Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Allweiler Pumps Manual
Hochgeladen von
Antreas_G1Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Allweiler Pumps Manual
Hochgeladen von
Antreas_G1Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ALLWEILER AG A Final Documentation
CUSTOMER/Kunde: Marinequip China Co. Ltd.
CUSTOMER-NO.: /Kunde-Nr.: 560707
YOUR ORDER NO/ Ihre A-Nr.: E-168/07/JL Blue Sky Hull JLZ070435 Jinling Shipyard
OUR ORDER NO/ Unsere A-Nr.: SAP: 1172839
Pos. Benennung
Denomination
Type Equipment
No.
Index
001 Cooling SW Pumps MA 125-250 U3.19D W133 V5
8032428
8032429
8032430
001
002 M/E J acket Cooling FW Pumps MA 65-250 U3.19D W134 V5
8032431
8032432
002
003 LT Cooling FW Pumps MA 150-315 U3.19D W134 V5
8032433
8032434
003
004 Air Cooler Chemical Pump NB 20-160 U3.1D W18 8032436 004
005 M/E J acket FW Pre-Pump NB 25-160 U3.1D W18 8032437 005
006 Heavy Fuel Oil Transfer Pump TRF 660 46 W203
8032438
8032439
006
007 MDO Transfer Pump TRF 660 46 W203 8032440 007
008 Lub. Oil Pumps MELO 250-1
8032560
8032561
008
009 Lub. Oil Transfer Pump TRE 40 46 W202 8032441 009
010 Cylinder Oil Pump TRE 20 46 W202 8032442 010
011 Fire & GS-Pump RVP 160 M AELD55 8032558 011
012 Bilge & GS-Pump RVP 160 M AELD55 8032559 012
013 Daily Bilge Pump AEB 1E 100 8032443 013
014 Ballast Pump
MA 200-250 U3.19D W133 V5
AELD55
8032444
8032445
014
015 Sludge Pump AEB 1E 100 8032446 015
016 Emergency Fire Pump NAM 65-250 U3.1D W3 ASED-C 8032447 016
017 Fresh Water Pumps NB 25-200 U3.1D W18
8032448
8032449
017
018 Hot Water Circulating Pump NB 20-160 U3.1D W18 8032450 018
019 Technical Water Pumps NB 25-200 U3.1D W18
8032451
8032452
019
020 Bilge Pump
MA 100-250 U3.19D W133 V5
AELD55
8032453 020
021 Harbour LT Cooling FW Pump MA 80-315 U3.19D W134 V5 8032435 021
022 Sewage Pump 3/HK 50-1-110 9008171 022
Order-no.:J inling Shipyard E-168-07-J L J LZ070434-35
Power Supply 3x440V -60Hz Date 07.09.2009
space heater
Pump Pump Motor Flange Motor Rated Rated Rated Istart / Pow. fac. Eff. Power Prot. Temp. Starting Space cable cable cable cable
Pos. Type Name Quantity Size Design Weight Output Speed Current IN cosO Supply Class Class Method heater glands size gland dia glands size gland dia
[kg] [kW] [1/min.] In [A] fold [] [%] [IP] (Y/N) (metric) (mm) (metric) (mm)
1 MA 125-250 U3.19D W133 V5 Cooling SW pumps 3 IEC 180 L-4 B5/V1 243 34,9 1764 58,7 7,9 0,86 91,6 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL Y 2xM40x1,5
32
1x M20x1,5
6-12
2 MA 65-250 U3.19D W134 V5 M/E J acket Cooling FW pumps 2 IEC 160 M-4 B5/V1 118 12,8 1764 22,6 8,9 0,84 88,6 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 2xM40x1,5
32
3 MA 150-315 U3.19D W134 V5 LT Cooling FW pumps 2 IEC 250 M-4 B5/V1 592 87,3 1776 137 7,9 0,89 94,1 440V/60Hz 55 F YD Y 2x M63x1,5
48
1x M20x1,5
6-12
4 NB 20-160 U3.1D W18 Air Cooler Chemical pump 1 IEC 80-2 B5/V1 10,8 1,3 3240 2,51 6,5 0,88 76,2 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 1x M20x1,5
max. 12
5 NB 25-160 U3.1D W18 M/E J acket FW Pre-pump 1 IEC 90 L-2 B5/V1 16,2 2,5 3312 4,74 6,5 0,87 81 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 1x M20x1,5
max. 12
6 TRF 660 - 46 W203 Heavy Fuel Oil Transfer pump 2 IEC 160 L-4 B5/V1 138 17,5 1764 31,2 8,9 0,85 90,1 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 2x M40 x1,5
32
7 TRF 660 - 46 W203 MDO Transfer pump 1 IEC 160 L-4 B5/V1 138 17,5 1764 31,2 8,9 0,85 90,1 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 2x M40 x1,5
32
8 MELO 250-1 Lub. Oil pumps 2 IEC 250 M-4 B5/V1 592 87,3 1776 137 7,9 0,89 94,1 440V/60Hz 55 F YD Y 2x M63 x1,5
48
1x M20x1,5
6-12
9 TRE 70 - 40 W202 Lub. Oil Transfer pump 1 IEC 90 L-2 B5/V1 19 3,5 3360 7,4 6,9 0,83 82,6 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 1x M20x1,5
max. 12
10 TRE 20 - 46 W202 Cylinder Oil pump 1 IEC 80-4 B5/V1 13,2 1,28 1680 3,04 6,5 0,76 76,5 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 1x M20x1,5
max. 12
11 RVP 160 M AELD55 Fire & GS-pump 1 IEC 225 M-4 B5/V1 328 52,4 1770 83 7,9 0,89 93 440V/60Hz 55 F YD Y 2x M50x1,5
39
1x M20x1,5
6-12
12 RVP 160 M AELD55 Bilge & GS-pump 1 IEC 225 M-4 B5/V1 328 52,4 1770 83 7,9 0,89 93 440V/60Hz 55 F YD Y 2x M63 x1,5
48
1x M20x1,5
6-12
13 AEB 1E 100 Daily Bilge pump 1 90L-4 SK 01 B5 21 1,8 1674 2,78 4,6 0,78 78,3 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 1x M20x1,5
max. 14
14
MA 200-250 U3.19D W133 V5
AELD55
Ballast pumps 1 IEC 250 M-4 B5/V1 592 87,3 1776 137 7,9 0,89 94,1 440V/60Hz 55 F YD Y 2x M63 x1,5
48
1x M20x1,5
6-12
15 AEB 1E 100 Sludge pump 1 90L-4 SK 01 B5 21 1,8 1674 2,78 4,6 0,78 78,3 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 1x M20x1,5
max. 14
16 NAM 65-250 U3.1D W3 ASED-C Emergency Fire pump 1 IEC 200 L-4 B5/V1 246 34,9 3540 55,3 7,9 0,9 92 440V/60Hz 55 F YD Y 2x M50x1,5
39
1x M20x1,5
6-12
17 NB 25-200 U3.1D W18 Fresh Water pumps 2 IEC 112 M-2 B5/V1 35,4 6,4 3480 11,1 7,5 0,88 85,7 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 2x M20x1,5
12
18 NB 20-160 U3.1D W18 Hot Water Circulating pump 1 IEC 80-2 B5/V1 10,8 1,3 3240 2,62 6,5 0,88 76,2 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 1x M20x1,5
max. 12
19 NB 25-200 U3.1D W18 Technical Water pumps 2 IEC 100 L-2 B5/V1 24 3,5 3444 6,35 8,1 0,86 82,6 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 1x M20x1,5
max. 12
20
MA 100-250 U3.19D W133 V5
AELD 55
Bilge Pump 1 IEC 180 M-4 B5/V2 177 21,5 1764 36,5 7,9 0,86 90,4 440V/60Hz 56 F DOL Y 2xM40x1,5
32
1x M20x1,5
6-12
21 MA 80-315 U3.19D W134 V5 Harbour LT Cooling FW pump 1 IEC 200 L-4 B5/V1 305 43,1 1770 69,4 7,9 0,88 92,6 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL Y 2x M50x1,5
39
1x M20x1,5
6-12
22 3/HK 50-1-100 Sewage pump 1 90L2 B5/V1 19 2,6 3500 4,75 7,3 0,88 82 440V/60Hz 55 F DOL N 1x M25x1,5
10-14
Marinequip China Co. Ltd.
Supplier: Hoyer
Positions for Gaugeboard, Motor Terminalbox and Autom. Aspirator
Centrifugal Pumps
Position List
No. Pump Denomination Qt. Type I / II / III / IV
View on
Pressure
Gauge in
Direction
Motor-
Terminal Box
Automatic
Aspirator in
Pos. of Arrow
001 Cooling SW pumps 3 MA 125-250 I C n. a.
002 M/E J acket Cooling FW pumps 2 MA 65-250 I C n. a.
003 LT Cooling FW pumps 2 MA 150-315 I C n. a.
021 Harbour LT Cooling FW pump 1 MA 80-315 I C n. a.
004 Air Cooler Chemical pump 1 NB 20-160 III A n. a.
005 M/E J acket FW Pre-pump 1 NB 25-160 III A n. a.
014 Ballast pumps 2 MA 200-250 I C 3
016 Emergency Fire pump 1 NAM 65-250 I C 3
017 Fresh Water pumps 2 NB 25-200 III A n. a.
018 Hot Water Circulating pump 2 NB 20-160 III A n. a.
019 Technical Water pumps 2 NB 25-200 III A n. a.
020 Bilge Pump 1 MA 100-250 I C 3
022 Sewage Transfer Pump 1 3/HK 50-1-110 Loose supply C (like NB) n.a.
Gauge Board and Automatic Aspirator can not be mounted at same position !
Manometerbrcke und Ansaugautomat knnen nicht auf gleicher Position angebracht werden !
1/1
Positions for Gaugeboard and Motor Terminalbox
SCREW PUMPS
Position List
No. Pump Denomination Qt. Type I / II / III / IV
View on Pr.
Gauge in
Direction
Motor-Terminal
Box
Remarks
006
Heavy Fuel Oil Transfer
pump
2 TRF 660 IV A
007 MDO Transfer pump 1 TRF 660 IV A
009 Lub. Oil Transfer pump 1 TRE 40 IV A
010 Cylinder Oil pump 1 TRE 20 IV A
Note: Arrow ( I ) Viewing Direction to Gaugeboard / Letters Position of Terminal Box
Bemerkung: Pfeil ( I ) Blickrichtung auf Manometerbrcke / Buchstaben Anordnung
Klemmenkasten
Positions for Gaugeboard and Motor Terminalbox
Multistage Centrifugal Pumps, Main L.O. Pumps, Excentric Screw Pumps and Piston Pumps
II
I
Position List
No. Pump Denomination Qt. Type I / II / III / IV
View on Pressure
Gauge in Direction
Motor-Terminal
Box
Remarks
008 Lub. Oil pumps 2 MELO 250-1 Lose supply C
013 Daily Bilge pump 1 AEB 1E 100 Lose supply A
015 Sludge pump 1 AEB 1E 100 Lose supply A
Tlf. (+45) 86 98 21 11
SVEND HYER A/S
Kder Gear Elmotorer
Induction motor
Drehstrom-Kfiglufermotor
Moteu cage
Motores de jaula de ardilla
Motore a Gabbia di Scoiattolo
Kortsluten motor
Elmotorer
Machine Instructions 3
Betriebsanleitung 6
Notice technigue 9
Instrucciones 13
Istruzioni 16
Motorinstruktioner 19
Motorinstruktioner 22
Svend Hyer A/S
Over Hadstenvej 48 DK 8370 Hadsten
Tel. (+45) 86 98 21 11 Fax (+45) 86 98 17 79
E-mail: svendhoyer@svendhoyer.dk http://www.svendhoyer.dk
HYER Motors
Motor Instructions
Declaration of Conformity
Declaration of Conformity with respect to the Low volta-
ge Directive 73/23/EEC amended by Directive 93/68
EEC are issued separately with individual motors.
The declaration of Conformity also satisfies the require-
ments of a Declaration of Incorporation with respect to
the Machinery Directive 89/392/EEC.
Validity
The instructions are valid for the following Hyer electri-
cal motor types, in motor operation.
Aluminiummotors MS 56-132
Cast motors Y90-355
(Additional information may be required for some motor
types due to special application and/or design conside-
rations.)
Activating the motor
Acceptance inspection
Immediately upon receipt check the motor for external
damage and if found, inform the forwarding agent right
away.
Check all rating plate informations, especially voltage
and winding connection (star or delta).
Turn shaft by hand to check free rotation, remove trans-
port locking if used.
Insulation resistance check
Measure insulation resistance before commissioning and
when winding dampness is suspected.
Resistance, measured at 25 C shall exceed the referen-
ce value, ie
Ri [M] (20 U) / (1000 + 2P),
Where U = voltage in Volts; P = power output in kW
WARNING
Windings should be discharged right away after measu-
rement to avoid risk for electric shock.
Insulation resistance reference value is halved for each
20 C rise in surrounding temperature.
If the reference resistance value is not secured, the win-
ding is too damp and must be oven dried.
Oven temperature should be 90 C for 12-16 hours follo-
wed by 105 C for 6-8 hours.
If drain hole plugs are fitted, they must be removed
during heating.
If windings get soaked in sea water, they normally need
to be rewound.
Direct start or star-delta start
The terminal box on standard single speed motors nor-
mally contains 6 winding terminals and at least one earth
terminal.
Earthing shall be carried out according to local regula-
tions before the motor is connected to the supply volta-
ge.
The voltage and connection are stamped on the rating
plate.
Direct starting
Y or winding connections may be used. eg 660 VY, 400
V indicates Y-connection for 660 V and -connection
for 400 V.
Star-Delta start (Y/):
The supply voltage must be equal to the rated voltage of
the motor in -connection.
Remove all connection links from the terminal block.
For two-speed and special motors, supply connection
must follow the instructions inside the terminal box.
Terminals and direction of rotation
Direction of rotation is clockwise when viewing the shaft
face at the motor drive end, when the line phase se-
quence L1, L2, L3 is connected to the terminals as
shown in enclosed drawing.
By interchanging the connection of any two line cables,
the direction and rotation is altered.
If the motor has a uni-directional fan check that the
direction of rotation is according to the arrow marked on
the motor.
Employment
Operating environment
The motor is meant for use in industrial environments.
Normal surrounding temperature limits -25 to +40 C.
Maximum altitude 1000m above sea level.
Security precautions
The motor is intended to be installed and used by quali-
fied personel who are familiar with relevant safety
requirements.
Safety equipment necessary for the prevention of acci-
dents at the mounting and operating site shall be provi-
ded in accordance with the normal regulations in the
local country.
WARNING
Small motors with supply current directly switched by
thermally sensitive switches can start automatically.
Important
the motor shall not be used to step on
the outer casing of the motor may be very hot, even
during normal operation
some special motor applications require special
instructions (eg using frequency converter supplies).
3
Handling
Storage
All motor storage should be done indoors, in dry, vibra-
tion free and dust free conditions.
Unprotected motor surfaces (shaft-ends and flanges)
should be given anti-corrosion coatings.
It is recommended that shafts are rotated periodically by
hand to prevent grease migration.
Anti condensation heaters, if fitted, should preferably be
energized.
The characteristics of electrolytic capacitors, if fitted to
single-phase motors, will require "reforming" following
periods of storage beyond 1-2 years. Contact Svend
Hyer A/S for details.
Installation
Base
The purchaser bears full responsibility for preparation of
the base.
Metal bases should be painted to avoid corrosion.
The base must be even, and sufficiently rigid to with-
stand possible short circuit forces. They shall be dimen-
sioned as to avoid the occurrence of vibration due to
resonance.
Base studs
Bolt the base studs to the feet of the motor and place a
1-2 mm shim between the stud and the feet.
Align the motor by using appropriate means.
Grout the studs with concrete, check alignment, and drill
holes for locating pins.
Drain holes
If the mounting designation differs from standard, check
that open drain holes face downwards.
Motors with closable plastic drain plugs are delivered
with these in the open position.
In extremely dusty environments all drain holes should
be closed.
Setup
Correct setup is essential to avoid problems with
bearings, vibrations and possible fractured shaft exten-
sions.
Connection
The normal motor design is with cable entries on both
sides and with terminal box on top.
Motors are available with top mounted terminal boxes
rotatable 4 x 90, and some with side mounted terminal
boxes.
Availability of these solutions is described in the product
catalogues.
If any cable entries are not in use, they must be closed.
Besides the main winding and earthing terminals the ter-
minal box can also contain connections for thermistors,
standstill heating elements, bimetallic switches, or PT
100 resistance elements.
WARNING
Voltage may be connected at standstill inside the termi-
nal box for heating elements or direct winding heating.
Connection diagrams for auxiliary elements are placed
inside the terminal box cover.
WARNING
The capacitor in single-phase motors can keep a charge
which appears across the motor terminals, even when
the motor has reached standstill.
Assembly and disassembling
Important
These two jobs must be carried out by qualified personel
using only suitable tools and working methods.
Bearings
Special care shall be taken with the bearings. Bearings
shall be removed using pullers and fitted by heating or
the use of specialized tools for the purpose.
Fitting coupling halves and pulleys
Coupling halves and pulleys shall be fitted using suitable
equipment and tools that do not damage the bearings.
Never fit a coupling half or pulley by hammering into
place or remove it using a lever pressed against the body
of the motor.
Equilibration
The rotor of the motor is dynamically balanced.
As standard, balancing has been carried out using a full
key.
Maintenance and greasing
Common check-up
check the motor at regular intervals
keep the motor clean and ensure free ventilation air-
flow
check the condition of shaft seals (eg V-ring) and
replace if necessary
check the condition of connections and mounting and
assembly bolts
check the bearing condition by listening for unusual
noise, vibration measurement, bearing temperature,
inspection of spent grease or SPM bearing monitoring
"When changes of condition occur, dismantle the
motor, check the parts and replace if necessary."
Greasing
Motors with eternal greased bearings.
Motors up to frame size 200 are normally fitted with eter-
nal greased bearings of the 2RS type. Bearing types are
specified in the respective product catalogues.
Motors fitted with 2RS-bearings can be regreased by
opening the motor, cleaning the bearings and bearing
housings, and filling these with new grease approxima-
tely to a level around 50-70%.
4
Guidelines for regreasing intervals are:
20.000 - 40.000 duty hours for > 4 pole motors.
10.000 - 20.000 duty hours for 2 and 2/4 pole motors.
The shorter times are valid for larger frame sizes.
Motors fitted with grease nipples
Grease the motor while running.
If grease outlet plug fitted, remove temporarily when
greasing, or permanently with automatic greasing.
If the motor is fitted with a greasing information plate,
follow the values given, otherwise use values as follows.
Frame Amount of 3600 3000 1800 1500 1000 500-900
size Grease (g) r/min r/min r/min r/min r/min r/min
Ball bearings
Lubrication intervals in duty hours
112. 132 15 4200 4800 7000 7800 10000 10500
160, 180 20 3200 4200 6000 7000 9000 10000
200, 225 25 1800 3100 5500 6500 8500 9000
250, 280 35 800 2000 5000 6000 8000 8500
315 50 800 2000 4600 5500 7500 8000
355 60 - 1000 4000 5000 7000 8000
Roller bearings
Lubrication intervals in duty hours
200, 225 25 900 1500 4300 5000 6500 7000
250, 280 35 400 1000 3300 4500 6300 6800
315 50 400 1000 2700 3800 6000 6500
355 60 - - 2200 3200 5500 6000
The table is prepared for horizontally mounted motors.
Greasing intervals for vertical motors are half of the
above values.
The grease amount in the table is used if small quantities
of fresh grease are replaced at regular intervals as above.
The table values are based on 80 C bearing temperatu-
re. The values should be halved for every 15 K increase
in bearing temperature.
If the maximum bearing temperature is 70 C, the table
values may be doubled.
WARNING
The maximum operating temperature of the grease and
bearings must not be exceeded.
Higher speed operation, eg frequency converter applica-
tions, or slower speed with heavy loading will require
shortened greasing intervals. Consult Svend Hyer A/S
in such cases.
Typically a doubling of speed will require a reduction of
greasing intervals to approx. 40% of values tabulated
above.
Suitability of bearings for high speed operation must also
be checked.
Lubricants
When regreasing, use only special ball bearing grease
with the following properties:
good quality lithium base or lithium complex grease
base oil viscosity 100-140 cST at 40 C
consistency NLGI grade 2 or 3
temperature range -30 C - +120 C, continuously.
Grease with the correct properties are available from all
the major lubricant manufacturers.
If the make of grease is changed and compatibility is
uncertain, grease several times at short intervals in order
to displace the old grease.
Highly loaded and/or slowly rotating bearings require
EP-grease.
If greasing intervals are short due to bearing temperatu-
res of 80 C or above, use high temperature greases
which normally permit approximately 15 K higher bearing
temperatures.
If the surrounding temperature is below -25 C consult
Svend Hyer A/S regarding the possible use of low tem-
perature grease.
WARNING
Many greases can cause skin irritation and eye inflama-
tion.
Follow all safety precautions specified by the manufac-
turer.
Spare parts
When ordering spare parts, the full type designation and
product code as stated on the rating plate must be spe-
cified. If the motor is stamped with a serial manufactu-
ring number, this should also be given.
5
W1
U
R 1
2 S
S
R
T
T
U1
V
V1
W
W1
Y
U
R 1
2 S
S
R
T
T
U1
V
V1
W
25
Connection diagram
Anschludiagram
Connection
Conexin
Collegamento
Anslutningdiagramm
Personal Notes:
26
27
Personal Notes:
Tlf. (+45) 86 98 21 11
SVEND HYER A/S
Kder Gear Elmotorer
Main office:
Svend Hyer A/S
Over Hadstenvej 48 DK 8370 Hadsten
Tel. (+45) 86 98 21 11 Fax (+45) 86 98 17 79
E-mail: svendhoyer@svendhoyer.dk http://www.svendhoyer.dk
Sverige:
Svend Hyer AB
Malmvgen 18 S-331 42 Vrnamo
Tel. (+46) 37 04 77 13 Fax (+46) 37 01 00 46
E-mail: svendhoyer@svendhoyer.se http://www.svendhoyer.dk
Norge:
Svend Hyer AS
Torvet 1 N-3256 Larvik
Tel. (+47) 33 18 00 11 Faks: (+47) 33 18 00 13
e-mail: svendhoyer@svendhoyer.no http://www.svendhoyer.dk
Deutschland:
Svend Hyer A/S
Over Hadstenvej 48 DK 8370 Hadsten
Tlf. 0800 1890415 Fax (+45) 86 98 17 79
E-mail: svendhoyer@svendhoyer.dk http://www.svendhoyer.dk
Betriebs- und Wartungsanleitung
Operating and Maintenance Instruction
Instructions de conduite et dentretien
B 1012
09/2000
D GB F
Diese Sicherheitshinweise sind aufzubewahren
These safety instructions must be kept available
Ces instructions de scurit doivent tre observes
Standard Stirnradgetriebe
Standard Helical Gearboxes
Rducteurs standard engrenages cylindriques
R:/Motorerbetriebsanleitung / E-Motoren / nord / Standard-Stirnrad-D-GB-neutral.pdf
Warnung
Es wird vorausgesetzt, da die
grundstzlichen Planungsarbeiten der Anlage
sowie Transport, Montage, Installation,
Inbetriebnahme, Wartung und Reparaturen
von qualifiziertem Personal ausgefhrt bzw.
durch verantwortliche Fachkrfte kontrolliert
werden. Bei Arbeiten am Getriebemotor mu
garantiert sein, da keinerlei Spannung
anliegt, und dieser gegen Wiedereinschaltung
gesichert ist.
Warnung
Vernderungen gegenber dem
Normalbetrieb (hhere Leistungsaufnahme,
Temperaturen, Schwingungen, Gerusche
usw. oder Ansprechen der berwachungs-
einrichtungen) lassen vermuten, da die
Funktion beeintrchtigt ist. Zur Vermeidung
von Strungen, die ihrerseits mittelbar oder
unmittelbar schwere Personen- oder
Sachschden bewirken knnten, mu das
zustndige Wartungspersonal dann
umgehend verstndigt werden.
Im Zweifelsfall die entspechenden
Betriebsmittel sofort abschalten!
Aufstellung, Vorbereitung
Transportsen am Getriebe sind fr das
Gewicht des Antriebs ausgelegt
Fundamente ausreichend bemessen und
schwingungsfrei ausfhren
Getriebe oder -motor fest und ohne
Verspannung montieren
ausreichende Belftung vorsehen
serienmiges Innengewinde nach DIN 332
zum Aufziehen von Verbindungselementen
auf die Wellen benutzen
Schlge auf die Wellen vermeiden
(Lagerbeschdigung!)
Maschine und Getriebe mglichst mit
elastischen Kupplungen verbinden
vor dem Einschalten Abtriebselemente
aufziehen bzw. Pafeder sichern
bei Aufsteckgetrieben mit Drehmoment-
sttze Gummipuffer verwenden
Elektrischer Anschlu
Motoranschlu nach Schaltbild vornehmen
bereinstimmung von Netzspannung und
Frequenz mit den Typenschild-Daten
sicherstellen
Sichere Schutzleiterverbindung herstellen
evtl. falsche Drehrichtung korrigieren durch
Vertauschen von 2 Phasen
Nicht bentigte Kabeleinfhrungsffnungen
und den Kasten selbst staub- und
wasserdicht verschlieen
berbelastung und Phasenausfall durch
Schutzschalter vorbeugen
Einstellen des Motorschutzschalters auf
Nennstrom
Schaltbilder auf der letzten Seite
Inbetriebnahme
bei lngeren Lagerzeiten besondere
Vorkehrungen treffen (siehe Werknormblatt
"Langzeitlagerung")
Lage der lstandschraube nach
Bauformtabellen des entsprechenden
Kataloges feststellen
Prfen des lstandes
Entfernen des Verschlustopfens vor
Inbetriebnahme (berdruck!), ggf. Druck-
entlftungsschraube montieren
Normale Erstbefllung: siehe Schmier-
stofftabelle
Luftgekhlte Motoren sind fr Umgebungs-
temperaturen von - 20C bis +40C sowie
Aufstellungshhen 1.000 m ber NN
ausgelegt
Der Einsatz im Ex-Bereich ist nicht zulssig,
sofern nicht ausdrcklich hierfr vorgesehen
Caution
It is presumed that fundamental project work
as well as all work with regard to transport,
assembly, installation, starting-up,
maintenance and repair is performed by
qualified personnel or supervised by skilled
labour taking overall responsibility. Make
absolutely sure that no voltage is applied at all
while work is being done on the geared motor.
Drive must also be secured against switching
on.
Caution
Any deviation from normal operating
conditions (increased power consumption,
temperature, vibrations, noise etc.) or warning
signals by monitoring equipment suggest
malfunction. Inform the responsible
maintenance personnel at once to prevent the
trouble from getting worse and causing,
directly or indirectly, serious physical injury or
material damage.
In case of doubt disconnect the machine
immediately!
Preparing and performing installation
Lifting devices on the drive are designed to
carry the drive weight
the foundation (base) should be of adequate
size and vibration-proof
install gear unit or geared motor rigid and
braceless
ensure sufficient ventilation
make use of tapped hole (DIN 332) to suit
fastening to the shaft end
avoid shocks on shafts (bearing damage!)
preferably use flexible coupling between
output shaft and driven machine
fit output elements to shaft end or secure
feather key before starting the motor
use torque arm with rubber buffer on shaft
mounting gearboxes
Connection of motor
Connect motor according to diagram
make sure that mains voltage/frequency are
in accordance with nameplate information
make secure protective conductor conection
if motor is running in reverse direction,
interchange two phases
Close unused cable entrances holes and the
box itself in a dust- and watertight manner.
install protective switches to prevent
overload and phase failure
set motor protection switch to nominal
current
wiring diagrams on the last page
Starting up
in case of long-time storage take special
precautions (as provided in works standard
sheet "Extended Storage")
check position of oil-level plug with help of
mounting position tables in applicable
catalogue
check oil-level
prior to starting-up, remove vent plug from
vent screw if necessary
if not specified otherwise, first oil filling as is
shown in list of lubricants
air-cooled motors are designed for ambient
temperautres between -20C and +40C and
for installation at altitudes 1.000 m above
M.S.L.
Their use in hazardous areas is prohibited
unless they are expressly intended for such
use (follow additional instructions)
Avertissement
Il est impratif que les travaux fondamentaux
de l'installation, ainsi que tous les travaux de
transport, montage, installation, mise en
exploitation, entretien et rparation soient
accomplis par du personnel qualifi et
contrls par des techniciens spcialiss
dans ce domaine. Avant toute intervention sur
le motorducteur, il faut s'assurer que celui-ci
n'est plus sous tension et que la remise sous
tension soit interdite.
Avertissement
Si en utilisation normale, des modifications de
fonctionnement apparaissent telles que
puissance absorbe trop leve, temprature
leve, vibrations fortes, bruit intense etc. ou
en rapport avec les contrles techniques, cela
laisse supposer que diffrentes fonctions de
l'appareil peuvent tre dtriores. Pour viter
ensuite des problmes, qui pourraient
entraner de graves accidents corporels ou de
graves dgats matriels, le personnel
d'entretien comptent doit immdiatement
tre inform.
Si vous tes dans le doute, coupez
immdiatement l'alimentation!
Mise en place, prparation
Le matriel utilis pour la manutention doit
tenir compte du poids de l'quipement
prendre largement les dimensions des
embases et les raliser exemptes de
vibrations
monter les rducteurs et motorducteurs
solidement et sans haubanage
prvoir une aration suffisante
prvoir le taraudage conforme la norme
DIN 332 pour monter des accouplements
sur les arbres d'entre et de sortie
viter de donner des coups sur les arbres
(cela pourrait dtriorer le roulement!)
lier autant que possible la machine et le
rducteur avec des accouplements
lastiques
avant la mise en service, enlever l'lment
d'accouplement ou/et fixer la clavette
utiliser pour l'excution arbre creux avec
bras de raction une bute en caoutchouc
Branchements lectriques
brancher le moteur selon le schma
s'assurer que la tension du rseau et la
frquence correspondent aux donnes
inscrites sur la plaque signaltique
Le cable de raccordement doit tre protg
corriger un ventuel mauvais sens de
rotation par une inversion de deux phases
Les entres de cbles non utilises doivent
tre obtures, la bote elle-mme devant
tre ferme de faon tre tanche l'eau
et la poussire
prvoir une protection lectrique contre les
surcharges, court-circuit et dfaut de phases
rgler la protection lectrique suivant
l'intensit nominale du moteur
schma de branchement la dernire page
Mise en fonctionnement
si un stockage longue dure du rducteur
est prvu, il faut prendre les dispositions
ncessaires (voir spcification "Stockage
longue dure")
vrifier que la vis de niveau d'huile
corresponde la position de montage du
rducteur (voir catalogue)
contrler le niveau d'huile
enlever la mche de la vis d'vent avant la
mise en route (pour viter une surpression)
ou fixer le clapet d'vent sur le rducteur
pour le premier remplissage voir le tableau
des lubrifiants
les moteurs autoventils sont dimensionns
pour des tempratures ambiantes comprises
entre -20C et +40C, ainsi que pour une
altitude 1000 mtres au-dessus du niveau
de la mer
Leur utilisation dans des atmosphres
explosives est interdite, moins qu'elles ne
soient expressment prvues cet effet
(respecter les indications supplmentaires)
Wartung
MOTOR
Staubablagerungen entfernen (berhitzung!)
Wlzlager ausbauen, reinigen und einfetten
Es ist zu beachten, da der gesamte Freiraum
um das Lager ca. 1/3 mit Fett gefllt ist
Schmierstoffsorten siehe unten
GETRIEBE
Wechseln des Schmierstoffes alle 10.000
Betriebsstunden oder sptestens nach 2
Jahren.
Doppelte Fristen bei synthetischen Produkten
Verkrzung der Schmierstoffwechselintervalle
bei extremen Betriebsbedingungen (hohe
Luftfeuchtigkeit, aggressive Umgebung und
hohe Temperaturschwankungen)
Verbinden des Schmierstoffwechsels mit
grndlicher Reinigung des Getriebes
Synthetische und mineralische Schmierstoffe
nicht miteinander mischen! Das gilt auch fr die
Entsorgung der Schmierstoffe!
Maintenance
MOTOR
remove dust deposit (overheating)
dismount anti-friction bearings for cleaning
and refill with grease
ensure that the bearing cage is packed to
about 1/3 with grease, distribute evenly
select proper type of lubricating grease from
following table
GEARBOX
change lubricant every 10.000 working hours
or after two years at the latest.
combine the lubricant change with thorough
cleaning of gear unit
lubricant changing intervals will be twice as
long if synthetic products are used
extreme working conditions (high air humidity,
aggressive media and large temperature
variations) call for reduced lubricant changing
intervals
Synthetic and mineral lubricants must not be
mixed either for filling or for disposal!
Entretien
DU MOTEUR
enlever la poussire du moteur
(chauffement)
dmonter les roulements, les nettoyer et les
regraisser
la cage des roulements doit tre remplie au
1/3 environ
lubrifiant voir tableau ci-aprs
DU REDUCTEUR
vidanger le lubrifiant aprs 10.000 heures de
fonctionnement ou au plus tard aprs 2 ans
d'utilisation.
profiter de la vidange pour effectuer un
nettoyage approfondi du rducteur
pour des lubrifiants synthtiques, ce dlai peut
tre doubl
rduire les intervalles entre les vidanges dans
des conditions d'utilisation extrmes
(hygromtrie leve, ambiance agressive ou
variations importantes des tempratures)
Des lubrifiants synthtiques et minraux ne
doivent pas tre mlangs! Ceci s'applique
galement pour le retraitement des lubrifiants!
LFLLMENGE [cm
3
] CAPACITY [cm
3
] QUANTITE DE LUBRIFIANT [cm
3
]
Waagerechte Anordnung
Horizontal position
Position horizontale
Senkrechte Anordnung
Vertical position
Position verticale
Stirnradgetriebe Helical Gearboxes Rducteurs engrenages cylindriques
zwei- und dreistufig double and triple reduction deux et trois train dengrenages
B 3 B 5 B 3/5 B 8/5 B 5a B 5b B 5c B 8 B 6 B 7 V 1 V 3 V1/5 V 5 V 6 V3/6
SK 0
SK 000
SK 01
SK 010
SK 20
SK 200
SK 25
SK 250
SK 30
SK 300
SK 33
SK 330
100
200
250
600
510
1300
700
1400
800
1400
1000
1500
100
200
250
600
510
1300
700
1400
800
1400
1000
1500
100
200
250
600
510
1300
700
1400
800
1400
1000
1500
100
200
250
600
510
1300
700
1400
800
1400
1000
1500
100
200
250
600
510
1300
700
1400
800
1400
1000
1500
100
200
250
600
510
1300
700
1400
800
1400
1000
1500
100
200
250
600
510
1300
700
1400
800
1400
1000
1500
100
200
250
600
510
1300
700
1400
800
1400
1000
1500
100
200
250
600
510
1300
700
1400
800
1400
1000
1500
100
200
250
600
510
1300
700
1400
800
1400
1000
1500
150
240
400
650
700
1400
1000
1500
1400
1500
1600
1580
150
240
400
650
700
1400
1000
1500
1400
1500
1600
1580
150
240
400
650
700
1400
1000
1500
1400
1500
1600
1580
150
240
400
650
700
1400
1000
1500
1400
1500
1600
1580
150
240
400
650
700
1400
1000
1500
1400
1500
1600
1580
150
240
400
650
700
1400
1000
1500
1400
1500
1600
1580
Die Normalbefllung der Getriebe ist Minerall. Synthetisches l ist gegen Mehrpreis lieferbar.
Standard lubricant for the gearboxes is mineral-oil. Synthetic oil is available at a surcharge.
Les rducteurs sont remplis dhuile minrale. Ils peuvent tre remplis dhuile synthtique contre supplment de prix.
HINWEIS / REMARK / REMARQUE:
lfllmengen sind ca.Angaben.
Filling quantities are approx. figures.
Les quantits d`huile sont donnes titre indicatif.
Hinweis:
Diese Tabelle stellt vergleichbare Schmierstoffe unter-
schiedlicher Hersteller dar. Innerhalb einer Viskositt und
Schmierstoffsorte kann der lhersteller gewechselt werden.
Beim Wechsel der Viskositt bzw. der Schmierstoffsorte mu
Rcksprache mit uns gehalten werden, da sonst keine
Gewhrleistung fr die Funktionstchtigkeit unserer Getriebe
bernommen werden kann.
Note:
This table lists compatible lubricants of different suppliers.
Within the same viscosity class and type of lubricant the
supplier can be chosen freely. In case you change the
viscosity class resp. the type of lubricant you should contact
us in advance as otherwise we cannot assure the proper
function of our drive and the warranty becomes void.
Indication:
Ce tableau prsente les lubrifiants comparables des
diffrents fabricants. Si l'on respecte les critres de viscosit
et le type de lubrifiant, on peut uiliser n'importe quelle marque
d'huile aprs ne vidange. Afin de pouvoir garantir un bon
fonctionnement de nos rducteurs, veuillez nous consulter
avant de remplacer un lubrifiant par un autre possdant des
caractristiques diffrentes de viscosit et de type.
Schmierstoffarten / Type of lubricant / Type de lubrifiant
Umgebungstemp.
Ambient temp.
Temp. ambiante
Schneckengetriebe
0 ... 40C
ISO VG 680
Degol BG 680
Degol BG 680
plus
-- Alpha SP 680 Falcon
CLP 680
-- Renolin
CLP 680
CLP 680 Plus
Klberoil
GEM 1-680
Mobilgear:
- 636
- XMP 680
Optigear
BM 680
Shell
Omala 680
Tribol
1100/680
ISO VG 220
- 5 ... 40C (normal)
Degol
BG 220
BG 220 plus
Energol
GR-XP
220
Alpha SP 220
Alpha MW220
Alpha MAX 220
Falcon
CLP 220
Spartan
EP 220
Renolin CLP 220
Renolin CLP 220
Plus
Klberoil
GEM 1-220
Mobilgear
630
Mobilgear
XMP 220
Optigear
BM 220
Shell
Omala 220
Tribol
1100 / 220
ISO VG 100
- 15 ... 25C
Degol
BG 100
BG 100 plus
Energol
GR-XP
100
Alpha SP 100
Alpha MW 100
Alpha MAX 100
Falcon CLP
100
Spartan
EP 100
Renolin CLP 100
Renolin CLP 100
Plus
Klberoil
GEM 1-100
Mobilgear:
- 627
- XMP 110
Optigear
BM 100
Shell
Omala 100
Tribol
1100 / 100
Schmierstoffart
Type of
lubricant
Type de
lubrifiant
Minerall
Mineral oil
Huile minrale
ISO VG 15
- 45 ... - 15C *
Vitamol
1010
Bartran
HV 15
Hyspin AWS 15
Hyspin SP 15
Hyspin ZZ 15
Astron
HVLP 15
Univis J13 Renolin B 15 HVI Isoflex MT
30 rot
Mobil DTE
11 M
Ultra 10 Shell Tellus
T 15
Tribol
943 AW 22
Schneckengetriebe
-5 ... 60C
ISO VG 680
Degol
GS 680
Energol
SG-XP 680
-- -- -- Renolin PG 680 Klbersynth
GH-6-680
Glygoyle
HE 680
Optiflex
A 680
Shell Tivela
S 680
Tribol
800 / 680
Synthetisches l
Synthetic oil
Huile synthtique
ISO VG 220
-25 ... 80C *
Degol
GS 220
Enersyn
SG-XP 220
Alphasyn
PG 220
Polydea
PGLP 220
Glycolube
220
Renolin PG 220 Klbersynth
GH-6-220
Glygoyle
HE 220
Optiflex
A 220
Shell
Tivela WB
Tivela S 220
Tribol
800/ 220
Schneckengetriebe
ISO VG 680
-5 ... 40C
-- -- -- -- -- Plantogear CLP
680
-- -- -- -- -- Biologisch
abbaubares l
Biodegradable oil
Huiles
biodgradables
ISO VG 220
-5 ... 40C
Degol
BAB 220
Biogear
SE 220
Carelub
GES 220
Ergon ELP
220
-- Plantogear CLP
220
Klberbio
GM2-220
-- Optisynt
BS 220
-- Tribol BioTop
1418 / 220
Schneckengetriebe
-5 ... 40C
ISO VG 680
-- -- -- -- -- Bel-Ray No-Tox
Synt.Worm Gear
Oil 680
Klberoil
4 UH1-680
Klbersynth
UH1 6-680
-- Optileb
GT 680
Shell
Cassida
Fluid GL680
Tribol
FoodProof
1800 / 680
Eural
Gear 220
-- Vitalube
GS 220
-- Gear Oil
FM 220
Bel-Ray No-Tox
Gear Oil 90
Klberoil
4 UH1-220
Mobil DTE
FM 220
Optileb
GT 220
Shell Cassida
Fluid GL220
Tribol
FoodProof
1810 / 220
Lebensmittel-
vertrgliches l
1)
Food-grad oil
1)
Huiles pour
environnement
alimentaire
1)
ISO VG 220
-25 ... 40C
Synt.Gear Oil 220 Klbersynth
UH1 6-220
oder
1800 / 220
Synth. Fliefett
Synth. fluid
grease
Graisse fluide
synthtique
- 25 ... 60C
Aralub
BAB EP0
Enersyn
GSF
Alpha Gel 00 -- Fliefett
S 420
Renolit LX-PG 00 Klbersynth
GE 46-1200
Klbersynth
UH1 14-1600
1)
Glygoyle
Grease 00
Obeen
UF 00
Tivela
Comp. A
Tivela GL 00
Tribol
800 / 1000
Schmierstoffarten fr Wlzlager / Type of lubricant for anti friction bearings / Type de librifiant pour roulements rouleaux
Schmierstoffart
Type of
lubricant
Type de
lubrifiant
Umgebungstemp.
Ambient temp.
Temp. ambiante
- 30 ... 60C
(normal)
Aralub
HL 2
Ener-
grease
LS 2
Spheerol AP 2
LZV-EP
Glissando 20 Mehr-
zweckfett
Beacon2
Renolit FWA 160 Klberplex
BEM 41-132
Mobilux 2 Longtime
PD 2
Shell
Alvania R2
Tribol
4020/220-2
Fett
(Minerallbasis)
Grease (mineral
oil basis)
Graisse (base
huile minrale)
* - 50 ... 40C
Aralub
SEL 2
-- Spheerol
EPL2
-- -- Renolit JP 1619 -- -- Longtime
PD 1
Shell Alvania
RL 2
Tribol
3785
Synthetisches
Fett
Synthetic grease
Graisse
synthtique
* - 25 ... 80C
Aralub
SKL 2
-- Product
783/46
Discor B EP
2 LF
Beacon
325
Renolit S 2
Renolit HLT 2
Isoflex Topas
NCA 52
Petamo
GHY 133 N
Mobiltemp
SHC 32
Optitemp
LG 2
Aero Shell
Grease
16 oder 7
Tribol
3499
Biologisch
abbaubares Fett
Biodegradable
Grease
Graisse
biodgradables
- 25 ... 40C
Aralub
BAB EP 2
BP Bio-
grease EP
2
Biotec Dolon E EP 2 -- Plantogel 2 S Klberbio
M 32-82
Schmierfett
UE 100 B
EF 584 Shell
Alvania
RLB 2
Molub-Alloy
BioTop 9488
Lebensmittelver-
trgliches Fett
1)
Food-grade
grease
1)
Graisse pour
environnement
alimentaire
1)
- 25 ... 40C
Eural
Grease EP 2
BP
Energreas
e
FM 2
Vitalube HT
Grease 2
Tamix FRA 1 Carum
330
Renolit
G 7 FG 1
Klbersynth
UH1 14-151
Mobil-
grease
FM 102
Obeen
UF 2
Shell Cassida
RLS 2
Molub-Alloy
Food-Proof
823-2 FM
* Bei Umgebungstemperaturen unterhalb -30C und oberhalb 60C sind Wellendichtringe in besonderer Werkstoffqualitt einzusetzen
* With ambient temperatures below -30C and above approx. 60C shaft sealing rings of a special material quality must be used
* Lors dune temprature ambiante infrieure -30C ou suprieure environ 60C, il y a lieu dutiliser des joints dtanchit spciaux
1)
Lebensmittelvertrgliche le + Fette nach Vorschrift H1 / FDA 178.3570
1)
Food grade lubricants with USDA-H1 approval FDA 178.3570
1)
Huiles pour environnement alimentaire + graisses suivant prescription H1 / FDA 178.3570
Drehstrom-Motor mit Kurzschluanker
Three phase squirrel-cage motor
Moteur triphas cage dcureull
I) Klemmbrett
Terminal board
Plaque bornes
II) Schalter
Switch
Dmarreur
B3 B5 B3 / B5
B8 / B5
B8
B5a
B5b
B6 B7
BAUFORMEN
MOUNTING POSITIONS
POSITIONS DE MONTAGE
Waagerechte Anordnung Horizontal position Position horizontale
V1 V3 V1 / V5
V5 V6 V3 / V6
B5c
Senkrechte Anordnung Vertical position Position verticale
Schaltbilder / Wiring diagrams / Schmas de branchement
Drehstrom-Motor mit Kurzschluanker, in Dahlander-Schaltung
Three phase squirrel-cage motor, Dahlander connection
Moteur triphas cage dcrureull, couplage Dahlander
Drehstrom-Motor, polumschaltbar, zwei getrennte Wicklungen
Three phase motor, polechanging, two separate windings, two speeds
Moteur triphas commutation de ples, deux bobinages spars,
deux vitesses
niedrige - Drehzahl - hohe
low - speed - high
infrieure - vitesse - suprieure
niedrige - Drehzahl - hohe
low - speed - high
infrieure - vitesse - suprieure
Index 01
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
MA 125-250 U3.19D W133 V5 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 180 L-4
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
603
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Cooling SW Pumps ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
001
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 320 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 25 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1764 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 2,9 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 28,7 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 3
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W133
CASING/Gehuse: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
34,9 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
included Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2180 LA-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 243
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 463,7
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M40 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 30
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1470
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 55,1/31,9
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,86
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 91,6
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,262
No load current (A).............. : 40,7
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 45,2
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 67,3
Max cable diameter (mm) ... : 28
Noise (dBa)......................... : 63
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 34,9
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1764
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 58,7
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,86
Efficiency (%)...................... : 91,6
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6311 C3 6311 C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
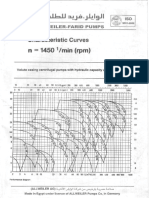
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
250
78,2%
25 m
28,7 kW
2,9 m
77,6 %
320 m/h
250 (P2)
25 m
28,7 kW
2,9 m
77,6 %
320 m/h
250
25 m
28,7 kW
2,9 m
77,6 %
320 m/h
250
25 m
28,7 kW
2,9 m
77,6 %
320 m/h
[m]
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
[kW]
10
15
20
25
[m]
2
3
4
[%]
0
20
40
60
[m/h] 0 40 80 120 160 200 240 280 320 360 400
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
MA 125-250/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No: Cooling SW Pump
Page
1764 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Sea water [100%] ; 32C; 1,03kg/dm; 0,76mm/s
125 01250 1217
Flow
Item:001
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
1
Index 02
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
MA 65-250 U3.19D W134 V5 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 160 M-4
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
315
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
M/E J acket Cooling FW Pumps ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
002
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 85 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 30 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1764 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 2 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 9,05 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 2
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W134
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ S-400 / Nodular Cast Iron
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
12,8 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2 160M-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 118
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 201
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M40 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 11
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1470
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 21,4/12,4
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,84
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 88,6
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,0747
No load current (A).............. : 9,75
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 38,10
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 51
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 19-28
Noise (dBa)......................... : 60
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 12,8
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1764
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 22,6
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,84
Efficiency (%)...................... : 88,6
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6309-2RS C3 6309-2RS C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
248
79,7%
30 m
9,05 kW
2 m
75,3 %
85 m/h
248 (P2)
30 m
9,05 kW
2 m
75,3 %
85 m/h
248
30 m
9,05 kW
2 m
75,3 %
85 m/h
248
30 m
9,05 kW
2 m
75,3 %
85 m/h
[m]
8
12
16
20
24
28
32
[kW]
4
8
[m]
2
4
6
8
[%]
0
20
40
60
[m/h] 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
MA 65-250/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No: M/E Jacket Cooling FW Pump
Page
1764 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Water, fresh water [100%] ; 70C; 0,978kg/dm; 0,409mm/s
065 01250 1217
Flow
Item:002
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
2
Index 03
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
MA 150-315 U3.19D W134 V5 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 250 M-4
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
1311
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
LT Cooling FW Pumps ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
003
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 570 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 35 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1776 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 3,62 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 66,6 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 2
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W134
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ S-400 / Nodular Cast Iron
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
87,3 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
included Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2 250M1-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 592
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 1082
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M63 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 75,0
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1480
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 129/74,8
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,89
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 94,1
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 1,12
No load current (A).............. : 50,0
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 59,1
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 76
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 32-42
Noise (dBa)......................... : 68
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 87,3
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1776
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 137
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,89
Efficiency (%)...................... : 94,1
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6314 C3 6313 C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
296
81,9%
35 m
66,6 kW
3,62 m
80,7 %
570 m/h
296 (P2)
35 m
66,6 kW
3,62 m
80,7 %
570 m/h
296
35 m
66,6 kW
3,62 m
80,7 %
570 m/h
296
35 m
66,6 kW
3,62 m
80,7 %
570 m/h
[m]
16
20
24
28
32
36
40
44
[kW]
20
30
40
50
60
[m]
2
3
4
[%]
0
20
40
60
[m/h] 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
MA 150-315/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No:LT Cooling FW Pump
Page
1770 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Water, fresh water [100%] ; 50C; 0,988kg/dm; 0,548mm/s
150 01315 1217
Flow
Item:003
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
3
Index 04
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
NB 20-160 U3.1D W18 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 80-2
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
37
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Air Cooler Chemical Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
004
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 2 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 30 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 3240 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 1,83 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 0,75 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W18
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ L-250 / Cast Iron
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
1,3 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : MS80 2-2
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 11
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x3,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 12,6
Cable Gland........................ : 1 pcs. M20 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 1,1
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 2700
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 230/400
Nominal current (A)............. : 4,37/2,51
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,88
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 76,2
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,00086
No load current (A).............. : 1,34
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 49,7
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 45,0
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 8-13
Noise (dBa)......................... : 53
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 1,3
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 3240
Voltage (Vac)...................... : Y 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 2,62
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,88
Efficiency (%)...................... : 76,2
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6205 2RS C3 6204 2RS C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
138
33,8%
30 m
0,746 kW
1,83 m
21,8 %
2 m/h
138 (P2)
30 m
0,746 kW
1,83 m
21,8 %
2 m/h
138
30 m
0,746 kW
1,83 m
21,8 %
2 m/h
138
30 m
0,746 kW
1,83 m
21,8 %
2 m/h
[m]
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
[kW]
0,4
0,6
0,8
1
[m]
1
2
3
[%]
0
10
20
[m/h] 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 2,5 3 3,5 4 4,5 5 5,5 6 6,5 7 7,5 8
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
NB 20-160/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No: Air Cooler Chemical Pump
Page
3240 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Water, pure [100%] ; 50C; 0,988kg/dm; 0,548mm/s
020 01160 0135
Flow
Item:004
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
5
Index 05
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
NB 25-160 U3.1D W18 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 90 L-2
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
39,2
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
M/E J acket FW Pre-Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
005
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 9 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 30 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 3312 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 2,88 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 1,68 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W18
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ L-250 / Cast Iron
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
2,52 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : MS90 L-2
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 16,2
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x3,1
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 24,2
Cable Gland........................ : 1 pcs. M20 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 2,2
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 2760
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 230/400
Nominal current (A)............. : 8,16/4,69
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,87
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 81,0
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,00184
No load current (A).............. : 2,14
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 45
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 67,5
Max cable diameter (mm) ... : 13
Noise (dBa)......................... : 57
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 2,52
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 3312
Voltage (Vac)...................... : Y 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 4,74
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,87
Efficiency (%)...................... : 81,0
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6206-2RS C3 6204-2RS C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
148
48%
30 m
1,68 kW
2,88 m
43,4 %
9 m/h
148 (P2)
30 m
1,68 kW
2,88 m
43,4 %
9 m/h
148
30 m
1,68 kW
2,88 m
43,4 %
9 m/h
148
30 m
1,68 kW
2,88 m
43,4 %
9 m/h
[m]
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
[kW]
0,5
1
1,5
[m]
0
4
8
[%]
0
10
20
30
40
[m/h] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
NB 25-160/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No:M/E Jacket FW Pre-Pump
Page
3312 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Water, pure [100%] ; 50C; 0,988kg/dm; 0,548mm/s
461 1302 021
Flow
Item:005
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
6
Index 06
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
TRF 660 46 W203 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 160 L-4
SAFETY RELIEF
VALVE/Sicherheits
ventil:
Incl., built in type
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
350
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Heavy Fuel Oil Transfer Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
006
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 40 m
3
/h Actually capacity: 45,1 m
3
/h
DIFFERENT.PRESS./Differerenzdr.: 40 Bar
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1764 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 3,2 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 7,02 KW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 2
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W203
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ L-250 / Cast Iron
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
17,5 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2 160L-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 138
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 277,7
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M40 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 15
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1470
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 28,5/16,5
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,85
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 90,1
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,0918
No load current (A).............. : 12,17
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 49,50
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 54
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 19-28
Noise (dBa)......................... : 60
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 17,5
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1764
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. :31,2
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,85
Efficiency (%)...................... : 90,1
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6309-2RS C3 6309-2RS C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
F
l
o
w
r
a
t
e
Q
[
m
/
h
]
42
44
46
48
50
52
1000,0 mm/s
25,8 mm/s
45.1 m/h
47.9 m/h
Differential pressure p [bar]
P
o
w
e
r
a
b
s
o
r
b
e
d
P
[
k
W
]
0
5
10
15
20
25
0 2 4 6 8 10
1000,0 mm/s
25,8 mm/s
7.02 kW
4 bar
15.58 kW
4 bar
Quotation no.
