitDokument41 SeitenArtemis I - Press KitLeonardo De León GranadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROPELLANTSDokument72 SeitenPROPELLANTSdinesh duraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIAA EbooksDokument9 SeitenAIAA Ebookssarah86304325Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rocket TypesDokument28 SeitenRocket TypesHarnil VaghasiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hybrid Rocket Propulsion For Future AircraftDokument40 SeitenHybrid Rocket Propulsion For Future AircraftSaravana Kumar100% (1)
- Physics RocketDokument18 SeitenPhysics RocketsahilNoch keine Bewertungen
- WBS US NavyDokument39 SeitenWBS US NavydddscriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary Design Review - Ad Lunam HopperDokument100 SeitenPreliminary Design Review - Ad Lunam HopperAniketh DevarasettyNoch keine Bewertungen
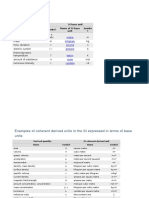
- Units and Conversion FactorsDokument30 SeitenUnits and Conversion FactorsBun YaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Missiles Propulsion 1Dokument110 SeitenMissiles Propulsion 1Bijin Chadayan0% (1)
- History of Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines in The United States PDFDokument30 SeitenHistory of Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines in The United States PDFfundamental_aeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 U.S. NATIONAL Chemistry Olympiad: National Exam - Part Ii Olympiad Examinations Task ForceDokument7 Seiten2010 U.S. NATIONAL Chemistry Olympiad: National Exam - Part Ii Olympiad Examinations Task ForceGurumurthy KalyanasundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic ProcessingDokument415 SeitenSeismic ProcessingMahmoud Said100% (1)
- Myanmar Cement-1Dokument14 SeitenMyanmar Cement-1Mohammed AbdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unha Launch Vehicle: Launch Report and Technological Summary of KMS-3-2 LaunchDokument11 SeitenThe Unha Launch Vehicle: Launch Report and Technological Summary of KMS-3-2 Launchapi-212957406Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jovian Atmosphere Jun 01Dokument28 SeitenJovian Atmosphere Jun 01Clifford StoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- WP SPS Supdoc 051129Dokument126 SeitenWP SPS Supdoc 051129Dork654651Noch keine Bewertungen
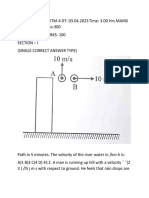
- Rocket Propulsion-2 ct-1 QP Key-2016Dokument3 SeitenRocket Propulsion-2 ct-1 QP Key-2016api-271354682Noch keine Bewertungen
- SI Base UnitsDokument20 SeitenSI Base UnitsSatish Kumar MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rockets, Orbits, and Universal GravitationDokument24 SeitenRockets, Orbits, and Universal GravitationAbhishek ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rockets, Orbits, and Universal GravitationDokument24 SeitenRockets, Orbits, and Universal GravitationSunil VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rocket Propulsion Unit-1Dokument47 SeitenRocket Propulsion Unit-1api-271354682100% (4)
- Core Mantle Change Impact Gas Oil FieldDokument165 SeitenCore Mantle Change Impact Gas Oil FieldVincent J. CataldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- S K AgarwalDokument39 SeitenS K AgarwalDhananjay YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 - Chapitre II - MicropropulsionDokument70 Seiten02 - Chapitre II - MicropropulsionAS asNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Mantle Change Impact Gas Oil FieldDokument161 SeitenCore Mantle Change Impact Gas Oil FieldVincent J. CataldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDMSP001786826Dokument2 SeitenHDMSP001786826babakafzaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASPS Transparencies 03Dokument26 SeitenASPS Transparencies 03Brian PreciousNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCEL 2005 Joslyn Creek Performance PresentationDokument70 SeitenDCEL 2005 Joslyn Creek Performance PresentationHarold PazosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary UnitsDokument6 SeitenQuantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary Unitshb360Noch keine Bewertungen
