Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
7a0809 Ec ch9 - Notes
Hochgeladen von
api-37286150 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten1 SeiteOriginaltitel
7a0809-ec-ch9_notes
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten1 Seite7a0809 Ec ch9 - Notes
Hochgeladen von
api-3728615Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
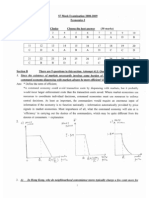
s7 summary on Fiscal and Mo! Pe
1. Recessionary (Deflationary) and Inflationary Gaps
A deflationary income gap can be closed by expansionary policies.
{An inflationary income gap can be closely by contractionary p
2. Crowding-out Effect
An expansionary policy will increase the interest rate and reduces interest-sensitive
private spending e.g. investment.
The crowding-out effect will reduce the policy effectiveness of fiscal policy.
GA (AD ® KEDG TN) DY D> Md MEDM)> rR D1Y
The reduction in investment will offset part of the increase in AD and restrain the
increase in national income.
3. Fiscal Policy is effective when
kis large (or the marginal withdrawals is smaller e.g. st, m);
eislarge; dissmall;and bis small
Fiscal policy is more effective if the LM curve is flatter.
Fiscal policy is more effective, if holding k constant, the IS curve is steeper.
4. Monetary Policy is effective when
kis large (or the marginal withdrawals is smaller e.g. st, m);
eissmall; dissmall;and bis large
Monetary policy is more effective if the IS curve is flatter (i.e. when k or b is larger)
Monetary policy is more effective if given the same d, the LM curve is steeper.
5. Special cases for fiscal policy and monetary policy
Most Effective Ineffective
IS Curve UM Curve IS Curve UM Curve
Fiscal Policy b: e=0 b=o e=0;
Vertical Horizontal Horizontal —_ Vertical
Monetary Policy b= 00; e=0; b=0; e= 0;
Horizontal Vertical Vertical Horizontal
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 7a0809 Pacc Exam Paper1 AnsDokument10 Seiten7a0809 Pacc Exam Paper1 Ansapi-3728615Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7a0809 Econ Exam Papers1&2 AnsDokument8 Seiten7a0809 Econ Exam Papers1&2 Ansapi-3728615Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7a0809 Pacc Exam Paper2 AnsDokument10 Seiten7a0809 Pacc Exam Paper2 Ansapi-3728615Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7a0809 Pa Ans - BudgetingDokument5 Seiten7a0809 Pa Ans - Budgetingapi-3728615Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kc7a0809-Ms-Textbk ch8 AnsDokument42 SeitenKc7a0809-Ms-Textbk ch8 Ansapi-3728615Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7a0809 Ec ch1 - NotesDokument2 Seiten7a0809 Ec ch1 - Notesapi-3728615Noch keine Bewertungen