Jinling Shipyard
Date
10.09.2007
Name
Fetgenheuer
Project no.
Item 006
CAP-3Screw Item 006 Page
Characteristic curves for
screw pumps
Pump type TRF Size of pump 660 Pitch angle 46
1 Liquid pumped Heavy Fuel Oil
2 Density 0,85 kg/dm Pump capacity 45,1 m/h 47,9 m/h 2
3 Rotor housing GG25 Power req. 7,0 kW 15,6 kW 3
4 I(rotor) 0,00380 kgm Starting torque 38,0 Nm 84,3 Nm 4
5 I(coupl) kgm Total efficiency 71,4 % 34,2 % 5
6 I(mag.coupl) kgm Differential pressure 4,0 bar 4,0 bar 6
7 I(total) 0,00380 kgm Speed 1764 1/min 1764 1/min 7
8 Calculation reference acc. to Temperature 60 C 60 C 8
9 VDMA Viscosity 25,8 mm/s 1000,0 mm/s 9
10 NPSH(pump) 3,2 mWs 9,0 mWs 10
11 Remarks 11
NPSH-value without safety margins
Item
Index 07
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
TRF 660 46 W203 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 160 L-4
SAFETY RELIEF
VALVE/Sicherheits
ventil:
Incl., built in type
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
350
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
MDO Transfer Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
007
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 40 m
3
/h Actually capacity: 45,1 m
3
/h
DIFFERENT.PRESS./Differerenzdr.: 40 Bar
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1764 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 3,2 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 7,02 KW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W203
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ L-250 / Cast Iron
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
17,5 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2 160L-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 138
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 277,7
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M40 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 15
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1470
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 28,5/16,5
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,85
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 90,1
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,0918
No load current (A).............. : 12,17
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 49,50
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 54
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 19-28
Noise (dBa)......................... : 60
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 17,5
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1764
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. :31,2
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,85
Efficiency (%)...................... : 90,1
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6309-2RS C3 6309-2RS C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
F
l
o
w
r
a
t
e
Q
[
m
/
h
]
42
44
46
48
50
52
1000,0 mm/s
25,8 mm/s
45.1 m/h
47.9 m/h
Differential pressure p [bar]
P
o
w
e
r
a
b
s
o
r
b
e
d
P
[
k
W
]
0
5
10
15
20
25
0 2 4 6 8 10
1000,0 mm/s
25,8 mm/s
7.02 kW
4 bar
15.58 kW
4 bar
Quotation no.
Jinling Shipyard
Date
10.09.2007
Name
Fetgenheuer
Project no.
Item 007
CAP-3Screw Item 007 Page
Characteristic curves for
screw pumps
Pump type TRF Size of pump 660 Pitch angle 46
1 Liquid pumped Marine Diesel Oil / mit Wasser
2 Density 0,85 kg/dm Pump capacity 45,1 m/h 47,9 m/h 2
3 Rotor housing GG25 Power req. 7,0 kW 15,6 kW 3
4 I(rotor) 0,00380 kgm Starting torque 38,0 Nm 84,3 Nm 4
5 I(coupl) kgm Total efficiency 71,4 % 34,2 % 5
6 I(mag.coupl) kgm Differential pressure 4,0 bar 4,0 bar 6
7 I(total) 0,00380 kgm Speed 1764 1/min 1764 1/min 7
8 Calculation reference acc. to Temperature 60 C 60 C 8
9 VDMA Viscosity 25,8 mm/s 1000,0 mm/s 9
10 NPSH(pump) 3,2 mWs 9,0 mWs 10
11 Remarks 11
NPSH-value without safety margins
Item
Index 08
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
MELO 250-1 W202 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 250 M-4
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
992
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Lub. Oil Pumps ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
008
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 230 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 45 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1776 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 3,47 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 44,1 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 2
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W2020
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ L-250 / Cast Iron
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Ball bearing
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
87,3 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
included Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2 250M1-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 592
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 1082
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M63 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 75,0
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1480
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 129/74,8
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,89
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 94,1
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 1,12
No load current (A).............. : 50,0
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 59,1
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 76
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 32-42
Noise (dBa)......................... : 68
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 87,3
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1776
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 137
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,89
Efficiency (%)...................... : 94,1
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6314 C3 6313 C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
318
62,9%
45 m
44,1 kW
3,47 m
57,2 %
230 m/h
318 (P2)
45 m
44,1 kW
3,47 m
57,2 %
230 m/h
318
45 m
44,1 kW
3,47 m
57,2 %
230 m/h
318
45 m
44,1 kW
3,47 m
57,2 %
230 m/h
[m]
8
12
16
20
24
28
32
36
40
44
48
[kW]
20
30
40
[m]
3
4
5
[%]
0
20
40
[m/h] 0 40 80 120 160 200 240 280 320 360 400 440 480 520 560
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
MELO 250-1
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No: Lub. Oil Pump
Page
1770 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
SAE 30 [100%] ; 50C; 0,895kg/dm; 68,4mm/s
K-11617
Flow
Item:008 25,8cst
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
7
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
(328)
44,2%
45 m
63,1 kW
3,47 m
40,8 %
230 m/h
(328)
45 m
63,1 kW
3,47 m
40,8 %
230 m/h
(328)
45 m
63,1 kW
3,47 m
40,8 %
230 m/h
(328)
45 m
63,1 kW
3,47 m
40,8 %
230 m/h
[m]
8
12
16
20
24
28
32
36
40
44
48
52
[kW]
30
40
50
60
[m]
3
4
5
[%]
0
10
20
30
[m/h] 0 40 80 120 160 200 240 280 320 360 400 440 480 520
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
MELO 250-1
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No: Lub. Oil Pump
Page
1770 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
SAE 30 [100%] ; 19C; 0,914kg/dm; 402mm/s
K-11617
Flow
Item:008 260cst
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
8
Index 09
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
TRE 40 46 W202 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 90 L-2
SAFETY RELIEF
VALVE/Sicherheits
ventil:
Incl., built in type
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
32
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Lub. Oil Transfer Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
009
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 5 m
3
/h Actually capacity: 5,2 m
3
/h
DIFFERENT.PRESS./Differerenzdr.: 35 Bar
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 3360 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 1,98 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 0,89 KW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W202
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ S-400 / Nodular Cast Iron
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
3,5 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : MS90 L2-2
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 19
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x3,6
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 38
Cable Gland........................ : 1 pcs. M20 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 3,0
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW 2800
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 6,37/3,48
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,83
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 82,6
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,00225
No load current (A).............. :
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ :
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... :
Max cable diameter (mm) ... : 13
Noise (dBa)......................... : 57
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 3,5
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 3360
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 7,4
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,83
Efficiency (%)...................... : 82,6
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6206 2RS C3 6204 2RS C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
F
l
o
w
r
a
t
e
Q
[
m
/
h
]
4.5
4.75
5
5.25
5.5
5.75
6
6.25
1000,0 mm/s
25,8 mm/s
5.21 m/h
5.69 m/h
Differential pressure p [bar]
P
o
w
e
r
a
b
s
o
r
b
e
d
P
[
k
W
]
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1000,0 mm/s
25,8 mm/s
0.891 kW
3.5 bar
2.61 kW
3.5 bar
Quotation no.
Jinling Shipyard
Date
10.09.2007
Name
Fetgenheuer
Project no.
Item 009
CAP-3Screw Item 009 Page
Characteristic curves for
screw pumps
Pump type TRE Size of pump 40 Pitch angle 46
1 Liquid pumped Cylinder Oil
2 Density 0,85 kg/dm Pump capacity 5,2 m/h 5,7 m/h 2
3 Rotor housing GGG40 Power req. 0,9 kW 2,6 kW 3
4 I(rotor) 0,00006 kgm Starting torque 2,6 Nm 7,5 Nm 4
5 I(coupl) kgm Total efficiency 56,9 % 21,2 % 5
6 I(mag.coupl) kgm Differential pressure 3,5 bar 3,5 bar 6
7 I(total) 0,00006 kgm Speed 3312 1/min 3312 1/min 7
8 Calculation reference acc. to Temperature 50 C 50 C 8
9 AWRStd Viscosity 25,8 mm/s 1000,0 mm/s 9
10 NPSH(pump) 2,0 mWs 7,9 mWs 10
11 Remarks 11
NPSH-value without safety margins
Item
Index 10
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
TRE 20 46 W202 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 80-4
SAFETY RELIEF
VALVE/Sicherheits
ventil:
Incl., built in type
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
30
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Cylinder Oil Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
010
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 1 m
3
/h Actually capacity:1,1 m
3
/h
DIFFERENT.PRESS./Differerenzdr.: 30 Bar
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1680 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 1,5 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 0,18 KW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W202
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ S-400 / Nodular Cast Iron
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
1,28 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : MS80 3-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 13,2
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,3
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 15,2
Cable Gland........................ : 1 pcs. M20 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 1,1
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1400
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 230/400
Nominal current (A)............. : 4,96/2,85
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,76
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 76,5
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 18-04-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,00190
No load current (A).............. : 1,35
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 61,8
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 56
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 8-13
Noise (dBa)......................... : 46
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 1,28
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1680
Voltage (Vac)...................... : Y 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 3,04
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,76
Efficiency (%)...................... : 76,5
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6205 2RS C3 6204 2RS C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
F
l
o
w
r
a
t
e
Q
[
m
/
h
]
0
0.25
0.5
0.75
1
1.25
1.5
1000,0 mm/s
25,8 mm/s
1.08 m/h
1.35 m/h
Differential pressure p [bar]
P
o
w
e
r
a
b
s
o
r
b
e
d
P
[
k
W
]
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
1000,0 mm/s
25,8 mm/s
0.182 kW
3 bar
0.52 kW
3 bar
Quotation no.
Jinling Shipyard
Date
10.09.2007
Name
Fetgenheuer
Project no.
Item 010
CAP-3Screw Item 010 Page
Characteristic curves for
screw pumps
Pump type TRE Size of pump 20 Pitch angle 46
1 Liquid pumped Cylinder Oil
2 Density 0,85 kg/dm Pump capacity 1,1 m/h 1,3 m/h 2
3 Rotor housing GGG40 Power req. 0,2 kW 0,5 kW 3
4 I(rotor) 0,00002 kgm Starting torque 1,0 Nm 3,0 Nm 4
5 I(coupl) kgm Total efficiency 49,5 % 21,6 % 5
6 I(mag.coupl) kgm Differential pressure 3,0 bar 3,0 bar 6
7 I(total) 0,00002 kgm Speed 1680 1/min 1680 1/min 7
8 Calculation reference acc. to Temperature 50 C 50 C 8
9 AWRStd Viscosity 25,8 mm/s 1000,0 mm/s 9
10 NPSH(pump) 1,5 mWs 2,7 mWs 10
11 Remarks 11
NPSH-value without safety margins
Item
Index 11
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
RVP 160 M MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 225 M-4
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
Vacuum pump
AELD55
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
995
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Fire & GS-Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
011
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 110/200 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 75/25 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1770 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 4,5 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 45 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W133
CASING/Gehuse: Bronze
IMPELLER/Laufrad: Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
52,4 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
included Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2 225 M-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 328
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 655,7
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M50 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 45
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1475
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 78,4/45,5
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,89
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 93,0
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 18-04-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,469
No load current (A).............. : 31,0
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 60
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 73
Max cable diameter (mm) ... : 27-35 mm
Noise (dBa)......................... : 66
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 52,4
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1770
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 83,0
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,89
Efficiency (%)...................... : 93,0
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6313 C3 6312 C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Index 12
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
RVP 160 M MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 225 M-4
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
Vacuum pump
AELD55
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
995
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Bilge & GS-Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
012
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 110/200 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 75/25 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1770 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 4,5 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 45 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W133
CASING/Gehuse: Bronze
IMPELLER/Laufrad: Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
52,4 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
included Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2 225 M-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 328
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 655,7
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M50 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 45
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1475
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 78,4/45,5
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,89
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 93,0
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 18-04-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,469
No load current (A).............. : 31,0
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 60
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 73
Max cable diameter (mm) ... : 27-35 mm
Noise (dBa)......................... : 66
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 52,4
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1770
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 83,0
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,89
Efficiency (%)...................... : 93,0
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6313 C3 6312 C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Index 13
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
AEB 1E 100
MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 90 L-4/SK01
SAFETY RELIEF
VALVE:
Sicherheitsventil
ASV 32-1-R , loose
supply
DRY RUNNING
PROTECTION:
Trockenlaufschutz
Solenoid valve, loose supply
D205DBZ
ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
013 TOTAL WEIGHT:
Gesamtgewicht:
56 kg
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard DENOMINATION:
Benennung
Daily Bilge Pump
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 5 m
3
/h
DIFFERENT.PRESS./Differerenzdr.: 35 bar
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1750/992 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 2 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 1,03 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff:
CASING/Gehuse: GG-25 / Cast Iron
STATOR/Stator: Perbunan Elastomere
ROTOR/Rotor: 1.4301 / St.Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Stuffing Box Seal / Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
1,73 kW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS
Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung:
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung: (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste: (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve:
IMPORTANT: PLEASE INDICATE PUMP NUMBER, WHEN ORDERING SPARES. FOR SERVICES PLEASE CONTACT OUR SERVICES OFFICE NEAREST TO YOU
(FOR DETAILS SEE OUR LEAFLET SERVICE WORLDWIDE).
Wichtig: Bei Ersatzteilbestellungen bitte die Pumpennummer angeben Fr Service wenden Sie sich bitte an unseren nchstgelegenen Kundendienst (Einzelheiten
entnehmen Sie bitte der Broschre Service Weltweit.
Datenblatt Auftrag Nr. :
data sheet
3 Phasen - Motor/Phase - Motor
Typ : 90 L/4 ( (NORD) ) Mot. Nr. :
Type: Mot. No. :
Leistung : 1,73 kW Stnderschaltung: Dreieck/Stern
Output : connection of stator :
Spannung : 259 / 450 V Frequenz : 60 Hz
Voltage : frequency :
Strom : 6,14 / 3,55 A Drehzahl : 1674 1/min
Current : Speed :
cos.phi : 0,777 Betriebsart: S1 Schutzart: IP 55
pf : made of operation: Type of enclure:
Drehrichtung: beide Bauform :
Direction of rotation : Design :
Vorschrift: EN 60034, DNV- ohne Abnahme
Classifikation Authorites:
Widerstand:(kalt)des Stnders,bei 20C: 4,67 Ohm Isol.Kl. : F
resistances:(cold) stator winding per half phase Insul.Cl.
Mewerte/measurement-values
U ( V ) I (A) n(1/min)/rpm f (Hz) Belastung /rating
259 / 450 3,04 / 1,8 1800 60 Leerlauf / no load
/ /
/ /
259 / 450 6,31 / 3,65 1674 60 Vollast / full load
Probe mit : 450 V und 3,65 A whrend 4 Stunden
Type-or-heat-run-test at and during hours
Temperaturerhhung ber umgebende Luft: 74,8 K , an der Stnderwicklung, gemessen
Temperatur rise above ambient temp. : at the stator winding
nach der Widerstandsmethode.
resistance method.
Wicklungsprfung : 1900 V , 5 sek. , Windungsprfung : 675 V, 1 min.
Winding test : Winding test :
Schalldruckpegel, L
pA
: 50 dB(A)
Noise level, L
pA
berlast :Bemessungsdrehmoment x 1,6 - 120 s Isolationswiderstand: > 100 MOhm
Overload : Insulation resistace :
Wirkungsgrad bei Bemessungsleistung ( % ) : 80,2
efficiency
Anlaufstrom / Bemessungsstrom : 4,5
starting current / rated current
Anlaufmoment / Bemessungsmoment: 2,1
starting torque / rated torque
Kippmoment / Bemessungsmoment : 2,4
maximum torque / rated torque
Datum: Unterschrift :
Date :
C
a
p
a
c
i
t
y
Q
[
m
/
h
]
0
2.5
5
7.5
10
12.5
15
17.5
20
22.5
25
p
=
0
,0
b
a
r
(
w
a
te
r
)
p
=
3
,5
b
a
r
(
P
u
m
p
e
d
liq
u
id
)
5.06 m/h
Speed n [1/min]
P
o
w
e
r
a
b
s
.
P
[
k
W
]
0
0.25
0.5
0.75
1
1.25
1.5
1.75
2
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800
p
=
3
,
5
b
a
r
(
P
u
m
p
e
d
liq
u
id
)
0.919 kW
392 1/min
Quotation No.
Jinling Shipyard
Date
17.09.2007
Prepared by
FETGENHEUER
Item. 013
CAP-ECC
Characteristic Curve for
Progressive Cavity Pumps
Size: 100 Pressure stages: 1 Elastomers: 70 Shore A non-uniform stator type
1 Pumped liquid Daily Bilge Pump 1 inlet pressure -0,5 bar 1
2 Temperature 50,0 C 2 discharge pressure: 3,0 bar 2
3 Density 1,0 kg/dm 3 Differential pressure 3,5 bar 3
4 Viscosity 1,0 mPas 4 Capacity 5,06 m/h 4
5 Solids content 0,0 % 5 Speed 392 1/min 5
6 Grain size 0,0 mm 6 NPSH 2,04 m 6
7 Fibre length 0,0 mm 7 Power 0,919 kW 7
8 Concentration 0,0 % 8 Torque 22,4 Nm 8
9 displacement volume 9 Axial force 937 N 9
10 v(Gm) for 400 1/min 10 Starting power Ma/Mn = 2 1,03 kW 10
11 11 Efficiency total 11
12 12 Tolerance acc. to VDMA 24284 12
13 Remarks 13
Starting torque Ma = 35,0...50,0 Nm
Basic curve No.:19-30-0100-126-4 Pos.: 013
Index 14
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
MA 200-250 U3.19D W133 V5 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 250 M-4
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
AELD55
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
1322
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Ballast Pumps ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
014
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 800 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 25 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1776 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 4,8 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 70,3 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 2
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W133
CASING/Gehuse: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Ball bearing
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
87,3 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
included Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2 250M1-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 592
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 1082
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M63 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 75,0
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1480
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 129/74,8
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,89
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 94,1
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 1,12
No load current (A).............. : 50,0
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 59,1
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 76
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 32-42
Noise (dBa)......................... : 68
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 87,3
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1776
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 137
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,89
Efficiency (%)...................... : 94,1
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6314 C3 6313 C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
278
80,4%
25 m
70,3 kW
4,8 m
79,6 %
800 m/h
278 (P2)
25 m
70,3 kW
4,8 m
79,6 %
800 m/h
278
25 m
70,3 kW
4,8 m
79,6 %
800 m/h
278
25 m
70,3 kW
4,8 m
79,6 %
800 m/h
[m]
8
12
16
20
24
28
32
36
[kW]
30
40
50
60
[m]
3
4
5
6
7
[%]
0
20
40
60
[m/h] 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
MA 200-250/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No: Ballast Pump
Page
1770 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Sea water [100%] ; 32C; 1,03kg/dm; 0,76mm/s
200 01250 1217
Flow
Item:014
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
9
Index 15
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
AEB 1E 100
MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 90 L-4/SK01
SAFETY RELIEF
VALVE:
Sicherheitsventil
ASV 32-1-R , loose
supply
DRY RUNNING
PROTECTION:
Trockenlaufschutz
Solenoid valve, loose supply
D205DBZ
ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
015 TOTAL WEIGHT:
Gesamtgewicht:
56 kg
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard DENOMINATION:
Benennung
Sludge Pump
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 5,4 m
3
/h
DIFFERENT.PRESS./Differerenzdr.: 40 bar
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1750/426 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 2 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 1,1 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff:
CASING/Gehuse: GG-25 / Cast Iron
STATOR/Stator: Perbunan Elastomere
ROTOR/Rotor: 1.4301 / St.Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Stuffing Box Seal / Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
1,73 kW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS
Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung:
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung: (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste: (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve:
IMPORTANT: PLEASE INDICATE PUMP NUMBER, WHEN ORDERING SPARES. FOR SERVICES PLEASE CONTACT OUR SERVICES OFFICE NEAREST TO YOU
(FOR DETAILS SEE OUR LEAFLET SERVICE WORLDWIDE).
Wichtig: Bei Ersatzteilbestellungen bitte die Pumpennummer angeben Fr Service wenden Sie sich bitte an unseren nchstgelegenen Kundendienst (Einzelheiten
entnehmen Sie bitte der Broschre Service Weltweit.
Datenblatt Auftrag Nr. :
data sheet
3 Phasen - Motor/Phase - Motor
Typ : 90 L/4 ( (NORD) ) Mot. Nr. :
Type: Mot. No. :
Leistung : 1,73 kW Stnderschaltung: Dreieck/Stern
Output : connection of stator :
Spannung : 259 / 450 V Frequenz : 60 Hz
Voltage : frequency :
Strom : 6,14 / 3,55 A Drehzahl : 1674 1/min
Current : Speed :
cos.phi : 0,777 Betriebsart: S1 Schutzart: IP 55
pf : made of operation: Type of enclure:
Drehrichtung: beide Bauform :
Direction of rotation : Design :
Vorschrift: EN 60034, DNV- ohne Abnahme
Classifikation Authorites:
Widerstand:(kalt)des Stnders,bei 20C: 4,67 Ohm Isol.Kl. : F
resistances:(cold) stator winding per half phase Insul.Cl.
Mewerte/measurement-values
U ( V ) I (A) n(1/min)/rpm f (Hz) Belastung /rating
259 / 450 3,04 / 1,8 1800 60 Leerlauf / no load
/ /
/ /
259 / 450 6,31 / 3,65 1674 60 Vollast / full load
Probe mit : 450 V und 3,65 A whrend 4 Stunden
Type-or-heat-run-test at and during hours
Temperaturerhhung ber umgebende Luft: 74,8 K , an der Stnderwicklung, gemessen
Temperatur rise above ambient temp. : at the stator winding
nach der Widerstandsmethode.
resistance method.
Wicklungsprfung : 1900 V , 5 sek. , Windungsprfung : 675 V, 1 min.
Winding test : Winding test :
Schalldruckpegel, L
pA
: 50 dB(A)
Noise level, L
pA
berlast :Bemessungsdrehmoment x 1,6 - 120 s Isolationswiderstand: > 100 MOhm
Overload : Insulation resistace :
Wirkungsgrad bei Bemessungsleistung ( % ) : 80,2
efficiency
Anlaufstrom / Bemessungsstrom : 4,5
starting current / rated current
Anlaufmoment / Bemessungsmoment: 2,1
starting torque / rated torque
Kippmoment / Bemessungsmoment : 2,4
maximum torque / rated torque
Datum: Unterschrift :
Date :
C
a
p
a
c
i
t
y
Q
[
m
/
h
]
0
2.5
5
7.5
10
12.5
15
17.5
20
22.5
25
p
=
0
,0
b
a
r
(
w
a
te
r
)
p
=
4
,0
b
a
r
(
P
u
m
p
e
d
liq
u
id
)
5.4 m/h
Speed n [1/min]
P
o
w
e
r
a
b
s
.
P
[
k
W
]
0
0.25
0.5
0.75
1
1.25
1.5
1.75
2
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800
p
=
4
,
0
b
a
r
(
P
u
m
p
e
d
liq
u
id
)
1.08 kW
426 1/min
Quotation No.
Jinling Shipyard
Date
17.09.2007
Prepared by
Fuchs
Item. 015
CAP-ECC
Characteristic Curve for
Progressive Cavity Pumps
Size: 100 Pressure stages: 1 Elastomers: 70 Shore A non-uniform stator type
1 Pumped liquid Sludge 1 inlet pressure -0,5 bar 1
2 Temperature 50,0 C 2 discharge pressure: 3,5 bar 2
3 Density 1,0 kg/dm 3 Differential pressure 4,0 bar 3
4 Viscosity 1,0 mPas 4 Capacity 5,4 m/h 4
5 Solids content 0,0 % 5 Speed 426 1/min 5
6 Grain size 0,0 mm 6 NPSH 2,06 m 6
7 Fibre length 0,0 mm 7 Power 1,08 kW 7
8 Concentration 0,0 % 8 Torque 24,2 Nm 8
9 displacement volume 9 Axial force 1071 N 9
10 v(Gm) for 400 1/min 10 Starting power Ma/Mn = 2 1,12 kW 10
11 11 Efficiency total 11
12 12 Tolerance acc. to VDMA 24284 12
13 Remarks 13
Starting torque Ma = 35,0...50,0 Nm
Basic curve No.:19-30-0100-126-4 Pos.: 015
Index 16
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
NAM 65-250 U3.1D W3 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 200 L-2
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
ASED-C
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
501
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Emergency Fire Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
016
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 72 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 75 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 3540 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 4,93 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 27,1 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W3
CASING/Gehuse: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
34,9 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
included Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2 200 L1-2
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 246
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,0
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 448
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M50 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 30
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 2950
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 52,3/30,3
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,90
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 92,0
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 18-09-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,124
No load current (A).............. : 18,7
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 43,7
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 69,3
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 27-35
Noise (dBa)......................... : 74
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 34,9
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 3540
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 55,3
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,90
Efficiency (%)...................... : 92,0
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Acc. to DNV standard Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6312 C3 6312 C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
(201)
65,1%
75 m
27,1 kW
4,93 m
55,9 %
72 m/h
(201)
75 m
27,1 kW
4,93 m
55,9 %
72 m/h
(201)
75 m
27,1 kW
4,93 m
55,9 %
72 m/h
(201)
75 m
27,1 kW
4,93 m
55,9 %
72 m/h
[m]
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
[kW]
10
20
30
[m]
4
8
12
[%]
0
20
40
[m/h] 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
NAM 65-250/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No: Emergency Fire Pump
Page
3500 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Sea water [100%] ; 32C; 1,03kg/dm; 0,76mm/s
065 01250 0135
Flow
Item:016
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
10
Index 17
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
NB 25-200 U3.1D W18 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 112 M-2
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
61,4
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Fresh Water Pumps ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
017
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 10 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 50 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 3480 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 2,08 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 4,7 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: Makers
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 2
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W18
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ L-250 / Cast Iron
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
6,4 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : MS112M1-2
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 35,4
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,5
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 66,6
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M20 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 5,5
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 2900
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 10,7/6,19
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,88
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 85,7
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,00720
No load current (A).............. : 3,6
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 38,2
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 66,0
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 8-13
Noise (dBa)......................... : 62
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 6,4
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 3480
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 11,1
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,88
Efficiency (%)...................... : 85,7
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6306 2RS C3 6306-2RS C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
(191)
28,9%
50 m
4,7 kW
2,08 m
28,7 %
10 m/h
(191)
50 m
4,7 kW
2,08 m
28,7 %
10 m/h
(191)
50 m
4,7 kW
2,08 m
28,7 %
10 m/h
(191)
50 m
4,7 kW
2,08 m
28,7 %
10 m/h
[m]
20
24
28
32
36
40
44
48
52
56
60
64
[kW]
1
2
3
4
[m]
1
1,5
2
[%]
0
5
10
15
20
25
[m/h] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
NB 25-200/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No:
Page
3480 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Water, pure [100%] ; 50C; 0,988kg/dm; 0,548mm/s
025 01200 0135
Flow
Item: 017 Frsh Water pumps
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
11
Index 18
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
NB 20-160 U3.1D W18 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 80-2
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
37
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Hot Water Circulating Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
018
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 2,18 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 23,8 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 3240 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 1,75 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 0,544 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: Makers
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 2
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W18
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ L-250 / Cast Iron
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
1,3 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : MS80 2-2
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 11
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x3,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 12,6
Cable Gland........................ : 1 pcs. M20 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 1,1
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 2700
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 230/400
Nominal current (A)............. : 4,37/2,51
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,88
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 76,2
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-01-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,00086
No load current (A).............. : 1,34
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 49,7
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 45,0
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 8-13
Noise (dBa)......................... : 53
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 1,3
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 3240
Voltage (Vac)...................... : Y 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 2,62
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,88
Efficiency (%)...................... : 76,2
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6205 2RS C3 6204 2RS C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
125
34,7%
23,8 m
0,544 kW
1,75 m
25,3 %
2,18 m/h
125 (P2)
23,8 m
0,544 kW
1,75 m
25,3 %
2,18 m/h
125
23,8 m
0,544 kW
1,75 m
25,3 %
2,18 m/h
125
23,8 m
0,544 kW
1,75 m
25,3 %
2,18 m/h
[m]
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
[kW]
0,4
0,6
[m]
1
2
3
4
[%]
0
10
20
30
[m/h] 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 2,5 3 3,5 4 4,5 5 5,5 6 6,5 7
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
NB 20-160/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No: Hot Water Circulating Pump
Page
3240 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Water, pure [100%] ; 80C; 0,972kg/dm; 0,358mm/s
020 01160 0135
Flow
Item:018
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
12
Index 19
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
NB 25-200 U3.1D W18 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 100 L-2
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
50
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Technical Water Pumps ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
019
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 2 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 50 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 3444 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 1,84 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 2,45 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: Makers
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 2
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W18
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ L-250 / Cast Iron
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
3,5 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : MS100L-2
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 24
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,8
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 38,1
Cable Gland........................ : 1 pcs. M20 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 3,0
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 2870
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 6,14/3,41
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,86
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 82,6
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 24-03-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,00253
No load current (A).............. : 2,43
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 40,0
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 59,0
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 8-13
Noise (dBa)......................... : 60
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 3,5
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 3444
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 6,35
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,86
Efficiency (%)...................... : 82,6
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DE/NDE .............. : 6206 2RS C3 6206-2RS C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
175
26,9%
50 m
2,45 kW
1,84 m
11 %
2 m/h
175 (P2)
50 m
2,45 kW
1,84 m
11 %
2 m/h
175
50 m
2,45 kW
1,84 m
11 %
2 m/h
175
50 m
2,45 kW
1,84 m
11 %
2 m/h
[m]
20
24
28
32
36
40
44
48
52
[kW]
1
1,5
2
2,5
3
3,5
[m]
1
1,5
2
[%]
0
5
10
15
20
[m/h] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
NB 25-200/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No: Technical Water Pump
Page
3444 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Water, pure [100%] ; 50C; 0,988kg/dm; 0,548mm/s
025 01200 0135
Flow
Item:019
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
13
Index 20
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
MA 100-250 U3.19D W133 V5 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 180 M-4
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
AELD55
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
527
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Bilge Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
020
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 200 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 25 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1764 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 2,86 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 17,8 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W133
CASING/Gehuse: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
21,5 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
n. a. Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2 180M-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 177
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 288,4
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M40 x 1,5
Starting time (sec.).............. : 10
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 18,5
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1470
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 34,5/20,0
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,86
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 90,4
Your order no...................... : xxxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxx
Date.................................... : 31-03-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxx-xxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,139
No load current (A).............. : 11,8
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 56,9
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 69
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 19-28
Noise (dBa)......................... : 62
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 21,5
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1764
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 36,5
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,86
Efficiency (%)...................... : 90,4
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6311 C3 6311 C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : XXXXXXXX
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
243
78,5% 25 m
17,8 kW
2,86 m
78,4 %
200 m/h
243 (P2)
25 m
17,8 kW
2,86 m
78,4 %
200 m/h
243
25 m
17,8 kW
2,86 m
78,4 %
200 m/h
243
25 m
17,8 kW
2,86 m
78,4 %
200 m/h
[m]
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
[kW]
5
10
15
[m]
2
3
4
[%]
0
20
40
60
[m/h] 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
MA 100-250/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No:
Page
1764 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Sea water [100%] ; 32C; 1,03kg/dm; 0,76mm/s
100 01250 1217
Flow
Item: 020 Bilge Pump
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
14
Index 21
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
MA 80-315 U3.19D W134 V5 MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
IEC 200 L-4
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
TOTAL WEIGHT approx.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
622
kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Harbour LT Cooling FW Pump ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
021
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA/Leistungsdaten
CAPACITY/Frdermenge: 270 m
3
/h
DELIVERY HEAD/Frderhhe: 35 m
SPEED OF ROTATION/Drehzahl: 1770 1/min
NPSH REQUIRED: 4,98 m WC
POWER ABSORBED/Leistungsbed. 33,4 kW
CLASSIFICATION/Klassifikation: LR
PUMP DATA/Pumpendaten
QUANTITY/Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL/Werkstoff: W134
CASING/Gehuse: EN-GJ S-400 / Nodular Cast Iron
IMPELLER/Laufrad: G-CuAl10Ni / Bronze
SHAFT/Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL/Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA/Motordaten
DESIGN/Bauform: IM V1 POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsabgabe:
43,1 KW
SUPPLY/Stromart 440 VOLTS/Volt 60 CYCLES
Hertz
HEATER ELEMENTS/
Heizelemente:
included Schutzart IP 55
CLASSIFICATION/
Klassifikation
Makers INSULATION CLASS: F
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE
INSTRUCTIONS/Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
DIMENSIONS DRAWING/Mazeichnung
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PERFORMANCE CURVES/Leistungskurve
Allweiler AG
D-78301 Radolfzell
Motortype........................... : Y2E2 200L1-4
Mounting............................. : B5 / V1, fixed bearing
Protection class................... : IP55
Insulation class.................... : F/B
Duty cycle............................ : S1-100%
Mass (kg) ............................ : 305
Starting torque d.o.l............. : x2,2
Starting current d.o.l. (A)..... : 548,3
Cable Gland........................ : 2 pcs. M50 x 1,5
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 50
Output (kW)......................... : 37
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1475
Voltage (Vac) ...................... : /Y 400/690
Nominal current (A)............. : 66,4/38,3
Power factor cos. Phi .......... : 4/4 load 0,88
Efficiency (%) ...................... : 92,6
Your order no...................... : xxxxx
Project no............................ : xxxxx
Mark.................................... : xxxxx
Our order no........................ : xxxxxx
Date.................................... : 26-09-2006
Certificate no....................... : xxxxxx
Moment of inertia J (kgm) . : 0,406
No load current (A).............. : 22,0
Temp. rise surface (K) ........ : 52,6
Temp. rise windings (K) ...... : 76
Cable diameter (mm) .......... : 27-35
Noise (dBa)......................... : 64
Frequency (Hz) .................. : 60
Output (kW)......................... : 43,1
Speed (min
-1
) ...................... : C-CW - 1770
Voltage (Vac)...................... : 440
Nominal current (A)............. : 69,4
Power factor cos. Phi.......... : 4/4 load 0,88
Efficiency (%)...................... : 92,6
Anti condensation heating : Consumption (W) : Voltage (V) :
Marine classification : Amb.temp. : 45
o
C
High voltage dielectric test between phases and earth during 1 min (Vac)............ : 2000
Overload test during 15 seconds overload torque (%FLT)..................................... : 160
Vibration severity according NEN/ISO 2373-1974 (half key)................................. : Class N or as specified below
Bearings DA/NDE .............. : 6312 C3 6312 C3
Special features .................. :
Motor serial numbers .......... : SHxxxxx-xxx
SVEND HYER A/S
MOTOR TEST CERTIFICATE
Charact. curves
Created by
Date
2007-09-10
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
306
80,2%
35 m
33,4 kW
4,98 m
76,1 %
270 m/h
306 (P2)
35 m
33,4 kW
4,98 m
76,1 %
270 m/h
306
35 m
33,4 kW
4,98 m
76,1 %
270 m/h
306
35 m
33,4 kW
4,98 m
76,1 %
270 m/h
[m]
12
16
20
24
28
32
36
40
44
48
[kW]
10
20
30
[m]
2
4
6
[%]
0
20
40
60
[m/h] 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260 280 300
1
Speed
DIN EN ISO 9906
Power data referred to:
Remarks:
Admissible minmum capacity 10 % * Q(opt) at continous operation
MA 80-315/01
Quotati on / Offer No.
Proj ect ID
Jinling Shipyard
Pos.No: Harbour LT Cooling FW Pump
Page
1770 1/min
Charact. curves acc. Class 2
Curve number:
Water, fresh water [100%] ; 50C; 0,988kg/dm; 0,548mm/s
080 01315 1217
Flow
Item:021
Fetgenheuer, Thomas
4
Index 22
1
ALLWEILER AG MAIN TECHNICAL DATA
Technische Daten
PUMP TYPE:
Pumpentyp:
3/HK 50-1-110
MOTOR TYPE:
Motor Typ:
90L2
PRIMING UNIT:
Ansaugeinheit:
n.a.
TOTAL WEIGHT ca.:
Gesamtgewicht ca.:
45 kg
DENOMINATION:
Benennung:
Sewage Pump
ITEM-NO:
Pos.Nr.:
022
CUSTOMER:
Kunde:
J inling Shipyard
PERFORMANCE DATA / Leistungsdaten
LIQUID TEMP. / Medium Temp: 32 C
CAPACITY / Frdermenge: 8 m
3
/h
DISCH. HEAD / Druck am Druckstutzen: 1,8 bar
Diff. Pressure / Diff. Druck: 1,8 bar
SUCTION HEAD / Druck am Saugstutzen 0 bar
DELIVERY HEAD / Frderhhe: 18 m
SPEED OF ROTATION / Drehzahl: 3420 rpm
NPSH REQUIRED: 1,45 m WC
POWER ABSORBED / Leistungsbedarf: 1,38 kW
CLASSIFICATION / Klassifikation: Makers
PUMP DATA / Pumpendaten
QUANTITY / Stckzahl: 1
MATERIAL / Werkstoff:
CASING / Gehuse: GG-25 Cast Iron
IMPELLER / Laufrad: CuSn10
SHAFT / Welle: Stainless Steel
SHAFT SEAL / Wellenabdichtung: Mechanical Seal
MOTOR DATA / Motordaten
DESIGN /
Bauform:
IM V1
POWER OUTPUT/
Leistungsangabe:
2,6 KW
VOLTAGE /
Spannung
440V
CYCLES
Frequenz
60 Hz
HEATER ELEMENTS /
Heizelemente:
n.a.
PROTECTION CLASS: IP
Schutzart: IP
55
CLASSIFICATION /
Klassifikation
Makers
INSULATION CLASS:
Isolationsklasse:
F
STARTING METHOD/
Anlauf Methode
DOL
IN THE FOLLOWING PLEASE FIND/ Nachfolgend finden Sie:
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS
Betriebs- und Wartungsvorschrift
SECTIONAL DRAWING/Schnittzeichnung: (see operating & maintenance instruction)
PARTS LIST/Stckliste: (see operating & maintenance instruction)
20.04.2009
6.21
Data sheet
MADE W ITH VERSION:
Manufacturer Customer
VEM motors Thurm GmbH
uere Dresdener Str. 35
D-08066 Zwickau
Three-phase motors with squirrel cage rotor, motors in marine version
Germanischer Lloyd
Type KPER 90 L2 FDS
Classific. Authority GL
Design output ( kW ) 2,6
Duty type S1
Number of poles ( - ) 2
Design frequency ( Hz ) 60
Design speed [rpm] 3420
Voltage ( V ) 440
Connection ( - ) Y
Current ( A ) 4,75
Relative pull-in current ( - ) 7,3
Relative starting torque ( - ) 2,4
Relative pull-up torque ( - ) 1,9
Relative pull-out torque ( - ) 2,4
Power factor ( - ) 0,88
Efficiency ( % ) 82
Th. cl. 155(F)
Coolant temperature ( C ) 45C
Altitude above sea level ( m ) 1000m
Degree of protection
Moment of inertia ( kgm
M ( kg ) otor weight
IP55
) 0,0017
19
6205 2Z C3
6205 2Z C3
-
Bearing, D-side
Bearing, N-side
Relubrication interval ( h )
Grease type Asonic GLY 32
Grease amount ( g ) -
Special details to bearings 1 none
Special details to bearings 2 Fixed bearing, D-side
Bearing monitoring none
Winding protection none
Winding protection 2 none
Anti-condensation heating none
Special versions 1 none
Special versions 2 none
Special versions 3 none
Special versions 4 none
Limit values to vibration velocity Class A
Balancing with half key
Colour system Moderate
Colour shade RAL 7031 blue-grey
Layer thickness 60 m
Deli very conditions and/or official regulations: DIN EN 60034-1
This document was produced electronically, all specifications are valid only after confirmation of the manufacturer
2
Seite 1/2
VEM motors GmbH Telefon: 0 39 43 / 68-0 Geschftsfhrer: Rechtsform: GmbH Commerzbank AG Dresdner Bank AG Deutsche Bank AG
Carl-Friedrich-Gau-Strae 1 Telefax: 0 39 43 / 68 21 20 Sitz: Wernigerode Dresden Wernigerode Wernigerode
D-38855 Wernigerode J rgen Sander Amtsgericht
Postfach-Nr. 101252 E-Mail: motors@vem-group.com Dr. Dietmar Puschkeit Stendal HRB 112964 BLZ 850 400 00 BLZ 800 800 00 BLZ 810 700 00
D-38842 Wernigerode www.vem-group.com Dr. Susanne Frie Ust.-Id. Nr. DE 212 649 455 Kto.-Nr. 800 15 88 Kto.-Nr. 350 50 30 00 Kto.-Nr. 250 04 03
3/HK50-1-110-F-V-W2
2009-08-26 2
Date: Page: Created by :
Isele, Patrick
Proj ect: Proj ect no.:
Impeller
, 0,0 NN
Charact. curves
D(sel )
Single channel impeller 110
Operating data
Speed: Bezugsfrequenz: Duty poi nt: Sucti on fl ange: Di scharge fl ange:
3420 1/min 60 8 m/h Q = H = 18 m DN 50 DN 50
Power data referred to: Water, pure [100%] ; 20C; 0,9983kg/dm; 1,005mm/s
Hz
Head
Shaft power P2
NPSH-values
Efficiency
130
62,9%
Eff.
100
50,4%
110
55,6%
18,3 m
1,38 kW
1,45 m
29,9 %
8,06 m/h
130 (P2)
100 (P2)
110 (P2)
18,3 m
1,38 kW
1,45 m
29,9 %
8,06 m/h
130
100
110
18,3 m
1,38 kW
1,45 m
29,9 %
8,06 m/h
130
100
110
18,3 m
1,38 kW
1,45 m
29,9 %
8,06 m/h
[m]
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
[kW]
0,8
1,2
1,6
2,4
2,8
[m]
[%]
10
20
30
40
50
60
[m/h]
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
36
38
40
42
44
46
1
Open
Laufradkonstrukti on: Laufradtyp: Outl et wi dth
35 mm
Version 2.0.1
Operating
and
Maintenance
Instructions
Centrifugal Pump with
Volute Casing
Operating manual MI / MA series
Version BA-2007.01
Print-No. 550 338
VM-No. 467.0005 GB
ALLWEILER AG Werk Radolfzell
Postfach 1140
Allweilerstr. 1
78301 Radolfzell
Germany
Phone: +49 (0) 7732-86-0
Fax: +49 (0) 7732-86-436
E-mail: info@allweiler.com
Internet: http://www.allweiler.com
We reserve the right to make technical changes.