- EAEE E4190 Photovoltaic Systems Engineering and SustainabilityDokument56 SeitenEAEE E4190 Photovoltaic Systems Engineering and SustainabilityarilovesmusicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel CellsDokument47 SeitenFuel CellsRatna KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics GK Questions Answers in English PDFDokument7 SeitenPhysics GK Questions Answers in English PDFlatish upadrashtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extraction of Antiparticles Concentrated in Planetary Magnetic FieldsDokument35 SeitenExtraction of Antiparticles Concentrated in Planetary Magnetic FieldsClifford StoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2.1 Radionuclides in The Environment - Income - EspDokument16 SeitenLecture 2.1 Radionuclides in The Environment - Income - Espcarolina.calamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Aerospace Engineering Octavian Thor Pleter, PHD, PHD, Mba (MBS)Dokument43 SeitenIntroduction To Aerospace Engineering Octavian Thor Pleter, PHD, PHD, Mba (MBS)Andrei StancaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Name: Instructor Name:: Report of Mechanical Equivalent. Thermodynamics LabDokument4 SeitenStudent Name: Instructor Name:: Report of Mechanical Equivalent. Thermodynamics Labعبد الرحمن أبوخاطر, أبو رزقNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 RadioactiveDokument9 Seiten6 RadioactiveAnna Latifah CammryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions For Class 1: Chen 733 Coal CombustionDokument6 SeitenQuestions For Class 1: Chen 733 Coal CombustionmahantmtechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spacecraft AssignmentDokument11 SeitenSpacecraft AssignmentMuhammad Khurram KhalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini-Magnetospheric Plasma Propulsion (M2P2) :: High Speed Interplanetary and Heliospheric MissionsDokument24 SeitenMini-Magnetospheric Plasma Propulsion (M2P2) :: High Speed Interplanetary and Heliospheric MissionsClifford StoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petroleum Engineering Assignment 2012 13Dokument26 SeitenPetroleum Engineering Assignment 2012 13Amir O. OshoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Physics N Excel Book Neville WarrenDokument359 SeitenPhysics Physics N Excel Book Neville Warrenjojo6bobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: Pse Odisha Probable Question Discussion For Osssc Cre-2024Dokument21 SeitenPhysics: Pse Odisha Probable Question Discussion For Osssc Cre-2024Bhuleswar MeherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuclear Fuel Management: Recommended BooksDokument9 SeitenNuclear Fuel Management: Recommended BooksUsman AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 3: Comparison of Test Approaches of Recent and Past Argentina Space Projects E. Roggero, M.CerocchiDokument23 SeitenSession 3: Comparison of Test Approaches of Recent and Past Argentina Space Projects E. Roggero, M.CerocchiSol RoggeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proceedings of The Second UN International Conference On The Peaceful Uses of Atomic EnergyDokument400 SeitenProceedings of The Second UN International Conference On The Peaceful Uses of Atomic EnergyMaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 SCIENCE 2003 Set1Dokument3 Seiten10 SCIENCE 2003 Set1anil.gelra5140Noch keine Bewertungen
- LHC at CernDokument96 SeitenLHC at CernshehabthegreatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sanitation Requirements in Space: The Issues of Space Debris and Its ManagementDokument16 SeitenSanitation Requirements in Space: The Issues of Space Debris and Its ManagementSudheesh SurendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Gas Well Drilling and Completion With High Energy LasersDokument30 SeitenImproving Gas Well Drilling and Completion With High Energy LasersnavegargratisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of A Newton: One Newton (N) Is The Force It Takes To Change The Speed of A 1 KG Mass by 1 M/s in 1 SecondDokument32 SeitenExample of A Newton: One Newton (N) Is The Force It Takes To Change The Speed of A 1 KG Mass by 1 M/s in 1 SecondJustin GentryNoch keine Bewertungen
- SI UnitsDokument17 SeitenSI Unitsbkgarg99Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE672 Project Report HamoodDokument17 SeitenEE672 Project Report HamoodHamood Riasat KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Power and Wind Turbines: BY Er - Karthikeyan, Me, Mba, (PH.D)Dokument25 SeitenWind Power and Wind Turbines: BY Er - Karthikeyan, Me, Mba, (PH.D)chandranmuthuswamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Notation IDokument2 SeitenScientific Notation IAlejandro AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE MainsDokument26 SeitenJEE MainsSachin MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Wind MillDokument133 SeitenPresentation On Wind MillRAJENDRA TELVEKARNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st PU Physics Model QP 3 PDFDokument6 Seiten1st PU Physics Model QP 3 PDFPrasad C M100% (2)