Table of contents
Table of contents
1 About this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1 Target groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.2 Other applicable documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.3 Warnings and symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.4 Technical terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 Intended use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2 General safety instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2.1 Product safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2.2 Operator's obligations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2.3 Obligations of personnel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.3 Specic hazards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.3.1 Hazardous pumped media . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3 Layout and function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.1 Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.1.1 Type plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.1.2 Pump type code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.2 Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.2.1 MI series (radial ingress) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.2.2 MA series (axial ingress) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.3 Shaft seals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.3.1 Mechanical seals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.4 Auxiliary systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.4.1 Automatic aspirator (if available) . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4 Transport, storage and disposal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.1 Transport . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.1.1 Unpacking and inspection on delivery . . . . . . 13
4.1.2 Lifting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.2 Preservation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4.3 Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4.4 Removing the preservative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4.5 Disposal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5 Setup and connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1 Preparing the setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.1 Checking the ambient conditions . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.2 Preparing the installation site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.3 Removing the preservative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.4 Installing the heat insulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.5 Fastening the pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.2 Installing the motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.2.1 Attach the motor to the pump. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.2.2 Fit the coupling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.3 Planning the piping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.3.1 Specifying supports and ange
connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.3.2 Specifying nominal diameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.3.3 Specifying pipe lengths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.3.4 Optimizing cross-section and direction
changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.3.5 Provide safety and control devices
(recommended) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.4 Connecting the pipes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.4.1 Keeping the piping clean . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.4.2 Installing auxiliary pipes (if available) . . . . . . . 17
5.4.3 Installing the suction pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.4.4 Installing the pressure pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.4.5 Inspection for stress-free pipe
connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.5 Electrical connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.5.1 Connecting the motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.5.2 Checking the direction of rotation . . . . . . . . . . . 17
6 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1 Preparations for the initial start-up . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1.1 Identifying the pump type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1.2 Removing the preservative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1.3 Lubricating the bearings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1.4 Filling and bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.2 Start-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.2.1 Switching on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.2.2 Switching off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.3 Shutting down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.4 Start-up following a shutdown period . . . . . . . 20
6.5 Operating the stand-by pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
7 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.1 Inspections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.2 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.2.1 Antifriction bearings lubricated with
grease . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.2.2 Mechanical seals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.3 Dismounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.3.1 Preparations for dismounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.3.2 Returning the pump to the manufac-
turer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.4 Installing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
7.5 Ordering spare parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
8 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
9 Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
9.1 Sectional drawings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
9.1.1 Auxiliary connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
9.1.2 Part numbers and designations . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
9.1.3 Sectional drawings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
9.2 Technical specications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
9.2.1 Ambient conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
9.2.2 Sound pressure levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
9.2.3 Tightening torques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
9.2.4 Cleaning agents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
9.2.5 Preservatives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
9.2.6 Flange loads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
9.3 Spare parts for two years of continuous
operation according to DIN 24296 . . . . . . . . . . 34
2 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Table of contents
9.4 Safety certicate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 3
Table of contents
List of gures
Fig. 1 Type plate (example) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Fig. 2 Pump type code (example) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Fig. 3 MI series structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Fig. 4 MA series structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Fig. 5 Automatic aspirator extension
example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Fig. 6 Fastening the lifting gear to the pump unit in
a vertical position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Fig. 7 Fastening the lifting gear to the pump unit in
a horizontal position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Fig. 8 Straight pipe lengths upstream and down-
stream of the pump (recommended) . . . . . . . 16
Fig. 9 MI series sectional drawing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Fig. 10 MA series sectional drawing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Fig. 11 Explosion drawing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Fig. 12 Flange loads at the pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
List of tables
Tab. 1 Target groups and their duties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Tab. 2 Other applicable documents and their
purpose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Tab. 3 Warnings and consequences of disregarding
them . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Tab. 4 Symbols and their meaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Tab. 5 Technical terms and their meaning . . . . . . . . . 6
Tab. 6 Measures to be taken if the pump is shut
down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Tab. 7 Measures depending on the behavior of the
pumped medium . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Tab. 8 Measures to be taken after prolonged
shutdown periods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Tab. 9 Measures for return . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Tab. 10 Fault number assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Tab. 11 Troubleshooting list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Tab. 12 Abbreviations of the connection
designations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Tab. 13 Designations of components according to
part numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Tab. 14 Ambient conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Tab. 15 Sound pressure levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Tab. 16 Tightening torques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Tab. 17 Cleaning agents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Tab. 18 Valvoline preservatives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Tab. 19 Maximum ange loads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Tab. 20 Spare parts for two years of continuous
operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
4 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
About this document
1 About this document
This manual
Is part of the pump
Applies to all pump series listed
Describes safe and appropriate operation during all oper-
ating phases
1.1 Target groups
Target group Duty
Operating company Keep this manual available at the operation site of the system,
including for later use.
Ensure that personnel read and follow the instructions in this
manual and the other applicable documents, especially all safety
instructions and warnings.
Observe any additional rules and regulations referring to the
system.
Qualied personnel, tter Read, observe and follow this manual and the other applicable
documents, especially all safety instructions and warnings.
Tab. 1 Target groups and their duties
1.2 Other applicable documents
Document Purpose
Order data sheet Technical specications, conditions of operation
Setup drawing Setup dimensions, connection dimensions etc.
Technical description Technical specications, operating limits
Sectional drawing Sectional drawing, part numbers, component designations
Automatic aspirator operating manual Technical documentation
Supplier documentation Technical documentation for parts supplied by subcontractors
Spare parts list Ordering spare parts
Declaration of conformity Conformity with standards
Tab. 2 Other applicable documents and their purpose
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 5
About this document
1.3 Warnings and symbols
Warning Risk level Consequences of disregard
DANGER
Immediate acute risk Death, grievous bodily harm
WARNING
Potentially acute risk Death, grievous bodily harm
CAUTION
Potentially hazardous situation Minor bodily harm
CAUTION
Potentially hazardous situation Material damage
Tab. 3 Warnings and consequences of disregarding them
Symbol Meaning
Safety warning sign
Take note of all information highlighted by the safety warning sign
and follow the instructions to avoid injury or death.
Instruction
1. , 2. , ... Multiple-step instructions
Precondition
Cross-reference
Information, advice
Tab. 4 Symbols and their meaning
1.4 Technical terms
Term Meaning
Sealing medium Medium for blocking or quenching shaft seals
Auxiliary systems Systems for operating the pump
Tab. 5 Technical terms and their meaning
6 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Safety
2 Safety
The manufacturer does not accept any liability for damage
resulting from disregard of the entire documentation.
2.1 Intended use
Only use the pump for pumping the agreed pumped media
( order data sheet).
Adhere to the operating limits and size-dependent mini-
mum ow rate.
Avoid dry running:
Initial damage, such as destruction of the mechanical seal
and plastic parts, will occur within only a few seconds.
Make sure the pump is only operated with, and never
without, a pumped medium.
Avoid cavitation:
Fully open the suction-side tting and do not use it to
adjust the ow rate.
Do not open the pressure-side tting beyond the
agreed operating point.
Avoid overheating:
Do not operate the pump while the pressure-side tting
is closed.
Observe the minimum ow rate ( order data sheet).
Avoid damage to the motor:
Do not open the pressure-side tting beyond the
agreed operating point.
Note the maximum permissible number of times the
motor can be switched on per hour ( manufacturer's
specications).
Consult the manufacturer about any other use of the pump.
Prevention of obvious misuse (examples)
Note the operating limits of the pump with regard to temper-
ature, pressure, ow rate and motor speed ( order data
sheet).
The power consumed by the pump increases with increas-
ing density of the pumped medium. To avoid overloading
the pump, coupling or motor, stay within the agreed density
( order data sheet).
Lower densities are allowed. Adapt the auxiliary systems
accordingly.
When pumping liquids containing solids, ensure the limits
for the proportion of solids and the grain size are main-
tained ( order data sheet, technical description).
When using auxiliary systems, ensure there is a continuous
supply of the appropriate operating medium.
2.2 General safety instructions
Take note of the following regulations before carrying out
any work.
2.2.1 Product safety
The pump has been constructed according to the latest tech-
nology and recognized technical safety rules. Nevertheless,
operation of the pump can still put the life and health of the
user or third parties at risk or damage the pump or other prop-
erty.
Only operate the pump if it is in perfect technical condition
and only use it as intended, staying aware of safety and
risks, and in adherence to the instructions in this manual.
Keep this manual and all other applicable documents com-
plete, legible and accessible to personnel at all times.
Refrain from any procedures and actions that would pose
a risk to personnel or third parties.
In the event of any safety-relevant faults, shut down the
pump immediately and have the fault corrected by appro-
priate personnel.
In addition to the entire documentation for the product,
comply with statutory or other safety and accident-preven-
tion regulations and the applicable standards and guide-
lines in the country where the pump is operated.
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 7
Safety
2.2.2 Operator's obligations
Safety-conscious operation
Only operate the pump if it is in perfect technical condition
and only use it as intended, staying aware of safety and
risks, and in adherence to the instructions in this manual.
Ensure that the following safety aspects are observed and
monitored:
Adherence to intended use
Statutory or other safety and accident-prevention reg-
ulations
Safety regulations governing the handling of hazard-
ous substances
Applicable standards and guidelines in the country
where the pump is operated
Make protective equipment available.
Qualied personnel
Make sure all personnel tasked with work on the pump
have read and understood this manual and all other appli-
cable documents, especially the safety, maintenance and
repair information, before they start any work.
Organize responsibilities, areas of competence and the
supervision of personnel.
Ensure that all work is carried out by specialist technicians
only:
Fitting, repair and maintenance work
Work on the electrical system
Make sure trainee personnel only work on the pump under
supervision of specialist technicians.
Safety equipment
Provide the following safety equipment and verify its func-
tionality:
For hot, cold and moving parts: safety guarding pro-
vided by the customer for the pump
For potential build up of electrostatic charge: ensure
appropriate grounding.
Warranty
Obtain the manufacturer's approval prior to carrying out
any modications, repairs or alterations during the warranty
period.
Only use genuine parts or parts that have been approved
by the manufacturer.
2.2.3 Obligations of personnel
All directions given on the pump must be followed (and kept
legible), e.g. the arrow indicating the direction of rotation
and the markings for uid connections.
Do not remove the safety guarding for hot, cold or moving
parts during operation.
Use protective equipment whenever necessary.
Only carry out work on the pump while it is not running.
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
Reinstall the safety equipment on the pump as required by
regulations after any work on the pump.
2.3 Specic hazards
2.3.1 Hazardous pumped media
Follow the safety regulations for handling hazardous sub-
stances when pumping hazardous media (e.g. hot, am-
mable, poisonous or potentially harmful).
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
8 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Layout and function
3 Layout and function
3.1 Labels
3.1.1 Type plate
NPSH kW 1/min P m n
m
3
/h H m Q
Nr Jahr
Typ
mm
2
/s kg/dm
3
D - 78315 Radolfzell / Germany
Typ und Nr.
1
2
3
4
6
7
10
9
8
angeben
Bei Ersatzteilbestellung
5
Fig. 1 Type plate (example)
1 Pump type
2 Year of manufacture
3 Differential head
4 Pump NPSH value
5 Kinematic viscosity
6 Power consumption
7 Density
8 Motor speed
9 Flow rate
10 Pump number
3.1.2 Pump type code
1
2
3
4
MI 80 315 / 01 / 310 U3.19D W133 S
5
6
7
8
Fig. 2 Pump type code (example)
1 Series (MI or MA)
2 Pressure ange DN [mm]
3 Nominal impeller diameter [mm]
4 Hydraulic number
5 Actual impeller diameter [mm]
6 Shaft seal
7 Material key
8 Installation type (S = pedestal, W = wall)
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 9
Layout and function
3.2 Layout
3.2.1 MI series (radial ingress)
Fig. 3 MI series structure
1 Flanged motor
2 Motor bell housing
3 Coupling with spacer piece
4 Coupling guard
5 Storage
6 Housing cover
7 Buffer
8 Shaft seal
9 Impeller
10 Volute casing
11 Shaft
12 Vacuum ange
13 Foot
14 Earth connection (optional)
10 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Layout and function
3.2.2 MA series (axial ingress)
Fig. 4 MA series structure
1 Flanged motor
2 Motor bell housing
3 Coupling with spacer piece
4 Coupling guard
5 Storage
6 Housing cover
7 Buffer
8 Shaft seal
9 Impeller
10 Volute casing
11 Shaft
12 Vacuum ange
13 Foot
14 Earth connection (optional)
3.3 Shaft seals
3.3.1 Mechanical seals
Mechanical seals have functional leaks.
Single mechanical seal
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 11
Layout and function
3.4 Auxiliary systems
3.4.1 Automatic aspirator (if available)
Information on the material, functional description and elec-
trical connection ( A25A automatic aspirator operating
manual).
1
Fig. 5 Automatic aspirator extension example
1 Automatic aspirator
The maintenance-free A25A automatic aspirator:
Used for automatic bleeding of pumps and suction pipes
Operates according to the ejector principle with pressure-
dependent control
Suitable for clean, chemically neutral water
12 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Transport, storage and disposal
4 Transport, storage and disposal
4.1 Transport
For details of weight ( documents for the particular
order).
Transport the pump unit lying down.
4.1.1 Unpacking and inspection on delivery
1. Unpack the pump/aggregate on delivery and inspect it for
damage.
2. Report any damage to the manufacturer immediately.
3. Dispose of packaging material according to local regula-
tions.
4.1.2 Lifting
DANGER
Death or crushing of limbs caused by falling or overturning
loads!
Use lifting gear appropriate for the total weight to be trans-
ported.
Fasten the lifting gear as illustrated in the following.
Attach the safety rope to the motor or motor lug to prevent
the pump from overturning.
Do not stand under suspended loads.
Set the load down on a level surface.
Fig. 6 Fastening the lifting gear to the pump unit
in a vertical position
Fig. 7 Fastening the lifting gear to the pump unit
in a horizontal position
Lift the pump/aggregate properly.
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 13
Transport, storage and disposal
4.2 Preservation
Not necessary for non-rusting materials
CAUTION
Material damage due to inappropriate treatment for stor-
age!
Treat the pump properly, inside and outside, for storage.
1. Choose a preservative appropriate for the type and dura-
tion of storage ( 9.2.5 Preservatives, Page 32).
2. Use the preservative specied by the manufacturer.
3. All bare metal parts should be treated, inside and outside.
4.3 Storage
CAUTION
Material damage due to inappropriate storage!
Treat and store the pump properly.
1. Seal all openings with blind anges, blind plugs or plastic
covers.
2. Make sure the storage room meets the following condi-
tions:
Dry
Dust-free
Frost-free
Vibration-free
3. Turn the shaft once a month.
4. Make sure the shaft and bearing change their rotational
position in the process.
4.4 Removing the preservative
Only necessary for pumps treated with preservative
WARNING
Risk of poisoning from preservatives and cleaning agents
in the foodstuffs and drinking water sector!
Only use cleaning agents which are compatible with the
pumped liquid ( 9.2.4 Cleaning agents, Page 32).
Completely remove all preservative.
CAUTION
High water pressure or spray water can damage bearings!
Do not clean the bearing areas with a water or steam jet.
CAUTION
Damage to seals due to incorrect cleaning agent!
Ensure the cleaning agent does not corrode the seals.
1. Choose a suitable cleaning agent for the application.
( 9.2.4 Cleaning agents, Page 32).
With Tectyl 506 EH: allow benzine to soak in for 10 minutes
(recommended).
2. Dispose of preservatives according to local regulations.
3. For storage times in excess of 6 months:
Replace the elastomer parts made of EP rubber
(EPDM).
Check all elastomer parts (O-rings, shaft seals) for
proper elasticity and replace them if necessary.
4.5 Disposal
Plastic parts can be contaminated by poisonous or radioac-
tive pumped media to such an extent that cleaning is insuf-
cient.
WARNING
Risk of poisoning and environmental damage caused by
pumped medium or oil!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Prior to disposal of the pump:
Catch and dispose of any escaping pumped medium
or oil in accordance with local regulations.
Neutralize residues of pumped medium in the pump.
Remove any preservative ( 4.4 Removing the pre-
servative , Page 14).
Remove and dispose of any plastic parts in accordance
with local regulations.
Dispose of the pump in accordance with local regulations.
14 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Setup and connection
5 Setup and connection
CAUTION
Material damage caused by dirt!
Do not remove any covers and transport and sealing cov-
ers until immediately before connecting the piping to the
pump.
Do not remove the transport seals until immediately before
setting up the pump.
5.1 Preparing the setup
5.1.1 Checking the ambient conditions
Make sure the required ambient conditions are fullled
( 9.2.1 Ambient conditions, Page 31).
5.1.2 Preparing the installation site
Ensure the installation site meets the following conditions:
Pump is freely accessible from all sides
Sufcient space for installation/removal of the pipes
and for maintenance and repair work, especially for the
removal and installation of the pump and the motor
Pump not exposed to external vibrations (damage to
bearings)
Frost protection
5.1.3 Removing the preservative
If the pump is to be put into operation immediately after
setup and connection: remove the preservative prior to
setup ( 4.4 Removing the preservative , Page 14).
5.1.4 Installing the heat insulation
Only necessary to maintain the temperature of the pumped
medium
CAUTION
Material damage caused by overheating!
Only install the heat insulation on the volute casing.
Install the heat insulation properly.
5.1.5 Fastening the pump
1. Remove any transport seals.
2. Install and fasten the pump ( installation drawing):
Base installation: screw the feet to the oor.
Wall attachment: screw the motor bell housing to the
wall.
5.2 Installing the motor
Only necessary if the pump aggregate is assembled on
site.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by knocks and bumps!
Keep the coupling halves properly aligned when slipping
them on.
Do not knock or hit any components of the pump.
5.2.1 Attach the motor to the pump.
1. Lift the motor ( manufacturer's specications).
2. Place the motor on the bell housing.
3. Screw in the motor bolts and tighten them.
5.2.2 Fit the coupling
1. Smear a very thin coat of molybdenum disulde (e.g.
Molykote) on the shaft end of the motor.
2. Insert shaft key.
3. Push on the motor-end half of the coupling and slightly
tighten the grub screw.
4. Fit the spacer and screw it to the pump shaft end.
5. Install the membrane package without tension. Position
the coupling hub. Use the distance specied by the cou-
pling manufacturer.
6. Tighten the grub screw on the coupling half.
7. Fit the coupling guard.
5.3 Planning the piping
5.3.1 Specifying supports and ange connections
CAUTION
Material damage due to excessive forces and torques
exerted by the piping on the pump!
Do not exceed the permissible limits ( 9.2.6 Flange
loads, Page 33).
1. Calculate the pipe forces taking every possible operating
condition into account:
Cold/warm
Empty/full
Unpressurized/pressurized
Shift in position of anges
2. Ensure the pipe supports have permanent low-friction
properties and do not seize up due to corrosion.
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 15
Setup and connection
5.3.2 Specifying nominal diameters
Keep the ow resistance in the pipes as low as possible.
1. Specify the nominal suction pipe diameter nominal suc-
tion ange diameter.
2. Specify the nominal pressure pipe diameter nominal
pressure ange diameter.
5.3.3 Specifying pipe lengths
C
D
B
A
Fig. 8 Straight pipe lengths upstream and downstream
of the pump (recommended)
A > 5 x nominal suction pipe diameter
B Nominal suction pipe diameter
C Nominal pressure pipe diameter
D > 5 x nominal pressure pipe diameter
Maintain the recommended minimum values when install-
ing the pump.
Suction side: shorter pipes are possible but may restrict
the hydraulic performance.
Pressure side: shorter pipes are possible but can result in
increased operating noise.
5.3.4 Optimizing cross-section and direction
changes
1. Avoid radii of curvature of less than 1.5 times the nominal
pipe diameter.
2. Avoid abrupt changes of cross-section along the piping
system.
5.3.5 Provide safety and control devices
(recommended)
Avoid impurities
1. Integrate a lter into the suction pipe.
2. To monitor impurities, install a differential pressure gauge
with a contact manometer.
Avoid reverse running
Install a non-return valve between the pressure ange and
the gate valve to ensure the medium does not ow back
when the pump is switched off.
Avoid running empty
1. For suction operation: install a foot valve in the suction pipe
to prevent the pump and suction pipe from running empty
during downtimes.
2. Use a suction strainer, depending on the solids content of
the pumped uid.
Make provisions for isolating and shutting off the pipes
For maintenance and repair work.
Provide shut-off devices in the suction and pressure pipes.
Allow the measurement of the operating conditions
1. Provide manometers for pressure measurements in suc-
tion and pressure pipes.
2. Provide for motor-side torque measurements.
3. Provide for pump-side temperature measurements.
16 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Setup and connection
5.4 Connecting the pipes
5.4.1 Keeping the piping clean
CAUTION
Material damage due to impurities in the pump!
Make sure no impurities can get into the pump.
1. Clean all piping parts and armatures prior to assembly.
2. Ensure no ange seals protrude inwards.
3. Remove any blind anges, plugs, protective foils and/or
protective paint from anges.
5.4.2 Installing auxiliary pipes (if available)
Follow the manufacturers' specications for any existing
auxiliary systems.
1. Connect the auxiliary pipes to the auxiliary connections so
that they are stress-free and do not leak (setup drawing).
2. To avoid air pockets, run the pipes with a continuous slope
up to the pump.
5.4.3 Installing the suction pipe
1. Remove the transport and sealing covers from the pump.
2. To avoid air pockets, run the pipes with a continuous slope
up to the pump.
3. Ensure no seals protrude inwards.
5.4.4 Installing the pressure pipe
1. Remove the transport and sealing covers from the pump.
2. Install the pressure pipe.
3. Ensure no seals protrude inwards.
5.4.5 Inspection for stress-free pipe connections
Piping installed and cooled down
1. Separate the pipe connecting anges from the pump.
2. Check whether the pipes can be moved freely in all direc-
tions within the expected range of expansion:
Nominal diameter < 150 mm: by hand
Nominal diameter > 150 mm: with small lever
3. Make sure the ange surfaces are parallel.
4. Reconnect the pipe connecting anges to the pump.
5.5 Electrical connection
DANGER
Risk of death due to electric shock!
Have all electrical work carried out by qualied electricians
only.
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and secure it
against being switched back on again before working on
the electrical system.
5.5.1 Connecting the motor
Follow the instructions of the motor manufacturer.
1. Connect the motor according to the connection diagram.
2. Make sure that no danger arises due to electrical energy.
3. Install an EMERGENCY STOP switch.
5.5.2 Checking the direction of rotation
DANGER
Risk of death due to rotating parts!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Secure the shaft key from being thrown out when checking
the direction of rotation.
Keep an adequate distance to rotating parts.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by running dry or wrong direction
of rotation!
Uncouple the motor from the pump.
1. Switch the motor on and immediately off again.
2. Check whether the direction of rotation of the motor corre-
sponds to the rotational direction arrow on the pump.
3. If the direction of rotation is different:
swap two phases ( 5.5.1 Connecting the motor,
Page 17).
4. Couple the motor to the pump again.
5. Fit the coupling guard again.
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 17
Operation
6 Operation
6.1 Preparations for the initial start-up
6.1.1 Identifying the pump type
Identify the pump type ( order data sheet).
Pump types vary e.g. with regard to bearing lubrication,
bearing bracket size, type of shaft seal and auxiliary sys-
tems.
6.1.2 Removing the preservative
Only necessary for pumps treated with preservative
( 4.4 Removing the preservative , Page 14).
6.1.3 Lubricating the bearings
Pumps with grease-lubricated roller bearings are ready for
operation upon delivery.
6.1.4 Filling and bleeding
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
media!
Safely collect any leaking pumped medium and dispose
of it in accordance with environmental rules and require-
ments.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by dry running!
Make sure the pump is lled properly.
Without an automatic aspirator
1. Open the suction-side armature.
2. Open the pressure-side armature.
3. Fill the pump and the suction pipe with pumped medium.
4. Verify that no pipe connections are leaking.
With an automatic aspirator
1. Open the suction-side armature.
2. Close the pressure-side armature.
3. Suction operation ( A25A automatic aspirator operating
manual).
4. Verify that no pipe connections are leaking.
6.2 Start-up
6.2.1 Switching on
Pump set up and connected properly
Motor set up and connected properly
All connections stress-free and sealed
All safety equipment installed and tested for functionality
Pump prepared, lled and bled properly
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
Allowthe pump to cool down completely before starting any
work.
DANGER
Risk of injury and poisoning caused by pumped medium
spraying out!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by dry running!
Make sure the pump is lled properly.
CAUTION
Risk of cavitation when throttling down the suction ow
rate!
Fully open the suction-side armature and do not use it to
adjust the ow rate.
Do not open the pressure-side armature beyond the oper-
ating point.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by overheating!
Do not operate the pump while the pressure-side armature
is closed.
Observe the minimum ow rate ( order data sheet).
1. Open the suction-side armature.
2. Close the pressure-side armature.
3. Switch on the motor and check it for smooth running.
4. Once the motor has reached its nominal speed, slowly
open the pressure-side armature until the operating point
is reached.
5. Make sure any temperature changes at pumps with hot
pumped liquids are below 50 K/h.
18 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Operation
6. After the initial stress caused by pressure and operating
temperature, check that the pump is not leaking.
6.2.2 Switching off
Pressure-side armature closed (recommended)
WARNING
Risk of injury due to hot pump parts!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
1. Switch off the motor.
2. Check all connecting bolts and tighten them if necessary.
6.3 Shutting down
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
media!
Safely collect any leaking pumped medium and dispose
of it in accordance with environmental rules and require-
ments.
Take the following measures whenever the pump is shut
down:
Pump is Measure
...shut down
for a prolonged
period
Take measures according to
the pumped liquid ( Table
7 Measures depending on
the behavior of the pumped
medium, Page 19).
...emptied Close the suction-side and
pressure-side armatures.
...dismounted Isolate the motor from its power
supply and secure it against
unauthorized switch-on.
...put into
storage
Follow the storage instructions
( 4.3 Storage, Page 14).
Tab. 6 Measures to be taken if the pump is shut down
Duration of shutdown (depending
on process)
Behavior
of pumped
medium
Short Long
Solids sediment Flush the
pump.
Flush the
pump.
Solidies/
freezes,
non-corrosive
Heat up or
empty the
pump and
containers.
Empty the
pump and
containers.
Solidies/
freezes,
corrosive
Heat up or
empty the
pump and
containers.
Empty the
pump and
containers.
Treat the
pump and
containers
with preser-
vative.
Remains liquid,
non-corrosive
Remains liquid,
corrosive
Empty the
pump and
containers.
Treat the
pump and
containers
with preser-
vative.
Tab. 7 Measures depending on the behavior
of the pumped medium
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 19
Operation
6.4 Start-up following a shutdown period
1. If the pump is shut down for more than 2 years, take the
following measures before restoring it to service:
Shutdown period Measure
> 2 years Replace elastomer seals
(O-rings, shaft sealing rings).
Replace antifriction bearings.
Tab. 8 Measures to be taken after prolonged
shutdown periods
2. Carry out all steps as for the initial start-up ( 6.2 Start-up,
Page 18).
6.5 Operating the stand-by pump
Stand-by pump lled and bled
Operate the stand-by pump at least once a week.
1. Completely open the suction-side armature.
2. Open the pressure-side armature to an extent that the
stand-by pump reaches its operating temperature and is
heated through evenly ( 6.2.1 Switching on, Page 18).
20 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Maintenance
7 Maintenance
Trained service technicians are available for tting and
repair jobs. Present a pumped medium certicate (DIN
safety data sheet or safety certicate) when requesting
service.
7.1 Inspections
The inspection intervals depend on the operational strain
on the pump.
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
media!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
1. Check at appropriate intervals:
Maintenance of minimum ow rate
Temperature of roller bearings < 120 C
Normal operating conditions unchanged
Coupling alignment and condition of elastic parts
2. For trouble-free operation, always ensure the following:
No dry running
No leaks
No cavitation
Suction-side gate valves open
Unobstructed and clean lters
Sufcient supply pressure
No unusual running noises or vibrations
No excessive leakage at the shaft seal
Proper functioning of auxiliary systems
Put the installed stand-by pump into operation at least
once a week
7.2 Maintenance
Service life of the antifriction bearings for operation within
the permissible operating range: > 2 years
Intermittent operation, high temperatures, low viscosities
and aggressive ambient and process conditions reduce the
service life of antifriction bearings.
Mechanical seals are subject to natural wear, which
strongly depends on the actual operating conditions.
Therefore, general statements regarding their service life
cannot be made.
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
DANGER
Risk of death due to electric shock!
Have all electrical work carried out by qualied electricians
only.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous or hot
pumped media!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Allow the pump to cool down completely before commenc-
ing any work.
Make sure the pump is unpressurized.
Empty the pump, safely collect the pumped medium and
dispose of the medium in accordance with environmental
rules and requirements.
7.2.1 Antifriction bearings lubricated with grease
As a precaution, replace antifriction bearings with lifetime
lubrication every 2 years (recommended).
7.2.2 Mechanical seals
Due to their function, mechanical seals always leak a bit
( manufacturer's specications).
In the event of a larger leak: replace the mechanical seal
and its auxiliary seals.
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 21
Maintenance
7.3 Dismounting
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
DANGER
Risk of death due to electric shock!
Have all electrical work carried out by qualied electricians
only.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous or hot
pumped media!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Allow the pump to cool down completely before commenc-
ing any work.
Make sure the pump is unpressurized.
Empty the pump, safely collect the pumped medium and
dispose of the medium in accordance with environmental
rules and requirements.
7.3.1 Preparations for dismounting
Pump unpressurized
Pump completely empty, ushed and decontaminated
Electrical connections isolated and motor secured against
switch-on
Pump cooled down
Coupling guard dismounted
With couplings with a spacer piece: spacer piece removed
Auxiliary systems shut down, unpressurized and emptied
Auxiliary piping, manometer lines, manometer and xtures
dismounted
In production, the pumps are constructed to a standard pro-
cess. The slide-in unit can be removed without removing
the motor, volute casing or piping.
When dismounting, observe the following:
Precisely mark the assembly orientation and position
of all components before dismounting.
Dismantle components concentrically without canting.
Dismount the pump ( sectional drawing).
7.3.2 Returning the pump to the manufacturer
Pump unpressurized
Pump completely empty
Electrical connections isolated and motor secured against
switch-on
Pump cooled down
Coupling guard dismounted
With couplings with a spacer piece: spacer piece removed
Auxiliary systems shut down, unpressurized and emptied
Manometer connections, manometer and xtures dis-
mounted
1. Enclose a truthfully (fully) completed document of compli-
ance when returning pumps or individual parts to the man-
ufacturer ( 9.4 Safety certicate, Page 35).
2. Take necessary measures, depending on the required
repair work, as listed in the table below when returning the
pump to the manufacturer.
Repair carried out Measure for return
...at the customer's
premises
Return the defective
component to the
manufacturer.
...at the
manufacturer's
premises
Flush the pump and
decontaminate it if it was
used to pump hazardous
media.
Return the complete pump
(not disassembled) to the
manufacturer.
...at the
manufacturer's
premises for
warranty repairs
Only if the pumped media
is hazardous: ush and
decontaminate the pump.
Return the complete pump
(not disassembled) to the
manufacturer.
Tab. 9 Measures for return
22 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Maintenance
7.4 Installing
Reinstall the components concentrically, without canting,
following the markings made.
1. When installing, observe the following:
Replace worn parts with genuine spare parts.
Replace seals, inserting them so that they cannot
rotate.
Maintain the specied tightening torques
( 9.2.3 Tightening torques, Page 32).
2. Clean all parts ( 9.2.4 Cleaning agents, Page 32). Do
not remove the prepared markings.
3. Install the pump ( sectional drawing).
4. Replace the antifriction bearings.
5. Install the pump in the system ( 5 Setup and connection,
Page 15).
7.5 Ordering spare parts
For trouble-free replacement in the event of any faults,
we recommend keeping complete slide-in units or spare
pumps available on site.
The application guidelines conforming to DIN 24296 rec-
ommend provisioning for two years of continuous use
( 9.3 Spare parts for two years of continuous operation
according to DIN 24296, Page 34).
Have the following information ready to hand when order-
ing spare parts ( type plate):
Pump type
Pump number
Year of manufacture
Part number
Designation
Quantity
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 23
Troubleshooting
8 Troubleshooting
For faults which are not specied in the following table or can-
not be traced back to the specied causes, please consult the
manufacturer.
Possible faults are identied by a fault number in the table
below. This number identies the respective cause and rem-
edy in the troubleshooting list.
Fault Number
Pump not pumping 1
Pumping rate insufcient 2
Pumping rate excessive 3
Pumping pressure insufcient 4
Pumping pressure excessive 5
Pump running roughly 6
Antifriction bearing temperatures too high 7
Pump leaking 8
Motor power uptake excessive 9
Tab. 10 Fault number assignment
Fault number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Cause Remedy
X
Supply/suction pipe and/or pressure pipe
closed by armature
Open the armature.
X
Automatic aspirator defective ( A25 automatic aspirator operating
manual).
X
Transport and sealing cover still in place Remove the transport and sealing
cover.
Dismount the pump and inspect it for
dry-running damage.
X X
Supply/suction pipe not bled properly or
not lled up completely
Fill up the pump and/or piping
completely and bleed them.
X X
Supply/suction pipe contains air pockets Install the armature for bleeding.
Correct the piping layout.
X X X
Motor speed insufcient Compare the required motor speed
with the specications on the pump
type plate. Replace the motor if
necessary.
Increase the motor speed if speed
control is available.
X X X X
Supply/suction pipe, pump or suction
screen blocked or encrusted
Clean the supply/suction pipe, pump
or suction screen.
X X X X Air is sucked in Seal the source of malfunction.
X X X X
Excessive amount of gas: pump is
cavitating
Consult the manufacturer.
X X X X Pressure pipe blocked Clean the pressure pipe.
X X
X
X
Pump running in the wrong direction Swap any two phases on the motor.
24 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Troubleshooting
Fault number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Cause Remedy
X X X X
Impeller out of balance or blocked Dismount the pump and inspect it for
dry-running damage.
Clean the impeller.
X X
Supply/suction pipe not fully opened Open the armature.
X X
Geodetic differential head and/or pipe ow
resistances too high
Remove sediments from the pump
and/or pressure pipe.
Install a larger impeller and consult the
manufacturer.
X X X
Supply/suction pipe cross-section too
narrow
Increase the cross-section.
Remove any encrustations from the
suction pipe.
Open the armature completely.
X X X
Hydraulic parts of the pump dirty, clotted
or encrusted
Dismount the pump.
Clean the parts.
X
X
X
Differential head excessive: NPSH
pump
larger than NPSH
system
Increase the supply pressure.
Consult the manufacturer.
X X X Pumped medium temperature too high:
pump is cavitating
Increase the supply pressure.
Lower the temperature.
Consult the manufacturer.
X X X Viscosity or specic gravity of the pumped
medium outside the range specied for
the pump
Consult the manufacturer.
X X X Pressure-side armature not opened
sufciently
Open the pressure-side armature.
X
X
X X
Pump parts worn Replace the worn pump parts.
X X X X Motor running on 2 phases Check the fuse and replace it if
necessary.
Check the cable connections and
insulation.
X X Viscosity lower than expected Machine the impeller down. Consult
the manufacturer and adjust the
impeller diameter.
X X X Geodetic differential head, pipe ow
resistances and/or other resistances lower
than specied
Throttle down the ow rate at the
pressure-side armature. Observe the
minimum ow rate.
Machine the impeller down. Consult
the manufacturer and adjust the
impeller diameter.
X X X X Pressure-side armature opened too wide Throttle down at the pressure-side
armature.
Machine the impeller down. Consult
the manufacturer and adjust the
impeller diameter.
X
X X X
X Motor speed too high Compare the required motor speed
with the specications on the pump
type plate. Replace the motor if
necessary.
Reduce the motor speed if speed
control is available.
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 25
Troubleshooting
Fault number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Cause Remedy
X X X X Impeller diameter too large Throttle down the ow rate at the
pressure-side armature. Observe the
minimum ow rate.
Machine the impeller down. Consult
the manufacturer and adjust the
impeller diameter.
X X
X Antifriction bearings in the pump defective Replace the antifriction bearing.
X X Defective antifriction bearing in motor Replace the antifriction bearing.
X Lubricant: too much, not enough or
unsuitable
Reduce, top up or replace the lubricant.
X
Connecting bolts not tightened correctly Tighten the connecting bolts.
X Mechanical seal worn Replace the mechanical seal.
X
Housing seal defective Replace the housing seal.
X X X X Pump distorted Check the pipe connections and pump
xings.
Check the coupling alignment.
Check the xing of the support foot.
X X
Coupling not properly aligned Align the coupling.
X Membrane package worn Replace the membrane package and
realign it.
Tab. 11 Troubleshooting list
26 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Appendix
9 Appendix
9.1 Sectional drawings
9.1.1 Auxiliary connections
Abbreviation Connection
FF2 Filling
FV1 Bleeding
PM1 Manometer
PM2 Manometer
Tab. 12 Abbreviations of the connection designations
9.1.2 Part numbers and designations
Part no. Designation
102.01 Volute casing
153.01 Vacuum ange
161.01 Housing cover
182.01 Foot
210.01 Shaft
230.01 Impeller
321.01 Deep groove ball bearing
341.01 Motor bell housing
360.01 Bearing cover
360.02 Bearing cover
400.06 Gasket
411.03 Seal ring
411.04 Seal ring
411.06 Seal ring
412.01 O-ring
412.11 O-ring
420.01 V-ring
420.02 V-ring
433.01 Mechanical seal
551.01 Spacer disk
565.01 Rivet
595.01 Buffer
681.01 Coupling guard
801.01 Flanged motor
855.01 Coupling with spacer piece
901.01 Hexagon head bolt
901.03 Hexagon head bolt
Part no. Designation
901.05 Hexagon head bolt
901.06 Hexagon head bolt
901.10 Hexagon head bolt
902.06 Stud bolt
903.03 Screw plug
903.04 Screw plug
903.06 Screw plug
908.01 Jacking screw
908.10 Jacking screw
922.01 Impeller nut
930.01 Circlip
932.01 Circlip
934.01 Spring washer
936.01 Spring ring
940.01 Shaft key
971.01 Type plate
972.01 Information plate
Tab. 13 Designations of components according
to part numbers
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 27
Appendix
9.1.3 Sectional drawings
MI series sectional drawing
Fig. 9 MI series sectional drawing
28 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Appendix
MA series sectional drawing
Fig. 10 MA series sectional drawing
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 29
Appendix
MA series explosion dawing
Fig. 11 Explosion drawing
30 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Appendix
9.2 Technical specications
More technical specications ( order data sheet).
9.2.1 Ambient conditions
Operation under other ambient conditions to be agreed with
the manufacturer
Relative humidity [%] Tempera-
ture [C]
Long-term Short-term
Setup
height
above sea
level [m]
20 to +40 85 100 1000
Tab. 14 Ambient conditions
9.2.2 Sound pressure levels
Measuring conditions:
Distance to the pump: 1 m
Operation: cavitation-free
Motor: IEC standard motor
Tolerance 3 dB
Lower-noise versions of the motors are available if the
expected noise levels exceed the permissible limits.
Sound pressure level [dB] for pump
with motor at speed [min
-1
]
Nominal motor
power PM [kW]
1450 1750 2900 3500
1.5 58 58.5 63 64
2.2 60 60.5 66 67
3.0 62 62.5 68 69
4.0 63 63.5 69 70
5.5 65 65.5 71 72
7.5 66 66.5 72 73
11.0 68 68.5 74 75
15.0 69 69.5 75 76
18.5 70 70.5 76 77
22.0 71 71.5 77 78
30.0 72 72.5 78 79
37.0 73 73.5 79 80
45.0 74 74.5 80 81
55.0 75 75.5 80 81
75.0 76 76.5 81 82
90.0 76 76.5 82 83
110.0 77 77.5 82 83
132.0 78 78.5 83 84
160.0 79 79.5 84 85
200.0 80 80.5 85 86
Tab. 15 Sound pressure levels
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 31
Appendix
9.2.3 Tightening torques
Part no. Thread
gage
Quality Tightening
torque [Nm]
901.01
M10
M12
M16
A4
11.3
19.5
47.0
901.03
M12
M16
M20
A4
23.0
55.0
110.0
901.05
M6
M8
8.8
2.8
6.5
901.06
M10
M12
8.8
13.5
23.0
901.10
M12
M16
M20
8.8
20.0
55.0
110.0
920.06
M12
M16
A4
23.0
55.0
922.01
M20 x 1.5
M24 x 1.5
M30 x 1.5
M36 x 1.5
M42 x 1.5
M48 x 1.5
A4
100.0
175.0
365.0
615.0
1000.0
1700.0
595.01
(Nut)
M20 8.8 110.0
Foundation
fastening
M20
M24
M30
8.8
110.0
190.0
380.0
Tab. 16 Tightening torques
9.2.4 Cleaning agents
Application area Cleaning agents
Foodstuffs and drinking
water sector
E.g. spirit, Ritzol 155, strong
alkaline soapy solution,
steam jet (for individual
parts only)
Other Benzine, wax solvents,
diesel, parafn, alkaline
cleaners
Tab. 17 Cleaning agents
9.2.5 Preservatives
Use Valvoline preservatives or similar (recommended).
Type of storage Storage
duration
[months]
Preservative
inside/
outside
Renew
[months]
inside/
outside
< 6 Tectyl 511 M
612 Tectyl 511 M
In closed, dry and
dust-free room
> 12 Tectyl 506 EH 48/48
< 6 Tectyl 542
612 Tectyl 542/
Tectyl 506 EH
In open air, central
European climate
> 12 Tectyl 506 EH 48/18
< 6 Tectyl 542/
Tectyl 506 EH
612 Tectyl 542/
Tectyl 506 EH
In open air,
tropical climate,
aggressive
industrial
atmosphere or
close to sea
> 12 Tectyl 506 EH 48/12
Tab. 18 Valvoline preservatives
32 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Appendix
9.2.6 Flange loads
Denition of the pipe forces and torques on the basis of EN
ISO 5199.
Fig. 12 Flange loads at the pump
Nominal ange
diameter [mm]
Forces [N] Torques [Nm]
Pump size
F
max
(x) F
max
(y) F
max
(z) F
M
max
(x)
M
max
(y)
M
max
(z) M
S 125 1350 1500 1200 2350 800 500 700 1200
65-250/01
D 65 700 800 650 1250 500 250 350 650
S 150 1700 1900 1500 2950 1000 600 750 1400
80-250/01
80-315/01
D 80 850 950 750 1500 550 300 400 750
S 150 1700 1850 1500 3000 1000 600 750 1400
100-250/01
D 100 1100 1250 1000 2000 600 350 450 850
S 200 2250 2500 2000 3900 1350 900 1050 2000
100-315/01
D 100 1100 1250 1000 1950 600 350 450 850
S 200 2250 2500 2000 3900 1350 900 1050 1900
125-250/01
125-315/01
D 125 1300 1500 1200 2300 800 500 700 1200
S 200 2250 2500 2000 3900 1400 900 1100 2000
150-250/01
D 150 1700 1900 1500 2950 1000 650 800 1450
S 250 2800 3150 2550 5000 2000 1350 1600 2900
150-315/01
D 150 1700 1900 1500 3000 1000 650 800 1450
S 250 2800 3100 2500 4850 2000 1300 1600 2900 200-250/01
200-315/01
200-500/02
D 200 2250 2500 2000 3900 1400 900 1100 2000
S 300 3350 3750 3000 5850 2800 1900 2200 4050
250-315/02
250-500/01
D 250 2800 3150 2550 4950 2000 1350 1600 2900
S 400 4500 5000 4000 7850 4600 3200 3750 6750
350-315/01
D 350 3900 4400 3500 6850 3650 2500 2950 5300
Tab. 19 Maximum ange loads
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 33
Appendix
9.3 Spare parts for two years of
continuous operation according
to DIN 24296
Number of identical pumps (including stand-by pumps)
2 3 4 5 6 or 7 8 or 9 > 9
Part no. Part designation
Set/quantity of spare parts
230.01 Impeller 1 1 1 2 2 3 30 %
210.01
922.0
930.01
934.01
936.01
940.01
Shaft
Impeller nut
Circlip
Spring washer or
Spring ring
Shaft key
1)
1 1 2 2 2 3 30 %
321.01
400.06
412.01
420.01
420.02
Groove ball bearing
Gasket
O-ring
V-ring S
V-ring A
1)
1 1 2 2 3 4 50 %
433... Mechanical seal 2 3 4 5 6 7 90 %
Various
400.06
411.03
411.04
411.06
412.01
412.11
420.01
420.02
Seal set with
Gasket
Seal ring
Seal ring
Seal ring
O-ring
O-ring
V-ring
V-ring
1)
4 6 8 8 9 12 150 %
Tab. 20 Spare parts for two years of continuous operation
1) Delivered as a mechanical unit (BG) or sales unit (VG)
34 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Appendix
9.4 Safety certicate
467.0005 GB 550 338 BA-2007.01 MI / MA series 35
Appendix
36 MI / MA series BA-2007.01 467.0005 GB 550 338
Centrifugal Pump with
Volute Casing
Operating manual NB / CLB series
Version BA-2006.05
Print-No. 550 148
VM-No. 468.0005 GB
ALLWEILER AG Werk Radolfzell
Postfach 1140
Allweilerstr. 1
78301 Radolfzell
Germany
Phone: +49 (0) 7732-86-0
Fax: +49 (0) 7732-86-436
E-mail: info@allweiler.com
Internet: http://www.allweiler.com
We reserve the right to make technical changes.
Table of contents
Table of contents
1 About this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.1 Target groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.2 Other applicable documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.3 Warnings and symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.4 Technical terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2 Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1 Intended use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2 General safety instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2.1 Product safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2.2 Obligations of the operating company . . . . . . 9
2.2.3 Obligations of personnel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.3 Specic hazards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.3.1 Explosion hazard area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.3.2 Hazardous pumped media . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3 Layout and function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1 Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1.1 Type plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1.2 ATEX plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1.3 Pump type code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.2 Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.3 Shaft seals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.3.1 Mechanical seals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.4 Auxiliary systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.4.1 Sealing systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4 Transport, storage and disposal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.1 Transport . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.1.1 Unpacking and inspection on delivery . . . . . . 13
4.1.2 Lifting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.2 Preservation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.3 Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.4 Removing the preservative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4.5 Disposal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5 Setup and connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1 Preparing the setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.1 Checking the ambient conditions . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.2 Preparing the installation site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.3 Preparing the foundation and surface . . . . . . 15
5.1.4 Installing the heat insulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.5 Removing the preservative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.2 Setting up the pump aggregate . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.2.1 Setting the pump aggregate on the
foundation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.2.2 Fastening the pump aggregate . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.3 Installing the motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.4 Planning the pipes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.4.1 Keeping the piping clean . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.4.2 Specifying supports and ange
connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.4.3 Specifying nominal diameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.4.4 Specifying pipe lengths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.4.5 Optimizing cross-section and direction
changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.4.6 Provide safety and control devices
(recommended) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.5 Connecting the pipes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.5.1 Installing auxiliary pipes (if available) . . . . . . . 18
5.5.2 Installing the suction pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.5.3 Installing the pressure pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.5.4 Inspection for stress-free pipe
connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.6 Electrical connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.6.1 Connecting the motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.6.2 Checking the direction of rotation . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.1 Preparations for the initial start-up . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.1.1 Identifying the pump type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.1.2 Removing the preservative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.1.3 Preparing auxiliary systems (if
available) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.1.4 Filling and bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.2 Start-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6.2.1 Switching on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6.2.2 Switching off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6.3 Shutting down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6.4 Start-up following a shutdown period . . . . . . . 21
6.5 Operating the stand-by pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.1 Inspections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.2 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.2.1 Mechanical seals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.3 Dismounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
7.3.1 Returning the pump to the manufac-
turer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
7.3.2 Preparations for dismounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
7.3.3 Removal of the anged motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
7.4 Installing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
7.5 Ordering spare parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
8 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
9 Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
9.1 Sectional drawings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
9.1.1 Auxiliary connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
9.1.2 Part numbers and designations of the NB
series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
9.1.3 Part numbers and designations of the CLB
series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
9.1.4 Sectional drawings of the NB series . . . . . . . . 31
9.1.5 Sectional drawings of the CLB series . . . . . . 35
9.2 Technical specications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
9.2.1 Stub shaft diameter at the shaft seal . . . . . . . 37
9.2.2 Ambient conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Table of contents
9.2.3 Parameters for auxiliary systems . . . . . . . . . . . 38
9.2.4 Sound pressure levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
9.2.5 Tightening torques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
9.2.6 Cleaning agents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
9.2.7 Preservatives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
9.2.8 Flange loads according to ISO 5199 . . . . . . . 39
9.3 Spare parts for two years of continuous
operation according to DIN 24296 . . . . . . . . . . 41
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 3
Table of contents
List of gures
Fig. 1 Type plate (example) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Fig. 2 ATEX plate (example) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Fig. 3 Pump type code (example) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Fig. 4 NB/CLB layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Fig. 5 Single mechanical seal with quenching
(sketch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Fig. 6 Fastening the lifting gear to the pump
aggregate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Fig. 7 Straight pipe lengths upstream and down-
stream of the pump (recommended) . . . . . . . 17
Fig. 8 Widening the stub shaft . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Fig. 9 Widening the stub shaft . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Fig. 10 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal sizes
with diameter 16 at the shaft seal . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Fig. 11 Attachment of the guard sheet to the motor
bell housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Fig. 12 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal
sizes with diameter 24 and 30 at the shaft
seal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Fig. 13 Housing cover version for sizes 2/40-250/01
and 2/50-250/01 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Fig. 14 Sizes with shaft diameter 24 at the shaft
seal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Fig. 15 Version with intermediate ring, sizes
40-250/01 and 50-250/01 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Fig. 16 Attachment of the guard sheet to the motor
bell housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Fig. 17 U3.9D, U3.12D Unbalanced mechanical
seal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Fig. 18 U3...K Unbalanced mechanical seal . . . . . 33
Fig. 19 U2...D Balanced mechanical seal . . . . . . . . 33
Fig. 20 Two-stage sizes with diameter 30 at the shaft
seal, unbalanced mechanical seal U3D and
U3.20D . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Fig. 21 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal sizes
with diameter 40 at the shaft seal . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Fig. 22 Version with intermediate ring, sizes
65-315/01, 80-315/01, 100-315/01,
65-400/01 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Fig. 23 Attachment of the guard sheet to the motor
bell housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Fig. 24 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal sizes
with diameter 30 at the shaft seal . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Fig. 25 Attachment of the guard sheet to the motor
bell housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Fig. 26 Jacking screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Fig. 27 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal . . . . . 35
Fig. 28 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal sizes
with diameter 40 at the shaft seal . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Fig. 29 Version with intermediate ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Fig. 30 Jacking screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Fig. 31 Jacking screws for version with intermediate
ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Fig. 32 Attachment of the guard sheet to the motor
bell housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Fig. 33 U3.11D Unbalanced mechanical
seal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Fig. 34 Empirical formulas for forces and
torques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Fig. 35 Flange loads at the pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Fig. 36 Correction factor M and operating
temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
4 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Table of contents
List of tables
Tab. 1 Target groups and their duties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Tab. 2 Other applicable documents and their
purpose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Tab. 3 Warnings and consequences of disregarding
them . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Tab. 4 Symbols and their meaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Tab. 5 Technical terms and their meaning . . . . . . . . . 7
Tab. 6 Quenching - variants and characteris-
tics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Tab. 7 Measures to be taken if the pump is shut
down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Tab. 8 Measures depending on the behavior of the
pumped medium . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Tab. 9 Measures to be taken after prolonged
shutdown periods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Tab. 10 Measures for return . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Tab. 11 Fault number assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Tab. 12 Troubleshooting list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Tab. 13 Abbreviations of the connection
designations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Tab. 14 Designations of components of the NB series
according to part numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Tab. 15 Designations of components of the CLB
series according to part numbers . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Tab. 16 Assignment of the pump size to the stub
shaft diameter NB series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Tab. 17 Assignment of the pump size to the stub
shaft diameter CLB series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Tab. 18 Ambient conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Tab. 19 Operating parameters for sealing medium in
open ow system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Tab. 20 Sound pressure levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Tab. 21 Tightening torques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Tab. 22 Cleaning agents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Tab. 23 Valvoline preservatives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Tab. 24 Flange loads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Tab. 25 Spare parts for two years of continuous
operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 5
About this document
1 About this document
This manual
Is part of the pump
Applies to the afore-mentioned pump series
Describes safe and appropriate operation during all oper-
ating phases
1.1 Target groups
Target group Duty
Operating company Keep this manual available at the site of operation of the system,
including for later use.
Ensure that personnel read and follow the instructions in this
manual and the other applicable documents, especially all safety
instructions and warnings.
Observe any additional rules and regulations referring to the
system.
Qualied personnel, tter Read, observe and follow this manual and the other applicable
documents, especially all safety instructions and warnings.
Tab. 1 Target groups and their duties
1.2 Other applicable documents
Document Purpose
ATEX additional instructions Operation in explosion hazard areas
Order data sheet Technical specications, conditions of operation
Setup drawing Setup dimensions, connection dimensions etc.
Technical description Technical specications, operating limits
Sectional drawing Sectional drawing, part numbers, component designations
Supplier documentation Technical documentation for parts supplied by subcontractors
Spare parts list Ordering spare parts
Safety certicate Returning the pump to the manufacturer
Declaration of conformity Conformity with standards
Tab. 2 Other applicable documents and their purpose
6 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
About this document
1.3 Warnings and symbols
Warning Risk level Consequences of disregard
DANGER
Immediate acute risk Death, grievous bodily harm
WARNING
Potentially acute risk Death, grievous bodily harm
CAUTION
Potentially hazardous situation Minor bodily harm
CAUTION
Potentially hazardous situation Material damage
Tab. 3 Warnings and consequences of disregarding them
Symbol Meaning
Safety warning sign
Take note of all information highlighted by the safety warning sign
and follow the instructions to avoid injury or death.
Instruction
1. , 2. , ... Multiple-step instructions
Precondition
Cross reference
Information, advice
Tab. 4 Symbols and their meaning
1.4 Technical terms
Term Meaning
Sealing medium Medium for blocking or quenching shaft seals
Auxiliary systems Systems for operating the pump
Tab. 5 Technical terms and their meaning
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 7
Safety
2 Safety
The manufacturer does not accept any liability caused by
disregarding the entire documentation.
2.1 Intended use
Only use the pump for pumping the agreed pumped media
( order data sheet).
Adhere to the operating limits and size-dependent mini-
mum ow rate.
Avoid dry running:
Initial damage, such as destruction of the mechanical seal
and plastic parts, will occur within only a few seconds.
Make sure the pump is only operated with, and never
without, a pumped medium.
Avoid cavitation:
Fully open the suction-side armature and do not use it
to adjust the ow rate.
Do not open the pressure-side armature beyond the
agreed operating point.
Avoid overheating:
Do not operate the pump while the pressure-side arma-
ture is closed.
Observe the minimum ow rate (order data sheet).
Avoid damage to the motor:
Do not open the pressure-side armature beyond the
agreed operating point.
Note the maximum permissible number of times the
motor can be switched on per hour (manufacturer's
specications).
Consult the manufacturer about any other use of the pump.
Prevention of obvious misuse (examples)
Note the operating limits of the pump concerning temper-
ature, pressure, ow rate and motor speed ( order data
sheet).
The power consumed by the pump increases with increas-
ing density of the pumped medium. To avoid overloading
the pump or motor, stay within the agreed density (order
data sheet).
Lower densities are allowed. Adapt the auxiliary systems
accordingly.
When pumping liquids containing solids, ensure the limits
for the proportion of solids and the grain size are main-
tained ( order data sheet, technical description).
When using auxiliary systems, ensure there is a continuous
supply of the appropriate operating medium.
2.2 General safety instructions
Take note of the following regulations before carrying out
any work.
2.2.1 Product safety
The pump has been constructed according to the latest tech-
nology and recognized technical safety rules. Nevertheless,
operation of the pump can involve risks to life and health of the
user or third parties and risk of damage to the pump and other
property.
Only operate the pump if it is in perfect technical condition
and only use it as intended, staying aware of safety and
risks, and in adherence to the instructions in this manual.
Keep this manual and all other applicable documents com-
plete, legible and accessible to personnel at all times.
Refrain from any procedures and actions that would
expose personnel or third parties to any risk.
In the event of any safety-relevant faults, shut down the
pump immediately and have the fault corrected by appro-
priate personnel.
In addition to the entire documentation for the product,
comply with statutory or other safety and accident-preven-
tion regulations and the applicable standards and guide-
lines in the country where the pump is operated.
8 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Safety
2.2.2 Obligations of the operating company
Safety-conscious operation
Only operate the pump if it is in perfect technical condition
and only use it as intended, staying aware of safety and
risks, and in adherence to the instructions in this manual.
Ensure that the following safety aspects are observed and
monitored:
Adherence to intended use
Statutory or other safety and accident-prevention reg-
ulations
Safety regulations governing the handling of hazard-
ous substances
Applicable standards and guidelines in the country
where the pump is operated
Make protective equipment available.
Qualied personnel
Make sure all personnel tasked with work on the pump
have read and understood this manual and all other appli-
cable documents, especially the safety, maintenance and
repair information, before they start any work.
Organize responsibilities, areas of competence and the
supervision of personnel.
Ensure that all work is carried out by specialist technicians
only:
Fitting, repair and maintenance work
Work on the electrical system
Make sure trainee personnel only work on the pump under
supervision of specialist technicians.
Safety equipment
Provide the following safety equipment and verify its func-
tionality:
For hot, cold and moving parts: safety guarding pro-
vided by the customer
For possible build up of electrostatic charge: ensure
appropriate grounding
Warranty
Obtain the manufacturer's approval prior to carrying out
any modications, repairs or alterations during the warranty
period.
Only use genuine parts or parts that have been approved
by the manufacturer.
2.2.3 Obligations of personnel
All directions given on the pump must be followed (and kept
legible), e.g. the arrow indicating the direction of rotation
and the markings for uid connections.
Do not remove the safety guarding for hot, cold or moving
parts during operation.
Use protective equipment if necessary.
Only carry out work on the pump while it is not running.
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
Reinstall the safety equipment on the pump as required by
regulations after any work on the pump.
2.3 Specic hazards
2.3.1 Explosion hazard area
( ATEX additional instructions).
2.3.2 Hazardous pumped media
Follow the safety regulations for handling hazardous sub-
stances when pumping hazardous (e.g. hot, ammable,
poisonous or potentially harmful) media.
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 9
Layout and function
3 Layout and function
3.1 Labels
3.1.1 Type plate
NPSH kW 1/min P m n
m
3
/h H m Q
Nr Jahr
Typ
mm
2
/s kg/dm
3
D - 78315 Radolfzell / Germany
Typ und Nr.
1
2
3
4
6
7
10
9
8
angeben
Bei Ersatzteilbestellung
5
Fig. 1 Type plate (example)
1 Pump type
2 Year of manufacture
3 Differential head
4 Pump NPSH value
5 Kinematic viscosity
6 Power consumption
7 Density
8 Motor speed
9 Flow rate
10 Serial number
3.1.2 ATEX plate
Technical File No.:
EX9 03 09 45910 002
II 2 G c b Tx
1
2
Fig. 2 ATEX plate (example)
1 Explosion protection mark
2 Reference to ATEX additional instructions
3.1.3 Pump type code
1
2
3
4
NB 40 200 / 01 / 180 U3D W3 38 / 300
5
6
7
8
9
Fig. 3 Pump type code (example)
1 NB or CLB series
2 Pressure ange DN [mm]
3 Nominal impeller diameter [mm]
4 Hydraulic number (NB series only)
5 Actual impeller diameter [mm]
6 Shaft seal
7 Material key
8 Stub shaft bore hole diameter [mm]
9 Outer diameter of motor bell housing or intermediate
ring or ange size of electric motor
10 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Layout and function
3.2 Layout
Fig. 4 NB/CLB layout
1 Impeller
2 Volute casing
3 Motor bell housing
4 Motor with xed bearing at drive end
5 Stub shaft
6 Shaft seal part
3.3 Shaft seals
Only one of the following shaft seals can be used.
3.3.1 Mechanical seals
Mechanical seals have functional leaks.
Single mechanical seal
Single mechanical seal with quenching
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 11
Layout and function
3.4 Auxiliary systems
3.4.1 Sealing systems
Quenching
1 2 3
Fig. 5 Single mechanical seal with quenching
(sketch)
1 Seal
2 Quench space
3 Quench medium connection
The pressure of the pumped medium is higher than the pres-
sure of the sealing medium during quenching. The seal sur-
faces are lubricated by the pumped medium.
Application examples:
Pumped media that can crystallize in the atmosphere and
thus cause damage to the seal in the long-term
Prevention of offensive odors
Cooling of seals
Variant Characteristics of the
sealing medium
Open ow system Supplied and drained
continuously
Unpressurized
Closed ow system Circulating in a closed
circuit
Unpressurized
Tab. 6 Quenching - variants and characteristics
12 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Transport, storage and disposal
4 Transport, storage and disposal
4.1 Transport
For weight specications ( documents for the particular
order).
4.1.1 Unpacking and inspection on delivery
1. Unpack the pump/aggregate on delivery and inspect it for
transport damage.
2. Report any transport damage to the manufacturer immedi-
ately.
3. Dispose of packaging material according to local regula-
tions.
4.1.2 Lifting
DANGER
Death or crushing of limbs caused by fallingor overturning
loads!
Use lifting gear appropriate for the total weight to be trans-
ported.
Fasten the lifting gear as illustrated below.
Do not stand under suspended loads.
Set the load down on a level surface.
Fig. 6 Fastening the lifting gear to the pump aggregate
4.2 Preservation
Not necessary for non-rusting materials
CAUTION
Material damage due to inappropriate treatment for stor-
age!
Treat the pump properly, inside and outside, for storage.
1. Choose a preservative appropriate for the type and dura-
tion of storage ( 9.2.7 Preservatives, Page 39).
2. Use the preservative specied by the manufacturer.
3. All bare metal parts should be treated, inside and outside.
4.3 Storage
CAUTION
Material damage due to inappropriate storage!
Treat and store the pump properly.
1. Seal all openings with blind anges, blind plugs or plastic
covers.
2. Make sure the storage room meets the following condi-
tions:
Dry
Frost-free
Vibration-free
3. Turn the shaft once a month.
4. Make sure the shaft and bearing change their rotational
position in the process.
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 13
Transport, storage and disposal
4.4 Removing the preservative
Only necessary for pumps treated with preservative
WARNING
Risk of poisoning from preservatives and cleaning agents
in the foodstuffs and drinking water sector!
Only use cleaning agents which are compatible with the
pumped medium ( 9.2.6 Cleaning agents, Page 39).
Completely remove all preservative.
CAUTION
High water pressure or spray water can damage bearings!
Do not clean bearing areas with a water or steam jet.
CAUTION
Damage to seals due to wrong cleaning agents!
Ensure the cleaning agent does not corrode the seals.
1. Choose the cleaning agent according to the application.
( 9.2.6 Cleaning agents, Page 39).
With Tectyl 506 EH: allow benzine to soak in for 10 minutes
(recommended).
2. Dispose of cleaning agents in accordance with local regu-
lations.
3. For storage times in excess of 6 months:
Replace the elastomer parts made of EP rubber
(EPDM).
Check all elastomer parts (O-rings, shaft seals) for
proper elasticity and replace them if necessary.
4.5 Disposal
Plastic parts can be contaminated by poisonous or radioac-
tive pumped media to such an extent that cleaning is insuf-
cient.
WARNING
Risk of poisoning and environmental damage by the
pumped medium or oil!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Prior to the disposal of the pump:
Catch and dispose of any escaping pumped medium
or oil in accordance with local regulations.
Neutralize residues of pumped medium in the pump.
Remove any preservative (4.4 Removing the pre-
servative, Page 14).
Remove any plastic parts and dispose of them in accor-
dance with local regulations.
Dispose of the pump in accordance with local regulations.
14 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Setup and connection
5 Setup and connection
For pumps in explosion hazard areas (ATEX additional
instructions).
CAUTION
Material damage caused by dirt!
Do not remove the transport seals until immediately before
setting up the pump.
Do not remove any covers or transport and sealing covers
until immediately before connecting the pipes to the pump.
5.1 Preparing the setup
5.1.1 Checking the ambient conditions
1. Make sure the required ambient conditions are fullled
( 9.2.2 Ambient conditions, Page 38).
2. For setup heights > 1000 m above sea level, consult the
manufacturer.
5.1.2 Preparing the installation site
Ensure the installation site meets the following conditions:
Pump is freely accessible from all sides
Sufcient space for installation/removal of the pipes
and for maintenance and repair work, especially for the
removal and installation of the pump and the motor
Pump not exposed to external vibrations (damage to
bearings)
Frost protection
5.1.3 Preparing the foundation and surface
Setup options:
With concrete foundation
With steel foundation frame
Without foundation
Make sure the foundation and surface meet the following
conditions:
Level
Clean (no oil, dust or other impurities)
Foundation and surface can support the weight of the
pump aggregate and all operating forces
Ensure the pump is stable and cannot tip over
With concrete foundation: standard concrete of
strength class B 25
5.1.4 Installing the heat insulation
Only necessary to maintain the temperature of the pumped
medium
CAUTION
Material damage caused by overheating!
Only install the heat insulation on the volute casing.
Install the heat insulation properly.
5.1.5 Removing the preservative
If the pump is to be put into operation immediately after
setup and connection: remove the preservative prior to
setup ( 4.4 Removing the preservative, Page 14).
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 15
Setup and connection
5.2 Setting up the pump aggregate
CAUTION
Material damage due to distortion of the pump!
Place the pump on the foundation and fasten it to it as
described in the following.
5.2.1 Setting the pump aggregate on the foundation
Implements, tools and materials:
Foundation bolts ( setup drawing)
Steel washers
Non-shrinking mortar/concrete
Spirit level
1. Lift the pump aggregate ( 4.1 Transport, Page 13).
2. Working frombelow, locate the foundation bolts in the xing
holes of the pump feet.
Follow the manufacturer's instructions when using adhe-
sive anchors.
3. Set the pump aggregate down on the foundation. When
doing this, sink the foundation bolts into the prepared
anchoring holes.
4. Use steel washers to align the pump aggregate to the
height and system dimensions.
5. Make sure the steel washers lie at against the pump feet,
in full contact.
6. Use the integrated spirit level to check whether the pump
is level end to end and side to side with a max. allowable
tilt of 1 mm/m.
7. Repeat the procedure until the pump is aligned properly.
5.2.2 Fastening the pump aggregate
1. Fill the anchoring holes with mortar grout.
2. When the concrete has set, bolt down the pump with the
specied torque at three points.
3. Before tightening the remaining bolts, compensate for any
unevenness in the surface using metal spacing shims next
to each bolt.
4. Screw all bolts tight.
5. Turn the pumpe by hand:
Ensure the pump can be turned without pressure
points.
5.3 Installing the motor
Only necessary if the pump aggregate is assembled on site
1. Observe the following during the installation:
Maintain the specied tightening torques
( 9.2.5 Tightening torques, Page 38).
2. Remove the retaining clamp for the stub shaft from the
motor bell housing (341.xx):
Undo the bolts/nuts (901.10/920.10) for this pur-
pose ( 9.1.4 Sectional drawings of the NB series,
Page 31).
3. Undo the hexagon head bolts (901.xx) and remove the
washers (554.xx).
4. Remove one half of the guard sheet (686.xx) from the
motor bell housing (341.xx).
The Allen key required to undo the cheese head screw
(914.xx) is inserted in one of the two cast-in recesses in
the motor bell housing.
5. Undo the cheese head screw (914.xx) on the stub shaft
(211.1/220.xx) and unscrew it completely ( 9.1.4 Sec-
tional drawings of the NB series, Page 31).
6. Install the anged motor and screwit tight ( 7.4 Installing,
Page 24).
7. Install the safety guarding.
5.4 Planning the pipes
5.4.1 Keeping the piping clean
CAUTION
Material damage due to impurities in the pump!
Make sure no impurities can enter the pump.
1. Clean all piping parts and armatures prior to assembly.
2. Ensure no ange seals protrude inwards.
3. Remove any blind anges, plugs, protective foils and/or
protective paint from anges.
5.4.2 Specifying supports and ange connections
CAUTION
Material damage due to excessive forces and torques
exerted by the piping on the pump!
Do not exceed the permissible limits (9.2.8 Flange loads
according to ISO 5199, Page 39).
1. Calculate the pipe forces, taking every possible operating
condition into account:
Cold/warm
Empty/full
Unpressurized/pressurized
Shift in position of anges
2. Ensure the pipe supports have permanent low-friction
properties and do not seize up due to corrosion.
16 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Setup and connection
5.4.3 Specifying nominal diameters
Keep the ow resistance in the pipes as low as possible.
1. Make sure the nominal suction pipe diameter is not smaller
than the nominal suction ange diameter.
2. Make sure the nominal pressure pipe diameter is not
smaller than the nominal pressure ange diameter.
5.4.4 Specifying pipe lengths
C
D
B
A
Fig. 7 Straight pipe lengths upstream and downstream
of the pump (recommended)
A > 5 x nominal suction pipe diameter
B Nominal suction pipe diameter
C Nominal pressure pipe diameter
D > 5 x nominal pressure pipe diameter
Maintain the recommended minimum values when install-
ing the pump.
Suction side: shorter pipes are possible but may restrict
the hydraulic performance.
Pressure side: shorter pipes are possible but can result in
increased operating noise.
5.4.5 Optimizing cross-section and direction
changes
1. Avoid radii of curvature of less than 1.5 times the nominal
pipe diameter.
2. Avoid abrupt changes of cross-section along the piping.
5.4.6 Provide safety and control devices
(recommended)
Avoid impurities
1. Integrate a lter in the suction pipe.
2. To monitor impurities, install a differential pressure gauge
with a contact manometer.
Avoid reverse running
Install a non-return valve between the pressure ange and
the gate valve to ensure the medium does not ow back
when the pump is switched off.
Make provisions for isolating and shutting off the pipes
For maintenance and repair work.
Provide shut-off devices in the suction and pressure pipes.
Allow measurements of the operating conditions
1. Provide manometers for pressure measurements in the
suction and pressure pipes.
2. Provide for motor-side torque measurements.
3. Provide for pump-side temperature measurements.
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 17
Setup and connection
5.5 Connecting the pipes
5.5.1 Installing auxiliary pipes (if available)
Follow the manufacturers' specications for any available
auxiliary systems.
1. Connect the auxiliary pipes to the auxiliary connections so
that they are stress-free and do not leak (setup drawing).
2. To avoid air pockets, run the pipes with a continuous slope
up to the pump.
5.5.2 Installing the suction pipe
1. Remove the transport and sealing covers from the pump.
2. To avoid air pockets, run the pipes with a continuous slope
up to the pump.
3. Ensure no seals protrude inwards.
4. For suction operation: install a foot valve in the suction pipe
to prevent the pump and suction pipe from running empty
during downtimes.
5.5.3 Installing the pressure pipe
1. Remove the transport and sealing covers from the pump.
2. Install the pressure pipe.
3. Ensure no seals protrude inwards.
5.5.4 Inspection for stress-free pipe connections
Piping installed and cooled down
1. Disconnect the pipe connecting anges from the pump.
2. Check whether the pipes can be moved freely in all direc-
tions within the expected range of expansion:
Nominal diameter < 150 mm: by hand
Nominal diameter > 150 mm: with a small lever
3. Make sure the ange surfaces are parallel.
4. Reconnect the pipe connecting anges to the pump.
5.6 Electrical connection
DANGER
Risk of death due to electric shock!
Have all electrical work carried out by qualied electricians
only.
DANGER
Risk of death due to rotating parts!
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
5.6.1 Connecting the motor
Follow the instructions of the motor manufacturer.
1. Connect the motor according to the connection diagram.
2. Make sure no danger arises due to electric power.
3. Install an EMERGENCY STOP switch.
5.6.2 Checking the direction of rotation
DANGER
Risk of death due to rotating parts!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Keep an adequate distance to rotating parts.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by dry running or wrong direction
of rotation!
Fill the pump with uid (to be pumped) and bleed it
( 6.1.4 Filling and bleeding, Page 19).
1. Switch the motor on and immediately off again.
2. Check whether the direction of rotation of the motor corre-
sponds to the arrow indicating the direction of rotation on
the pump.
3. If the direction of rotation is different: swap two phases.
18 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Operation
6 Operation
For pumps in explosion hazard areas (ATEX additional
instructions).
6.1 Preparations for the initial start-up
6.1.1 Identifying the pump type
Identify the pump type ( order data sheet).
The pump types vary e.g. with regard to the shaft seal,
auxiliary systems.
6.1.2 Removing the preservative
Only necessary for pumps treated with preservative
( 4.4 Removing the preservative, Page 14).
6.1.3 Preparing auxiliary systems (if available)
The manufacturer does not accept any liability for damage
arising from the installation or use of a third-party or unap-
proved auxiliary system.
Sealing systems
1. Verify that the sealing medium is suitable to mix (i.e. com-
patible) with the pumped medium.
2. Identify the sealing system:
( order data sheet)
(3.4.1 Sealing systems, Page 12).
3. Install the sealing system ( manufacturer's specica-
tions).
4. Make sure the parameters required for the installed sealing
systemare met ( 9.2.3 Parameters for auxiliary systems,
Page 38).
6.1.4 Filling and bleeding
Auxiliary systems ready for operation
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
media!
Safely collect any leaking pumped medium and dispose
of it in accordance with environmental rules and require-
ments.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by dry running!
Make sure the pump is lled properly.
1. Fill the pump and the suction pipe with pumped medium.
2. Open the suction-side armature.
3. Open the pressure-side armature.
4. If available: open the auxiliary systems and check the ow
rate.
5. Verify that no pipe connections are leaking.
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 19
Operation
6.2 Start-up
6.2.1 Switching on
Pump aggregate set up and connected properly
All connections stress-free and sealed
Any available auxiliary systems are ready for operation
All safety equipment installed and tested for functionality
Pump prepared, lled and bled properly
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
Allow the pump to cool down completely before starting any
work.
DANGER
Risk of injury and poisoning caused by pumped medium
spraying out!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by dry running!
Make sure the pump is lled properly.
CAUTION
Risk of cavitation when throttling down the suction ow
rate!
Fully open the suction-side armature and do not use it to
adjust the ow rate.
Do not open the pressure-side armature beyond the oper-
ating point.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by overheating!
Do not operate the pump while the pressure-side armature
is closed.
Observe the minimum ow rate (order data sheet).
1. Open the suction-side armature.
2. Close the pressure-side armature.
3. Switch on the motor and check it for smooth running.
4. Once the motor has reached its nominal speed, open the
pressure-side armature slowly until the operating point is
reached.
5. For pumps with hot pumped media, make sure any tem-
perature changes do not exceed 50 C/h.
6. After the initial stress caused by pressure and operating
temperature, check that the pump is not leaking.
6.2.2 Switching off
Pressure-side armature closed (recommended)
WARNING
Risk of injury due to hot pump parts!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
1. Switch off the motor.
2. Check all connecting bolts and tighten them if necessary.
6.3 Shutting down
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
media!
Safely collect any leaking pumped medium and dispose
of it in accordance with environmental rules and require-
ments.
20 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Operation
Take the following measures whenever the pump is shut
down:
Pump is Measure
...shut down
for a prolonged
period
Take measures depending on
the pumped medium ( Table
8 Measures depending on
the behavior of the pumped
medium, Page 21).
...emptied Close the suction-side and
pressure-side armatures.
...dismounted Isolate the motor from its power
supply and secure it against
unauthorized switch-on.
...put into
storage
Follow the storage instructions
( 4.3 Storage, Page 13).
Tab. 7 Measures to be taken if the pump is shut down
Duration of shutdown (depending
on process)
Behavior
of pumped
medium
Short Long
Solids sediment Flush the
pump.
Flush the
pump.
Solidifying/
freezing,
non-corrosive
Heat up or
empty the
pump and
containers.
Empty the
pump and
containers.
Solidifying/
freezing,
corrosive
Heat up or
empty the
pump and
containers.
Empty the
pump and
containers.
Treat the
pump and
containers
with preser-
vative.
Remains liquid,
non-corrosive
Remains liquid,
corrosive
Empty the
pump and
containers.
Treat the
pump and
containers
with preser-
vative.
Tab. 8 Measures depending on the behavior
of the pumped medium
6.4 Start-up following a shutdown period
1. If the pump is shut down for over 1 year, take the following
measures before starting it up again:
Shutdown period Measure
> 1 year For versions with roller
bearings without lifetime
lubrication: relubricate
> 2 years Replace elastomer seals
(O-rings, shaft sealing rings).
Replace antifriction bearings.
Tab. 9 Measures to be taken after prolonged
shutdown periods
2. Carry out all steps as for the initial start-up ( 6.2 Start-up,
Page 20).
6.5 Operating the stand-by pump
Stand-by pump lled and bled
Operate the stand-by pump at least once a week.
1. Completely open the suction-side armature.
2. Open the pressure-side armature to the extent that the
stand-by pump reaches its operating temperature and is
heated through evenly (6.2.1 Switching on, Page 20).
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 21
Maintenance
7 Maintenance
For pumps in explosion hazard areas (ATEX additional
instructions).
Trained service technicians are available for tting and
repair jobs. Present a pumped medium certicate (DIN
safety data sheet or safety certicate) when requesting
service.
7.1 Inspections
The inspection intervals depend on the operational strain
on the pump.
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
media!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
1. Check at appropriate intervals:
Maintenance of minimum ow rate
Normal operating conditions unchanged
No impermissible vibrations
2. For trouble-free operation, always ensure the following:
No dry running
No leaks
No cavitation
Suction-side gate valves open
Unclogged and clean lters
Sufcient supply pressure
No unusual running noises or vibrations
No excessive leakage at the shaft seal
Proper functioning of auxiliary systems
Put the installed stand-by pump into operation at least
once a week
7.2 Maintenance
The stub shaft of the pump and the motor shaft are con-
nected rmly together. Notes on maintenance of the bear-
ing (operating manual of the motor manufacturer).
Mechanical seals are subject to natural wear, which
strongly depends on the actual operating conditions.
Therefore, general statements regarding their service life
cannot be made.
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
DANGER
Risk of death due to electric shock!
Have all electrical work carried out by qualied electricians
only.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous or hot
pumped media!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Allow the pump to cool down completely before commenc-
ing any work.
Make sure the pump is unpressurized.
Empty the pump, safely collect the pumped medium and
dispose of it in accordance with environmental rules and
requirements.
7.2.1 Mechanical seals
Mechanical seals have functional leaks (manufacturer's
specications).
Single mechanical seals with quenching: any drastic rise
in the level of the quenching system indicates a major leak
at the product-side mechanical seal.
In the event of a larger leak: replace the mechanical seal
and its auxiliary seals and check the integrity of the auxiliary
systems.
22 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Maintenance
7.3 Dismounting
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
DANGER
Risk of death due to electric shock!
Have all electrical work carried out by qualied electricians
only.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous or hot
pumped media!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Allow the pump to cool down completely before commenc-
ing any work.
Make sure the pump is unpressurized.
Empty the pump, safely collect the pumped medium and
dispose of it in accordance with environmental rules and
requirements.
7.3.1 Returning the pump to the manufacturer
Pump unpressurized
Pump completely empty
Electrical connections isolated and motor secured against
switch-on
Pump cooled down
Auxiliary systems shut down, unpressurized and emptied
Manometer lines, manometer and xtures dismounted
1. Enclose a truthfully (fully) completed safety certicate when
returning pumps or individual parts to the manufacturer.
Order a safety certicate from the manufacturer if neces-
sary.
2. Take necessary measures, depending on the required
repair work, as listed in the table below when returning the
pump to the manufacturer.
Repair carried out Measure for return
...at the customer's
premises
Return the defective
component to the
manufacturer.
...at the
manufacturer's
premises
Flush the pump and
decontaminate it if it was
used to pump hazardous
media.
Return the complete pump
(not disassembled) to the
manufacturer.
...at the
manufacturer's
premises for
warranty repairs
Only in the event of
hazardous pumped media:
ush and decontaminate the
pump.
Return the complete pump
(not disassembled) to the
manufacturer.
Tab. 10 Measures for return
7.3.2 Preparations for dismounting
Pump unpressurized
Pump completely empty, ushed and decontaminated
Electrical connections isolated and motor secured against
switch-on
Pump cooled down
Auxiliary systems shut down, unpressurized and emptied
Manometer lines, manometer and xtures dismounted
In production, the pumps are constructed to a standard pro-
cess. The slide-in unit can be removed without removing
the volute casing and piping.
1. When dismounting, observe the following:
Mark the precise orientation and position of all compo-
nents before dismounting.
Dismantle components concentrically without canting.
2. Dismount the pump (sectional drawing).
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 23
Maintenance
7.3.3 Removal of the anged motor
Fig. 8 Widening the stub shaft
1 Cheese head screw
2 Stub shaft
3 Shaft key groove of the motor shaft
Tighten the jack screw with a screwdriver without applying
any excessive force.
1. Widening the stub shaft (220.xx/211.1):
Unscrew the cheese head screw (914.xx).
Screw the cheese head screw (M10 x 40 or M12 x 40
ISO 1207, not included in the scope of delivery) into
the stub shaft.
2. Remove the anged motor.
7.4 Installing
The shaft key is not required for the installation.
Stub shaft, free from oil and grease
CAUTION
Material damage caused by knocks and bumps!
Do not knock or hit any components of the pump.
Reinstall the components concentrically, without canting,
in accordance with the markings made.
1. Observe the following during the installation:
Replace worn parts with genuine spare parts.
Replace seals, inserting them so that they cannot
rotate.
Maintain the specied tightening torques
(9.2.5 Tightening torques, Page 38).
2. Clean all parts ( 9.2.6 Cleaning agents, Page 39). Do
not remove any prepared markings.
3. Install the pump ( sectional drawing).
4. Install the pump in the system ( 5 Setup and connection,
Page 15).
Installation of the anged motor
Fig. 9 Widening the stub shaft
1 Cheese head screw
2 Stub shaft
3 Shaft key groove of the motor shaft
Tighten the jack screw with a screwdriver without applying
any excessive force.
1. Widening the stub shaft (220.xx/211.1):
Screw the cheese head screw (M10 x 40 or M12 x 40
ISO 1207, not included in the scope of delivery) into
the stub shaft.
2. Install the anged motor, while ensuring:
The slot of the stub shaft (220.xx/211.1) is opposite to
the shaft key groove of the motor shaft
The stub shaft (220.xx/211.1) is against the collar of the
motor shaft
3. Undo and unscrew the jack screw. Screw in the cheese
head screw (914.06/914.16) and tighten it with a torque
wrench (9.2.5 Tightening torques, Page 38).
4. Install the safety equipment:
Guard sheet for the motor bell housing
5. Install the auxiliary devices:
Manometer lines and xtures at the pump
Auxiliary pipes
6. Turn the pumpe by hand:
Ensure the pump can be turned without pressure
points.
24 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Maintenance
7.5 Ordering spare parts
For trouble-free replacement in the event of faults, we rec-
ommend keeping entire slide-in units or spare pumps avail-
able on site.
The application guidelines conforming to DIN 24296 rec-
ommend provisioning for two years of continuous use
( 9.3 Spare parts for two years of continuous operation
according to DIN 24296, Page 41).
Have the following information ready to hand when order-
ing spare parts ( type plate):
Short designation of the pump
Pump number
Year of manufacture
Part number
Designation
Quantity
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 25
Troubleshooting
8 Troubleshooting
For faults which are not specied in the following table or can-
not be traced back to the specied causes, please consult the
manufacturer.
Possible faults are identied by a fault number in the table
below. This number identies the respective cause and rem-
edy in the troubleshooting list.
Fault Number
Pump not pumping 1
Pumping rate insufcient 2
Pumping rate excessive 3
Pumping pressure insufcient 4
Pumping pressure excessive 5
Pump running roughly 6
Pump leaking 7
Motor power uptake excessive 8
Tab. 11 Fault number assignment
Fault number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Cause Remedy
X Supply/suction pipe and/or pressure pipe
closed by armature
Open the armature.
X X Supply/suction pipe not fully opened Open the armature.
X X Stub shaft loose Tighten the stub shaft rmly
( 7.4 Installing, Page 24).
X X X X Supply/suction pipe, pump or suction
strainer blocked or encrusted
Clean the supply/suction pipe, pump or
suction strainer.
X X X
Supply/suction pipe cross-section too
narrow
Increase the cross-section.
Remove any encrustations from the
suction pipe.
Open the armature completely.
X Transport and sealing cover still in place Remove the transport and sealing cover.
Dismount the pump and inspect it for
dry-running damage.
X X X Differential head excessive: NPSH
pump
larger than NPSH
system
Increase the supply pressure.
Consult the manufacturer.
X X Supply/suction pipe not bled properly or not
lled up completely
Fill up the pump and/or piping completely
and bleed them.
X X
Supply/suction pipe contains air pockets Install the armature for bleeding.
Correct the piping layout.
X X X X Air is sucked in Seal the source of malfunction.
X X X X Excessive amount of gas: pump is
cavitating
Consult the manufacturer.
X X X Pumped medium temperature too high:
pump is cavitating
Increase the supply pressure.
Lower the temperature.
Consult the manufacturer.
26 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Troubleshooting
Fault number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Cause Remedy
X X X Viscosity or specic gravity of the pumped
medium outside the range specied for the
pump
Consult the manufacturer.
X X Geodetic differential head and/or pipe ow
resistances too high
Remove sediments from the pump
and/or pressure pipe.
Install a larger impeller and consult the
manufacturer.
X X X Pressure-side armature not opened wide
enough
Open the pressure-side armature.
X X X X Pressure pipe blocked Clean the pressure pipe.
X X X X Pump running in the wrong direction Swap any two phases on the motor.
X X X Motor speed too low Compare the required motor speed with
the specications on the pump type
plate. Replace the motor if necessary.
Increase the motor speed if speed
control is available.
X X X Pump parts worn Replace the worn pump parts.
X X X X Pressure-side armature opened too wide Throttle down at the pressure-side
armature.
Machine the impeller down. Consult the
manufacturer and adjust the impeller
diameter.
X X X Geodetic differential head, pipe ow
resistances and/or other resistances lower
than specied
Throttle down the ow rate at the
pressure-side armature. Observe the
minimum ow rate.
Machine the impeller down. Consult the
manufacturer and adjust the impeller
diameter.
X X Viscosity lower than expected Machine the impeller down. Consult the
manufacturer and adjust the impeller
diameter.
X X X X Motor speed too high Compare the required motor speed with
the specications on the pump type
plate. Replace the motor if necessary.
Reduce the motor speed if speed control
is available.
X X X X Impeller diameter too large Throttle down the ow rate at the
pressure-side armature. Observe the
minimum ow rate.
Machine the impeller down. Consult the
manufacturer and adjust the impeller
diameter.
X X X X
Impeller out of balance or blocked Dismount the pump and inspect it for
dry-running damage.
Clean the impeller.
X X X
Hydraulic parts of the pump dirty, clotted or
encrusted
Dismount the pump.
Clean the parts.
X Defective antifriction bearing in motor Replace the antifriction bearing.
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 27
Troubleshooting
Fault number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Cause Remedy
Lubricant: too much, not enough or
unsuitable
Reduce, top up or replace the lubricant.
X
Connecting bolts not tightened properly Tighten the connecting bolts.
X Mechanical seal worn Replace the mechanical seal.
X Housing seal defective Replace the housing seal.
X
Shaft sleeve is inltrated Replace the shaft sleeve and/or O-ring.
X X X Pump distorted Check the pipe connections and pump
attachment.
X X X X Motor running on 2 phases Check the fuse and replace it if
necessary.
Check the cable connections and
insulation.
Tab. 12 Troubleshooting list
28 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Appendix
9 Appendix
9.1 Sectional drawings
9.1.1 Auxiliary connections
Abbreviation Connection
FD, FD1 Pumped medium / emptying
FF Filling
FV, FV1 Filling / Bleeding
LO Leak / egress
PM1 Pressure gauge
PM2 Pressure gauge
Tab. 13 Abbreviations of the connection designations
9.1.2 Part numbers and designations of the NB series
Part no. Designation
102.01 Volute casing
108.01 Stage casing
161... Housing cover
171.01 Impeller
220... Stub shaft
230.01 Impeller
230.02 Impeller, rst stage
230.03 Impeller, second stage
341.01 Motor bell housing
400.01 Gasket
400.02 Gasket
411.01 Seal ring
411.02 Seal ring
411.04 Seal ring
411.05 Seal ring
412.01 O-ring
412.07 O-ring
433... Mechanical seal
509.01 Intermediate ring
509.02 Intermediate ring
514.01 Threaded ring
525.01 Spacer sleeve
525.02 Spacer sleeve
554.07 Washer
565.01 Rivet
Part no. Designation
672.01 Vent
686.01 Guard sheet
801.01 Flanged motor
901.01 Hexagon head bolt
901.02 Hexagon head bolt
901.07 Hexagon head bolt (Ribe-Triform)
901.10 Hexagon head bolt
902.01 Stud bolt
902.08 Stud bolt
903.01 Screw plug
903.02 Screw plug
903.04 Screw plug
904.05 Grub screw
914.01 Cheese head screw
914.02 Cheese head screw
914.06 Cheese head screw
914.10 Cheese head screw
920.01 Nut
920.03 Nut
922.01 Impeller nut
936.01 Spring ring
940.01 Shaft key
940.03 Shaft key
971.01 Name plate
Tab. 14 Designations of components of the NB series
according to part numbers
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 29
Appendix
9.1.3 Part numbers and designations of the CLB series
Part no. Designation
102.1 Volute casing
161.1 Housing cover
211.1 Stub shaft
230.1 Impeller
341.1 Motor bell housing
400.1 Gasket
400.2 Gasket
411.1 Seal ring
411.2 Seal ring
433.1 Mechanical seal
509.1 Intermediate ring
509.2 Intermediate ring
525.1 Spacer sleeve
525.2 Spacer sleeve
554.1 Washer
560.1 Rivet
681.1 Guard sheet
801.1 Flanged motor
901.19 Hexagon head bolt
902.1 Stud bolt
902.2 Stud bolt
902.10 Stud bolt
903.1 Screw plug
903.2 Screw plug
908.1 Jacking screw
908.2 Jacking screw
914.16 Cheese head screw
914.17 Cheese head screw
920.1 Hexagon nut
920.2 Hexagon nut
920.10 Hexagon nut
922.2 Impeller nut
930.1 Spring ring
940.1 Shaft key
970.1 Name plate
Tab. 15 Designations of components of the CLB series
according to part numbers
30 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Appendix
9.1.4 Sectional drawings of the NB series
Fig. 10 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal sizes with diameter 16 at the shaft seal
Fig. 11 Attachment of the guard sheet to the motor bell housing
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 31
Appendix
Fig. 12 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal sizes with diameter 24 and 30 at the shaft seal
Fig. 13 Housing cover version for sizes 2/40-250/01
and 2/50-250/01
Fig. 14 Sizes with shaft diameter 24 at the shaft seal
Fig. 15 Version with intermediate ring, sizes
40-250/01 and 50-250/01
Fig. 16 Attachment of the guard sheet to the
motor bell housing
32 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Appendix
Fig. 17 U3.9D, U3.12D Unbalanced mechanical seal
Fig. 18 U3...K Unbalanced mechanical seal
Fig. 19 U2...D Balanced mechanical seal
Fig. 20 Two-stage sizes with diameter 30 at the shaft seal,
unbalanced mechanical seal U3D and U3.20D
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 33
Appendix
Fig. 21 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal sizes with diameter 40 at the shaft seal
400.02
509.01
901.02
901.01
400.01
Fig. 22 Version with intermediate ring, sizes 65-315/01,
80-315/01, 100-315/01, 65-400/01
554.07
901.07
686.01
Fig. 23 Attachment of the guard sheet to the
motor bell housing
34 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Appendix
9.1.5 Sectional drawings of the CLB series
Fig. 24 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal sizes with diameter 30 at the shaft seal
Fig. 25 Attachment of the guard
sheet to the motor bell
housing
Fig. 26 Jacking screws Fig. 27 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical
seal
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 35
Appendix
Fig. 28 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal sizes with diameter 40 at the shaft seal
Fig. 29 Version with
intermediate ring Fig. 30 Jacking screws
Fig. 31 Jacking screws for version with intermediate
ring
Fig. 32 Attachment of the guard sheet to the motor bell housing Fig. 33 U3.11D Unbalanced mechanical seal
36 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Appendix
9.2 Technical specications
More technical specications (order data sheet).
9.2.1 Stub shaft diameter at the shaft seal
Pump size
NB
Diameter of the stub shaft at
the shaft seal [mm]
20-160
25-160
16
32-125
40-125
50-125
65-125
24
25-200
32-160
32-200
40-160
40-200
40-250
50-160
50-200
50-250
65-160
65-200
80-160
100-160
30
single stage
2/25-200
2/32-200
2/40-250
2/50-250
30
two stages
Pump size
NB
Diameter of the stub shaft at
the shaft seal [mm]
65-250
65-315
65-400
80-200
80-250
80-315
100-200
100-250
100-315
125-200
125-250
150-200
40
Tab. 16 Assignment of the pump size to the stub
shaft diameter NB series
Pump size
CLB
Diameter of the stub shaft at
the shaft seal [mm]
25-160
25-200
32-160
32-200
40-160
40-200
50-160
50-200
65-160
80-160
30
32-250
40-250
40-315
50-250
50-315
65-200
65-250
80-200
80-250
100-200
40
Tab. 17 Assignment of the pump size to the stub
shaft diameter CLB series
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 37
Appendix
9.2.2 Ambient conditions
Operation under other ambient conditions should be
agreed with the manufacturer
Relative humidity [%] Tempera-
ture [C]
Long-term Short-term
Setup
height
above sea
level [m]
20 to +40 85 100 1000
Tab. 18 Ambient conditions
9.2.3 Parameters for auxiliary systems
Sealing medium in open ow system
Sealing
medium for
Volume [l/h] Pressure
Quenching 150 Unpressurized
Tab. 19 Operating parameters for sealing medium
in open ow system
9.2.4 Sound pressure levels
Measuring conditions:
Distance to the pump: 1 m
Operation: cavitation-free
Motor: IEC standard motor
Tolerance 3 dB
Lower-noise versions of the motors are available if the
expected noise levels exceed the permissible limits.
Sound pressure level [dB] for pump
with motor at speed [min
-1
]
Nominal motor
power PM [kW]
1450 1750 2900 3500
1.5 58 58.5 63 64
2.2 60 60.5 66 67
3.0 62 62.5 68 69
4.0 63 63.5 69 70
5.5 65 65.5 71 72
7.5 66 66.5 72 73
11.0 68 68.5 74 75
15.0 69 69.5 75 76
18.5 70 70.5 76 77
22.0 71 71.5 77 78
30.0 72 72.5 78 79
37.0 73 73.5 79 80
Tab. 20 Sound pressure levels
9.2.5 Tightening torques
Part no. Thread
gage
Quality Tightening
torque [Nm]
NB
901.01
M8
M10
M12
4.6
8.8
8.8
8
35
63
901.02
M8
M12
8.8
22
63
901.10
M8
M10
M12
M16
8.8
8.8
5.6
8.8
22
35
35
150
902.01/
920.01
M10
M16
5.8
24
100
903.01
903.02
903.04
G
G
St
10
15
904.05 M8 A4 12
914.06
M8
M10
12.9
25
50
914.10 M16 8.8 167
922.01
M12 x 1.5
M16 x 1.5
M20 x 1.5
M24 x 1.5
1.4571
20
52
106
177
CLB
902.1/920.1
M10
M12
A4-80
35
60
902.2/920.2 M12 A4-80 60
902.10
M12
M16
8.8
60
160
903.1
903.2
G
G
St
10
30
914.16
M8
M10
12.9
25
50
914.17 M16 8.8 160
922.2
M20 x 1.5
M24 x 1.5
1.4021
210
350
Tab. 21 Tightening torques
38 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Appendix
9.2.6 Cleaning agents
Application area Cleaning agents
Foodstuffs and drinking
water sector
E.g. spirit, Ritzol 155, strong
alkaline soapy solution,
steam jet (for individual
parts only)
Other Benzine, wax solvents,
diesel, parafn, alkaline
cleaners
Tab. 22 Cleaning agents
9.2.7 Preservatives
Use Valvoline preservatives or similar (recommended).
Type of storage Storage
duration
[months]
Preservative
inside/
outside
Renew
[months]
inside/
outside
612 Tectyl 511 M In closed, dry and
dust-free room
> 12 Tectyl 506 EH 48/48
612 Tectyl 542 In open air, central
European climate
> 12 Tectyl 506 EH 48/18
612 Tectyl 542/
Tectyl 506 EH
In open air,
tropical climate,
aggressive
industrial
atmosphere or
close to sea
> 12 Tectyl 506 EH 48/12
Tab. 23 Valvoline preservatives
9.2.8 Flange loads according to ISO 5199
Empirical formulas for forces and torques
Fig. 34 Empirical formulas for forces and torques
z
y
x
y
x
z
S
D
Fig. 35 Flange loads at the pump
Formulas for conditions to be checked
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 39
Appendix
To calculate the maximumpermissible ange load: multiply
the table value with the correction factor M, depending on
the material and temperature ( Figure Correction factor
M and operating temperature, Page 40).