- Lecture 1 UCSDDokument50 SeitenLecture 1 UCSDBrian LewisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Call of the Cosmic Wild. Relativistic Rockets for the New Millennium.: 3Rd Expanded Edition.Von EverandCall of the Cosmic Wild. Relativistic Rockets for the New Millennium.: 3Rd Expanded Edition.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Technology: Sources, Systems and Frontier ConversionVon EverandEnergy Technology: Sources, Systems and Frontier ConversionNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Jet Propulsion (Mme 4071 PPT-1)Dokument20 SeitenAn Introduction To Jet Propulsion (Mme 4071 PPT-1)Peter GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thrust Force Analysis of Spike Bell NozzleDokument6 SeitenThrust Force Analysis of Spike Bell NozzleAswith R ShenoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDC8 Paper143Dokument5 SeitenSDC8 Paper143Hugo AranhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dessertation FINALDokument16 SeitenDessertation FINALeshaan guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aero Engine Maintenance and Repair Two Marks With AnswerDokument7 SeitenAero Engine Maintenance and Repair Two Marks With AnswerHariharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stage Separation of Space Launch VehiclesDokument12 SeitenStage Separation of Space Launch Vehiclesvasanraja100% (1)
- Modern Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines: 2000 OutlookDokument58 SeitenModern Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines: 2000 OutlookErtuğrul Eren DurakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jet Propulsion EnginesDokument10 SeitenJet Propulsion EnginesAanshu SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review On Cleaner and Safer Propellant Materials For Space Vehicles and Their Characterisation - Paper-TitleDokument2 SeitenA Review On Cleaner and Safer Propellant Materials For Space Vehicles and Their Characterisation - Paper-Titlemonkey loveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rockdonnell Presentation - INSSDC 2018Dokument47 SeitenRockdonnell Presentation - INSSDC 2018Not FakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GDJP PPT Unit IV and VDokument68 SeitenGDJP PPT Unit IV and VtagoreboopathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AJ10-133 SpecsDokument39 SeitenAJ10-133 SpecsStrawichDanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tsiolkovsky Rocket Equation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument8 SeitenTsiolkovsky Rocket Equation - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediamechmaster4uNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomechanics Analysis On RunningDokument4 SeitenBiomechanics Analysis On Runningshaon2k3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Belton Michael J.S. - Mitigation of Hazardous Impacts Due To Asteroids and CometsDokument435 SeitenBelton Michael J.S. - Mitigation of Hazardous Impacts Due To Asteroids and CometsMaria TeresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combined Ducted Rocket and Solid Fuel Ramjet CycleDokument8 SeitenCombined Ducted Rocket and Solid Fuel Ramjet CycleendoparasiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feep Microthruster Technology Status and Potential ApplicationsDokument7 SeitenFeep Microthruster Technology Status and Potential ApplicationskirancallsNoch keine Bewertungen
- STAIF-2003-118 Technologies To Improve Ion Propulsion System Performance, Life and EfficiencyDokument11 SeitenSTAIF-2003-118 Technologies To Improve Ion Propulsion System Performance, Life and EfficiencyDr. Shahin IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Attitude and Orbital Dynamics Simulator: NtroductionDokument5 SeitenSatellite Attitude and Orbital Dynamics Simulator: NtroductionJ.Y.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aprendiz de TodoDokument19 SeitenAprendiz de Todofabian lopezNoch keine Bewertungen