Values for NB, CLB, CNB series Pump size
F
v max
(z)
[N]
F
h max
(x, y)
[N]
M
t max
[Nm]
20160 1300 1000 200
25160 2000 1400 400
25200 1900 1400 350
32125 2300 1600 500
32160 2300 1600 500
32200 2100 1500 450
32250 2500 1700 550
40125 2700 1800 650
40160 2700 1800 650
40200 2400 1700 550
40250 2800 1900 700
40315 2900 2000 700
50125 3200 2100 800
50160 3200 2100 800
50200 2800 1900 700
50250 3200 2200 850
50315 3300 2200 850
65125 4200 2800 1200
65160 4200 2800 1200
65200 4500 2900 1300
65250 4000 2600 1100
65315 4700 3100 1400
65400 3200 2200 850
80160 5300 3400 1650
80200 5600 3600 1700
80250 4900 3200 1400
80315 5900 3800 1850
100160 5000 3200 1500
100200 7000 4400 2300
100250 7900 5000 2700
Values for NB, CLB, CNB series Pump size
F
v max
(z)
[N]
F
h max
(x, y)
[N]
M
t max
[Nm]
100315 7200 4600 2400
125200 7300 4600 2400
125250 9700 6100 3450
150200 12600 8000 4800
Tab. 24 Flange loads
1
1,0
0,9
0,8
0,7
0,6
0,5
0,4
0,3
0,2
0,1
0
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
[ C]
2
3
4
M
5
Fig. 36 Correction factor M and operating temperature
1 Non-alloyed steel cast
2 Austenitic steel cast
3 Spheroidal iron EN-GJS-400
4 Gray cast iron EN-GJL-200
5 Bronze G-CuAl10Ni
40 NB / CLB series BA-2006.05 468.0005 GB 550 148
Appendix
9.3 Spare parts for two years of
continuous operation according
to DIN 24296
Number of identical pumps (including stand-by pumps)
2 3 4 5 6 or 7 8 or 9 > 9
Part no. Part designation
Set/quantity of spare parts
171.01
Impeller (all two-stage
pump sizes)
1 1 1 2 2 3 30 %
211.1
914.16
922.2
930.1
940.1
Stub shaft
Cheese head screw
Impeller nut
Spring ring
Shaft key
1 1 2 2 2 3 30 %
220.01
914.16
922.01
936.01
940.01
Stub shaft
Cheese head screw
Impeller nut
Spring ring
Shaft key
1 1 2 2 2 3 30 %
220.02
914.16
922.01
936.01
940.03
Stub shaft
Cheese head screw
Impeller nut
Spring ring
Shaft key
1 1 2 2 2 3 30 %
230.01
230.1
Impeller (all
single-stage pump
sizes)
1 1 1 2 2 3 30 %
230.02
230.03
514.01
904.05
Impeller, rst stage
Impeller, second stage
Threaded ring
Grub screws
1 1 1 2 2 3 30 %
400.1/01
400.2/02
Gasket (set)
Gasket (for version
with intermediate ring)
4 6 8 8 9 12 150 %
433... Mechanical seal 2 3 4 5 6 7 90 %
Tab. 25 Spare parts for two years of continuous operation
) Delivered as a mechanical unit (BG) or sales unit (VG)
468.0005 GB 550 148 BA-2006.05 NB / CLB series 41
Appendix
42 N B / C L B s e r ie s B A - 20 06 .0 5 46 8. 00 05 G B 5 50 1 48
Appendix
46 8. 00 05 G B 5 50 1 48 B A - 20 06 .0 5 N B / C L B s er ie s 43
Appendix
44 N B / C L B s e r ie s B A - 20 06 .0 5 46 8. 00 05 G B 5 50 1 48
1 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
Screw pumps
This instruction is valid for all TRF pump models shown on page 2
Contents Page
List of components 2
Exploded view/Ordering code/ Service intervals 3
Changing ball bearing/Inspection of rotors and shaft seal 4
Sectional view/List of tools 5
Shaft seal 6
Dismantling 6
Reassembly 8
Tuning valve 11
Pressure relief valve 11
Maintenance and Service
Instruction
TRF
Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
2 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
Valid for all TRF pumps with sizes: 660, 940, 1300, 1700, 2500.
With code for shaft seal: 18.4 = Viton elastomers
18.5 = Nitril elastomers
List of components
Pos No Denomination Qty G053A Note
113 Key 1
1020 Power rotor (CW-rot.) 1
122 Ball bearing 1 x
123 Locking washer 1 x
124 Bearing nut 1 x
130 Support ring 1 x
132 Retaining ring 1 x
202 Idler rotor (CW-rot.) 2
401 Pump body 1
424 Sleeve 1
424A Gasket 1 x
425 Screw 4
429 Spindle 1
429A Pin 1
430 Piston 1 1)
432 Pin 1 1)
437 O-ring 1 x
451 Screw 4-6
453 Screw 8
455 Screw 8
462 Plug 1
462A Sealing washer 1 x
463 Plug 1
463A Sealing washer 1 x
480 Valve housing 1 4)
501 Front cover 1
506 O-ring 1 x
509A Rotating ring 1 x
509C Rubber ring 1 x
509D Washer 1 x
509E Spring 1 x
511 Seat 1 x
511A O-ring 1 x
520 Bearing disc 1
521 Screw 4
526 Grease nipple 1
526A Protective cap 1
537 Deaeration plug 1
537A Washer 1
551 Rear cover 1 2)
556 Gasket 1 x
601 Top cover 1 4)
602 Gasket 2 x 4)
605 O-ring 1 x 4)
606 Bottom cover 1 4)
608 Valve spindle 1 4)
612 Regulating nut 1 4)
613 Pin 1 4)
6140 Valve piston 1 4)
615 Spring 1 x 4)
621 Wheel 1 4)
622 Nut 1 4)
622A Key 1 4)
623 Valve plate 1 4)
636 Shock valve 0-2 3)4)
655 Washer 1 4)
656 Sleeve 1 4)
657 Spring 1 x 4)
658 Distance sleeve 1 4)
Note:
1) Valid for sizes
1300, 1700, 2500
2) Valid for pump
without valve,
item no
601 - 658, 480
excluded
3) Number of
shock valves:
pump size
660, 940:0
1300, 1700:1
2500:2
4) Valid for pump
with valve
Components included
in Spare part kit:
3 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
Service intervals
The intervals for inspection and replacement of wear
parts vary greatly with the properties of the pumped
liquid and can only be determined by experience.
Except for the ball bearing, all internal parts of the
TRF-pump are lubricated by the pumped liquid.
Pumping liquid which contain abrasive materials, or
liquid that is corrosive, will significantly reduce
service life and call for shorter service intervals.
Wear in the pump will normally show as unnormal:
Vibration
Noise
Loss of capacity
Reduction in flow/pressure
Leakage
We recommend planned inspection and overhaul at
regular intervals, not exceeding 3 years. It is recom-
mended always to have the spares included in
minor spare part kit G053A available.
Ordering code
Recommended spare parts kit
Every shutdown for service of a plant is costly.
The time for repair should therefore be limited to a
minimum which can be accomplished by keeping a
spare pump. The changed pump can later be
repaired at a suitable place and can then be used as
a spare pump.
For maintenance the following spare parts kits are
recommended:
Kit To be used for
G053A Repair after damage or greater wear
Spare parts sets Pump size
Pos No 660 940 1300 1700 2500
G053A Set 10 bar 70191303 70191304 70191305 70191306 70191307
Spring 16 bar 70021352 70021352 70021774 70021774 70022079
Fig. 1
Before commencing any work, read this instruction carefully! Failure to comply with these instructions may
cause damage and personal injury!
For more information about technical data and performance we refer to the TRF Product description. Fore more informa-
tion about the pumps installation, Start-up and trouble shooting we refer to the "Installation and Start-up instruction"
Ident no. 550 802 for low pressure pumps.
451
526 A
526
122
123
124
130 132
511
511 A
509 A
509 C
509 D
102
202
509 E
462 A
401
506
1010
201
501
462
636
556
455 606
602
612
613
615
658
453
480
551
608
656
657
605
602
601
621
623
622
455
437
429
425
424
424 A
430
429 A
432
463 A
463
622 A
655
6140
520
521
113
113
537
537A
!
Exploded view
T
u
n
i
n
g
P
a
r
t
s
4 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
Inspection of shaft seal
As the seal faces of a mechanical shaft seal are lubri-
cated by the fluid a certain leakage will always be
present. Ten drops per hour can be considered as
acceptable.
An external visual inspection of the pump is advis-
able at least every two days to assure that the shaft
seal is not leaking too much. Excessively leaking shaft
seals should be changed without delay, as the leakage
normally will grow worse and cause additional
damage. Follow the instructions in the dismantling/
reassembly session.
When working with a shaft seal, cleanliness is of
utmost importance. Avoid touching the seal faces.
If necessary, the seal faces should be cleaned imme-
diately prior to assembly, using a dust free cloth and
clean solvent.
For lubrication of shaft seal read instructions in fig 23.
Changing ball bearing
The TRF-pump is fitted with an external grease
lubricated ball bearing.
When delivered, the ball bearings are filled with
grease of type B.
Whenever the ball bearing is removed, it is recom-
mended to exchange it for a new one.
Fit the new ball bearing properly greased and re-
grease it after one hour of running, while the pump is
operating.
Inspection of rotors
To reach the idler rotors in a quicker way than
described in the dismantling section, loosen the rear
cover (480) with valve. Screw out the idler rotors
backwards.
Internal clearances in the pump, which are vital for
its proper function, may have been affected by wear.
Acceptable wear can be determined only by experi-
ence of the actual application. As a rule of thumb the
following max clearance values may apply:
Between rotor and bores: 0.2 mm
Between rotor flanks: 0.4 mm
For light duties (low pressure, medium viscosity)
even bigger clearances may be acceptable but for
low visc./high pressure duties the limit will be
lower. Also watch if there are major scratches on
these parts.
If the pumps operating temperature ex-
ceeds 60C let the pump cool off before any
service, maintenance or dismantling work
is commenced to avoid burn injury.
All work carried out on the pump has to be
performed in such a manner that risks for
personal injury are observed!
When handling liquids that may harm skin
use gloves and/or protective clothing.
!
!
!
!
!
!
Use an appropriate type of grease, as per table and
grease gun suitable for grease nipple (pos 473)
according to DIN 71412 (ISO 6392).
On vertical mounted units the greasing intervals are
reduced to half.
Installed in dusty or dirty premises or in a corrosive
environment it should be lubricated at more fre-
quent intervals.
If using others than these recommended greases
check if it is possible to mix them with each other,
otherwise clean before using a new grease.
Pump size Grease Temp Grease Speed, rpm
amount max type 1750 1450 1150 950
gram C Lubricating intervals in working hours
70 A 10 000 10 000 10 000 10 000
660 90 A 3 900 4 700 5 300 5 900
940 15 90 B 7 900 9 500 10 000 10 000
110 B 3 100 3 700 4 200 4 700
130 B 1 200 1 500 1 600 1 800
155 C 450 600 650 650
70 A 9 000 10 000 10 000 10 000
1300 90 A 3 500 3 900 4 700 5 300
1700 23 90 B 7 100 7 900 9 500 10 000
2500 110 B 2 800 3 100 3 700 4 200
130 B 1 100 1 200 1 500 1 600
155 C 300 450 600 600
Recommended
greases:
Type A
BP Energrease LS3
Esso Beacon 3
Mobil Mobilux 2
Shell Alvania G3
Texaco Multifak EP 2
Type B
BP Energrease, HTG2
Chevron Industrial
Grease Heavy
Esso Unirex N3
Mobil Mobiltemp,
SHC 100
Shell Darina 2
Texaco Hytex EP 2
Type C
Mobilith SHC 460
Lubrication intervals
When handling liquids which may involve
fire hazards appropriate precautions to
avoid danger are to be taken.
In case of failure for a system with elevated
pressure, fluid jets may cause injury and/or
damage.
Oil leakage may make the floor slippery
and cause personal injury.
5 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
Sectional view
Fig. 4
List of tools necessary for dismantling and reassembly
Fig. 3
Slide
calliper
Puller
Allen
key
Grease
Mounting
sleeve
Screw
driver
Plastic
mallet
Pairs of
Pliers
Hook
spanner
Crow
bar
A
C
F
4
I
M
O
A
B
Oil can
401
506
451
511A
509A
509C
509D
509E
511
122
123
124
132
130
462A 462 613 606 455
602
612
658
615
6140
608
655
480
656
657
602
601
605
622A
621
622 623
463A 463
424
429
437
425
424A
430 432 429A
Tuning valve
for pump
size 660, 940
Tuning valve
for pumpsize
1300, 1700, 2500
d
D
GREASE
L
Socket
wrench
Mounting sleeve
dimensions (mm)
Pump
size d L
660 46 150
940 51 150
1300 66 150
1700 66 150
2500 66 150
Threaded bar
UNC 5/8
Washer
70
With
Rear
cover
(without
valve)
551
With
valve
6 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
Shaft seal - assembly drawing
B.
Fig. 5
Dismantling
A.
Fig. 7 Fig. 6
For most installations repair can be done with
the pump in place by removing the motor.
Turn the electricity OFF.
Close the valves.
Disconnect the electric motor.
For horizontal installation drain the pump by
loosen screws 453 3-4 turns and loosen 480
valve housing.
Loosen and remove screws 521.
Pull out the power rotor 1020 with the
help of coupling half or an eye bolt fitted
in the power rotor.
ATTENTION
Be careful when the threaded part of the
rotor passes the bore in the cover.
Connecting and disconnecting of electric
cables must be done only by personnel
authorized to do such work.
Before any maintenance work, ensure that
the driver is deenergized and the pump
hydraulically isolated.
511 511A 509A 509C 509D 509E
Make sure to mount these parts in right
order and in right direction.
ATTENTION
Use appropriate vessels to collect oil
spillage when opening the pump
!
Pump and/or motor should be lifted
with straps securely attached so that the
centre of gravity is located in order to
avoid tipping.
A
C
F
5
I
M
O
A
B
ON OFF
A
C
F
2
2
I
M
O
A
B
521
A
C
F
2
3
I
M
O
A
B
A
C
F
2
4
I
M
O
A
B
1020
!
7 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
D.
G.
Fig. 10 Fig. 11
Fig. 9
Fig. 12
C.
F.
Note the axial position of the coupling half.
Release the stop screw.
A
C
F
7
I
M
O
A
B
Remove the coupling half.
E.
Remove the washer 520.
Remove the key 113.
A
C
F
8
I
M
O
A
B
Unlock the
locking washer
123 with a
screw driver.
H.
A
C
F
9
I
M
O
A
B
Loosen the
bearing nut 124.
A
C
F
1
0
I
M
O
A
B
Remove the bearing
nut 124 and the
locking washer 123.
Fig. 8
Fig. 13
520
113
123
124
124
123
8 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
A
C
F
1
2
I
M
O
A
B
1
2
3
A
C
F
2
5
I
M
O
A
B
L.
Fig. 14 Fig. 15
Fig. 16
J. I.
Use a crowbar to press the seat 511 back-
wards on the shaft so that a space arises
between the seat and the ball bearing. Place
the puller feet into this space and pull off the
ball bearing 122.
M.
A
C
F
1
1
I
M
O
A
B
1 Remove the support ring 130 and the
retaining ring 132 (Use a pair of pliers here).
2 Remove the seat 511.
3 Remove the shaft seal 509.
Loosen the screws 451 and remove the front
cover 501 and the O-ring 506.
Take out the two idler rotors and check
for wear.
A.
Lubricate the idler rotors and fit them into
the pump body.
Note the open position of the idler
rotors.
Fig. 17
Fig. 18
511 122
451
506
501
Reassembly
A
C
F
2
6
I
M
O
A
B
A
C
F
2
7
'
I
M
O
A
B
Open position
132 130
511
509
K.
Fig. 19
Remove the Deaeration plug 537, the washer
537A and the Deaeration pipe.
9 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
A
C
F
2
8
I
M
O
A
B
GREASE
B.
D.
E.
Fig. 20
Fig. 23
Lubricate the O-ring 506 with grease and fit
it to the recess in the pump body.
Fit the front cover 501 and the screws 451
and tighten them.
ATTENTION
Note the position of the drain hole.
A
C
F
1
8
I
M
O
A
B
If necessary, replace the O-ring 511A.
A
C
F
1
9
I
M
O
A
B
Lubricate the seal face
on the seat 511 with
grease. We recommend
grease of Graphite or
Molybdendisulphite
type.
Fit the seat on the
power rotor 1020 and
push it beyond the
groove for the retaining
ring.
Fit the retaining ring
132 with a pair of pliers.
Fit the support ring 130.
Fig. 22
506
451
501
130
132
511
511A
511
C.
Fig. 21
A
C
F
1
7
I
M
O
A
B
Lubricate all surfaces
of the power rotor
1020.
Fit the shaft seal 509
on place.
509
1020
retaining
ring
groove
F.
Lubricate the shaft.
Press the ball bearing 122 to its position on
the shaft by means of a mounting sleeve
resting on the inner race of the ball bearing
and a threaded bar UNC 5/8, nut and
washer.
Fig. 24
A
C
F
2
0
'
I
M
O
A
B
Mounting
sleeve
10 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
A
C
F
2
9
'
I
M
O
A
B
Fig. 30
Fig. 28
G.
Fit the locking
washer 123 and
the bearing nut
124.
Tighten the
bearing nut 124.
Lock the washer
123.
H.
I.
Fit the washer 520.
Fit the key 113 back in place.
Lubricate and fit the power rotor 1020 into
the pump by carefully guide it into the idler
rotors openings, see fig 19.
Tighten the screws 521 crosswise to help the
rotor to reach its final position.
J.
Check that the pump shaft moves freely.
Fit the electric motor back to the pump.
Check the correct setting of shaft coupling
according to Alignment and shaft
couplings and proceed according to
instruction under Start-up in the Installa-
tion Manual.
Fig. 25 Fig. 26
Fig. 27
124
123
L.
Press the shaft coupling
to its original position
with help of a threaded
bar UNC 5/8, nut and
washer.
Tighten the stop screw.
A
C
F
2
1
'
I
M
O
A
B
520
113
1020
K.
Fig. 29
Put the deaeration pipe back in place through
the connecting frame into the front cover 501.
Carefully fill the seal area space completely
with thin oil (f.ex. ISO VG 46) through the
deaeration pipe.
Put the washer 537A and Deaeration plug 537
back in place again.
A
C
F
2
4
I
M
O
A
B
11 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
Tuning valve
Pressure relief valve
Remove the nut 622 and the valve plate 623.
Pull off the hand wheel 621 and remove the key
622A.
Remove the screws 455 and the cover 601.
Take out the spring 657.
Remove the old O-ring 605 (if its leaking) with a
small screw driver. Before fitting the new O-ring
lubricate it and the valve sprindle 608 with
engine oil.
Fit the spring 657.
Remove the old gasket 602 from the top cover
601. Make sure it is removed completely. Fit the
new gasket.
Lubricate the bore in the cover 601 and put back
in place, make sure the O-ring 605 is not dam-
aged. Tighten the screws 455 crosswise.
Fit the key 622A and the wheel 621.
Fit the washer 623 and the nut 622.
Untight the screws 425.
Remove the sleeve 424 from the pump
body.
Remove the retaining pin 429A.
ATTENTION
Spring tension.
636
455
606
602
612
613
615
658
453
480
608
656
657
605
602
601
621
623
622
455
622A
655
6140
A
C
F
3
1
I
M
O
A
B
Unscrew the spindle 429 from the sleeve
424 until you see the O-ring 437.
Replace the O-ring 437 if its leaking.
Replace the gasket 424A.
Reassemble the valve in reverse order.
Adjust the tuning according to the instruc-
tions in the installations manual.
Fig. 31 Fig. 32
Fig. 33
425
429A
424
429
437
A. B.
424A
12 Ident No. 550 804
October 2001
Subject to technical alterations
ALLWEILER AG
Postfach 1140 78301 Radolfzell
Allweilerstrae 1 78315 Radolfzell
Germany
Tel. +49 (0) 7732 86-0
Fax +49 (0) 7732 86-436
E-mail: service@allweiler.de
Internet: http://www.allweiler.com
1
Operating and Maintenance Instructions VM No.: 732.0002 GB
with Dismounting and Edition: 12.03
Mounting Instructions Ident No.: 174 700
Eccentric Screw Pumps
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N,
AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
Order No.: Ident No. of Pump:
Machine No.: Pump Type:
Operating data, dimensions and other additional information can be found in the order-specific part of the documentation.
Contents
1. General
2. Safety
3. Transport and Intermediate
Storage
4. Description
5. Installation/Mounting
6. Start-up/Shutdown
7. Maintenance/Repair
8. Operating Faults, Causes
and Remedial Action
Important note:
This operating manual is to be supplemented
by the order-related information.
Retain
for future
use!
These Operating and Maintenance In-
structions contain information from the
pump manufacturer. They may need to
be supplemented by instructions of the
operator company for its personnel.
These instructions do not take account
of specific information relating to opera-
tion and maintenance of the process
plant into which the pump is integrated.
Such information can only be given by
the persons responsible for construction
and planning of the plant (plant manu-
facturer).
Such specific instructions relating to
operation and maintenance of the
process plant into which the pump is
integrated have priority over the in-
structions of the pump manufacturer.
The plant manufacturer must on princi-
ple observe the limits of use!
Refer to the operating instructions of the
plant manufacturer!
2
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
Table of Contents
1. General
1.1 Application and range of utilization
1.2 Performance data
1.3 Abbreviation
1.4 Warranty
1.5 Testing
2 . Safety
2.1 Marking of hints in the operating instructions
2.2 Personnel qualification and personnel training
2.3 Dangers in case of non-compliance with the safety hints
2.4 Responsible working
2.5 Safety hints for the user/operator
2.6 Safety hints for maintenance, inspection and mounting
operations
2.7 Independent reconstruction and spare parts production
2.8 Inadmissible modes of operation
2.9 Operation in potentially explosive environments
3. Transport and intermediate storage
3.1 Packing
3.2 Transportation
3.3 Preservation and storage of eccentric screw pumps
4. Description
4.1 Structural design
4.1.1 Bearing and lubrication
4.1.2 Shaft seal
4.1.3 Dimensions/branch position/flanges
4.2 Sound pressure level
4.3 Mode of operation
4.4 Aggregate construction
4.4.1 Drive
4.4.2 Base plate
5. Installation/Mounting
5.1 Installation
5.2 Foundation
5.2.1 Arrangement of a steel foundation plate
5.2.2 Arrangement of concrete foundations
5.2.3 Fastening of the pump aggregate on the concrete
foundations
5.2.4 Arrangement of concrete foundations for poured
base plates
5.2.5 Alignment of the pump aggregate
5.2.6 Pouring of base plate
5.3 Base plate
5.4 Space requirements for maintenance and servicing
5.5 Mounting the pipelines
5.5.1 Nominal widths
5.5.2 Supports and flange connections
5.5.3 Cleaning the pipelines prior to attachment
5.6 Mounting of auxiliary pipelines for additional facilities
5.7 Safety and control devices
5.7.1 Manometer and vacuometer
5.7.2 Safety devices in the discharge pipeline
5.8 Electrical connections
6. Start-up/Shutdown
6.1 Preparations for start-up
6.1.1 Filling the pump with liquid
6.1.2 Turning on the additional facilities for shaft seals (if
provided)
6.1.3 Quality and properties of the flushing/sealing and
quenching liquids
6.1.4 Activating the additional facility for heating or cooling
the stuffing box casing and/or the suction casing
(double-jacket casing)
6.1.5 Breaking away of the pump
6.1.6 Control of the sense of rotation
6.2 Start-up
6.2.1 Start-up
6.2.2 Drive
6.2.3 Checking the delivery values
6.2.4 Protection against running dry
6.3 Shutdown
6.3.1 Shutoff
6.3.2 Measures in case of longer periods of standstill
7. Maintenance/Repair
7.1 Maintenance
7.1.1 General monitoring
7.1.2 Maintenance of components
7.1.2.1 Joints of the joint shaft
7.1.2.2 Shaft sealing
7.1.2.3 Drive engines and (variable speed gear) drive
7.1.2.4 Packing ring dimensions (for Chapter 7.1.2.2), lubri-
cant quantities for joints (for Chapter 7.1.2.1) and
flushing liquid flows (for Chapter 6.1.2)
7.2 Repair (mounting and dismounting instructions)
7.2.1 Dismounting of the eccentric screw pump
7.2.1.1 Dismounting the stator
7.2.1.2 Dismounting the rotor and rotor-side joint
7.2.1.3 Dismounting the joint shaft and the drive-side joint
7.2.1.4 Dismounting the shaft seal and plug-in shaft
7.2.2 Assembly of the eccentric screw pump
7.2.2.1 Mounting the shaft seal and plug-in shaft
7.2.2.2 Mounting the rotor and joints
7.2.2.3 Mounting the stator
7.3 Replacement parts/Spare parts
7.4 Sectional drawings with spare parts list and recommended
replacement parts/spare parts for series AEB1L, AEB.E,
AEB.N, AEB.H, , AEDB1E, AEDB2N; Design IE, ZE
8. Operating faults, causes and remedial action
3
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
1. General
1.1 Application and range of utilization
The eccentric screw pumps are self-priming, rotary
positive-displacement pumps for handling and dosing
low to high-viscosity, neutral or aggressive, pure or
abrasive, gaseous liquids or liquids which tend to
froth, even with fibre and solids contents.
The range of utilization is to be
taken from the order data sheet.
1.2 Performance data
The exact performance data applying to the pump
are to be taken from the order data sheet and are
engraved on the name plate.
1.3 Abbreviation
The abbreviation of the eccentric screw pumps is set
up according to the following scheme:
Example:
This abbreviation is embossed on the type plate.
1.4 Warranty
Our liability for shortcomings in the supply is laid down
in our delivery conditions. No liability will be under-
taken for any damages caused by non-compliance
with the operating instructions and service conditions.
If at any later date the operating conditions happen to
change (e.g. different liquid pumped, speed, viscosity,
temperature or pressure conditions), it must be
checked by us from case to case and confirmed, if
necessary, whether the pump is suited for these pur-
poses. In case no special agreements were made,
pumps supplied by us may, during the warranty pe-
riod, be opened or varied only by us or our authorized
contractual service stations; otherwise, our liability for
any defects will cease.
1.5 Testing
Prior to leaving our factory, all pumps are subjected to
a leakage and performance test. Only properly
operating pumps leave the factory achieving the
performances assured by us. Thus, compliance with
the following operating instructions ensures proper
operation.
2. Safety
These operating instructions contain basic hints to be
observed in case of installation, operation and main-
tenance. Therefore, prior to mounting and commis-
sioning, these operating instructions must by all
means be read by the fitter as well as the pertinent
expert personnel/customer and must always be avail-
able at the place of installation of the machine/ plant.
Not only are the general safety hints listed under this
main item Safety to be observed, but also the spe-
cial safety hints such as for private use added to the
other main items.
2.1 Marking of hints in the operating instructions
The safety hints contained in these operating instruc-
tions which, in case of non-compliance, may cause
danger to personnel, are particularly marked with the
general danger symbol
in case of warning against electric voltage with
For safety hints, non-compliance with which may
cause dangers to the machine and its functions, the
word
is inserted.
Hints directly attached to the machine such as
! directional marker
! signs for fluid connections
must by all means be observed and maintained in
completely legible condition.
2.2 Personnel qualification and personnel training
The personnel for operation, maintenance, inspection
and mounting must have the corresponding qualifica-
tion for these operations. Range of liability, compe-
tence and the supervision of the personnel must be
exactly controlled by the customer. If the personnel do
not have the required knowledge, same must be
trained and instructed. If required, this may be ef-
fected by the manufacturer/ supplier on behalf of the
machine customer. In addition, it must be ensured by
the customer that the contents of the operating in-
structions are fully understood by the personnel.
2.3 Dangers in case of non-compliance with the
safety hints
Non-compliance with the safety hints may result in
danger not only to persons, but also to environment
and machine. Non-compliance with the safety hints
may lead to the loss of any claims for damages. In
detail, non-compliance may, for example, entail the
following dangers:
4
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
! failure of important functions of the machine/plant
! failure of specified methods for maintenance and
servicing
! danger to persons by electrical, mechanical and
chemical influences
! danger to the environment by leakage of danger-
ous substances
2.4 Responsible working
The safety hints mentioned in these operating instruc-
tions, the current national rules for the prevention of
accidents as well as any internal working, operating
and safety regulations of the owner must be ob-
served.
2.5 Safety hints for the user/operator
! If hot or cold machine parts lead to dangers, these
parts must be protected against accidental contact
at the site.
! Protection against accidental contact for moving
parts must not be removed when the machine is
in operation.
! When operating pump aggregates in a dust-laden
environment (e.g. milling, chipboard manufacture,
bakeries), the surface of the pumps and motors
must be cleaned at regular intervals, depending
on local conditions, in order to maintain the cool-
ing effect and eliminate the possibility of sponta-
neous combustion. Please also see explosion pro-
tection regulations (BGR 104)
! Leakages (e.g. of the shaft seal) of dangerous
materials to be handled (e.g. explosive, toxic, hot)
must be discharged so as not to result in danger
to persons and the environment. Legal stipula-
tions are to be observed.
! Dangers by electrical energy are to be excluded
(for details with regard hereto, please refer e.g. to
the regulations of the VDE and the local energy
supply associations).
2.6 Safety hints for maintenance, inspection and
mounting operations
The customer shall see to it that all maintenance, in-
spection and mounting operations are performed by
authorized and qualified expert personnel who have
sufficiently informed themselves by thoroughly study-
ing the operating instructions.
Basically, operations at the machine must be per-
formed during standstill only. The mode of operation
for stopping the machine described in the operating
instructions must by all means be observed.
Pumps or aggregates handling noxious liquids must
be decontaminated.
Immediately upon completion of the operations, all
safety and protective devices must be mounted and
made operational again.
Prior to restarting, the items listed in Chapter Prepa-
ration for start-up are to be observed.
2.7 Independent reconstruction and spare parts pro-
duction
Reconstruction of or changes to the machine are only
admissible after consultation with the manufacturer.
Original spare parts and accessories authorized by
the manufacturer serve safety purposes. The use of
other parts may cancel the liability for the conse-
quences resulting therefrom.
2.8 Inadmissible modes of operation
The operating safety of the machine supplied is only
ensured with due application according to Chapter 1
General of the operating instructions. The limit val-
ues given in the data sheet must by no means be ex-
ceeded.
2.9 Operation in potentially explosive environments
Observe the instructions of the ATEX additional oper-
ating manual when operating the pump respectively
aggregate in potentially explosive environments.
3. Transport and intermediate storage
3.1 Packing
The symbols applied to the packing must be ob-
served.
During transportation and storage, suction and outlet
side and auxiliary connections of the pump must be
closed with plugs. During installation of the pump ag-
gregate, the plugs must be removed.
3.2 Transportation
The pump or pump aggregate is to be safely trans-
ported to the place of installation, if required by
means of lifting gear.
Observe the general regulations on the lifting of
loads. Cranes and stopper ropes may not be at-
tached to the suspension brackets of motors.
When transporting the pump by crane, place the
stopper ropes safely around the suction casing. With
complete pump aggregates, an additional rope must
be slung around the drive engine.
The stopper ropes have to be slung around the pump
respectively pump aggregate so that these are ex-
actly balanced when lifted.
During transportation toppling of the
aggregate due to nose-heaviness
has to be ruled out.
Transport damages
Check the pump for damage on
receipt. Any damage detected must
be notified immediately.
3.3 Preservation and storage of eccentric screw
pumps
See our document VM 2102/
4. Description
4.1 Structural design
Self-priming, one or two-stage eccentric screw pump.
The conveyor elements are rotor and stator. The input
torque is transmitted via the drive shaft and the joint
shaft to the rotor.
Pressure casing, stator and suction casing are held
together by external casing connection screws (clamp
bolts).
The stuffing box or mechanical seal housing is lo-
cated between the suction casing and the bearing
bracket.
4.1.1 Bearing and lubrication
Joint shaft with liquid-proof clad bolt joints. Greasing
with joint oil.
Bearing of the drive shaft/plug-in shaft in the rein-
forced bearings of the drive.
5
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
4.1.2 Shaft seal
Through uncooled or cooled stuffing box or cooled or
uncooled, maintenance-free, non-released, singular
or double-action mechanical seal.
4.1.3 Dimensions/branch position/flanges
The dimensions of the pump respectively the pump
aggregate, the branch position and flange dimensions
are to be taken from the tables of dimensions.
4.2 Sound pressure level
The sound pressure level of the pump is below 70 dB
(A).
4.3 Mode of operation
Self-priming, rotating positive-displacement pump.
Conveyor elements are the rotating helical rotor and
the static stator. Both touch in transection with series
AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H in two points each and with
series AEB1L, AEDB.E, AEDB.N in three points each,
which form two sealing lines seen across the length of
the conveyor elements with series AEB.E, AEB.N,
AEB.H and three sealing lines with series AEB1L,
AEDB.E, AEDB.N. The content of the sealed cham-
bers that form with the rotation of the rotor is shifted
axially and totally continuously from the suction to the
outlet side of the pump. No turbulence occurs despite
the rotation of the rotor. The unvarying chamber vol-
ume rules out crushing forces and thus guarantees
very gentle, low-pulsation conveyance.
4.4 Aggregate construction
4.4.1 Drive
By means of non-explosion-protected or explosion-
protected electric motors, geared motors or variable
speed gear motors.
4.4.2 Base plate
Horizontal pumps are generally mounted on a joint
base plate with the drive. The base plates are made
of steel.
5. Installation/Mounting
5.1 Installation
The pumps can be installed horizontally or vertically
with bearing upwards.
5.2 Foundation
The foundation design depends on the size of the
pump and/or the pump aggregate and the local instal-
lation conditions.
For exact data on the pump and aggregate dimen-
sions, please refer to our tables of dimensions.
The foundation may be designed as concrete founda-
tion or load-carrying foundation frame, for example of
the steel type.
All foundation designs are subject to the following:
The foundation must be designed so that it can take
the weight of the pump aggregate on the entire sur-
face.
5.2.1 Arrangement of a steel foundation plate
A steel foundation plate must be designed in such a
way that the base plate makes full contact and can be
secured with bolts or by welding.
If only some of the areas of the base
plate are supported, the plate sags
in the center or the pump aggregate can be twisted.
This influences the alignment of the pump aggregate
can cause high noise emission and damage.
5.2.2 Arrangement of concrete foundations
Concrete foundations must be horizontal, straight and
clean and must fully absorb the load exerted on the
foundations. Concrete foundations must be designed
in such a way that the base plate makes full contact
and can be secured with suitable bolts (see our ag-
gregate drawing).
If only some of the areas of the base
plate are supported, the plate sags
in the center or the pump aggregate can be twisted.
This influences the alignment of the pump aggregate
and can cause high noise emission and damage.
5.2.3 Fastening of the pump aggregate on the concrete
foundations
After aligning the pump aggregate on the concrete
foundations the securing bolts are diagonally and
evenly tightened.
5.2.4 Arrangement of concrete foundations for poured
base plates
When shuttering the concrete foundations it must be
observed that a gap for aligning the pump aggregate
and applying the mortar compound remains between
the top of the finished foundation block and the bot-
tom of the base plate.
The set concrete foundations must be straight, even
and clean. Any traces of oil must be removed from
the foundations. The recessed anchor holes for the
foundation bolts must be cleaned and removed and
cleaned out with air. Prior to the installation of the
pump aggregate the surface of the concrete founda-
tions must be roughened and cleaned to ensure a
good bonding between the foundation block and the
mortar compound.
5.2.5 Alignment of the pump aggregate
The pump aggregate must be aligned to the defined
height and system dimensions. This is done by
means of suitable steel inlays that are placed directly
next to each fixing screw. The total height of the steel
inlays is defined by the fixed system dimensions of
the plant. The steel inlays and the base plate must lie
flush.
If the attachment holes are more than 750 mm apart,
we recommend additional steel inlays at a distance of
750 mm each.
Alignment with steel shims
5.2.6 Pouring of base plate
After alignment on the concrete foundations , a low
shrinkage mortar compound must be poured over the
entire length of the base plate, covering also the an-
chor holes with the connected foundation bolts.
6
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
Once the mortar compound has set on the base plate
and in the anchor holes, the foundation bolts must be
diagonally and evenly tightened.
Note: When pouring or adding the mortar compound
it must be observed that the base plate makes full
contact. Tap the plate to ensure that no cavities have
formed underneath.
5.3 Base plate
The base-plate has to be attached tension-free to the
base.
5.4 Space requirements for maintenance and servic-
ing
The pump must be accessible from
all sides in order to be able to per-
form the required sight inspections.
There must be enough room for maintenance and
service work, especially for the exchange of the con-
veyor elements. The stator and rotor dismounting di-
mensions are listed in the pump respectively pump
aggregate dimension sheet. Also make sure that all
pipelines can be attached/detached without obsta-
cles.
5.5 Mounting the pipelines
5.5.1 Nominal widths
The nominal widths of the suction and pressure pipes
should be designed according to the nominal widths
of the pipe connections. Gross deviations, especially
on the suction side, require consultation with the fac-
tory.
5.5.2 Supports and flange connections
The pipelines must be connected tension-free to the
pump via the flange connectors. They have to be
supported near the pipe and should be easy to screw
on in order to avoid strains. After loosening the
screws, the flanges may neither be slanted nor
springy and also not rest on each other under pres-
sure. Possible thermal stress on the pipelines has to
be kept away from the pump by means of suitable
measures, e.g. the installation of compensators.
5.5.3 Cleaning the pipelines prior to attachment
The pipelines, sliders and valves on the suction side
must be rinsed respectively cleaned under all circum-
stances before mounting the pump.
Leftover assembly parts like screws, nuts, welding
beads, pieces of steel, etc. destroy the inside parts of
the pump. Any warranty claim is void when damages
are caused by such leftover materials. Flange seals
may not protrude to the inside. Blind flanges, stoppers
protective foils and/or lacquers on flanges and sealing
strips have to be completely removed.
5.6 Mounting of auxiliary pipelines for additional
facilities
All auxiliary pipelines for supplying the shaft seal and
the possible double-jacket casing for heating and
cooling the pump have to be connected tension-free
and sealing.
The pipes for the quenching liquid with single-acting
mechanical seals with quench (design: G0Q) and the
sealing liquid with double-action mechanical seal (de-
sign: G0D) should be installed with a large flowtrough
profile. The quenching respectively sealing liquid dis-
charge takes place at the highest connection of the
mechanical seal housing.
The flow direction of the flushing, sealing and quench-
ing liquid is indicated with arrows in the section draw-
ings.
In order to ensure self-deairing, the pipes must be in-
stalled continuously rising, short and favorable for the
flow.
The formation of air pockets and gas bubbles has to
be prevented, install deairing connections if required.
The heating/cooling liquid discharge must be con-
nected to the highest connection of the possible dou-
ble-jacket casing.
5.7 Safety and control devices
5.7.1 Manometer and vacuometer
A manometer and vacuometer have to be connected
to the pressure and suction pipe.
5.7.2 Safety devices in the discharge pipeline
If there is a shut-off device in the pressure pipe or if
there is the possibility that the pressure pipe may be-
come clogged, a safety device must be provided, e.g.
a bypass with integrated pressure relief valve, space
membrane, motor protection switch, etc.
Eccentric screw pumps are positive-
displacement pumps and can theoretically gen-
erate an infinitely high pressure.
In case of a closed pressure pipe, e.g. because of
clogging or accidental closing of the valve, the
pressure generated by the pump may reach a
multiple of the admissible plant pressure. This
may cause pipes to burst, which must be espe-
cially prevented when handling dangerous con-
veyor substances. Therefore, the corresponding
safety equipment (e.g. pressure switches) also
has be installed in the plant.
5.8 Electrical connections
Only an expert may attach the power cables of the
coupled drive engine in accordance with the circuit
diagram of the engine manufacturer. The valid guide-
lines of the Electrician's Association and the public
power companies have to be observed.
Danger through electric energy must be ruled out.
6. Start-up/Shutdown
6.1 Preparations for start-up
6.1.1 Filling the pump with liquid
The pump may not run dry! For
initial start-up and after longer peri-
ods of standstill, the pump must be
filled with liquid.
Even a few rotations without liquid may damage the
stator. For that reason, the suction casing must be
filled with water or conveyor liquid prior to start-up for
lubricating the stator and rotor. After long periods of
standstill, meaning when it must be assumed that the
residual liquid in the pump has evaporated or after re-
pairs, you have to repeat the filling process.
After filling, the pump works in self-priming mode.
Deairing is not necessary, as the pump can convey a
liquid-gas mixture.
6.1.2 Turning on the additional facilities for shaft seals
(if provided)
If the pumps are charged with a flushing/sealing or
quenching liquid, the available shut-off slides must be
opened before putting the pump into operation for the
first time and set to the following pressure values:
7
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
! Supply of the stuffing box with flushing or
sealing liquid (Design P02, P03, and P04).
Note: Stuffing box with flushing or sealing cham-
ber ring require a flushing respectively sealing liq-
uid for maintaining the function.
The required flushing respectively sealing liquid
pressure for pumps with stuffing box is
P02 = 0.1 to 0.5 bar
(above inner pressure of the suction casing)
P03 = 0.5 bar
(above inner pressure of the suction casing)
P04 = 0 to 0.5 bar
(Flushing and sealing liquid see Chapter 6.1.3.).
! Supply of single-acting, non-relieving me-
chanical seal with choke ring (Design G0S and
G0T)
Note: These mechanical seals require a flushing
liquid in order to maintain their function, which car-
ries off the emerging friction heat and limits the
penetration of the conveyor liquid into the sealing
chamber.
The required flushing liquid pressure is 0.1 to 0.5
bar above the inner pressure of the suction cas-
ing. The required flushing liquid flow for carrying
off the dissipation of the mechanical seal is listed
in the table in Chapter 7.1.2.4 (flushing liquid see
Chapter 6.1.3).
! Supply of double-action, non-relieving me-
chanical seal (Design G0D)
Note: These mechanical seals require a sealing
liquid in order to maintain their function, which car-
ries off the emerging friction heat and limits the
penetration of the conveyor liquid into the sealing
gap.
The circulation of the sealing
liquid must be secured prior to
each start-up.
The sealing liquid pressure must be approx. 1.5 to
2 bar above the pressure on the inside of the suc-
tion casing. The flowthrough quantity must be
regulated in such a way that the exit temperature
does not exceed approx. 60C and is at least 30 K
below the boiling temperature at operating pres-
sure. The temperature difference between input
and output may amount to at most 15 K. (Sealing
liquid see Chapter 6.1.3).
! Supply of the single-acting mechanical seal
with quench (Design G0Q)
The space between the mechanical seal counter-
ring and the shaft seal ring must be charged with
quenching liquid. The max. admissible pressure
difference between the quenching liquid pressure
and the pressure in the suction casing is p = 0,5
bar. The max. quenching liquid pressure is 3 bar.
(Quenching liquid see Chapter 6.1.3).
6.1.3 Quality and property of flushing/sealing and
quenching liquid
Any liquid may be used as
sealing/flushing or quenching liquid
under consideration of the corrosion resistance of all
touching parts and the compatibility with the medium
to be sealed. The liquid must be free from solid sub-
stances, may not be prone to deposits, should have a
high boiling point as well as a good heat conductivity
and low viscosity. Clean and soft water fulfils these
requirements to a high degree.
6.1.4 Activating the additional facility for heating or
cooling the stuffing box casing and/or the suction
casing (double-jacket casing)
If the pumps are equipped with these additional fea-
tures, all shut-off devices for heating or cooling sys-
tems must be opened. The following pressure and
temperature limits must be observed.
! Supply of the cooled or heated stuffing box
and/or suction casing (double-jacket casing)
with suitable liquid media
Only liquid media may be used as heating or
cooling liquid under consideration of the corrosion
resistance of all touching parts.
The maximum heating or cooling liquid pressure
is 6 bar. The maximum heating temperature may
not exceed 150C and the cooling temperature
may not be below -40C.
Note: The design temperature is listed in the or-
der data sheet.
6.1.5 Breaking away of the pump
When initially starting the pump or after longer periods
of standstill, you have to make sure that the drive en-
gine turns the pump effortlessly. Should this not be
easily possible due to the high adhesion between the
rotor and the stator in new state, use suitable tools on
the feather key section of the drive shaft to free the
pump.
The drive shaft may not be damaged here!
6.1.6 Control of the sense of rotation
The normal rotation direction of the
pump seen from the drive against
the drive shaft is to the left. Here the suction connec-
tion is located on the side of the shaft seal so that the
shaft seal is relieved. In special cases, e.g. when
sucking from a vacuum or conveying media that do
not tolerate gas cavities, the pump rotates to the right.
This switches the suction and the outlet side around.
The rotation direction of the pump
must correspond to the rotation
direction arrow "n" on the pump's type plate. A wrong
rotation direction may cause damages to the pump. In
order to control the rotation direction, briefly press the
on/off switch of the engine.
6.2 Start-up
6.2.1 Start-up
Prior to starting the pump, all shut-off devices on the
suction and outlet side have to be opened.
6.2.2 Drive
Turn the motor on.
Observe the product-specific
peculiarities of the drive. See
operating instructions by the drive manufacturer.
8
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
6.2.3 Checking the delivery values
Once the drive has reached its operating speed,
check the intake pressure and the pump end pres-
sure via the vacuometer and the manometer.
The motor may not be overloaded. The power intake
can be monitored with an ammeter. Check the tem-
perature and the viscosity of the conveyor liquid in
this context. The resulting values must be compared
with the order data sheet respectively acceptance
protocol.
6.2.4 Protection against running dry
When no more conveyor media is sucked in by the
pump, the thermal energy emerging in the conveyor
elements of the eccentric screw pump through dry
friction and milling work is no longer carried off in a
sufficient quantity, which thermally destroys the stator
elastomer after a short time already. There are differ-
ent protectors against running dry for protecting the
conveyor elements that are adapted to the respective
operating conditions (consultation with the factory).
6.3 Shutdown
6.3.1 Shutoff
Turn the motor off.
6.3.2 Measures in case of longer periods of standstill
If longer operational breaks are intended and if there
is danger of frost, the pump must be emptied. To do
so, unscrew the screw plug (502) from the suction
casing (505) and afterwards conserve the pump (see
Chapter 3.3).
7. Maintenance/Repair
7.1 Maintenance
! For service and maintenance work, observe the
details in Chapter 2 Safety.
! Regular monitoring and maintenance work on the
pump and the drive extends the service life.
7.1.1 General monitoring
1. The pump may not run dry.
2. The drive engine may not be overloaded.
3. Check the suction and pressure pipes for tight-
ness.
4. An installed stuffing box must drip slightly during
operation. An installed mechanical seal may not
have any strong leaks.
5. Observe pressure and temperature monitoring
devices and compare them with the order data
sheet respectively acceptance protocol.
6. Additional installations like flushing, sealing and
quenching of the shaft seal must be monitored if
provided.
7. Additional equipment for heating or cooling the
stuffing box casing and/or suction casing must be
monitored, if provided.
7.1.2 Maintenance of components
7.1.2.1 Joints of the joint shaft
The joints of the joint shaft are lubricated with ALL-
WEILER special joint oil type B or oil ET1510 ISO 460
by Tribol Lubricants GmbH, Mnchengladbach, if the
pumps are deployed in the food industry, with ALL-
WEILER special joint oil type BL or oil 1810/460 by
Tribol Lubricants GmbH, Mnchengladbach.
Other lubricants were not tested by
us and can therefore not be recom-
mended!
The joints are lubricated for life. We do however rec-
ommend checking the joint sleeve for tightness when
opening the pump for other reasons and exchanging
the joint oil after 8,000 operating hours. The table in
Chapter 7.1.2.6 shows the allocation of the pump size
to the oil quantity in cubic centimeters. For changing
the joint oil, refer to the disassembly and assembly in-
structions.
7.1.2.2 Shaft sealing
Shaft sealing either takes place via a stuffing box or a
mechanical seal.
Stuffing box
Possibly increased leaks on the stuffing box during
the first operating hours normally decrease on their
own during the warm-up time.
If necessary, slightly tighten the hexagon nuts (202)
on the gland (203).
Please observe that there has to be a slight leak on
the stuffing box. This dissipates the friction heat that
forms on the sealing surface.
If the leaking losses increase disproportionately and if
this cannot be reduced by slightly tightening the
hexagon nuts (202) several times, the packing rings
have lost their shape elasticity and must be replaced.
! Dismounting the old packing rings and clean-
ing the stuffing box casing
After relieving the pump from pressure and re-
moving the stuffing box casing, you can take out
the old packing rings. Use a packing puller with
elastic shaft. Afterwards, carefully clean the stuff-
ing box space and the drive shaft in the area of
the packing rings. Used-up drive shafts respec-
tively shaft protection casings must be renewed
(see disassembly and assembly instructions).
! Mounting the packing rings
As a rule, you may only install
packing rings that correspond to
the required operating conditions of the pump.
The dimensions and required number of pre-
pressed packing rings and ring cuts respectively
cut lengths are listed in the table in Chapter
7.1.2.4.
With cuts we recommend the straight vertical cut
to the shaft. In order to achieve a gap-free, paral-
lel position of the cutting ends when closing the
packing ring, the cutting angle should be approx.
20 to both cut ends (see figure 1).
Figure 1: Cutting packing rings
9
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
Pre-pressed packing rings or ring cuts have to be
carefully turned open axial and radial so that they can
just about be slid across the shaft. Bending the rings
may lead to damages.
When mounting in the packing space, carefully re-
bend the packing rings to ring shape. The cutting
joints have to be shifted by 90 here. Each ring has to
be slid into the stuffing box space individually with the
cutting ends facing forward by means of the gland.
The sealing chamber ring or flushing ring have to be
installed sequentially.
You may never use pointed objects
for this work. Danger of damaging
the shaft and deforming the packing material!
! Start-up the stuffing box after re-packaging
The stuffing box may only be tightened slightly
prior to start-up. When starting the pump, 50 to
200 drops per minute are an admissible leakage
quantity.
During the warm-up process of approx. 30 min-
utes, adjust a minimum leakage of 2 to 20 drops
per minute by evenly tightening the gland (203)
step by step via the hexagon nuts (202).
The stuffing box temperature
may not rise abnormally during
this process. Approx. 20 to 60C above the con-
veyor liquid temperature are admissible. In case
of a rapid rise in temperature, the gland must be
loosened immediately and the warm-up process
repeated. The leakage can be carried off via the
threaded boring located in the strip tank in the
bearing socket.
Rule out damages to persons and the environ-
ment through leakage of dangerous substances!
Mechanical seal
Non-relieved mechanical seals in all material pairings
and designs are applied. The mechanical seal is
maintenance-free.
In case of heavy leaks due to wear and tear, you
have to exchange the mechanical seal (see disas-
sembly and assembly instructions).
As the running dry of the mecha-
nical seals must be avoided, the
pump may only be operated in filled state and, if pro-
vided, with activated additional installations (see
Chapter 6.1.2).
7.1.2.3 Drive engines and (variable speed gear) drive
See the operating and maintenance instructions by
the manufacturers.
10
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
7.1.2.4 Packing ring dimensions (for Chapter 7.1.2.2), lubricant quantities for joints (for Chapter 7.1.2.1) and flushing liquid
flows (for Chapter 6.1.2)
Pump size
AEB1E 50 100 200
380
550
750
1000
1450 2700
AEDB1E 75 150 300 560 1200 2300 4250
AEB2E 50 100 200 380 750 1450 2700
AEB1N 25 50 100 200 380 750 1450
AEB2N 25 50 100 200 380 750 1450
AEDB2N 38 75 150 300 560 1200 2300
AEB1L
51
101
201 381
551
751
1001
1451
2701 5001
Pump series
AEB.H 12 25 50 - - - -
Number of packing rings for
design P01!
6 6 6 6 6 6 6
Dimensions of packing rings for
cut rings
37 /
25 x 6
42 /
30 x 6
51 /
35 x 8
59 /
43 x 8
73 /
53 x 10
80 /
60 x 10
99 /
75 x 12
Dimensions of packing rings for
cut rings L
M
x S
104,2
x 6
121
x 6
144,5
x 8
171,4
x 8
211,8
x 10
235,3
x 10
292,5
x 12
Oil quantity in cm
3
per joint
10 18 37 52 87 169 290
Flushing liquid flow
water l/min
0,05 0,07 0,09 0,11 0,11 0,15 0,21
! With shaft seal designs P02, P03 and P04, the quantity reduces by 1.
11
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
7.2 Repair (dismounting and mounting instructions)
General
Qualified customer service fitters are available for as-
sembly and repair work upon request.
Prior to repairs performed by your own personnel or
our expert fitters, make sure that the pump is com-
pletely empty and clean.
This especially applies to pumps, which are sent to
our factory or one of our authorized repair shops for
repair.
We will not accept repair orders for pumps filled with
conveyor media for reasons of protecting our employ-
ees and the environment. Otherwise we will charge
the customer/operator the costs for environmentally-
conform disposal.
In case of pumps operated with dangerous sub-
stances ! and/or conveyor media that are dangerous
to the environment, the customer/operator has to in-
form his own respectively our fitters on-site in case of
repairs or our factory respectively authorized work-
shop in case of returning the pump about this circum-
stance. In these cases, you need to submit a con-
veyor media certificate, e.g. in the shape of a DIN
safety data sheet together with your request for a fit-
ter.
! Dangerous substances are:
! toxic substances
! substances detrimental to health
! caustic substances
! irritating substances
! explosive materials
! fire-promoting, highly, easily and normally in-
flamable materials
! carcinogenic substances
! embryo-damaging substances
! substances that damage the genetic material
! substances which are dangerous for human be-
ings in any other way
With all work on-site, the owner's own respectively our
fitters have to be informed about dangers that may
arise in connection with repairs.
These instructions contain the most important disas-
sembly and assembly work. The assembly steps de-
scribed in the individual chapters have to be observed
under all circumstances.
7.2.1 Dismounting of the eccentric screw pump
The following work steps have to be performed prior
to disassembly:
! Detach the power supply cables to the motor. It
must not be possible to turn the motor on.
! All shut-off devices in the feed and pressure pipes
have to be closed.
! Drain the conveyor liquid from the suction casing.
Unscrew the screw plug for that purpose (502).
Note: Use a receiver.
! Deinstall all feed and pressure pipes as well as all
auxiliary pipelines.
! Loosen the screws on the pump feet and take
them off.
7.2.1.1 Dismounting the stator
! Remove the hexagon nuts (609) and washers
(610) from the clamp bolts (611).
! Pull off the pressure casing (504).
! Remove the clamp bolts (611) and supports
(612), if provided.
! Pull the stator (402) off the rotor (401).
Note: In case of difficulties with dismounting, turn
the stator (402) with pliers at the same time. To do
so, arrest the plug-in shaft (125).
! In case of stators made of plastic or metal, take off
the stator seals (403) and (404).
7.2.1.2 Dismounting the rotor and rotor-side joint
Dismounting the rotor and the rotor-side joint takes
place after dismounting the stator (402). See Chapter
7.2.1.1.
! Remove the hexagon nuts (607) and serrated
lock washers (608) as well as the hexagon screws
(606).
! Pull the suction casing (505) across the rotor
(401). Make sure that the finely crafted rotor is not
damaged.
! Take off the gasket for suction casing (501).
! Saw open the lock on the joint clamp (306) with a
metal saw and press it out on both sides with a
screwdriver.
! Take the joint clamp (306) off the joint sleeve
(308) (see figure 2).
Figure 2: Removing the joint clamp
! Lift the joint sleeve (308) with a screwdriver and
pull it off axially towards the joint shaft (307).
! Catch the oil filling in a container.
! Drive the joint sleeve (304) across the collar of the
joint shaft (307). Do not deflect the joint shaft
(307) (see figure 3).
Figure 3: Dismounting the joint sleeve
! Push out the joint bolt (301).
! With a brass driver, drive out the two sleeves for
the joint bolts halfway (303). Slant the joint shaft
(307) for that purpose (see figure 4).
12
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
Figure 4: Dismounting the sleeves for joint bolts
! Pull the rotor (401) off the joint shaft (307).
! Press out the joint bush (302) from the joint shaft
(307) (n/a with AEB1L 51, AEB1L 101, AEB1E
50, AEB2E 50, AEB1N 25, AEB2N 25, AEDB1E
75, AEDB 2N 38, AEB4H 12).
! Drive out the sleeve for the joint bolt (303) all the
way out of the rotor (401) with the brass spike.
7.2.1.3 Dismounting the joint shaft and drive side joint
Disassembly of the joint shaft and the joint of the drive
side takes place after dismounting the stator (402)
and the rotor (401). See Chapter 7.2.1.1 and 7.2.1.2.
! Dismount the joint on the drive side as described
in Chapter 7.2.1.2.
! Pull the joint shaft (307) off the plug-in shaft (125).
! Press the joint bush (302) out of the joint shaft
(307).
! Completely drive the sleeve for the joint bolt (303)
out of the plug-in shaft (125) with the brass spike.
7.2.1.4 Dismounting the shaft seal and plug-in shaft
Note: In case of pumps with shaft sealing by means
of stuffing box, you can change the packing rings as
described in Chapter 7.1.2.2 without dismounting the
plug-in shaft. Dismounting the plug-in shaft is required
when the pump is equipped with a mechanical seal.
In case of damages to the plug-in shaft in the area of
the shaft seal, the pump must also be dismounted as
described in the following.
! Dismount the stator (402) (see Chapter 7.2.1.1).
! Remove the hexagon nuts (607) and serrated
lock washers (608) as well as the hexagon screws
(606).
! Pull the suction casing (505) across the rotor
(401). Make sure that the finely crafted rotor is not
damaged.
! Take off the gasket for suction casing (501).
! Pull the thrower (123) off the clamp set (123).
! Loosen the clamp bolts of the clamp set (123)
evenly and in sequence.
! To do so, turn the plug-in shaft (125), if required.
Should the outer ring of the clamp set not come
off the inner ring on its own, you can unscrew
some of the clamp bolts and screw them into the
neighboring removing thread. Then untightening
is effortless.
Never pull out the clamp bolts all the way (danger
of accidents).
! Pull the plug-in shaft (125) with all parts of the
shaft seal and the clamp set (123) out of the lan-
tern socket.
! Pull the clamp set (123) off the plug-in shaft (125).
Dismounting the stuffing box
! Remove the self-locking hexagon nut (202) and
take off the gland halves (203).
! Pull the stuffing box casing (204) off the drive
shaft (118).
! Take off the stuffing box packing (207) with design
P02 including the flushing ring (208) and with de-
signs P03 and P04 including the sealing chamber
ring (209) from the stuffing box casing (204).
! For the design with shaft protection sleeve, pull off
the shaft protection sleeve (206) and the O seal-
ing ring (115) from the drive shaft (118).
Dismounting the single-acting mechanical
seal
! Pull off the mechanical seal housing (214) with the
counter-ring of the mechanical seal (219) (atmos-
phere side) off the plug-in shaft (125).
Note: Make sure that you pull off the casing with
the mechanical seal counter-ring concentric and
that it doesn't get jammed in order to prevent da-
mage to the counter-ring.
! Press the mechanical seal counter-ring and the
O-ring out of the mechanical seal housing (214).
Exert pressure evenly.
! Drive out the retaining pin (220).
! Loosen the grub screws in the rotating part of the
mechanical seal if provided (219) and pull the me-
chanical seal off the drive shaft (118).
Prior to loosening the grub
screws, mark respectively
measure the position of the mechanical seal on
the shaft protection sleeve or the drive shaft. Do
not slide the O-ring across the pressure spot of
the screw!
Dismounting the mechanical seal, single-
acting with throttle ring
! Remove the hexagon screws (245).
! Pull the mechanical seal housing (214) with the
counter-ring of the mechanical seal (atmosphere
side) (219) off the plug-in shaft (125).
Note: Make sure that you pull off the casing with
the mechanical seal counter-ring concentric and
that it doesn't get jammed in order to prevent
damage to the counter-ring.
! Pull off the O-ring (218).
! Press the mechanical seal counter-ring and the
O-ring out of the mechanical seal housing (214).
Exert pressure evenly.
! Drive out the retaining pin (220).
! Loosen the grub screws in the rotating part of the
mechanical seal (219) and pull the mechanical
seal off the plug-in shaft (125).
13
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
Prior to loosening the grub
screws, mark respectively
measure the position of the mechanical seal on
the shaft protection sleeve or the drive shaft. Do
not slide the O-ring across the pressure spot of
the screw!
! Pull the mechanical seal cover (215) with the
throttle ring (234) off the plug-in shaft (125).
! Open the throttle ring (234) and remove it with the
O-ring (235).
! Pull the retaining pins (236) out of the mechanical
seal cover (215).
Dismounting the mechanical seal, single-
acting with quench
! Pull the mechanical seal housing (214) with the
counter-ring of the mechanical seal (atmosphere
side) (219) off the plug-in shaft (125).
Note: Make sure that you pull off the casing with
the mechanical seal counter-ring concentric and
that it doesn't get jammed in order to prevent
damage to the counter-ring.
! Press the mechanical seal counter-ring and the
O-ring out of the mechanical seal housing (214).
Exert pressure evenly.
! Drive out the retaining pin (220).
! Loosen the grub screws in the rotating part of the
mechanical seal if provided (219) and pull the me-
chanical seal off the plug-in shaft (125).
Prior to loosening the grub
screws, mark respectively
measure the position of the mechanical seal on
the shaft protection sleeve or the drive shaft. Do
not slide the O-ring across the pressure spot of
the screw!
! Press the shaft seal ring (232) out.
Dismounting the mechanical seal, double-
action
! Remove the hexagon screws (245).
! Pull the mechanical seal housing (214) with the
counter-ring of the mechanical seal (atmosphere
side) (219) off the plug-in shaft (125).
Note: Make sure that you pull off the casing with
the mechanical seal counter-ring concentric and
that it doesn't get jammed in order to prevent
damage to the counter-ring.
! Pull off the O-ring (218).
! Loosen the grub screws in the rotating part of the
mechanical seal (219) and pull the mechanical
seal off the plug-in shaft (125).
Prior to loosening the grub
screws, mark respectively
measure the position of the mechanical seal on
the shaft protection sleeve or the drive shaft. Do
not slide the O-ring across the pressure spot of
the screw!
! Pull the mechanical seal cover (215) with the
counter-ring of the mechanical seal (product side)
(219) from the drive shaft (118).
Note: Make sure that you pull off the casing with
the mechanical seal counter-ring concentric and
that it doesn't get jammed in order to prevent
damage to the counter-ring.
! Press the mechanical seal counter-rings and O-
rings out of the mechanical seal housing (214)
and the mechanical seal cover (215). Exert pres-
sure evenly.
! Remove the retaining pins (220) and (236).
7.2.2 Assembly of the eccentric screw pump
General
Assembly of the individual pump components after
careful cleaning takes place in reverse direction.
7.2.2.1 Mounting the shaft seal and plug-in shaft
Mounting the stuffing box
! Slide the stuffing box casing (204) onto the plug-in
shaft (125).
! Install the stuffing box (207) with design P02 in-
cluding flushing ring (208) and with designs P03
and P04 including sealing chamber ring (209) into
the stuffing box casing (204). Also see Chapter
7.1.2.2 Mounting new packing rings.
Installation of the mechanical seal, general
Mechanical seals are high-quality precision parts. The
assembly instructions of the mechanical seal manu-
facturers must be observed. During installation, gentle
treatment and utmost cleanliness are prerequisites for
trouble-free functioning. To ease assembly, you may
lubricate the surfaces across which the O-rings glide
with lubricants like for example silicon oil, polydiol or
soft soap.
Do not use any normal oil.
Note: Make sure that parts that glide on top of each
other are always exchanged in pairs. When using
double PTFE-coated O-rings, make sure that the
seam of the outer coating points away from the as-
sembly direction. Otherwise the coating may open re-
spectively strip off (see figure 5).
Figure 5: Seam of the outer coating points away from
the assembly direction
Mounting the single-acting mechanical seal
! Drive the retaining pin (220) into the mechanical
seal housing (214).
! Press the mechanical seal counter-ring (219) with
the O-ring into the cleaned mechanical seal hous-
ing (214) concentrically.
Note: Ensure even distribution of pressure and
observe the retaining pin. The retaining pin (220)
may not protrude on the inside.
! Slide the rotating part of the mechanical seal
(219) onto the plug-in shaft (125).
Note: Observe the fitting dimension respectively
position of the mechanical seal exactly as marked
during disassembly.
! Insert grub screws, if provided, into the rotating
part of the mechanical seal (219) with the screw
fitting agent Loctite No. 241 or similar and tighten.
14
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
! Slide the mechanical seal housing (214) with the
mechanical seal counter-ring (219) across the
plug-in shaft (125).
Note: When sliding the mechanical seal housing
onto the drive shaft, make sure that the mechani-
cal seal housing is not jammed in order to avoid
damage to the mechanical seal counter-ring.
Installation of the mechanical seal, single-
acting with throttle ring
! Press the throttle ring (234) with the O-ring (235)
concentrically into the mechanical seal cover
(215).
Note: Observe even pressure distribution.
! Drive in the retaining pin (236) with a spike into
the mechanical seal cover (215). The retaining pin
may not protrude on the inside.
! Slide the mechanical seal cover (215) across the
plug-in shaft (125).
! The subsequent installation of the mechanical
seal takes place as described in Chapter Installa-
tion of the single-acting mechanical seal.
! Pull the O-ring (218) onto the mechanical seal
housing (214).
Slide the mechanical seal housing (214) with the
mechanical seal counter-ring (219) across the
drive shaft (118) and attach with the hexagon
screws (245) on the mechanical seal cover (215).
Installation of the mechanical seal, single-
acting with quench
! Installation of the mechanical seal takes place as
described in the Chapter Mounting the single-
acting mechanical seal.
! Drive in the retaining pin (220) with sealing agent
(251) Loctite No. 640 or similar.
! Press the shaft seal ring (232) into the cleaned
mechanical seal housing (214). Do not grease the
sealing lip.
Note: The sealing lip of the shaft seal must al-
ways point towards the side to be sealed (in-
wards).
Press the ring in with a suitable pressing stamp.
Make sure that the pressure force is exerted as
close as possible on the outer diameter of the
shaft seal ring.
In order to widen the sealing lip
of the shaft seal ring, the
mechanical seal housing (214) with the integrated
shaft seal ring (232) must initially be slid onto the
plug-in shaft (125) in reverse direction with the
shaft seal ring forward.
After widening, pull off the mechanical seal hous-
ing (214) off the plug-in shaft (125) and reinsert it
quickly with the flange side pointing forward onto
the plug-in shaft in the correct position.
Mounting the double-action mechanical seal
! Drive the retaining pin (236) into the mechanical
seal cover (215).
! Press the mechanical seal counter-ring (219) with
the O-ring concentrically into the mechanical seal
cover (215).
Note: Observe even pressure distribution and the
retaining pin. The retaining pin may not protrude
on the inside.
! Slide the mechanical seal cover (215) across the
plug-in shaft (125).
! The subsequent installation of the mechanical
seal takes place as described in the Chapter In-
stallation of the single-acting mechanical seal.
! Pull the O-ring (218) onto the mechanical seal
housing (214).
! Slide the mechanical seal housing (214) with the
mechanical seal counter-ring (219) across the
plug-in shaft (125) and attach with the hexagon
screws (245) on the mechanical seal cover (215).
Mounting the plug-in shaft
! The clamp sets (123) are delivered ready for in-
stallation. Therefore, they should not be dis-
mounted prior to initial tensioning.
! Deinstalled clamp sets (123) do not need to be
taken apart and relubricated prior to renewed ten-
sioning.
! Only clean and relubricate the clamp set (123)
when it is dirty.
! Use a solid-substance lubricant with a friction
value of = 0.04.
Lubricant Retail form/
manufacturer
Molykote 321 R
(sliding lacquer)
Spray/
Dow Corning
Molykote Spray
(powder spray)
Spray/
Dow Corning
Molykote G Rapid Spray or paste/ Dow
Corning
Aemasol MO 19 R Spray or paste/ A.C.
Matthes
Molykombin UMFT 1 Spray/
Klber Lubric.
Unimoly P 5 Powder/
Klber Lubric.
! In case of damaged cone surfaces, the clamp set
must be replaced.
! Grease the clamp bolt threads and head support
with Molykote and screw in the clamp bolts
manually until the heads of the clamp bolts come
to rest at the inner ring of the clamp set.
Do not tighten the clamp bolts
before sliding the plug-in shaft
(125) onto the drive shaft.
Clean and degrease the shaft of
the drive and the boring of the
plug-in shaft (125).
! Slide the thrower (123) onto the plug-in shaft
(125).
! Slightly grease the seat of the clamp set (123) on
the plug-in shaft (125) and slide the clamp set
(123) all the way onto the plug-in shaft (125).
! Slide the plug-in shaft (125) all the way onto the
drive shaft.
! Tighten the clamp bolts of the clamp set (123) in
sequence. To do so, turn the plug-in shaft if nec-
essary.
15
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
All clamp bolts have to be tight-
ened until the front surfaces of
the outer and inner ring are plane and the screw
pick-up increases strongly (see function state in
figure 6). The admissible screw pick-ups [Nm] are
engraved in the clamp set (123).
Figure 6: Clamp sets in the inner collar
! Check the right position of the clamp set (123) on
the plug-in shaft (125) in accordance with figure 6,
detail X.
! Pull the thrower (123) onto the clamp set (123).
7.2.2.2 Mounting the rotor and joints
! Drive the sleeve for the joint bolt (303) halfway
into the rotor (401) and the plug-in shaft with the
brass spike.
! Press the joint bush (302) into the joint shaft (307)
in such a way that the longitudinal axis of the oval
boring (marked by 2 notches) aligns with the
longitudinal axis of the joint shaft and that the joint
sleeve protrudes evenly on both sides of the joint
shaft. Not available with AEB1L 51, AEB1L 101,
AEB1E 50, AEB2E 50, AEB1N 25, AEB2N 25,
AEDB1E 75, AEDB 2N 38, AEB4H 12) (see figure
7).
Figure 7: Pressing in the joint sleeve
! Slide the joint clamps (306), the joint collar (308)
and the joint sleeve (304) onto the shaft of the
joint shaft (307).
! Slide the joint shaft (307) into the head of the rotor
(401) respectively the plug-in shaft (125).
! Slide the joint bolt (301) into the joint bush (302)
and completely drive in the sleeves for the joint
bolts (303).
! Emerize the joint sleeve (304) until smooth at the
outer diameter if required and pull onto the head
of the rotor (401) respectively the plug-in shaft.
! After pulling on the joint sleeve (304), secure this
against axial shifting on the head of the rotor (401)
respectively the plug-in shaft (125).
To do so, drive the end of the
joint sleeve (304) with a puncher
blow into the grove at the head of the rotor (401)
respectively the plug-in shaft (125) (see figure 8).
Figure 8: Securing the joint sleeve
! Pull on the joint collar (308) with a screwdriver, lift
on top with a screwdriver, guide the spray pipe of
the oil bottle underneath the collar and fill the joint
cavity with ALLWEILER special joint oil type B or
oil ET 1510 ISO 460 by Tribol Lubricants GmbH,
Mnchengladbach. For application in the food in-
dustry with ALLWEILER special joint oil type BL or
oil 1810/460 by Tribol Lubricants GmbH,
Mnchengladbach. For the filling quantity, see the
table in Chapter 7.1.2.4.
! Check, whether the bent loop of the joint clamp
(306) is attached to the joint clamp lock. If not,
press down with a common pair of flat-nosed pli-
ers (see figure 9).
Figure 9: Press down joint clamp loop onto joint clamp
lock
! Insert the joint clamps (306) into the circumferen-
tial grooves of the joint collar (308) and tighten.
16
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
Note: Use the following clamping tools for this
purpose:
For pump sizes smaller/equal
AEB1N 200, AEB2N 200, AEDB2N 300
AEB1E 380, AEB2E 380, AEDB1E 560
AEB1L 751, AEB.H 100
AE.H 100 the clamping tool with the name PoK-It
II.
For pump sizes larger/equal
AEB1N 380, AEB2N 380, AEDB2N 560
AEB1E 750, AEB2E 750, AEDB1E 1200
AEB1L 1001, AEB.H 200 the clamping tool with
the name Band-It together with the adapter J050.
You can purchase the above named tools from
us.
When clamping the joint clamps, proceed as fol-
lows:
Clamping with clamping tool Band-It and
adapter J050.
! Insert the band end of the joint clamp (306) into
the clamping tool with adapter up to the joint
clamp lock.
! Hold down the clamp end with the eccentric lever
of the clamping tool and tighten the joint clamp
(306) by turning the crank (figure 12).
Figure 12: Tighten the joint clamp with the clamping
tool Band-It and adapter J050
Note: The right tightening of the joint clamps (306) is
portrayed in figure 14.
Right Wrong Wrong
Joint clamp
(306) has
slightly drawn in
the outer collar
form and has a
tight fit.
Joint clamp
(306) is too
loose and may
slide off.
Joint clamp
(306) too tight.
Collar is dam-
aged (stripped
off).
Figure 11: Tightening the joint clamps
! Check that the joint clamp (306) is positioned in
the joint collar (308) across the entire circumfer-
ence in the collar groove.
! Slowly turn the clamping tool by approx. 60 up-
wards until the shear hook reaches behind the
joint clamp lock (see figure 12).
! Tighten the pressure screws by hand until the joint
clamp has a tight fit.
Figure 12: Shearing the joint clamp
! Turn the pressure screw with a spanner or ratchet
clockwise until the joint clamp is sheared off.
If the joint clamp is lifted up
slightly on the sheared off side,
adjust this by careful realignment. Do not hammer
or hit on the joint clamp lock, otherwise you may
damage the collar.
Note: Joint clamps made of hastelloy cannot be
sheared off with the clamping tool. After canting at
the joint clamp lock, shear off the joint clamp with
a pair of metal shears and deburr the cutting
edges (see figure 16).
Clamping with the clamping tool PoK-It II
! When using the clamping tool PoK-It II, cant the
joint clamp (306) after tightening on the joint
clamp lock by swiveling the clamping tool in such
a way that the clamp cannot slide back through
the lock. After canting at the joint clamp lock,
shear off the joint clamp with a pair of metal
shears and deburr the cutting edges (see figure
13).
Figure 13: Canting and shearing the joint clamp
Check whether the joint clamp is bent
in such a way that it cannot slide
back through the joint clamp lock (see figure 16). If
this is not the case, remove the joint clamp and re-
place it with a new one.
17
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
7.2.2.3 Mounting the stator
! Prior to pulling on, grease the stator (402) and ro-
tor (401) with lubricant (silicone oil, polydiol, soft
soap or similar).
Do not use any normal oil.
! With stators made of plastic or metal, insert stator
seals (403) and (404).
Note: With stators made of plastic, the stator seal
(403) with the O-ring must always lie on the outlet
side.
! Pull the stator onto the rotor (401).
Note: In case of difficulty, turn the stator (402)
with pliers at the same time. To do so, arrest the
plug-in shaft (125).
! Screw the pressure casing (504), support (612), if
provided, stator (402) and suction casing (505)
together with the clamp bolts (611) and the hexa-
gon nuts (609). Tighten the hexagon screws
evenly.
7.3 Replacement parts/spare parts
All stated pumps with the different shaft seal and
bearing designs are portrayed in the following sec-
tional drawings with parts list. The replacement
parts/spare parts are listed in the parts list.
Recommended replacement parts/spare parts:
R = large repair set
r = small repair set
For reasons of operational safety, you may only stock
and install original replacement parts supplied by us.
In this context, we refer to the statements in Chapter
2.7.
When ordering replacement parts/spare parts, state
the following:
Machine number
Abbreviation of the pump
Part number
Denomination and part quantity
or Ident No. and quantity
Note: The machine number and abbreviation of the
pump is embossed on the type plate.
The identity number and quantity are indicated in the
enclosed separate replacement parts list.
Part no. Denomination Pcs.
122 Lantern socket 1
123 Clamp set 1
125 Plug-in shaft R 1
201 T-head bolt 2
202 Self locking nut 2
203 Gland 1
204 Stuffing box casing 1
207 Stuffing box packing R, r !
208 Flushing ring 1
209 Sealing ring 1
212 Screw plug 1
213 Sealing tape 1
214 Mechanical seal housing 1
215 Mechanical seal cover 1
218 O-ring R 1
219 Mechanical seal R 1
220 Retaining pin 1
232 Shaft seal ring R 1
234 Throttle ring R 1
235 O-ring R 1
236 Retaining pin R 2
245 Hexagon nut 3
251 Sealing material 1
301 Joint bolt R, r 2
302 Joint sleeve R, r 2 "
303 Sleeve for joint bolt R, r 4
304 Joint collar R, r 2
305 Joint oil R, r !
306 Joint clamp R, r 4
307 Joint shaft R, r 1
308 Joint bush R, r 2
401 Rotor R, r 1
402 Stator R, r 1
403 Stator gasket, outlet-side R, r 1
404 Stator gasket, suction-side R, r 1
501 Gasket for suction casing R, r 1
502 Screw plug 1
503 Seal ring R 1 #
504 Pressure casing 1 #
505 Suction casing 1
506 Suction casing cover 2
507 Gasket R 2
508 Tap bolt 8
509 Nut 8
512 Reducing flange 1
513 O-ring R 1
525 Washer 8
601 Type plate 1
602 Half-round head grooved pin 4
603 Information plate "Start-up" 1
604 Information plate "Suction" 1
605 Information plate "Pressure" 1
606 Hexagon screw 4
607 Hexagon nut 4
608 Serrated lock washer 4
609 Hexagon nut 4
610 Washer 4
611 Clamp bolt 4
612 Support 1 $
613 Hexagon nut 2 %
Recommended spare parts:
R = large repair set
r = small repair set
! see Chapter 7.1.2.4
$ 2 pcs. with AEB4H 100-IE, AEB4H 200-IE
# 2 pcs. with connection piece position 2 and 4
% 4 pcs. with AEB4H 100-IE, AEB4H 200-IE
" n/a with AEB1L 51, AEB1L 101, AEB1E 50, AEB2E 50,
AEB1N 25, AEB2N 25, AEDB1E 75, AEDB2N 38, AEB4H 12
18
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
7.4 Sectional drawings with spare parts list and recommended replacement parts/spare parts for series AEB1L, AEB.E,
AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N; Designs IE, ZE
Sectional drawing for series AEB1L, AEB.N, AEDB1E, AEDB2N; Design IE
Stator with even elastomer wall thickness Winding protection on joint shaft
Stator of plastic material Worm on joint shaft
Stator of metal
19
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
Sectional drawing for series AEB.H; Design IE
P02 Stuffing box with flushing ring P03 Stuffing box with internal sealing
chamber ring
P04 Stuffing box with external sealing
chamber ring
G0K and G0N, mechanical seal, single-
acting
G0S and G0T, mechanical seal, single-
acting with throttle ring
G0Q mechanical seal, single-acting with
quench
G0D mechanical seal, double-acting
2
0
S
e
r
i
e
s
A
E
B
1
L
,
A
E
B
.
E
,
A
E
B
.
N
,
A
E
B
.
H
,
A
E
D
B
1
E
,
A
E
D
B
2
N
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
E
,
Z
E
S
e
c
t
i
o
n
a
l
d
r
a
w
i
n
g
f
o
r
s
e
r
i
e
s
A
E
B
.
N
;
D
e
s
i
g
n
Z
E
2
1
S
e
r
i
e
s
A
E
B
1
L
,
A
E
B
.
E
,
A
E
B
.
N
,
A
E
B
.
H
,
A
E
D
B
1
E
,
A
E
D
B
2
N
D
e
s
i
g
n
I
E
,
Z
E
S
e
c
t
i
o
n
a
l
d
r
a
w
i
n
g
f
o
r
s
e
r
i
e
s
A
E
B
.
H
;
D
e
s
i
g
n
Z
E
22
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
8. Operating faults, causes and remedial action
No. Operating troubles Cause and remedial action
Pump
does
not
start
Pump
does not
draw
Discharge
not
achieved
Pressure
height not
achieved
Pump
discharges
unevenly
Pump
emits
noises
Pump
is
stuck or no
longer
discharges
Motor
gets too
warm
Stator
wears down
prematurely
Leaking
shaft seal
a b c d e f g h i k
ALLWEILER eccentric screw pumps work disrup-
tion-free at all times when they are deployed in
accordance with the operating conditions stated in
our order confirmation and when the operating
instructions are observed.
1 ! !
High adhesion between the rotor and stator in a
new state after longer periods of standstill. Turn
pump by hand with auxiliary tools.
2 !
Check the rotation direction with the arrow on the
pump. In case of wrong direction, reverse the
polarity on the motor.
3 ! ! ! ! ! Check suction pipe and shaft seal for tightness.
4 ! ! ! !
Check suction height poss. increase suction pipe
diameter install larger filters open suction valve
all the way.
5 ! ! ! Check viscosity of the conveyor media.
6 ! ! !
Check the rotation speed of the pump check
rotation speed and power consumption of the drive
motor check voltage and frequency.
7 ! ! Avoid air bubbles in the conveyor medium.
8 ! ! ! ! !
Check pressure height open slider in the pres-
sure pipe all the way, remove congestion in the
pressure pipe.
9 ! ! ! ! !
Pump runs partially or completely dry.
Check whether there is sufficient conveyor media
on the suction side.
10 ! !
Increase the rotation speed with thin media and
large suction volume
11 ! ! !
Reduce rotation speed with viscous media
danger of cavitation.
12 !
Check longitudinal clearance of the joint bolts,
poss. joint bush wrongly mounted.
13 ! ! ! ! !
Check for foreign objects in the pump, dismount
pump, remove foreign objects, replace defect
parts.
14 ! ! ! !
Stator and rotor worn out. Dismount pump, replace
defect parts.
15 ! ! ! !
Joint parts (f, g) and/or drive shaft resp. shaft
protector sleeve (b, c) worn out: dismount pump,
replace defect parts.
16 ! ! ! ! Suction pipe partially or completely obstructed.
17 ! ! ! ! !
Check the temperature of the conveyor media
stator expansion too large stator stuck on the
rotor stator poss. burnt or swollen.
18 ! ! ! ! !
Stuffing box: exchange obsolete rings (b,c,k),
loosen gland (a,h), tighten gland (b,c,k)
19 ! ! ! !
Solid substance content and/or graining too large
reduce rotation speed: install a sieve with admis-
sible mesh width in front of the pump.
20 ! ! ! !
Solid substances sediment when the pump stands
still and harden. Rinse pump immediately, if nec-
essary dismount and clean.
21 ! ! ! ! !
Medium hardens when undercutting a certain
temperature limit heat pump.
23
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
VM 732.0002 GB / 12.03 Ident-Nr. 174 700
Series AEB1L, AEB.E, AEB.N, AEB.H, AEDB1E, AEDB2N
Design IE, ZE
Technical alterations reserved.
ALLWEILER AG
Business Unit Eccentric Screw Pumps
Postfach 200123 & 46223 Bottrop
Kirchhellener Ring 77-79 & 46244 Bottrop
Germany
Tel. +49 (0)2045 966-60
Fax. + 49 (0)2045 966-679
E-Mail: service-ge@allweiler.de
Internet: http://www.allweiler.com
1
Technical specifications and operating
instructions Safety valve type ASV
Membrane-type angular overflow valve
Operational data for safety valve according to order data sheet
Order No.: Identification No.:
Machine No.: Safety valve:
1. General information
1.1 Over-pressure
Eccentric spiral pumps are displacement pumps and
are theoretically capable of generating unlimited pres-
sure. When the pressure line is closed, the pressure
generated by the pump can lead to destruction of the
pipe or pump.
1.2 Use/area of application
Allweilers type ASV safety valves are an important
component of eccentric spiral pump installations.
They protect pumps, fittings, and pipes from exces-
sive pressure.
Fig. 1: Safety valve installation diagram
1.3 Code designation
1.4 Warranty
Our delivery conditions define the extent of our liability
for defective products. We accept no liability for dam-
ages that arise from failure to observe the operating
and maintenance instructions and the operating con-
ditions.
2. Safety
The safety notices described under point 2 in the
Maintenance and operating instructions for eccentric
spiral pumps must be observed at all times.
2.1 Safety notices for the owner/operator
Depressurize the system before opening the
valve (chapters 4 and 5).
3. Description
3.1 Structural design
The safety valve consists of a lower part, which
exhibits an angular shape, and an upper part,
which contains the individual functional parts.
The following variations of overflow valves are
available as standard equipment:
Design type D: with flange connection according to
DIN 2633
Design type R: with welding stud for piping
Design type A: with flange connection according
ANSI B16.5 class 150.
Description Part No. Description Part No.
Valve housing 1 Spring(s) 8
Membrane: 2 Adjustment screw 9
Pressure plate 3 O-ring 10
Glycerol 4 Lid 11
Cap 5 Sealing 12
Hexagon screw 6 Type plate 13
Hexagon nut 7 Round head
grooved pin
14
Fig. 2: Safety valve sectional drawing
Safety Valve Type ASV
2
Fig. 3: Allweiler safety valve dimensions
Membrane Type
CSM PTFE
coated
a b e h D s M !
ASV 20-1-R 153071 153078
ASV 20-2-R 153074 153081
52 27 80 140 27,5 3,0 1,7
ASV 20-1-D 153084 153090
ASV 20-2-D 153087 153093
91 66 80 179 - - 3,6
ASV 20-1-A 183154 196574
ASV 20-2-A 196575 196576
105,4 80,4 80 193,4 - - 4,0
ASV 32-1-R 153072 153079
ASV 32-2-R 153075 153082
65 35 100 192 43,0 3,5 3,2
ASV 32-1-D 153085 153091
ASV 32-2-D 153088 153094
106 76 100 233 - - 6,6
ASV 32-1-A 196570 196571
ASV 32-2-A 196572 196573
123,1 93,1 100 250,1 - - 7,0
ASV 50-1-R 153073 153080
ASV 50-2-R 153076 153083
90 43 140 226 61,0 3,5 7,2
ASV 50-1-D 153086 153092
ASV 50-2-D 153089 153095
136 89 140 272 - - 13,2
ASV 50-1-A 196577 196578
ASV 50-2-A 196579 196580
154,5 107,5 140 290,5 - - 14,0
! weight in kg
3.2 Material
Cap/pressure plate: Gray casting/steel
Valve housing: 1.4408 / 1.4571
Membrane: CSM
PTFE coated
3.3 Operational range
Pressure limits and flow rate according to characteris-
tic diagrams for Allweiler safety valves (fig. 5).
3.3.1 Temperature range
Membrane CSM: 0
o
C... 75
o
C
PTFE membrane coated: 0
o
C... 110
o
C
3.4 Method of operation (fig. 2)
The membrane uses the pressure springs initial ten-
sion (corresponds to the adjusted opening pressure)
to close the inlet channel. If the liquid pressure acting
on the membrane reaches the adjusted opening
pressure, the membrane will be lifted and the liquid
will flow into the outlet channel. The membrane will
reclose the outlet channel only when the liquid pres-
sure falls below the adjusted opening pressure. A
damping liquid (glycerol) prevents undesirable oscilla-
tions in the membrane and associated vibration
noises.
3.5 Prfung/Kennzeichnung
The safety valve is tested at the factory and set to the
opening pressure specified in the data sheet.
The following information is provided on the type
plate: type, order number, opening pressure.
A colored dot is placed between the lid and the cap to
provide a seal.
4. Set-up/installation
4.1 Setting up the valve
The safety valve is designed for the flow to come from
the bottom. The cap must stand vertically towards the
top. The valve must be installed in a way that no
static, dynamic, or thermal stresses can be trans-
ferred from the pipe and/or blow-off line to the over-
flow valve. An arrow indicates the proper flow direc-
tion.
4.2 Installing the valve
4.2.1 Installing with an Allweiler overflow line
In most cases, the safety valve will be installed to-
gether with an Allweiler overflow line between the
pressure and suction lines of an eccentric spiral
pump. In this way, proper installation is automatically
ensured.
Fig. 4: Safety valve with overflow line
The following standard variations of safety valves are
possible:
! Design type 1: with welding neck flanges
! Design type 2: with raised edge flanges
! Other design types available upon request
Safety Valve Type ASV
3
4.3 Adjustment
4.3.1 Basic settings
The safety valve is set at the factory to the opening
pressure (specified in the data sheet) that is suitable
for the respective application. As long as the opera-
tional conditions do not change, there is no need to
make any further adjustments.
4.3.2 Making readjustments (fig. 2)
Do the following to adjust the safety valve:
! Screw the lid (11) from the cap (5)
! Set the adjustment screw (9) while observing
the characteristic diagrams for Allweiler safety
valves (fig. 5).
Turn screw counterclockwise to decrease
the opening pressure.
Turn screw clockwise to increase the open-
ing pressure
! Screw the lid (11) into the cap (5)
5. Replacing the membrane
5.1 Disassembly (fig. 2)
! Remove the lid (11) with the O-ring (10).
! Use a caliper gauge to measure the position
(depth) of the adjustment screw (9).
! Turn the adjustment screw (9) counterclockwise
to remove it.
! Remove the pressure spring(s) (8).
! Loosen the hexagon nuts (7) and remove the
hexagon screws (6).
! Remove the cap (5) from the valve housing (1).
! Remove the pressure plate (3) with glycerol (4)
from the membrane.
! The membrane (2) is uncovered and can be ex-
changed.
5.2 Assembly (fig. 2)
! Place the membrane (2) onto the valve housing
(1) from the top.
! Place the pressure plate (3) centered onto the
membrane and fill completely with glycerol.
! Move the cap (5) from the top over the pressure
plate (3) and set the cap onto the membrane
(2) in a way that the membrane is centered be-
tween the valve housing (1) and the cap (5) in
the provided cut-out in the cap (5).
! Use the hexagon screws (6) and the hexagon
nuts (7) to screw together the cap (5) and the
valve housing (1).
! Insert the pressure spring(s) (8) and turn in the
adjustment screw (5) in a clockwise direction
until it reaches the depth you measured earlier.
! Screw the lid (11) with the O-ring (10) into the
cap (5).
6. Characteristic diagrams for Allweiler
safety valves (fig. 5)
The characteristic diagrams shown below can be
used for design purposes and for assigning the
proper valve sizes to various operational conditions.
They show the holding pressure in bar over the vol-
ume flow Q in liters per minute. The safety valves ad-
justed opening pressure serves as the parameter.
Safety Valve Type ASV
VM 701.0004 GB / 10.03 Ident-Nr. 153999
Pumped liquid: Water Temperature: 20
o
C
Fig. 5: Characteristic diagrams for Allweiler ASV safety valves
Subject to technical changes.
A Member of the
COLFAX PUMP GROUP
ALLWEILER AG
Geschftsbereich Exzenterschneckenpumpen
Postfach 200123 # 46223 Bottrop
Kirchhellener Ring 77-79 # 46244 Bottrop
Germany
Tel. +49 (0)2045 966-60
Fax. + 49 (0)2045 966-679
E-Mail: service-ge@allweiler.de
Internet: http://www.allweiler.com
Type ASV 20 - 2 - R (D) (A)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
0 20 40 60 80 100
8 bar
6 bar
4 bar
2 bar
10bar
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
p
[
b
a
r
]
Type ASV 20 - 1 - R (D) (A)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
0 20 40 60 80 100
4 bar
3 bar
2 bar
5 bar
.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
0
100 200 300 400
10bar
8 bar
6 bar
4 bar
2 bar
Type ASV 32 - 2 - R (D) (A)
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
p
[
b
a
r
]
Resonant range
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
0 200 400 600 800 1000
Type ASV 50 - 2 - R (D) (A)
6 bar
4 bar
2 bar
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
p
[
b
a
r
]
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
0 100 200 300 400
6 bar
4 bar
3 bar
2 bar
5 bar
1 bar
Type ASV 32 - 1 - R (D) (A)
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
p
[
b
a
r
]
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0 200 400 600 800 1000
Type ASV 50 - 1 - R (D) (A)
4 bar
3 bar
2 bar
5 bar
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
p
[
b
a
r
]
Volume flow Q [l/min]
Volume flow Q [l/min] Volume flow Q [l/min]
Volume flow Q [l/min]
S
e
t
o
p
e
n
i
n
g
p
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
P
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
p
[
b
a
r
]
Volume flow Q [l/min] Volume flowQ [l/min]
S
e
t
o
p
e
n
i
n
g
p
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
S
e
t
o
p
e
n
i
n
g
p
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
S
e
t
o
p
e
n
i
n
g
p
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
S
e
t
o
p
e
n
i
n
g
p
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
S
e
t
o
p
e
n
i
n
g
p
r
e
s
s
u
r
e
1. General informati on 3. Description
1.1 Dry-running
Dry-running occurs when there is an absence of
pumped liquid at the suction side. When this hap-
pens, the heat energy that is generated by dry friction
and flexing work in the pumping elements of the ec-
centric screw pump will no longer be carried off in a
sufficient amount, thereby destroying after just a few
revolutions the elastomer found in the inner contour of
the stator.
1.2 Use/area of application
The magnetic valve is a device designed to be in-
stalled on the suction side of an eccentric screw
pump for the purpose of delaying the damage that is
caused by dry-running during both starting and opera-
tion.
The magnetic valve does not provide dryrunning
protection.
When pumped liquid is absent for an extended
period of time, the destruction of the stator
elastomer will only be delayed, not prevented!
It is not possible to predict the duration of dry-
running before the elastomer is damaged!
1.3 Warranty
Our delivery conditions define the extent of our liability
for defective products. We accept no liability for dam-
ages that arise from failure to observe the operating
and maintenance instructions and the operating con-
ditions.
2. Safety
Always observe the notices contained in section 2 of
the maintenance and operating instructions for eccen-
tric screw pumps.
2.1 Safety notices for the owner/operator
Always observe the information provided in the mag-
netic valve manufacturers operating instructions.
Technical specifications and operating
instructions
Magnetic valve D205DBZ
Servo-controlled 2/2-way magnetic valve
for use with eccentric screw pumps
Operational data for magnetic valve according to order data sheet
Order No.: Identification No.:
Machine No.: Magnetic valve: Type 205 DBZ
3.1 Structural design
Servo-controlled 2/2-way magnetic valve
3.2 Dimensioned drawing
3.3 Technical specifications
Valve designation:
Pumped liquid:
Liquid temperature:
Housing material:
Gasket material:
Connection:
Rated diameter:
Flow rate Kv:
Pressure range, min.:
Pressure range, max.:
Weight:
Protection type:
Coil designation:
Coil voltage:
Coil power:
Switching function:
D205 DBZ
water, oil
-10 C to +90 C
brass
NBR
G
13 mm
63 Lpm
0.3 bar
16 bar
0.4 kg
IP65 (with plug)
Series 7000
230/240 V 50/60 Hz AC
18VA (stopping) AC
36VA (pick-up)
DC 14W
normally closed
1
100
Magnet i c val ve
3.4 Oper at i on
5. Electrical connection
5.1 Structural design
by DIN connector (scope of supply)
5.2 Dimensioned drawing
When the pump is in operation, the magnetic valve facilitates
injection of rinsing water into the suction housing of the
eccentric screw pump. When there is an absence of pumped
liquid, the injected rinsing water removes heat from the pump
elements and reduces friction between the rotor and stator.
The magnetic valve does not provide dry-running protection.
When pumped liquid is absent for an extended period of time,
the destruction of the stator elastomer will only be delayed,
not prevented!
5.3 Technical specification
Rated voltage (Max.): 250V AC -300V DC
Power rating: 10 A (Rated)/16A (Max.)
Wire cross-section: 1.5 mm
2
(Max.)
Cable diameter: 6-8mm (PG9)
Protection class: IP65 - EN 60529
Insulation class: group C - VDE 01 10
4. Set-up/installation
The magnetic valve is normally installed on the eccentric
screw pumps lateral rinsing connection on the suction
housing.
A Member of the
COLFAX P UMP GROUP
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
Diese Betriebsvorschrift enthlt grundlegende
Hinweise, die bei Aufstellung, Betrieb und War-
tung zu beachten sind. Daher ist diese Betriebs-
vorschrift unbedingt vor Montage und Inbetrieb-
nahme vom Monteur sowie dem zustndigen
Fachpersonal/ Betreiber zu lesen und mu stn-
dig am Einsatzort des Maschine/Anlage verfgbar
sein.
These operating instructions contain basic informati-
on to be observed during installation, operation and
maintenance. For this reason the operating instructi-
ons should always be read by the mechanic as well
as responsible operator before assembly and start-
up and should be available at all times at the place of
installation of the machine/system.
Betriebsanleitung / Operating instructions
Kommissions-Nr. / Serial No.
Typ / Type
Bestell-Nr. / Order No.
Spannung / Voltage
Schaltplan / Circuit diagram
AELD
230V 50/60Hz
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
2
Inhaltsverzeichnis Table of contents
1 Allgemeines
2 Sicherheitshinweise
2.1 Kennzeichnung von Hinweisen in der Betriebsan-
leitung
2.2 Personalqualifikation und Schulung
2.3 Gefahren bei Nichtbeachtung der Sicherheitshin-
weise
2.4 Sicherheitsbewutes Arbeiten
2.5 Sicherheitshinweise fr Betreiber
2.6 Hinweise fr Wartungs-, Inspektions- und Mon-
tagearbeiten
2.7 Eigenmchtiger Umbau und Ersatzteilherstellung
2.8 Unzulssige Betriebsweisen
2.9 Transport
3 Allgemeine Beschreibung
3.1 Hinweis zu Sonderausfhrungen
3.2 Verwendung
3.3 Ausfhrung
3.4 Funktion
4 Installation
5 Inbetriebnahme
1 General
2 Safety
2.1 Marking of information in these operating instruc-
tions
2.2 Personnel qualifications and training
2.3 Hazards ipon failure to observe safety information
2.4 Safety-conscious operation
2.5 Safety instructions for operator
2.6 Information on maintenance, inspection and as-
sembly work
2.7 Unauthorized conversion or production of replace-
ment parts
2.8 Impermissible methods of operation
2.9 Transport
3 General Description
3.1 Note for special design
3.2 Application
3.3 Design
3.4 Function
4 Installation
5 Commissioning
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
3
6 Wartung und Instandhaltung
6.1 Demontage und Montage des Druckluftejektors
6.2 Demontage und Montage des Dsensystems
6.3 Demontage und Montage des Absperrventils
7 Anhang
7.1 Produktdaten
7.2 Mablatt
7.3 Installationsbeispiel
7.4 Ersatzteile
7.5 Schaltplan
6 Maintenance and repair
6.1 Disassembly and assembly of the compressed air
ejector
6.2 Disassembly and assembly of the jet system
6.3 Disassembly and assembly of the shut-off system
7 Appendix
7.1 Product data
7.2 Dimensions
7.3 Installation example
7.4 Spare parts
7.5 Circuit diagram
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
4
1. Allgemeines
Diese Betriebsanleitung enthlt grundlegende Hinweise,
die bei Aufstellung, Betrieb und Wartung zu beachten
sind. Daher ist diese Betriebsanleitung unbedingt vor
Montage und Inbetriebnahme vom Monteur sowie dem
zustndigen Fachpersonal/Betreiber zu lesen und mu
stndig am Einsatzort der Maschine/Anlage verfgbar
sein.
Ein strungsfreier Betrieb der Maschine/Anlage kann
nur erreicht werden, wenn diese sorgfltig montiert und
richtig gewartet wird. Es ist unbedingt darauf zu achten,
da die vorliegende Betriebsanleitung beachtet wird
und die Maschine/Anlage nicht fr andere als die von
uns angegebenen Betriebsverhltnisse eingesetzt wird.
Die Betriebsanleitung bercksichtigt nicht die ortsbezo-
genen Sicherheitsbestimmungen, fr deren Einhaltung
auch seitens des hinzugezogenen Montagepersonals,
der Betreiber verantwortlich ist. Das Fabrikschild an der
Maschine/Anlage nennt die Baureihe/Gre, die Werks-
Nr., die wir bei Rckfragen, Nachbestellung und insbe-
sondere bei Bestellung von Ersatzteilen stets anzuge-
ben bitten. Im Schadensfalle wenden Sie sich bitte an
unsere nchstgelegene Kundendienststelle.
1. General
These operating instructions contain basic information
to be observed during installation, operation and main-
tenance. For this reason the operating instructions
should always be read by the mechanic as well as re-
sponsible personnel/operator before assembly and
start-up and should be available at all times in the vicin-
ity of the machine/system.
Malfunction-free operation of the machine/system is
only possible when it is assembled carefully and main-
tained properly. Always ensure that these operating
instructions are observed and that the machine/system
is not used for other operating conditions as those
specified by us. The operating instructions do not take
in consideration local safety regulations for which the
operator is responsible for maintaining also on the part
of installation personnel used. The factory rating plate
on the machine/system specifies the model/size, serial
number, which we request you to specify on any que-
ries, subsequent orders and particularly when ordering
replacement parts. In the event of damage please con-
tact our nearest customer service point.Safety informa-
tion, which can result in a hazard for the machine and
its functions when not observed, is indicated by the
following word:
Achtung Caution
Diese Anlage darf nicht ber die auf dem Fabrikschild
festgelegten Grenzwerte bezglich Menge, Drehzahl,
Druck und Temperatur oder andere in der Betriebsan-
leitung-Vertragsdokumentation enthaltenen Anweisun-
gen betrieben werden. Vorgeschriebene elektrische
Anschluwerte sowie Montage- und Wartungsanwei-
sungen sind unbedingt einzuhalten. Das Handhaben
der Maschine/Anlage auerhalb der vorgenannten Be-
dingungen fhrt zu berbeanspruchungen, denen sie
nicht standhalten kann. Das Nichtbeachten dieser War-
nungen kann zu Personen- und Sachschden fhren.
Zur Beachtung
Die Beschreibungen und Instruktionen in dieser Be-
triebsanweisung betreffen die Standardausfhrung.
Diese Betriebsanleitung bercksichtigt weder alle Kon-
struktionseinzelheiten und Varianten noch alle mgli-
chen Zuflligkeiten und Ereignisse, die bei Montage,
Betrieb und Wartung auftreten knnen.
Vorraussetzung fr das Handhaben der Anlage ist der
Einsatz von fachlich geschultem Personal. Sofern nicht
alle Informationen und Anweisungen in dieser Betrieb-
sanleitung gefunden werden, fragen Sie bei der
nchstgelegenen Kundendienststelle nach.
Der Hersteller bernimmt fr die Anlage keine Verant-
wortung, wenn diese Betriebsanleitung nicht beachtet
wird.
This system must not be operated beyond the limits
specified on the factory rating plate in terms of quantity,
rotary speed, pressure and temperature or other in-
structions contained in the operating instructions and
contract documents. Always observe prescribed electri-
cal connection values as well as installation and warn-
ing information. Operation of the machine/system out-
side of the specified conditions leads to excessive
stress, which it cannot withstand. Failure to observe this
warning can lead to personnel injury and property dam-
age.
Note
The descriptions and instructions in these operating
instructions apply to the standard version. These oper-
ating instructions cannot take into consideration all de-
sign details and variations nor all possibilities and
events, which can occur during installation, operation
and maintenance.
The system should be operated only by properly trained
personnel. If you cannot find all information or instruc-
tions in these operating instructions, please ask at the
nearest customer service point.
The manufacturer assumes no liability for the system
when these operating instructions are not observed.
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
5
2. Sicherheitshinweise
2.1 Kennzeichnung von Hinweisen in der Betriebsan-
leitung
Die in der Betriebsanleitung enthaltenen Sicherheit-
shinweise, die bei Nichtbeachtung Gefhrdungen fr
Personen hervorrufen knnen, sind mit dem allge-
meinen Gefahrsymbol
Sicherheitszeichen nach DIN 4844 - W 9,
bei Warnungen vor elektrischer Spannung mit
Sicherheitszeichen nach DIN 4888 - W 8
besonders gekennzeichnet.
Bei Sicherheitshinweisen, deren Nichtbeachtung Ge-
fahren fr die Maschinen und deren Funktion hervorru-
fen kann, ist nachfolgendes Wort eingefgt.
2. Safety
2.1 Marking of information in these operating instruc-
tions
Safety information contained in these operating instruc-
tions, which could result in hazards for humans when
not observed, is generally marked with the following
hazard symbol:
Safety symbol according to DIN 4844 - W 9.
Warnings for electrical voltage are marked with
safety sign according to DIN 4888 - W 8
Safety information, which can result in a hazard for the
machine and its functions when not observed, is indi-
cated by the following word:
Achtung Caution
Direkt an der Maschine angebrachte Hinweise wie z.B.
- Drehrichtungspfeil
- Kennzeichen fr Fluidanschlsse mssen unbedingt
beachtet und in vollstndig lesbarem Zustand ge-
halten werden.
2.2 Personalqualifikation und Schulung
Das Personal fr Bedienung, Wartung, Inspektion und
Montage mu die entsprechende Qualifikation fr diese
Arbeiten aufweisen. Verantwortungsbereich, Zustndig-
keit und die berwachung des Personals mssen durch
den Betreiber genau geregelt sein. Liegen bei dem Per-
sonal nicht die ntigen Kenntnisse vor, so ist dieses zu
schulen und zu unterweisen. Dies kann, falls erforder-
lich, im Auftrag des Betreibers der Maschine durch den
Hersteller/Lieferer erfolgen. Weiterhin ist durch den
Betreiber sicherzustellen, da der Inhalt der Betrieb-
sanleitung durch das Personal voll verstanden wird.
2.3 Gefahren bei Nichtbeachtung der Sicherheitshin-
weise
Die Nichtbeachtung der Sicherheitshinweise kann
sowohl eine Gefhrdung von Personen als auch fr
Umwelt und Maschine zur Folge haben. Die Nicht-
beachtung der Sicherheitshinweise kann zum Verlust
jeglicher Schadensersatzansprche fhren. Im einzel-
Information attached directly to the machines such as
- Direction of rotation arrows
- Markings for fluid connections must be observed
under all circumstances and kept in a completely
legible condition.
2.2 Personnel qualifications and training
The personnel for operation, maintenance, inspection
and installation must be properly qualified for such
work. The range of responsibility and supervision of the
personnel must be regulated precisely by the operator.
It the personnel does not possess the required knowl-
edge, they must be trained and/or instructed. If neces-
sary this can be accomplished by the manufac-
turer/supplier upon request of the machine operator.
Moreover, the operator must ensure that the personnel
is completely familiar with the contents of the these
operating instructions.
2.3 Hazards upon failure to observe safety information
Failure to observe the safety instructions can result in a
hazard to humans as well as for the environment and
the machine. Failure to observe the safety instructions
can void all liability claims. In detail failure to observe
the safety instructions can result in the following haz-
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
6
nen kann Nichtbeachtung beispielsweise folgende Ge-
fhrdungen nach sich ziehen:
- Versagen wichtiger Funktionen der Maschine/An-
lage
- Versagen vorgeschriebener Methoden zur Wartung
und Instandhaltung
- Gefhrdung von Personen durch elektrische,
mechanische und chemische Einwirkungen
- Gefhrdung der Umwelt durch Leckage von gefhr-
lichen Stoffen
2.4 Sicherheitsbewutes Arbeiten
Die in dieser Betriebsanweisung aufgefhrten Sicher-
heitshinweise, die bestehenden nationalen Vorschriften
zur Unfallverhtung sowie eventuelle interne Arbeits-,
Betriebs-, und Sicherheitsvorschriften sind zu beachten.
2.5 Sicherheitshinweise fr den Betreiber
- Fhren warme und kalte Maschinenteile zu Ge-
fahren, mssen diese Teile bauseits gegen Berh-
rung gesichert sein.
- Berhrungsschutz fr sich bewegende Teile darf bei
in Betrieb befindlicher Maschine nicht entfernt wer-
den.
- Leckagen ( z.B. an der Wellenabdichtung) gefhrli-
cher Medien (z.B. explosiv, giftig, warm) mssen so
abgefhrt werden, da keine Gefhrdung fr Per-
sonen und Umwelt entsteht. Gesetzliche Bestim-
mungen sind einzuhalten.
- Gefhrdungen durch elektrische Energie sind
auszuschlieen (Einzelheiten hierzu sind z.B. in den
Vorschriften des VDE und der rtlichen Energiever-
sorgungsunternehmer)
2.6 Hinweise fr Wartungs-, Inspektions- und Mon-
tagearbeiten.
Der Betreiber hat dafr zu sorgen, da alle Wartungs-,
Inspektions- und Montagearbeiten von autorisierten und
qualifizierten Fachpersonal ausgefhrt werden, da sich
durch eingehendes Studium der Betriebsanleitung aus-
reichend informiert hat.
Grundstzlich sind Arbeiten an der Maschine nur im
Stillstand durchzufhren. Die in der Betriebsanleitung
beschriebene Vorgehensweise zum Stillsetzen der Ma-
schine/Anlage mu unbedingt eingehalten werden. Bei
Maschinen/Anlagen, die mit nachstehend aufgefhrten
Gefahrstoffen und/oder umweltgefhrdenden Frder-
medien betrieben werden, mu der Kunde/Betreiber im
Reparaturfall oder bei einer Rcksendung an unser
Werk bzw. unsere Vertragswerkstatt das eigene bzw.
unser Personal vor Ort unaufgefordert informieren. In
diesem Fall ist uns mit der Anforderung eines Kunden-
dienst-Monteuers ein Frdergutnachweis, z.B. in Form
eines DIN-Sicherheitsblattes vorzulegen.
Alternativ fordern Sie ein Unbedenklichkeits-
bescheinigungs-Formular an und fllen dieses
wahrheitsgem, korrekt und vollstndig aus. Senden
ards:
- Failure of important machine/system functions
- Failure of specified methods for maintenance and
repair
- Hazards for humans resulting from electrical shock,
mechanical and chemical effects.
- Hazard for the environment resulting from leakage of
dangerous substances.
2.4 Safety-conscious operation
The safety instructions contained in these operating
instructions, the existing national regulations on acci-
dent prevention as well as all internal operating, labour
and safety regulations must be observed.
2.5 Safety instructions for operator
- If hot and cold machine parts present a hazard, such
parts must be secured against unintentional contact.
- Contact guards for moving parts should never be
removed from machines while in operation.
- Leakage ( e.g. at shaft seals) of dangerous sub-
stances (e.g. explosive, toxic, hot) must be elimi-
nated in such a manner that hazards do not result
for humans or the environment. Observe all legal
regulations.
- Hazards resulting from electrical power must be
excluded (for details see VDE regulations and regu-
lations of local power company).
2.6 Information on maintenance, inspection and as-
sembly work
The operator must ensure that all maintenance, inspec-
tion and assembly work is accomplished by authorized
and qualified personnel, who have informed themselves
by studying the operating instructions in detail.
Work should be performed on the machine only when it
is standing still as a matter of principle. The procedures
described in the operating instructions for shutting down
the machine/system must be maintained under all cir-
cumstances. On machines/systems, which are operated
with the hazardous substances listed below and/or envi-
ronment polluting substances, the customer/operator
must inform his own or our personnel locally or our plant
or authorized workshop when the machine is returned,
before repair is performed. In such cases it is necessary
to submit to us a certificate on the substances trans-
ported, e.g. in the form of a DIN safety sheet, when a
customer service mechanic is requested.
As an alternative you can request a safety certification
form and fill it out truthfully, correctly and completely.
Return this form filled out to the point where the repair is
to be performed or present it to our requested service
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
7
Sie das ausgefllte Formular an die mit der Reparatur
beauftragte Stelle oder legen Sie dieses unserem
angefordertem Kundendienst-Monteur vor.
Gefahrstoffe:
- giftige Stoffe
- gesundheitsgefhrdende Stoffe
- tzende Stoffe
- Reizstoffe
- explosionsgefhrliche Stoffe
- brandfhrende, hoch- und leichtentzndliche Stoffe
- krebserzeugende Stoffe
- fruchtschdigende Stoffe
- erbgutverndernde Stoffe
- Stoffe die auf sonstige Weise dem Menschen ge-
fhrlich sind
Bei allen Arbeiten vor Ort ist das eigene bzw. unser
Montagepersonal auf Gefahren, welche im Zusammen-
hang mit Reparaturen entstehen knnen, aufmerksam
zu machen.
Die in der Betriebsanleitung beschriebenen Mon-
tageschritte sind konsequent einzuhalten.
Unmittelbar nach Abschlu der Arbeiten mssen alle
Sicherheits- und Schutzeinrichtungen wieder ange-
bracht und in Funktion gesetzt werden.
Vor der erneuten Inbetriebnahme sind die im Abschnitt
Inbetriebnahme aufgefhrten Punkte zu beachten.
2.7 Eigenmchtiger Umbau und Ersatzteilherstellung
Umbau und Vernderungen der Maschine/Anlage sind
nur nach Absprache mit dem Hersteller zulssig. Origi-
nalersatzteile und vom Hersteller autorisiertes Zubehr
dienen der Sicherheit. Fr Schden, die durch die Ver-
wendung von Nicht-Originalteilen und Zubehr entste-
hen, ist jedwede Haftung des Herstellers aus-
geschlossen.
2.8 Unzulssige Betriebsweisen
Die Betriebssicherheit der gelieferten Maschine/Anlage
ist nur bei bestimmungsgemer Verwendung entspre-
chend Kapitel 1 - Allgemeines - der Betriebsanleitung
gewhrleistet. Die im Datenblatt angegebenen
Grenzwerte drfen auf keinen Fall berschritten wer-
den.
2.9 Transport
Beim Transport der Maschine/Anlage sind die dafr
vorgesehenen Transportsen (sofern vorhanden) fr
die Tragseile zu verwenden.
Die Kranvorrichtung und die Tragseile mssen ausrei-
chend dimensioniert sein.
mechanic.
Hazardous substances:
- Toxic substances
- Health endangering substances
- Caustic substances
- Irritating substances
- Explosive substances
- Combustible, highly and easily inflammable sub-
stances
- carcinogenic substances
- Embryo-damaging substances
- Gene-mutating substances
- Substances dangerous for humans in other manners
When tasks are carried out on site, your own personnel
or ours are to be cautioned at all times about the haz-
ards which can occur when carrying out re-
pair/maintenance tasks.
The assembly procedure described in the Operating
Instructions is to be strictly adhered to.
Directly after ending work, all safety and protection
measures must be brought into effect once more and
applied.
Before a re-starting of operation, the points listed and
described in the Section Putting into / out operation
must be observed.
2.7 Unauthorised conversion or production of replace-
ment parts
Conversion or modification of the machine/system is
permissible only with the manufacturer's approval.
Original parts and accessories authorized by the
manufacturers ensure safety. Damage resulting from
the use of non-original parts and accessories exclude
any liability on the part of the manufacturer.
2.8 Impermissible methods of operation.
The operating safety of the delivered machine/system is
ensured only when used as intended according to
Chapter 1 - General - in the operating instructions. The
limits specified in the data sheet must not be exceeded
under any circumstances.
2.9 Transport
When transporting the machine/system use the trans-
port eyes (if present) intended for this purpose for the
hoisting cables.
The crane and hoisting cables must be sufficiently di-
mensioned.
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
8
3. Allgemeine Beschreibung 3. General Description
3.1 Hinweise zu Sonderausfhrungen
Bitte beachten Sie bei Sonderausfhrungen die Seite
Sonderausfhrung.
3.1 Note for special design
In case of special design please pay attention to the
page named Special design.
3.2 Verwendung
Ansaugautomat fr Kreiselpumpen, fr die ein kurzzeiti-
ger Trockenlauf zulssig ist.
Fr Kreiselpumpen, fr die ein Trockenlauf nicht zuls-
sig ist, empfehlen wir die Typenreihen AELE, AELC und
AELG.
3.2 Application
Automatic aspirator designed for centrifugal pumps
where dry running is admissable for short periods of
time.
We recommend the following ranges for centrifugal
pumps where dry running is not admissable: AELE,
AELC and AELG.
3.3 Bauart
Druckgesteuerter Ansaugautomat mit Druckluftejektor
als Vakuumerzeuger. Durch das Polyamid Dsensy-
stem ist das Gert weitgehend unempfindlich gegen
aggressive Flssigkeiten wie z.B. Seewasser.
Komponenten:
- Druckluftejektor mit integriertem Absperrventil
- Druckluft-Magnetventil
- Druckschalter
- Klemmenkasten
3.3 Design
Pressure controlled automatic aspirator with a com-
pressed-air ejector acting as a vacuum generator. Due
to the polyamide nozzle system, the unit is resistant, to
a large degree, against aggressive fluids (eg. see wa-
ter). Components:
- Compressed-air ejector with integrated shut-off valve
- Compressed-air solenoid valve
- Pressure switch
- Terminal box
3.4 Funktion
Bei Einschaltung der Kreiselpumpe schaltet zunchst
nur der Ansaugautomat ein. Nach Ablauf des Zeitrelais
in der Pumpensteuerung schaltet die Kreiselpumpe zu.
Der Ansaugautomat schaltet ber den Druckschalter
ab, sobald die Kreiselpumpe den Frderdruck aufge-
baut hat. Sinkt der Frderdruck durch Gasanfall
whrend des Pumpenbetriebes wieder ab, schaltet der
Ansaugautomat zur Nachevakuierung ein.
Wird ein lngerer Trockenlauf der Pumpe zugelassen,
so kann auf das Zeitrelais in der Pumpensteuerung
verzichtet werden.
3.4 Operation
When the centrifugal pump is turned on, only the auto-
matic aspirator will be activated. After the time-limit
relay sequence has been completed, the centrifugal
pump is also activated. As soon as the centrifugal pump
has built up the necessary discharge pressure, the aspi-
rator is switched off via the pressure switch. Should the
discharge pressure fall again during pump operation
through gas accumulation, the automatic aspirator
starts up once more for re-evacuation.
lf a longer period of dry running is permissible, the time-
limit relay sequence in the pumping control system does
not have to be carried out..
4. Installation 4. Installation
Achtung Caution
Grundstzlich mssen alle Entlftungsleitungen
vom Anschlupunkt zum Ansaugautomaten hin
stetig steigend verlegt werden. Fr die zu whlen-
den Nennweiten der Entlftungsleitungen gilt als
Anhaltspunkt die Gre der dafr vorgesehenen
Anschlsse am Ansaugautomaten.
Das Langnippel und die dazugehrige Gegenmutter
drfen bei der Installation nicht verdeht werden.
Fundamentally every ventilating pipe is to be in-
stalled ascending from the ventilating point to the
priming unit. As a indication for selecting the nomi-
nal size of the ventilating pipes please refer to the
respective connection size at the priming unit.
The long nippel and the corresponding check nut
may not to be twisted.
Der Ansaugautomat wird als betriebsfertige Montage-
einheit geliefert und gem Installationsbeispiel im An-
hang min. 300mm oberhalb des hchsten zu entlften-
The automatic aspirator is delivered as a ready-to-install
unit and is to be fitted, according to installation example
inside appendix, min. 300mm above the highest point to
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
9
den Punktes (z.B. dem Pumpengehuse) angeordnet.
Dieser Entlftungspunkt wird ber eine steigend zu
verlegende Entlftungsleitung mit dem Anschlu A ver-
bunden. Der Abluftstutzen B darf nicht abgesperrt wer-
den. Der Anschlu C ist mit Druckseite der Kreisel-
pumpe zu verbinden.
Die maximale Aufstellungshhe ber dem niedrigsten
saugseitigen Flssigkeitsstand darf bei Wasser als
Frdermedium nicht mehr als 7 m, abzglich der dyna-
mischen Verluste des Saugsystems betragen.
be evacuated (e.g. the pumpe casing).
The highest point to be evacuated will be connected to
connection A by means of an ascending air vent pipe.
Exhaust nozzle B must not be shut-off. The connection
C has to be connected to the discharge side of the cen-
trifugal pump.
In case of water as pumping media the maximum in-
stallation height over the lowest intake-sided liquid level
must not exceed 7 m, minus the dynamical losses of
the suction system.
Achtung Caution
Die Nennweite der Rohrleitung zur Druckluftversor-
gung mu so gewhlt werden, da die erforderliche
Arbeits-Druckluft am Anschlu P des Ansaugauto-
mat whrend des Betriebes anliegt.
The nominal size of the piping for compressed-air
supply has to be selected, that the required working
air is available at the connection P of the automatic
aspirator during operation.
ber den Anschlu P ist der Ansaugautomat mit
Druckluft oder hnlichem Treibgas zu versorgen.
Via connection P the automatic aspirator is to be sup-
plied with compressed air or equivalent driving gas.
5. Inbetriebnahme
Bei der Inbetriebnahme sind folgende Schritte zu
beachten:
- Rohranschlsse und Rohrleitungen auf ord-
nungsgeme Verlegung und Dichtigkeit ber-
prfen.
- Elektroanschlsse kontrollieren.
- Druckluftanschlu kontrollieren
5. Commissioning
For commissioning pay attention to following steps:
- Check all pipe connections and pipes for proper lay
and leakage.
- Check all electrical connections.
- Check the compressed air connection
Achtung Caution
Abweichungen bei Sonderausfhrungen beachten. Please pay attention to modification for special design.
6. Wartung und Instandsetzung
Das System arbeitet mit geringem Wartungsaufwand.
Folgende Kontrollen bzw. Arbeiten sollten je nach
Frdermedium, Betriebsart und Betriebsdauer in
festzulegenden Zeitabstnden durchgefhrt werden.
- Kontrolle aller Komponenten auf ordnungsgeme
Funktion
6. Maintenance and repair
The system functions with slightly maintenance work.
Following inspections respectively work should be per-
formed in fixed intervals which depend on pumping
medium, operation mode and operation time.
- Check all components for proper function
6.1 Demontage und Montage eines Druckluftejektors
Vor Beginn der Demontage ist der Druckluftejektor
elektrisch frei zu schalten.
6.1 Disassembly and assembly of the compressed air
ejector
Before starting work, the compressed air ejector
must be switched to a power off mode.
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
10
Vor Beginn der Demontage ist der Druckluftejektor
von der Druckluftversorgung zu trennen.
Anzugsdrehmomente fr die Schraubverbindungen sind
der dementsprechenden DIN-Norm zu entnehmen.
Before starting work, the compressed air ejector
must be disconnected from the compressed air
supply.
Starting torque for the thread connections are to be
taken from the corresponding DIN-Norm.
Achtung Caution
Wir empfehlen alle Dichtungen bei Instandsetzungs-
arbeit zu ersetzen.
Demontage des Druckluftejektors:
- Kabelstecker am Magnetventil des Druckluftejetors
abnehmen.
- Abluft- und Druckluftleitung lsen.
- Befestigungsschrauben des Druckluftejektor ent-
fernen und Druckluftejektor abnehmen.
Die Montage erfolgt in umgekehrter Reihenfolge.
We advise to exchange all sealings at reapir work.
Disassembly of the compressed air ejector:
- Take off cable plugat the solenoid valve of the com-
pressed air ejector.
- Loosen the exhaust and compressed air pipe.
- Loosen the assembling screws of the compressed
air ejector and remove the compressed air ejector
Assembly takes place in reversed order.
6.2 Demontage und Montage des Dsensystems
- Druckluftejektor einspannen und Langnippel heraus-
drehen.
- Mischdse aus dem Gehuse herausziehen.
- Treibdse aus dem Gehuse herausnehmen.
Der Zusammenbau erfolgt in umgekehrter Reihenfolge.
6.2 Disassembly and assembly of the jet system
- Fix the compressed air ejector and turn out the long
nibble.
- Pull out the mixing jet of the casing
- Take out the driving jet of the casing.
Assembly takes place in reversed order.
Achtung Caution
Bei der Montage ist das Langnippel fest in das Gehuse
zu schrauben. Die montierte Gegenmutter darf dabei
nicht verdreht werden. Das Langnippel ist mit
Schraubensicherungsmittel (z.B. Loctite) neu einzuset-
zen.
The long nipple has to be screwed on the casing pow-
erful. The check nut may not to be twisted.The long
nipple must be fitted with a bolt protection medium (e.g.
Loctite).
6.3 Demontage und Montage des Absperrventils
- Lsen des Druckschaltergehuse am Drucklufte-
jektor
Druckschaltergehuse steht unter Federdruck
- Entnahme der Druckfeder und lsen der Mutter an
der Federfhrung. Zum Gegenhalten die Mutter am
Kolben verwenden (Dsenseite).
- Federfhrung, Fhrungsring und Ventildichtung aus
Druckluftejektor entnehmen.
6.3 Disassembly and assembly of the shut-off valve
- Loosen the pressure switch casing at the com-
pressed air ejector
Pressure switch casing is spring pressurized.
- Take out the compression spring and loosen the
safety nut at the spring seating. Use the safety nut at
the piston (jet side) for supporting.
- Take out spring seating, guide ring and valve seling
of the compressed air ejektor.
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
11
- Kolbenstange mit montiertem Kolben entnehmen.
Der Zusammenbau erfolgt in umgekehrter Reihenfolge.
- Take out the Piston rod with mounted piston.
Assembly takes place in reversed order.
Achtung Caution
Bei der Montage des Kolbens ist der Dichtring mit
einem entsprechend geformten Werkzeug durch den
Druckluftanschlu einzudrcken.
When assembling the piston the gasket is to be
pressed via compressed air supply by a similar formed
tool.
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
12
7. Anhang 7. Appendix
7.1. Produktdaten 7.1. Product data
Betriebsspannung 220V-230V 50/60 Hz Operating voltage
Schutzart IP65 Enclosure
Leistungsaufnahme 16 VA Power input
Nenndruck PN 10 Nominal pressure
Arbeits-Druckluft erforderlich 5 - 7 bar Compressed working air required
Material: Material:
Ejektorgehuse GCuSn10 Bronze GCuSn10 Ejector casing
Dsensystem Polythylen Polyetylene Nozzle system
Innenteile Edelstahl Stainless Steel Inner parts
Dichtungen NBR NBR Sealings
Dsengre: 35 45 55 65 Size of Nozzle:
Saugvolumenstrom max. Nl/min 300 500 700 1000 Suction capacity max.
Luftverbrauch bei 6 bar l/min 70 120 180 240 Air consumption at 6 bar
Druckstufe: U V W Pressure-Stage:
Einschaltpunkt bar 0,3 0,6 1,1 Switch-on Point
Ausschaltpunkt bar 0,5 1,1 1,6 Switch-off Point
Anschlsse: Connections:
Entlftung Saugseitig
Entlftung Druckseitig
Abluft Drainage
Druckschalter
Kabel
Arbeits-Druckluft
A1
A2
B
C
E
P
Venting suction side
Venting discharge side
Exhaust, Drainage
Pressure switch
Cable
Compressed working air
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
13
7.2 Mablatt 7.2 Dimensions
13409c/A4
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
14
7.3 Installationsbeispiel 7.3 Installation example
14899/A4
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
15
14900/A4
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
16
7.4 Ersatzteile 7.4 Spare parts
13342d/A4
TYP/TYPE AELD 35/45/55/65 PD-AELD-11-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
17
7.5 Schaltplan 7.5 Circuit diagramm
Schaltplan des Ansaugautomaten Circuit diagramm of the aspirator
Empfohlene Anschluschaltung mit zeitverzgerter
Einschaltung der Kreiselpumpe.
Recommended connecting plan for time delayed
starting of the centrifugal pumps.
30177/A3
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
Diese Betriebsvorschrift enthlt grundlegende
Hinweise, die bei Aufstellung, Betrieb und War-
tung zu beachten sind. Daher ist diese Betriebs-
vorschrift unbedingt vor Montage und Inbetrieb-
nahme vom Monteur sowie dem zustndigen
Fachpersonal/ Betreiber zu lesen und mu stn-
dig am Einsatzort des Maschine/Anlage verfgbar
sein.
These operating instructions contain basic informati-
on to be observed during installation, operation and
maintenance. For this reason the operating instructi-
ons should always be read by the mechanic as well
as responsible operator before assembly and start-
up and should be available at all times at the place of
installation of the machine/system.
Betriebsanleitung / Operating instructions
Kommissions-Nr. / Serial No.
Typ / Type
Bestell-Nr. / Order No.
Spannung / Voltage
Schaltplan / Circuit diagram
61.11111
123
ASED-C
230V 50Hz
30357a/A3
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
2
Inhaltsverzeichnis Table of contents
1 Allgemeines
2 Sicherheitshinweise
2.1 Kennzeichnung von Hinweisen in der Betriebsan-
leitung
2.2 Personalqualifikation und Schulung
2.3 Gefahren bei Nichtbeachtung der Sicherheitshin-
weise
2.4 Sicherheitsbewutes Arbeiten
2.5 Sicherheitshinweise fr Betreiber
2.6 Hinweise fr Wartungs-, Inspektions- und Monta-
gearbeiten
2.7 Eigenmchtiger Umbau und Ersatzteilherstellung
2.8 Unzulssige Betriebsweisen
2.9 Transport
3 Allgemeine Beschreibung
3.1 Hinweis zu Sonderausfhrungen
3.2 Verwendung
3.3 Komponenten
3.4 Funktionsbeschreibung
3.5 Steuerung
4 Installation
5 Inbetriebnahme
1 General
2 Safety
2.1 Marking of information in these operating instructi-
ons
2.2 Personnel qualifications and training
2.3 Hazards ipon failure to observe safety information
2.4 Safety-conscious operation
2.5 Safety instructions for operator
2.6 Information on maintenance, inspection and as-
sembly work
2.7 Unauthorized conversion or production of replace-
ment parts
2.8 Impermissible methods of operation
2.9 Transport
3 General Description
3.1 Note for special design
3.2 Application
3.3 Components
3.4 Functional description
3.5 Control
4 Installation
5 Commissioning
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
3
6 Wartung und Instandhaltung
6.1 Ersatzteile
6.2 Demontage- und Montage der Vakuumpumpe
7 Anhang
7.1 Produktdaten
7.2 Mablatt
7.3 Installationsbeispiel
7.4 Strungen
7.5 Schaltplan
7.6 Armaturen
6 Maintenance and repair
6.1 Spare parts
6.2 Disassembly and assembly of the vacuum pump
7 Appendix
7.1 Product data
7.2 Dimensions
7.3 Installation example
7.4 Disturbances
7.5 Circuit diagram
7.6 Fittings
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
4
1. Allgemeines
Diese Betriebsanleitung enthlt grundlegende Hinweise,
die bei Aufstellung, Betrieb und Wartung zu beachten
sind. Daher ist diese Betriebsanleitung unbedingt vor
Montage und Inbetriebnahme vom Monteur sowie dem
zustndigen Fachpersonal/Betreiber zu lesen und mu
stndig am Einsatzort der Maschine/Anlage verfgbar
sein.
Ein strungsfreier Betrieb der Maschine/Anlage kann
nur erreicht werden, wenn diese sorgfltig montiert und
richtig gewartet wird. Es ist unbedingt darauf zu achten,
da die vorliegende Betriebsanleitung beachtet wird
und die Maschine/Anlage nicht fr andere als die von
uns angegebenen Betriebsverhltnisse eingesetzt wird.
Die Betriebsanleitung bercksichtigt nicht die ortsbezo-
genen Sicherheitsbestimmungen, fr deren Einhaltung
auch seitens des hinzugezogenen Montagepersonals,
der Betreiber verantwortlich ist. Das Fabrikschild an der
Maschine/Anlage nennt die Baureihe/Gre, die Werks-
Nr., die wir bei Rckfragen, Nachbestellung und insbe-
sondere bei Bestellung von Ersatzteilen stets anzuge-
ben bitten. Im Schadensfalle wenden Sie sich bitte an
unsere nchstgelegene Kundendienststelle.
1. General
These operating instructions contain basic information
to be observed during installation, operation and main-
tenance. For this reason the operating instructions
should always be read by the mechanic as well as re-
sponsible personnel/operator before assembly and
start-up and should be available at all times in the vici-
nity of the machine/system.
Malfunction-free operation of the machine/system is
only possible when it is assembled carefully and main-
tained properly. Always ensure that these operating
instructions are observed and that the machine/system
is not used for other operating conditions as those spe-
cified by us. The operating instructions do not take in
consideration local safety regulations for which the ope-
rator is responsible for maintaining also on the part of
installation personnel used. The factory rating plate on
the machine/system specifies the model/size, serial
number, which we request you to specify on any que-
ries, subsequent orders and particularly when ordering
replacement parts. In the event of damage please con-
tact our nearest customer service point.
Achtung Caution
Diese Anlage darf nicht ber die auf dem Fabrikschild
festgelegten Grenzwerte bezglich Menge, Drehzahl,
Druck und Temperatur oder andere in der Betriebsan-
leitung-Vertragsdokumentation enthaltenen Anweisun-
gen betrieben werden. Vorgeschriebene elektrische
Anschluwerte sowie Montage- und Wartungsanwei-
sungen sind unbedingt einzuhalten. Das Handhaben
der Maschine/Anlage auerhalb der vorgenannten Be-
dingungen fhrt zu berbeanspruchungen, denen sie
nicht standhalten kann. Das Nichtbeachten dieser War-
nungen kann zu Personen- und Sachschden fhren.
Zur Beachtung
Die Beschreibungen und Instruktionen in dieser Be-
triebsanweisung betreffen die Standardausfhrung.
Diese Betriebsanleitung bercksichtigt weder alle Kon-
struktionseinzelheiten und Varianten noch alle mgli-
chen Zuflligkeiten und Ereignisse, die bei Montage,
Betrieb und Wartung auftreten knnen.
Vorraussetzung fr das Handhaben der Anlage ist der
Einsatz von fachlich geschultem Personal. Sofern nicht
alle Informationen und Anweisungen in dieser Betriebs-
anleitung gefunden werden, fragen Sie bei der nchst-
gelegenen Kundendienststelle nach.
Der Hersteller bernimmt fr die Anlage keine Verant-
wortung, wenn diese Betriebsanleitung nicht beachtet
wird.
This system must not be operated beyond the limits
specified on the factory rating plate in terms of quantity,
rotary speed, pressure and temperature or other in-
structions contained in the operating instructions and
contract documents. Always observe prescribed electri-
cal connection values as well as installation and war-
ning information. Operation of the machine/system out-
side of the specified conditions leads to excessive
stress, which it cannot withstand. Failure to observe this
warning can lead to personnel injury and property da-
mage.
Note
The descriptions and instructions in these operating
instructions apply to the standard version. These opera-
ting instructions cannot take into consideration all de-
sign details and variations nor all possibilities and
events, which can occur during installation, operation
and maintenance.
The system should be operated only by properly trained
personnel. If you cannot find all information or instructi-
ons in these operating instructions, please ask at the
nearest customer service point.
The manufacturer assumes no liability for the system
when these operating instructions are not observed.
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
5
2. Sicherheitshinweise
2.1 Kennzeichnung von Hinweisen in der Betriebsan-
leitung
Die in der Betriebsanleitung enthaltenen Sicherheits-
hinweise, die bei Nichtbeachtung Gefhrdungen fr
Personen hervorrufen knnen, sind mit dem allgemei-
nen Gefahrsymbol
Sicherheitszeichen nach DIN 4844 - W 9,
bei Warnungen vor elektrischer Spannung mit
Sicherheitszeichen nach DIN 4888 - W 8
besonders gekennzeichnet.
Bei Sicherheitshinweisen, deren Nichtbeachtung Gefah-
ren fr die Maschinen und deren Funktion hervorrufen
kann, ist nachfolgendes Wort eingefgt.
2. Safety
2.1 Marking of information in these operating instructi-
ons
Safety information contained in these operating instruc-
tions, which could result in hazards for humans when
not observed, is generally marked with the following
hazard symbol:
Safety symbol according to DIN 4844 - W 9.
Warnings for electrical voltage are marked with
safety sign according to DIN 4888 - W 8
Safety information, which can result in a hazard for the
machine and its functions when not observed, is indi-
cated by the following word:
Achtung Caution
Direkt an der Maschine angebrachte Hinweise wie z.B.
- Drehrichtungspfeil
- Kennzeichen fr Fluidanschlsse mssen unbedingt
beachtet und in vollstndig lesbarem Zustand ge-
halten werden.
2.2 Personalqualifikation und Schulung
Das Personal fr Bedienung, Wartung, Inspektion und
Montage mu die entsprechende Qualifikation fr diese
Arbeiten aufweisen. Verantwortungsbereich, Zustndig-
keit und die berwachung des Personals mssen durch
den Betreiber genau geregelt sein. Liegen bei dem Per-
sonal nicht die ntigen Kenntnisse vor, so ist dieses zu
schulen und zu unterweisen. Dies kann, falls erforder-
lich, im Auftrag des Betreibers der Maschine durch den
Hersteller/Lieferer erfolgen. Weiterhin ist durch den
Betreiber sicherzustellen, da der Inhalt der Betriebs-
anleitung durch das Personal voll verstanden wird.
2.3 Gefahren bei Nichtbeachtung der Sicherheitshin-
weise
Die Nichtbeachtung der Sicherheitshinweise kann so-
wohl eine Gefhrdung von Personen als auch fr Um-
welt und Maschine zur Folge haben. Die Nichtbeach-
tung der Sicherheitshinweise kann zum Verlust jeglicher
Schadensersatzansprche fhren. Im einzelnen kann
Information attached directly to the machines such as
- Direction of rotation arrows
- Markings for fluid connections must be observed
under all circumstances and kept in a completely le-
gible condition.
2.2 Personnel qualifications and training
The personnel for operation, maintenance, inspection
and installation must be properly qualified for such
work. The range of responsibility and supervision of the
personnel must be regulated precisely by the operator.
It the personnel does not possess the required know-
ledge, they must be trained and/or instructed. If neces-
sary this can be accomplished by the manufactu-
rer/supplier upon request of the machine operator. Mo-
reover, the operator must ensure that the personnel is
completely familiar with the contents of the these ope-
rating instructions.
2.3 Hazards upon failure to observe safety information
Failure to observe the safety instructions can result in a
hazard to humans as well as for the environment and
the machine. Failure to observe the safety instructions
can void all liability claims. In detail failure to observe
the safety instructions can result in the following ha-
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
6
Nichtbeachtung beispielsweise folgende Gefhrdungen
nach sich ziehen:
- Versagen wichtiger Funktionen der Maschine/An-
lage
- Versagen vorgeschriebener Methoden zur Wartung
und Instandhaltung
- Gefhrdung von Personen durch elektrische, me-
chanische und chemische Einwirkungen
- Gefhrdung der Umwelt durch Leckage von gefhr-
lichen Stoffen
2.4 Sicherheitsbewutes Arbeiten
Die in dieser Betriebsanweisung aufgefhrten Sicher-
heitshinweise, die bestehenden nationalen Vorschriften
zur Unfallverhtung sowie eventuelle interne Arbeits-,
Betriebs-, und Sicherheitsvorschriften sind zu beachten.
2.5 Sicherheitshinweise fr den Betreiber
- Fhren warme und kalte Maschinenteile zu Gefah-
ren, mssen diese Teile bauseits gegen Berh-rung
gesichert sein.
- Berhrungsschutz fr sich bewegende Teile darf bei
in Betrieb befindlicher Maschine nicht entfernt wer-
den.
- Leckagen ( z.B. an der Wellenabdichtung) gefhrli-
cher Medien (z.B. explosiv, giftig, warm) mssen so
abgefhrt werden, da keine Gefhrdung fr Perso-
nen und Umwelt entsteht. Gesetzliche Bestimmun-
gen sind einzuhalten.
- Gefhrdungen durch elektrische Energie sind aus-
zuschlieen (Einzelheiten hierzu sind z.B. in den
Vorschriften des VDE und der rtlichen Energiever-
sorgungsunternehmer)
2.6 Hinweise fr Wartungs-, Inspektions- und Monta-
gearbeiten.
Der Betreiber hat dafr zu sorgen, da alle Wartungs-,
Inspektions- und Montagearbeiten von autorisierten und
qualifizierten Fachpersonal ausgefhrt werden, da sich
durch eingehendes Studium der Betriebsanleitung aus-
reichend informiert hat.
Grundstzlich sind Arbeiten an der Maschine nur im
Stillstand durchzufhren. Die in der Betriebsanleitung
beschriebene Vorgehensweise zum Stillsetzen der Ma-
schine/Anlage mu unbedingt eingehalten werden. Bei
Maschinen/Anlagen, die mit nachstehend aufgefhrten
Gefahrstoffen und/oder umweltgefhrdenden Frder-
medien betrieben werden, mu der Kunde/Betreiber im
Reparaturfall oder bei einer Rcksendung an unser
Werk bzw. unsere Vertragswerkstatt das eigene bzw.
unser Personal vor Ort unaufgefordert informieren. In
diesem Fall ist uns mit der Anforderung eines Kunden-
dienst-Monteuers ein Frdergutnachweis, z.B. in Form
eines DIN-Sicherheitsblattes vorzulegen.
Alternativ fordern Sie ein Unbedenklichkeitsbescheini-
gungs-Formular an und fllen dieses wahrheitsgem,
korrekt und vollstndig aus. Senden Sie das ausgefllte
zards:
- Failure of important machine/system functions
- Failure of specified methods for maintenance and
repair
- Hazards for humans resulting from electrical shock,
mechanical and chemical effects.
- Hazard for the environment resulting from leakage of
dangerous substances.
2.4 Safety-conscious operation
The safety instructions contained in these operating
instructions, the existing national regulations on acci-
dent prevention as well as all internal operating, labour
and safety regulations must be observed.
2.5 Safety instructions for operator
- If hot and cold machine parts present a hazard, such
parts must be secured against unintentional contact.
- Contact guards for moving parts should never be
removed from machines while in operation.
- Leakage ( e.g. at shaft seals) of dangerous substan-
ces (e.g. explosive, toxic, hot) must be eliminated in
such a manner that hazards do not result for hu-
mans or the environment. Observe all legal regula-
tions.
- Hazards resulting from electrical power must be
excluded (for details see VDE regulations and regu-
lations of local power company).
2.6 Information on maintenance, inspection and as-
sembly work
The operator must ensure that all maintenance, inspec-
tion and assembly work is accomplished by authorized
and qualified personnel, who have informed themselves
by studying the operating instructions in detail.
Work should be performed on the machine only when it
is standing still as a matter of principle. The procedures
described in the operating instructions for shutting down
the machine/system must be maintained under all cir-
cumstances. On machines/systems, which are operated
with the hazardous substances listed below and/or envi-
ronment polluting substances, the customer/operator
must inform his own or our personnel locally or our plant
or authorized workshop when the machine is returned,
before repair is performed. In such cases it is necessary
to submit to us a certificate on the substances trans-
ported, e.g. in the form of a DIN safety sheet, when a
customer service mechanic is requested.
As an alternative you can request a safety certification
form and fill it out truthfully, correctly and completely.
Return this form filled out to the point where the repair is
to be performed or present it to our requested service
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
7
Formular an die mit der Reparatur beauftragte Stelle
oder legen Sie dieses unserem angefordertem Kun-
dendienst-Monteur vor.
Gefahrstoffe:
- giftige Stoffe
- gesundheitsgefhrdende Stoffe
- tzende Stoffe
- Reizstoffe
- explosionsgefhrliche Stoffe
- brandfhrende, hoch- und leichtentzndliche Stoffe
- krebserzeugende Stoffe
- fruchtschdigende Stoffe
- erbgutverndernde Stoffe
- Stoffe die auf sonstige Weise dem Menschen ge-
fhrlich sind
Bei allen Arbeiten vor Ort ist das eigene bzw. unser
Montagepersonal auf Gefahren, welche im Zusammen-
hang mit Reparaturen entstehen knnen, aufmerksam
zu machen.
Die in der Betriebsanleitung beschriebenen Montage-
schritte sind konsequent einzuhalten.
Unmittelbar nach Abschlu der Arbeiten mssen alle
Sicherheits- und Schutzeinrichtungen wieder ange-
bracht und in Funktion gesetzt werden.
Vor der erneuten Inbetriebnahme sind die im Abschnitt
Inbetriebnahme aufgefhrten Punkte zu beachten.
2.7 Eigenmchtiger Umbau und Ersatzteilherstellung
Umbau und Vernderungen der Maschine/Anlage sind
nur nach Absprache mit dem Hersteller zulssig. Origi-
nalersatzteile und vom Hersteller autorisiertes Zubehr
dienen der Sicherheit. Fr Schden, die durch die Ver-
wendung von Nicht-Originalteilen und Zubehr entste-
hen, ist jedwede Haftung des Herstellers ausgeschlos-
sen.
2.8 Unzulssige Betriebsweisen
Die Betriebssicherheit der gelieferten Maschine/Anlage
ist nur bei bestimmungsgemer Verwendung entspre-
chend Kapitel 1 - Allgemeines - der Betriebsanleitung
gewhrleistet. Die im Datenblatt angegebenen Grenz-
werte drfen auf keinen Fall berschritten werden.
2.9 Transport
Beim Transport der Maschine/Anlage sind die dafr
vorgesehenen Transportsen (sofern vorhanden) fr
die Tragseile zu verwenden.
Die Kranvorrichtung und die Tragseile mssen ausrei-
chend dimensioniert sein.
mechanic.
Hazardous substances:
- Toxic substances
- Health endangering substances
- Caustic substances
- Irritating substances
- Explosive substances
- Combustible, highly and easily inflammable substan-
ces
- carcinogenic substances
- Embryo-damaging substances
- Gene-mutating substances
- Substances dangerous for humans in other manners
When tasks are carried out on site, your own personnel
or ours are to be cautioned at all times about the ha-
zards which can occur when carrying out re-
pair/maintenance tasks.
The assembly procedure described in the Operating
Instructions is to be strictly adhered to.
Directly after ending work, all safety and protection
measures must be brought into effect once more and
applied.
Before a re-starting of operation, the points listed and
described in the Section Putting into / out operation
must be observed.
2.7 Unauthorised conversion or production of replace-
ment parts
Conversion or modification of the machine/system is
permissible only with the manufacturer's approval. Ori-
ginal parts and accessories authorized by the manu-
facturers ensure safety. Damage resulting from the use
of non-original parts and accessories exclude any liabi-
lity on the part of the manufacturer.
2.8 Impermissible methods of operation.
The operating safety of the delivered machine/system is
ensured only when used as intended according to
Chapter 1 - General - in the operating instructions. The
limits specified in the data sheet must not be exceeded
under any circumstances.
2.9 Transport
When transporting the machine/system use the trans-
port eyes (if present) intended for this purpose for the
hoisting cables.
The crane and hoisting cables must be sufficiently di-
mensioned.
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
8
3. Allgemeine Beschreibung
3.1 Hinweise zu Sonderausfhrungen
Bitte beachten Sie bei Sonderausfhrungen die vorher-
gende Seite Sonderausfhrung.
3.2 Verwendung
Ansaugeinheit zur Evakuierung von Kreiselpumpen zur
Frderung von sauber bis mig verschmutzten Fls-
sigkeiten. Das System ist fr solche Kreiselpumpen
ausgelegt, die vorwiegend unter Zulaufbedingungen
arbeiten.
3.3 Komponenten
Komponenten der anschlufertigen Standardausfh-
rung:
- Flssigkeitsring-Vakuumpumpe mit 1-Phasen
Wechselstrommotor.
- Betriebsflssigkeitsbehlter.
- Vakuumgesteuertes Absperrventil Typ VEP, Be-
schreibung Druckblatt. 40401.
- Druckwchter Typ PSA, Druckblatt 90101 (modifi-
ziert).
3.4 Funktionsbeschreibung
Bei Einschaltung der Kreiselpumpe schaltet zunchst
nur die Ansaugeinheit ein. Entweder nach Ablauf eines
Zeitrelais in der Pumpensteuerung oder parallel schaltet
die Kreiselpumpe ein. Der Ansaugautomat schaltet ber
den angebauten Druckschalter ab, sobald die Kreisel-
pumpe den Frderdruck aufgebaut hat. Sinkt der Fr-
derdruck durch Luft- bzw. Gasanfall whrend des Be-
triebes der Kreiselpumpe unter den Einschaltdruck des
Druckschalters, schaltet sich der Ansaugautomat zur
Nachevakuierung erneut ein.
3.5 Steuerung
Eingebaute Drucksteuerung. Zum Betrieb ist eine ab-
gesicherte Versorgungsspannung erforderlich.
3. General description
3.1 Note for special design
In case of special design please pay attention to the
previous page named Special design.
3.2 Application
Priming unit for evacuation of centrifugal pumps pum-
ping clean or slightly contaminated fluids. The unit is
designed for such centrifugal pumps, which mainly ope-
rates under intake pressure condition.
3.3 Components
Components of the standard executions ready for ope-
ration:
- Liquid-ring vacuum pump with 1-phase electrical
motor
- Service liquid tank..
- Vacuum controlled shut-off valve type VEP, descrip-
tion leaflet 40401.
- Pressure Switch type PSA, leaflet no. 90101 (modi-
fied).
3.4 Functional description
When the centrifugal pump is turned on at first the pri-
ming unit will be activated. Either after a time delay or
parallel, the centrifugal pump is also activated. The unit
is switched off via the integrated pressure switch as
soon as the centrifugal pump has built up its discharge
pressure. If during operation of the centrifugal pump
and through air- or gas accumulation the discharge
pressure drops down under the switch point of the pres-
sure switch, the priming unit starts up once more for re-
evacuation.
3.5 Control
Integrated pressure control. A fuse protected operating
voltage is required for operation.
4. Installationshinweise 4. Installation instructions
Achtung Caution
Grundstzlich mssen alle Entlftungsleitungen
vom Anschlupunkt zum Ansaugeinheit hin stetig
steigend verlegt werden. Fr die zu whlenden
Nennweiten der Entlftungsleitungen gilt als An-
haltspunkt die Gre der dafr vorgesehenen An-
schlsse am Ansaugeinheit.
Die Ansaugeinheit wird oberhalb dem hchsten zu ent-
lftenden Punkt aufgestellt. Die maximale Aufstellungs-
hhe ber dem niedrigsten saugseitigen Flssigkeits-
Fundamentally every ventilating pipe is to be in-
stalled ascending from the ventilating point to the
priming unit. As a indication for selecting the nomi-
nal size of the ventilating pipes please refer to the
respective connection size at the priming unit.
The suction system has to be installed above the hig-
hest ventilating point. In case of water as pumping me-
dia the maximum installation height over the lowest
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
9
stand darf bei Wasser nicht mehr als 8 m, abzglich der
dynamischen Verluste des Saugsystems betragen.
Die Evakuierung erfolgt ber steigend zu verlegende
Leitungen an den Anschlu A.
ber den Anschlu B erfolgt die Erstauffllung des
Betriebsflssigkeitsbehlters.
ber dem Abluftanschlu B tritt die angesaugt Luft aus.
Ein Gegendruck ist zu vermeiden. Zeitweise kann hier
etwas Betriebsflssigkeit austreten.
Betriebsflssigkeit:
Die Flssigkeitsring-Vakuumpumpe bentigt whrend
des Betriebes geeignete Flssigkeit wie z.B. Wasser.
Die Betriebsflssigkeit darf nicht zum Schumen neigen
und die Bauteile der Pumpe nicht angreifen. Die Vaku-
umpumpe wird ber den angebauten Betriebsflssig-
keitsbehlter versorgt. Dieser ist vor der ersten Inbe-
triebnahme mit geeignetem Medium aufzufllen.
intake-sided liquid level must not exceed 8 m, minus the
dynamical losses of the suction system.
The evacuation occurs via pipes to be installed ascen-
ding to the connection A.
The service liquid tank must be filled up for the first start
up via connection B.
Via the exhaust connection B the aspirated air escapes.
Back pressure must be avoided. Small quantity of liquid
can escape from time to time.
Service liquid:
The liquid ring vacuum pumps require suitable liquid
such as water during operation. The service liquid must
not tend to bubbles and must not attack the compo-
nents of the pump. The vacuum pump is supplied by an
attached service liquid tank, which has to be filled with
adequate service liquid before first commissioning.
5. Inbetriebnahme
Bei der Inbetriebnahme sind folgende Schritte zu be-
achten:
- Rohranschlsse und Rohrleitungen auf ordnungs-
geme Verlegung und Dichtigkeit berprfen.
- Elektroanschlsse kontrollieren.
- Auffllen des Betriebsflssigkeitstankes mit geeig-
netem Medium ber den Anschlu B
5. Commissioning
For commissioning pay attention to following steps:
- Check all pipe connections and pipes for proper lay
and leakage.
- Check all electrical connections.
- Fill up the service liquid tank with adequate medi-
um via connection B
Achtung Caution
Ein Betrieb der Vakuumpumpe ohne Betriebsfls-
sigkeit ist nicht zulssig und fhrt zu Beschdigun-
gen.
- Drehrichtungskontrolle der Vakuumpumpe
Vakuumpumpe kurzzeitig einschalten und die Dreh-
richtung der Vakuumpumpe entsprechend dem
Drehrichtungspfeil kontrollieren
Operation of the vacuum pump without service liquid
is not permitted and cause damage.
- Direction of rotation control of the vacuum pump.
Switch on the vaccum pump shorthly and check the
direction of rotation of the vacuum pump by using
the rotation arrow.
Achtung Caution
Abweichungen bei Sonderausfhrungen beachten. Please pay attention to modification for special design.
6. Wartung und Instandsetzung
Die Ansaugeinheit arbeitet mit geringem Wartungsauf-
wand. Folgende Kontrollen bzw. Arbeiten sollten je nach
Frdermedium, Betriebsart und Betriebsdauer in fest-
zulegenden Zeitabstnden durchgefhrt werden.
- Kontrolle aller Komponenten auf ordnungsgeme
Funktion
- Kontrolle der Wellenabdichtung der Vakuumpumpe
an der Leckageffnung des Gehuseoberteils.
6. Maintenance and repair
The priming unit operates with slightly maintenance
work. Following inspections respectively work should be
performed in fixed intervals which depend on pumping
medium, operation mode and operation time.
- Check all components for proper function
- Check the shaft seal of the vacuum pump through a
leakage opening on the upper part of the vacuum
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
10
6.1 Ersatzteile
Als Ersatzteil ist ein Dichtungssatz bestehend aus Glei-
tringdichtung und Gehusedeckeldichtung unter der
Ersatzteilnummer 5048 erhltlich.
6.2 Demontage und Montage
Die Demontage / Montage der Vakuumpumpe hat ge-
m dem folgenden Schema zu erfolgen.
pump casing.
6.1 Spare parts
A set of sealings including the mechanical seal and the
casing seal is available as spare part no. 5048.
6.2 Disassembly and assembly of the vacuum pump
The vacuum pump can be assembled / dismantled as
shown in the following scheme.
Vor Beginn der Demontage ist die Vakuumpumpe
elektrisch frei zu schalten.
Anzugsdrehmomente fr die Schraubverbindungen sind
der dementsprechenden DIN-Norm zu entnehmen.
Before starting work, the vacuum pump must be
switched to a power off mode.
Starting torque for the thread connections are to be
taken from the corresponding DIN-Norm.
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
11
Achtung Caution
Sind die Zentrierrnder der Motorlagerschilde mit
Dichtmasse versehen, so sind die Dichtmassenreste zu
entfernen. Zur Montage mit flssiger Dichtmasse be-
netzen oder Dichtmassenraupe auflegen und sofort
montieren.
Die Demontage der Steuerscheibe aus dem Pumpen-
deckel ist nur in wenigen Fllen notwendig, z.B. zum
Subern oder Austauschen der im Deckel befindlichen
Teile. Sollte sich die Steuerscheibe bei der Demontage
lsen oder gelst werden, so sind alte Dichtmassenre-
ste zu entfernen. Zur Montage die Auflageflche der
Steuerscheibe im Deckel mit flssiger Dichtmasse be-
netzen und sofort Steuerscheibe in Deckel einlegen und
ca. 5 sec fest andrcken! Dabei mu darauf geachtet
werden, da Betriebswasserbohrung und Kavitation-
schutzbohrung nicht durch Dichtmasse verschlossen
wird (Sichtkontrolle).
Bei der Montage des Laufrades auf die Lage achten!
Schaufelradien gehuseseitig orientieren! Laufrad mu
lose auf der Welle sitzen!
Bei der Montage der Gleitringdichtung ist die Pafeder-
nut auf geeignete Weise abzudecken!
Beim Aufdrcken des Lfterrades mu das Pumpenteil
demontiert und die Welle abgesttzt werden.
Alle Schrauben sind mit geeignetem Schraubensiche-
rungsmittel zu sichern.
If sealing compound has been used on the centring
rims of the motor end shields, any compound residues
must be removed. To assemble the vacuum pump,
moisten the centring rims with liquid sealing compound
or apply a bead of compound and join the parts together
immediately.
It is only rarely necessary to dismantle the port plate
from the pump cover, e.g. in order to clean or replace
parts inside the cover. If the port plate is loosened eithet
intentionally or accidentally during dismantling, any resi-
dues of old sealing compound must be removed. To
assemble the port plate, moisten the seat inside the
cover with liquid sealing compound, then fit the port
plate into the cover immediatley and press it firmly for
approximately 5 seconds. Be careful not to block the
service liquid hole or the cavitation protection hole with
the sealing compound (visual inspection).
Make sure you assemble the impeller in the correct
position! Align the blade radii on the casing side! The
impeller must sit loosely on the shaft!
Cover over the featherkey way when assembling the
mechanical seal!
The pump section must be dismantled and the shaft
supported in order to press on the fan impeller.
Lock all screws with adequate srew lock compound.
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
12
7. Anhang 7. Appendix
7.1 Produktdaten 7.1 Product data
Betriebsspannung V 115 / 230 Operating voltage
Schutzart IP 54 Protection
Nenndruck PN 10 Nominal pressure
Gewicht kg 17 Weight
Frequenz Hz 50 60 Frequency
Saugleistung * l / min 120 150 Suction capacity *
Drehzahl min
-1
3000 3600 Rotations
Antriebsleistung kW 0,3 0,4 Power input
* angesaugter Gasstrom, bezogen auf Luft
(15C, 1013mbar)
* aspirated gas, refered to air (15C, 1013mbar)
Druckstufe: U V W Pressure-Stage:
Einschaltpunkt bar 0,3 0,6 1,1 Switch-on Point
Ausschaltpunkt bar 0,5 1,1 1,6 Switch-off Point
Material: Material:
Pumpengehuse Bronze (G-Cu Al 10 Ni) Bronze (G-Cu Al 10 Ni) Pump casing
Pumpenlaufrad Bronze (G-Cu Al 10 Ni) Bronze (G-Cu Al 10 Ni) Pump impeller
Steuerscheibe Edelstahl (X6CrNiTi 1810) Stainless steel (X6CrNiTi 1810) Control disc
Ventil Bronze (G-Cu Sn 10) Bronze (G-Cu Sn 10) Valve
Behlter Kupfer Copper Tank
Dichtungen NBR NBR Sealings
Anschlsse: Connections:
Entlftung A Venting
Abluft, Drainage B Exhaust, Drainage
Druckschalter C Pressure Switch
Abweichungen bei Sonderausfhrung beachten. Please pay attention to modification in case of special
design.
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
13
7.2 Mablatt 7.2 Dimensions
14511/A4
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
14
7.3 Installationsbeispiel 7.3 Installation example
14539/A4
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
15
7.4 Strungen 7.4 Disturbances
Strung Ursache Abhilfe
Motor luft nicht an, kein Laufgerusch Unterbrechnung in mindestens zwei Leitungen
der Stromversorgung
Sicherungen, Klemmen und Zuleitung berpr-
fen
Motor luft nicht an, Brummgerusch Unterbrechung in einer Leitung der Stromver-
sorgung
Pumpe sitzt fest
Sicherungen, Klemmen und Zuleitung berpr-
fen
Pumpe durchdrehen, evtl entleeren und su-
bern oder siehe auch "Pumpe blockiert"
Pumpe blockiert Laufrad festsitzend
Laufrad defekt
Motorlager defekt
s. "Motor luft nicht an, Brummgerusch"
Laufrad ersetzen
Lager ersetzen
Motorschalter lst nach Einschalten
wieder aus
Kurzschlu in der Wicklung
Motor berlastet
Gegendruck im Druckstutzen zu hoch
mitgefrderter Flssigkeitsanteil zu hoch
Pumpe sitzt fest
Wicklung prfen lassen
Betriesflssigkeitsstrom drosseln
Gegendruck verringern
Flssigkeitsanteil verringern
s. "Motor luft nicht an, Brummgerusch" oder
"Pumpe blockiert"
Pumpe erzeugt kein Vakuum keine Betriebsflssigkeit vorhanden
groe Undichtigkeit in der Anlage
falsche Drehrichtung
Zufuhr des Betriebsflssigkeitsstromes prfen
Anlage abdichten
Drehrichtung ndern durch Vertauschen von 2
elektr. Anschluleitungen
Pumpe erzeugt zu geringes Vakuum Pumpe zu klein
Betriebsflssigkeitstrom zu gering
Betriebsflssigkeit zu warm > 15C
kleine Undichtigkeit in der Anlage
Gleitringdichtung undicht
grere Pumpe einsetzen
Betriebsflssigkeitsstrom bis zum 2,5-fachen
erhhen
Betriebsflssigkeitstrom khlen bzw. erhhen
Anlage abdichten
Gleitringdichtung berprfen
Anomale, kreischende Gerusche Kavitation der Pumpe
Betreibsflssigkeitsstrom zu gro
Kavitationschraube ffnen
Betriebsflssigkeitsstrom prfen und reduzieren
Pumpe undicht Dichtung Dichtungen berprfen
Disturbance Cause Remedy
Motor doesn't start; no motor noise At least two of the power supply leads are
interrupted
Check the fuses, terminals and supply leads
Motor doesn't start; humming noise One of the supply leads is interrupted
Pump is jammed
Check the fuses, terminals and supply leads
Turn the pump impeller, draining and cleaning it
if necessary or see also under "Pump jammed"
Pump jammed The impeller is stuck
The impeller is defective
Motor bearing defective
See "Motor doesn't start; huming noise"
Replace the impeller
Replace bearing
Motor circuit-breaker trips when the
motor is switched on
Winding short-circuit
Motor overloaded
Counterpressure in discharge too high
Too much liquid compressant entrained
Pump stuck
Check the motor winding
Reduce the service liquid supply
Reduce the counterpressure
Reduce quantity of compressant
See under "Motor doesn't start; humming noise"
or "Pump jammed"
Pump doesn't generate vacuum No service liquid
Severe leak in the system
Wrong direction of rotation
Check service liquid supply
Repair any leaks in the system
Revers the direction of rotation by changing
over two of the leads
Pump produces to little vacuum Pump too small
Service liquid supply too low
Service liquid too warm (>15C)
Slight leak in the system
Slide ring packing leaking
Use a bigger pump
Increase service liquid supply to maximum
value (2.5 times nominal value)
Cool the service liquid supply or increase the
service liquid supply
Repair the leak in the system
Check the slide ring packing
Abnormal noises Pump cavitation
Service liquid supply too high
Open the cavitation protection screw
Check the service liquid supply and reduce it
Pump leaking Gaskets, seal Check all gaskets and seal
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
16
7.5 Schaltplan 7.5 Circuit diagram
TYP/TYPE ASED-C PD-ASED C-10-D-GB.DOC
vatec-Maschinenbau GmbH e-mail: service@vatec.de www.vatec.de
17
7.6 Armaturen 7.6 Fittings
Centrifugal Pump with
Volute Casing
Operating manual NIM / NAM series
Version BA-2006.03
Print-No. 550 018
VM-No. 467.0001 GB
ALLWEILER AG Werk Radolfzell
Postfach 1140
Allweilerstr. 1
78301 Radolfzell
Germany
Phone: +49 (0) 7732-86-0
Fax: +49 (0) 7732-86-436
Email: info@allweiler.com
Internet: http://www.allweiler.com
We reserve the right to make technical changes.
Table of contents
Table of contents
1 About this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1 Target groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.2 Other applicable documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.3 Warnings and symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.4 Technical terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 Intended use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2 General safety instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2.1 Product safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2.2 Obligations of the operating company . . . . . . 8
2.2.3 Duties of the personnel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.3 Special hazards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.3.1 Hazardous pumped media . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3 Layout and function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.1 Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.1.1 Type plate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.1.2 Pump type code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.2 Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.3 Shaft seals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.3.1 Mechanical seals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.3.2 Packing gland . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.4 Auxiliary systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.4.1 Automatic aspirator (if available) . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4 Transport, storage and disposal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.1 Transport . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.1.1 Unpacking and inspection on delivery . . . . . . 12
4.1.2 Lifting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.2 Preservation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.3 Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.4 Removing the preservative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
4.5 Disposal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5 Setup and connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.1 Preparing the setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.1.1 Checking the ambient conditions . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.1.2 Preparing the installation site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.1.3 Installing the heat insulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.1.4 Removing the preservative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.1.5 Fastening the pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.2 Installing the motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.3 Planning the piping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.3.1 Keeping the piping clean . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.3.2 Specifying supports and ange
connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.3.3 Specifying nominal diameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.3.4 Specifying pipe lengths . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.3.6 Optimizing cross-section and direction
changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.3.7 Provide safety and control devices
(recommended) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.4 Connecting the pipes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.4.1 Installing auxiliary pipes (if available) . . . . . . . 16
5.4.2 Installing the suction pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.4.3 Installing the pressure pipe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.4.4 Inspection for stress-free pipe
connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.5 Electrical connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.5.1 Connecting the motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.5.2 Checking the direction of rotation . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.6 Checking the alignment of the
coupling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
6 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1 Preparations for the initial start-up . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1.1 Identifying the pump type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1.2 Removing the preservative . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1.3 Lubricating the bearings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1.4 Preparing auxiliary systems (if
available) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.1.5 Filling and bleeding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.2 Start-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.2.1 Switching on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.2.2 Switching off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.3 Shutting down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.4 Start-up following a shutdown period . . . . . . . 20
6.5 Operating the stand-by pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
7 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.1 Inspections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.2 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.2.1 Antifriction bearings lubricated with
grease . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.2.2 Mechanical seals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.2.3 Packing gland . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.3 Dismounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.3.1 Returning the pump to the manufac-
turer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
7.3.2 Preparations for dismounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
7.4 Installing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
7.5 Ordering spare parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
8 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
9 Appendix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
9.1 Sectional drawings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
9.1.1 Auxiliary connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
9.1.2 Part numbers and designations . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
9.1.3 Sectional drawings of the NIM series . . . . . . . 29
9.1.4 Sectional drawings of the NAM series . . . . . . 34
9.2 Technical specications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
9.2.1 Ambient conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
9.2.2 Preservatives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
9.2.3 Sound pressure levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
9.2.4 Tightening torques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
9.2.5 Cleaning agents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
9.2.6 Lubricants . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
2 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Table of contents
9.3 Spare parts for two years of continuous
operation according to DIN 24296 . . . . . . . . . . 38
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 3
Table of contents
List of gures
Fig. 1 Type plate (example) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Fig. 2 Pump type code (example) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Fig. 3 Layout of NIM (left) NAM (right) . . . . . . . . . . 10
Fig. 4 Automatic aspirator extension
example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Fig. 5 Fastening the lifting gear to the pump
aggregate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Fig. 6 Straight pipe lengths upstream and down-
stream of the pump (recommended) . . . . . . . 15
Fig. 7 Checking the lateral displacement . . . . . . . . . . 17
Fig. 8 Checking the angular displacement . . . . . . . . 17
Fig. 9 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal Base
installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Fig. 10 Version with split rings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Fig. 11 Attachment of the pump feet to the bell
housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Fig. 12 Version with intermediate ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Fig. 13 U1B Packing gland with self-locking . . . . . 30
Fig. 14 Wall attachment version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Fig. 15 Bearing and impeller retention version . . . . . 30
Fig. 16 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal Base
installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Fig. 17 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal Base
installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Fig. 18 Version with V2 split ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Fig. 19 Attachment of the pump feet to the bell
housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Fig. 20 Leak/egress on housing cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Fig. 21 X detail on housing cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Fig. 22 C01 connection on volute casing . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Fig. 23 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal Base
installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Fig. 24 Version with split rings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Fig. 25 Attachment of the pump feet to the bell
housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Fig. 26 Version with intermediate ring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Fig. 27 U1B Packing gland with self-locking . . . . . 35
Fig. 28 Wall attachment version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Fig. 29 Bearing and impeller retention version . . . . . 35
List of tables
Tab. 1 Target groups and their duties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Tab. 2 Other applicable documents and their
purpose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Tab. 3 Warnings and consequences of disregarding
them . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Tab. 4 Symbols and their meaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Tab. 5 Technical terms and their meaning . . . . . . . . . 6
Tab. 6 Measures to be taken if the pump is shut
down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Tab. 7 Measures depending on the behavior of the
pumped medium . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Tab. 8 Measures to be taken after prolonged
shutdown periods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Tab. 9 Measures for return . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Tab. 10 Fault number assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Tab. 11 Troubleshooting list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Tab. 12 Abbreviations of the connection
designations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Tab. 13 Designations of components according to
part numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Tab. 14 Ambient conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Tab. 15 Valvoline preservatives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Tab. 16 Sound pressure levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Tab. 17 Tightening torques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Tab. 18 Cleaning agents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Tab. 19 Grease types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Tab. 20 Minimum amounts for grease lubrica-
tion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Tab. 21 Spare parts for two years of continuous
operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
About this document
1 About this document
This manual
Is part of the pump
Applies to the afore-mentioned pump series
Describes safe and appropriate operation during all oper-
ating phases
1.1 Target groups
Target group Duty
Operating company Keep this manual available at the site of operation of the system,
including for later use.
Ensure that personnel read and follow the instructions in this
manual and the other applicable documents, especially all safety
instructions and warnings.
Observe any additional rules and regulations referring to the
system.
Qualied personnel, tter Read, observe and follow this manual and the other applicable
documents, especially all safety instructions and warnings.
Tab. 1 Target groups and their duties
1.2 Other applicable documents
Document Purpose
Order data sheet Technical specications, conditions of operation
Setup drawing Setup dimensions, connection dimensions etc.
Technical description Technical specications, operating limits
Sectional drawing Sectional drawing, part numbers, component designations
Automatic aspirator operating manual Technical documentation
Supplier documentation Technical documentation for parts supplied by subcontractors
Spare parts list Ordering spare parts
Safety certicate Returning the pump to the manufacturer
Declaration of conformity Conformity of the pump with standards
Tab. 2 Other applicable documents and their purpose
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 5
About this document
1.3 Warnings and symbols
Warning Risk level Consequences of disregard
DANGER
Immediate acute risk Death, grievous bodily harm
WARNING
Potentially acute risk Death, grievous bodily harm
CAUTION
Potentially hazardous situation Minor bodily harm
CAUTION
Potentially hazardous situation Material damage
Tab. 3 Warnings and consequences of disregarding them
Symbol Meaning
Safety warning sign
Take note of all information highlighted by the safety warning sign
and follow the instructions to avoid injury or death.
Instruction
1. , 2. , ... Multiple-step instructions
Precondition
Cross reference
Information, advice
Tab. 4 Symbols and their meaning
1.4 Technical terms
Term Meaning
Sealing medium Medium as seal barrier/buffer uid or for quenching of shaft seals
Auxiliary systems Systems for operating the pump
Tab. 5 Technical terms and their meaning
6 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Safety
2 Safety
The manufacturer does not accept any liability for damage
resulting from disregard of the entire documentation.
2.1 Intended use
Only use the pump for pumping the agreed pumped media
( order data sheet).
Adhere to the operating limits and size-dependent mini-
mum ow rate.
Avoid dry running:
Initial damage, such as destruction of the mechanical seal
and plastic parts, will occur within only a few seconds.
Make sure the pump is only operated with, and never
without, a pumped medium.
Avoid cavitation:
Fully open the suction-side armature and do not use it
to adjust the ow rate.
Do not open the pressure-side armature beyond the
agreed operating point.
Avoid overheating:
Do not operate the pump while the pressure-side arma-
ture is closed.
Observe the minimum ow rate ( order data sheet).
Avoid damage to the motor:
Do not open the pressure-side armature beyond the
agreed operating point.
Note the maximum permissible number of times the
motor can be switched on per hour ( manufacturer's
specications).
Consult the manufacturer about any other use of the pump.
Prevention of obvious misuse (examples)
Note the operating limits of the pump concerning temper-
ature, pressure, ow rate and motor speed ( order data
sheet).
The power consumed by the pump will increase with
increasing density of the pumped medium. To avoid
overloading the pump, coupling or motor, stay within the
agreed density ( order data sheet).
Lower densities are allowed. Adapt the auxiliary systems
accordingly.
When pumping liquids containing solids, ensure that the
limits for the proportion of solids and the grain size are
maintained ( order data sheet, technical description).
When using auxiliary systems, ensure that there is a con-
tinuous supply of the appropriate medium.
2.2 General safety instructions
Take note of the following regulations before carrying out
any work.
2.2.1 Product safety
The pump has been constructed according to the latest tech-
nology and recognized technical safety rules. Nevertheless,
operation of the pump can involve risks to life and health of the
user or third parties and risk of damage to the pump and other
property.
Only operate the pump if it is in perfect technical condition
and only use it as intended, staying aware of safety and
risks, and in adherence to the instructions in this manual.
Keep this manual and all other applicable documents com-
plete, legible and accessible to personnel at all times.
Refrain from any procedures and actions that would
expose personnel or third parties to any risk.
Should there be any safety-relevant fault, shut down the
pump immediately and have the fault corrected by appro-
priate personnel.
In addition to the entire documentation for the product,
always comply with statutory or other safety and accident-
prevention regulations and with the applicable standards
and guidelines in the country where the pump is operated.
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 7
Safety
2.2.2 Obligations of the operating company
Safety-conscious operation
Only operate the pump if it is in perfect technical condition
and only use it as intended, staying aware of safety and
risks, and in adherence to the instructions in this manual.
Ensure that the following safety aspects are observed and
monitored:
Adherence to intended use
Statutory or other safety and accident-prevention reg-
ulations
Safety regulations governing the handling of hazard-
ous substances
Applicable standards and guidelines in the country
where the pump is operated
Make protective equipment available.
Qualied personnel
Make sure all personnel tasked with work on the pump
have read and understood this manual and all other appli-
cable documents, especially the safety, maintenance and
repair information, before they start work.
Organize responsibilities, who is in charge of any specic
duty and how personnel is supervised.
Ensure that all work is carried out by specialist technicians
only:
Fitting, repair and maintenance work
Work on the electrical system
Make sure trainee personnel is supervised by a specialist
technician when working on the pump.
Safety equipment
Provide the following safety equipment and verify their
functionality:
For hot, cold and moving parts: guard provided by the
customer to prevent contact with the pump
For possible build up of electrostatic charge: ensure
appropriate grounding
Warranty
Obtain the manufacturer's approval prior to carrying out
any modications, repairs or alterations during the warranty
period.
Only use original parts or parts that have been approved
by the manufacturer.
2.2.3 Duties of the personnel
All directions given on the pump must be followed (and kept
legible), e.g. the arrow indicating the direction of rotation
and the markings for uid connections.
Do not remove the guards to prevent contact with hot, cold
or moving parts during operation.
Use protective equipment if necessary.
Only carry out work on the pump while it is not running.
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
Reinstall the safety equipment on the pump as required by
regulations after any work on the pump.
2.3 Special hazards
2.3.1 Hazardous pumped media
Follow the safety regulations for handling hazardous sub-
stances when pumping hazardous media (e.g. hot, am-
mable, poisonous or potentially harmful).
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
8 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Layout and function
3 Layout and function
3.1 Labels
3.1.1 Type plate
NPSH kW 1/min P m n
m
3
/h H m Q
Nr Jahr
Typ
mm
2
/s kg/dm
3
D - 78315 Radolfzell / Germany
Typ und Nr.
1
2
3
4
5 6
7
10
9
8
angeben
Bei Ersatzteilbestellung
Fig. 1 Type plate (example)
1 Pump type
2 Year of manufacture
3 Differential head
4 Pump NPSH value
5 Kinematic viscosity
6 Power consumption
7 Density
8 Motor speed
9 Flow rate
10 Serial number
3.1.2 Pump type code
1
2
3
4
NIM 80 200 / U3D 01 W1
5
6
/ 180
7
Fig. 2 Pump type code (example)
1 NIM or NAM series
2 Pressure ange DN [mm]
3 Nominal impeller diameter [mm]
4 Hydraulic no.
5 Actual impeller diameter [mm]
6 Shaft seal
7 Material key
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 9
Layout and function
3.2 Layout
3
4
5
6
1
7
8
2
Fig. 3 Layout of NIM (left) NAM (right)
1 Motor
2 Coupling with extension piece
3 Bell housing
4 Shaft
5 Bearing bracket
6 Shaft seal
7 Impeller
8 Volute casing
3.3 Shaft seals
Only one of the following shaft seals can be used.
3.3.1 Mechanical seals
Mechanical seals have functional leaks.
Single mechanical seal
Single mechanical seal with quenching
3.3.2 Packing gland
The packing gland must always leak slightly to carry the
frictional heat away.
10 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Layout and function
3.4 Auxiliary systems
3.4.1 Automatic aspirator (if available)
Information on the material, functional description and
electrical connection ( A25 automatic aspirator operat-
ing manual).
1
Fig. 4 Automatic aspirator extension example
1 Automatic aspirator
The maintenance-free A25 automatic aspirator:
Used for automatic bleeding of pumps and suction pipes
Operates according to the ejector principle with pressure-
dependent control
Suitable for clean, chemically neutral water
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 11
Transport, storage and disposal
4 Transport, storage and disposal
4.1 Transport
For details of weight ( documents for the particular
order).
4.1.1 Unpacking and inspection on delivery
1. Unpack the pump/aggregate on delivery and inspect it for
damage.
2. Report any damage to the manufacturer immediately.
3. Dispose of packaging material according to local regula-
tions.
4.1.2 Lifting
DANGER
Death or crushing of limbs caused by falling or overturning
loads!
Use lifting gear appropriate for the total weight to be trans-
ported.
Fasten the lifting gear as illustrated below.
Do not stand under suspended loads.
Set the load down on a level surface.
Fig. 5 Fastening the lifting gear to the pump aggregate
Lift the pump/aggregate properly.
4.2 Preservation
Not necessary for non-rusting materials
CAUTION
Material damage due to inappropriate treatment for stor-
age!
Treat the pump properly, inside and outside, for storage.
1. Choose a preservative appropriate for the type and dura-
tion of storage ( 9.2.2 Preservatives, Page 36).
2. Use the preservative specied by the manufacturer.
3. All bare metal parts should be treated, inside and outside.
4.3 Storage
CAUTION
Material damage due to inappropriate storage!
Treat and store the pump properly.
1. Seal all openings with blind anges, blind plugs or plastic
covers.
2. Make sure the storage room meets the following condi-
tions:
Dry
Frost-free
Vibration-free
3. Turn the shaft once a month.
4. Make sure the shaft and bearing change their rotational
position in the process.
12 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Transport, storage and disposal
4.4 Removing the preservative
Only necessary for pumps treated with preservative
WARNING
Risk of poisoning from preservatives and cleaning agents
in the foodstuffs and drinking water sector!
Only use cleaning agents which are compatible with the
pumped medium ( 9.2.5 Cleaning agents, Page 37).
Completely remove all preservative.
CAUTION
High water pressure or spray water can damage bearings!
Do not clean the bearing areas with a water or steam jet.
CAUTION
Damage to seals due to incorrect cleaning agent!
Ensure the cleaning agent does not corrode the seals.
1. Choose a suitable cleaning agent for the application.
( 9.2.5 Cleaning agents, Page 37).
With Tectyl 506 EH: allow benzine to soak in for 10 minutes
(recommended).
2. Dispose of preservatives according to local regulations.
3. For storage times in excess of 6 months:
Replace the elastomer parts made of EP rubber
(EPDM).
Check all elastomer parts (O-rings, shaft seals) for
proper elasticity and replace them if necessary.
4.5 Disposal
Plastic parts can be contaminated by poisonous or radioac-
tive pumped media to such an extent that cleaning is insuf-
cient.
WARNING
Risk of poisoning and environmental damage caused by
pumped medium or oil!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Prior to disposal of the pump:
Catch and dispose of any escaping pumped medium
or oil in accordance with local regulations.
Neutralize residues of pumped medium in the pump.
Remove any preservative ( 4.4 Removing the pre-
servative , Page 13).
Remove and dispose of any plastic parts in accordance
with local regulations.
Dispose of the pump in accordance with local regulations.
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 13
Setup and connection
5 Setup and connection
CAUTION
Material damage caused by dirt!
Do not remove the transport seals until immediately before
setting up the pump.
Do not remove any covers and transport and sealing cov-
ers until immediately before connecting the piping to the
pump.
5.1 Preparing the setup
5.1.1 Checking the ambient conditions
1. Make sure the required ambient conditions are fullled
( 9.2.1 Ambient conditions, Page 36).
2. For setup heights > 1000 m above sea level, consult the
manufacturer.
5.1.2 Preparing the installation site
Ensure the installation site meets the following conditions:
Pump is freely accessible from all sides
Sufcient space for installation/removal of the pipes
and for maintenance and repair work, especially for the
removal and installation of the pump and the motor
Pump not exposed to external vibrations (damage to
bearings)
Frost protection
5.1.3 Installing the heat insulation
Only necessary to maintain the temperature of the pumped
medium
CAUTION
Material damage caused by overheating!
Only install the heat insulation on the volute casing.
Install the heat insulation properly.
5.1.4 Removing the preservative
If the pump is to be put into operation immediately after
setup and connection: remove the preservative prior to
setup ( 4.4 Removing the preservative , Page 13).
5.1.5 Fastening the pump
The pump can also be attached to the wall with angles.
Install and fasten the pump ( setup drawing).
5.2 Installing the motor
Only necessary if the pump aggregate is assembled on
site.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by knocks and bumps!
Keep the coupling halves properly aligned when pushing
on the motor.
Do not knock or hit any components of the pump.
1. Smear a very thin coat of molybdenum disulde (e.g.
Molykote) on the shaft ends of the pump and motor.
2. Insert shaft keys.
3. Without a mounting rig: remove the rubber buffers and
warm up both halves of the coupling to approx. 100 C.
4. Slide on the pump-side and motor-side coupling halves
until the shaft ends are ush with the center of the coupling.
When doing this, ensure the prescribed spacing between
the two halves of the coupling is maintained ( assembly
instructions for the coupling).
5. Tighten the grub screws on both halves of the coupling.
6. Screw in the motor bolts and tighten them.
5.3 Planning the piping
5.3.1 Keeping the piping clean
CAUTION
Material damage due to impurities in the pump!
Make sure no impurities can get into the pump.
1. Clean all piping parts and armatures prior to assembly.
2. Ensure no ange seals protrude inwards.
3. Remove any blind anges, plugs, protective foils and/or
protective paint from anges.
5.3.2 Specifying supports and ange connections
CAUTION
Material damage due to excessive forces and torques
exerted by the piping on the pump!
Do not exceed permissible limits.
1. Calculate the pipe forces taking every possible operating
condition into account:
Cold/warm
Empty/full
Unpressurized/pressurized
Shift in position of anges
2. Ensure the pipe supports have permanent low-friction
properties and do not seize up due to corrosion.
14 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Setup and connection
5.3.3 Specifying nominal diameters
Keep the ow resistance in the pipes as low as possible.
1. Specify the nominal suction pipe diameter nominal suc-
tion ange diameter.
2. Specify the nominal pressure pipe diameter nominal
pressure ange diameter.
5.3.4 Specifying pipe lengths
C
D
B
A
Fig. 6 Straight pipe lengths upstream and downstream
of the pump (recommended)
A > 5 x nominal suction pipe diameter
B Nominal suction pipe diameter
C Nominal pressure pipe diameter
D > 5 x nominal pressure pipe diameter
Maintain the recommended minimum values when install-
ing the pump.
Suction side: shorter pipes are possible but may restrict
the hydraulic performance.
Pressure side: shorter pipes are possible but can result in
increased operating noise.
5.3.6 Optimizing cross-section and direction
changes
1. Avoid radii of curvature of less than 1.5 times the nominal
pipe diameter.
2. Avoid abrupt changes of cross-section along the piping
system.
5.3.7 Provide safety and control devices
(recommended)
Avoid impurities
1. Integrate a lter into the suction pipe.
2. To monitor impurities, install a differential pressure gauge
with a contact manometer.
Avoid reverse running
Install a non-return valve between the pressure ange and
the gate valve to ensure the medium does not ow back
when the pump is switched off.
Make provisions for isolating and shutting off the pipes
For maintenance and repair work.
Provide shut-off devices in the suction and pressure pipes.
Allow the measurement of the operating conditions
1. Provide manometers for pressure measurements in suc-
tion and pressure pipes.
2. Provide for motor-side torque measurements.
3. Provide for pump-side temperature measurements.
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 15
Setup and connection
5.4 Connecting the pipes
5.4.1 Installing auxiliary pipes (if available)
Follow the manufacturers' specications for any existing
auxiliary systems.
1. Connect the auxiliary pipes to the auxiliary connections so
that they are stress-free and do not leak (setup drawing).
2. To avoid air pockets, run the pipes with a continuous slope
up to the pump.
5.4.2 Installing the suction pipe
1. Remove the transport and sealing covers from the pump.
2. To avoid air pockets, run the pipes with a continuous slope
up to the pump.
3. Ensure no seals protrude inwards.
4. For suction operation: install a foot valve in the suction pipe
to prevent the pump and suction pipe from running empty
during downtimes.
5.4.3 Installing the pressure pipe
1. Remove the transport and sealing covers from the pump.
2. Install the pressure pipe.
3. Ensure no seals protrude inwards.
5.4.4 Inspection for stress-free pipe connections
Piping installed and cooled down
1. Separate the pipe connecting anges from the pump.
2. Check whether the pipes can be moved freely in all direc-
tions within the expected range of expansion:
Nominal diameter < 150 mm: by hand
Nominal diameter > 150 mm: with small lever
3. Make sure the ange surfaces are parallel.
4. Reconnect the pipe connecting anges to the pump.
5.5 Electrical connection
DANGER
Risk of death due to electric shock!
Have all electrical work carried out by qualied electricians
only.
DANGER
Risk of death due to rotating parts!
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
5.5.1 Connecting the motor
Follow the instructions of the motor manufacturer.
1. Connect the motor according to the connection diagram.
2. Make sure that no danger arises due to electrical energy.
3. Install an EMERGENCY STOP switch.
5.5.2 Checking the direction of rotation
DANGER
Risk of death due to rotating parts!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Secure the shaft key from being thrown out when checking
the direction of rotation.
Keep an adequate distance to rotating parts.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by running dry or wrong direction
of rotation!
Uncouple the motor from the pump.
1. Switch the motor on and immediately off again.
2. Check whether the direction of rotation of the motor corre-
sponds to the rotational direction arrow on the pump.
3. If the direction of rotation is different: swap two phases.
4. Couple the motor to the pump again.
16 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Setup and connection
5.6 Checking the alignment of the
coupling
The motor and pump can be aligned precisely only at the
factory.
DANGER
Risk of death due to rotating parts!
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
CAUTION
Material damage due to incorrect alignment of the cou-
pling!
If there is any lateral or angular displacement, align the
motor exactly with the pump.
For detailed information and special couplings: ( manu-
facturer's specications).
Checking the alignment of the coupling
Implements, tools and materials:
Dial gage (can be used for couplings with a spacer
piece)
Other suitable tools, e.g. laser alignment instrument
Fig. 7 Checking the lateral displacement
1. Check the lateral displacement with a dial gage:
Carry out the measurement as illustrated.
Permissible radial deviation, measured at the coupling
circumference: < 0.2 mm
Fig. 8 Checking the angular displacement
2. Check the angular displacement with a dial gage:
Carry out the measurement as illustrated.
3. Send the pump to the factory for inspection and alignment
in the event of impermissible lateral or angular displace-
ment.
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 17
Operation
6 Operation
6.1 Preparations for the initial start-up
6.1.1 Identifying the pump type
Identify the pump type ( order data sheet).
Pump types vary e.g. with regard to bearing lubrication,
bearing bracket size, type of shaft seal and auxiliary sys-
tems.
6.1.2 Removing the preservative
Only necessary for pumps treated with preservative
( 4.4 Removing the preservative , Page 13).
6.1.3 Lubricating the bearings
Pumps with grease-lubricated roller bearings are ready for
operation upon delivery.
6.1.4 Preparing auxiliary systems (if available)
The manufacturer does not accept any liability for damage
arising from the installation or use of a third-party or unap-
proved auxiliary system.
6.1.5 Filling and bleeding
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
media!
Safely collect any leaking pumped medium and dispose
of it in accordance with environmental rules and require-
ments.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by dry running!
Make sure the pump is lled properly.
Without automatic aspirator (supply operation)
1. Fill the pump and the suction pipe with pumped medium.
2. Open the suction-side armature.
3. Open the pressure-side armature.
4. If available: open the auxiliary systems and check the ow
rate.
5. Verify that no pipe connections are leaking.
With automatic aspirator (suction operation)
1. Fill the pump and the suction pipe with pumped medium.
2. Open the suction-side armature.
3. Close the pressure-side armature.
4. If available: open the auxiliary systems and check the ow
rate.
5. Verify that no pipe connections are leaking.
6. Start suction operation (A25 operating manual manufac-
turer instructions).
18 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Operation
6.2 Start-up
6.2.1 Switching on
Pump set up and connected properly
Motor set up and connected properly
Motor exactly aligned with the pump
All connections stress-free and sealed
Any existing auxiliary systems are ready for operation
All safety equipment installed and tested for functionality
Pump prepared, lled and bled properly
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
Allowthe pump to cool down completely before starting any
work.
DANGER
Risk of injury and poisoning caused by pumped medium
spraying out!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by dry running!
Make sure the pump is lled properly.
CAUTION
Risk of cavitation when throttling down the suction ow
rate!
Fully open the suction-side armature and do not use it to
adjust the ow rate.
Do not open the pressure-side armature beyond the oper-
ating point.
CAUTION
Material damage caused by overheating!
Do not operate the pump while the pressure-side armature
is closed.
Observe the minimum ow rate ( order data sheet).
1. Open the suction-side armature.
2. Close the pressure-side armature.
3. Switch on the motor and check it for smooth running.
4. Once the motor has reached its nominal speed, slowly
open the pressure-side armature until the operating point
is reached.
5. For pumps with hot pumped media, make sure any tem-
perature changes do not exceed 50 C/h.
6. After the initial stress caused by pressure and operating
temperature, check that the pump is not leaking.
7. If the pumped media is hot, briey switch off the pump
at operating temperature and check the alignment of the
coupling ( 5.6 Checking the alignment of the coupling,
Page 17).
8. If present, set a slight leak on the packing gland.
6.2.2 Switching off
Pressure-side armature closed (recommended)
WARNING
Risk of injury due to hot pump parts!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
1. Switch off the motor.
2. Check all connecting bolts and tighten them if necessary.
6.3 Shutting down
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
media!
Safely collect any leaking pumped medium and dispose
of it in accordance with environmental rules and require-
ments.
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 19
Operation
Take the following measures whenever the pump is shut
down:
Pump is Measure
...shut down
for a prolonged
period
Take any measures depending
on the pumped medium
( Table 7 Measures
depending on the behavior of
the pumped medium, Page 20).
...emptied Close the suction-side and
pressure-side armatures.
...dismounted Isolate the motor from its power
supply and secure it against
unauthorized switch-on.
...put into
storage
Follow the storage instructions
( 4.3 Storage, Page 12).
Tab. 6 Measures to be taken if the pump is shut down
Duration of shutdown (depending
on process)
Behavior
of pumped
medium
Short Long
Solids sediment Flush the
pump.
Flush the
pump.
Solidies/
freezes,
non-corrosive
Heat up or
empty the
pump and
containers.
Empty the
pump and
containers.
Solidies/
freezes,
corrosive
Heat up or
empty the
pump and
containers.
Empty the
pump and
containers.
Treat the
pump and
containers
with preser-
vative.
Remains liquid,
non-corrosive
Remains liquid,
corrosive
Empty the
pump and
containers.
Treat the
pump and
containers
with preser-
vative.
Tab. 7 Measures depending on the behavior
of the pumped medium
6.4 Start-up following a shutdown period
1. If the pump is shut down for > 1 year, take the following
measures before starting it up again:
Shutdown period Measure
> 1 year For versions with roller
bearings without lifetime
lubrication: relubricate
> 2 years Replace elastomer seals
(O-rings, shaft sealing rings).
Replace antifriction bearings.
Tab. 8 Measures to be taken after prolonged
shutdown periods
2. Carry out all steps as for the initial start-up ( 6.2 Start-up,
Page 19).
6.5 Operating the stand-by pump
Stand-by pump lled and bled
Operate the stand-by pump at least once a week.
1. Completely open the suction-side armature.
2. Open the pressure-side armature to an extent that the
stand-by pump reaches its operating temperature and is
heated through evenly ( 6.2.1 Switching on, Page 19).
20 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Maintenance
7 Maintenance
For pumps in explosion hazard areas ( ATEX additional
instructions).
Trained service technicians are available for tting and
repair jobs. Present a pumped medium certicate (DIN
safety data sheet or safety certicate) when requesting
service.
7.1 Inspections
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous pumped
media!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
1. Check at appropriate intervals:
Maintenance of minimum ow rate
Temperature of roller bearings < 120 C
Normal operating conditions unchanged
Coupling alignment and condition of elastic parts
2. For trouble-free operation, always ensure the following:
No dry running
No leaks
No cavitation
Suction-side gate valves open
Unobstructed and clean lters
Sufcient supply pressure
No unusual running noises or vibrations
No excessive leakage at the shaft seal
Proper functioning of auxiliary systems
Put the installed stand-by pump into operation at least
once a week
7.2 Maintenance
Service life of the antifriction bearings for operation within
the permissible operating range: > 2 years
Intermittent operation, high temperatures, low viscosities
and aggressive ambient and process conditions reduce the
service life of antifriction bearings.
Mechanical seals are subject to natural wear, which
strongly depends on the actual operating conditions.
Therefore, general statements regarding their service life
cannot be made.
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
DANGER
Risk of death due to electric shock!
Have all electrical work carried out by qualied electricians
only.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous or hot
pumped media!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Allow the pump to cool down completely before commenc-
ing any work.
Make sure the pump is unpressurized.
Empty the pump, safely collect the pumped medium and
dispose of the medium in accordance with environmental
rules and requirements.
7.2.1 Antifriction bearings lubricated with grease
1. As a precaution, replace antifriction bearings with lifetime
lubrication every 2 years (recommended).
2. Fill any open antifriction bearings without guard disks with
grease ( 9.2.6 Lubricants, Page 37).
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 21
Maintenance
7.2.2 Mechanical seals
Due to their function, mechanical seals always leak a bit
( manufacturer's specications).
Single mechanical seals with quenching: any drastic rise
in the level of the quenching system indicates a major leak
at the product-side mechanical seal.
In the event of a larger leak: replace the mechanical seal
and its auxiliary seals and check the integrity of the auxiliary
systems.
7.2.3 Packing gland
The packing gland must always leak slightly to carry the
frictional heat away.
Larger leaks in the initial hours of operation lessen during
the running-in period.
If there is increased leakage: gently tighten the hexagon
nuts on the gland.
7.3 Dismounting
DANGER
Risk of injury due to running pump!
Do not touch the running pump.
Do not carry out any work on the running pump.
Isolate the motor from its supply voltage and keep it locked
in that state when carrying out any tting or maintenance
work.
DANGER
Risk of death due to electric shock!
Have all electrical work carried out by qualied electricians
only.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous or hot
pumped media!
Use protective equipment when carrying out any work on
the pump.
Allow the pump to cool down completely before commenc-
ing any work.
Make sure the pump is unpressurized.
Empty the pump, safely collect the pumped medium and
dispose of the medium in accordance with environmental
rules and requirements.
7.3.1 Returning the pump to the manufacturer
Pump unpressurized
Pump completely empty
Electrical connections isolated and motor secured against
switch-on
Pump cooled down
Coupling guard dismounted
With couplings with a spacer piece: spacer piece removed
Auxiliary systems shut down, unpressurized and emptied
Manometer connections, manometer and xtures dis-
mounted
1. Always enclose a truthfully (fully) completed safety certi-
cate when returning pumps or individual parts to the man-
ufacturer. Order a safety certicate from the manufacturer
if necessary.
2. Take necessary measures, depending on the required
repair work, as listed in the table below when returning the
pump to the manufacturer.
Repair carried out Measure for return
...at the customer's
premises
Return the defective
component to the
manufacturer.
...at the
manufacturer's
premises
Flush the pump and
decontaminate it if it was
used to pump hazardous
media.
Return the complete pump
(not disassembled) to the
manufacturer.
...at the
manufacturer's
premises for
warranty repairs
Only if the pumped media
is hazardous: ush and
decontaminate the pump.
Return the complete pump
(not disassembled) to the
manufacturer.
Tab. 9 Measures for return
22 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Maintenance
7.3.2 Preparations for dismounting
Pump unpressurized
Pump completely empty, ushed and decontaminated
Electrical connections isolated and motor secured against
switch-on
Pump cooled down
Coupling guard dismounted
With couplings with a spacer piece: spacer piece removed
Auxiliary systems shut down, unpressurized and emptied
Manometer connections, manometer and xtures dis-
mounted
In production, the pumps are constructed to a standard pro-
cess. The slide-in unit can be removed without removing
the volute casing and piping.
When dismounting, observe the following:
Precisely mark the assembly orientation and position
of all components before dismounting.
Dismantle components concentrically without canting.
Dismount the pump ( sectional drawing).
7.4 Installing
Reinstall the components concentrically, without canting,
following the markings made.
1. When installing, observe the following:
Replace worn parts with genuine spare parts.
Replace seals, inserting them so that they cannot
rotate.
Maintain the specied tightening torques
( 9.2.4 Tightening torques, Page 37).
2. Clean all parts ( 9.2.5 Cleaning agents, Page 37). Do
not remove the prepared markings.
3. Install the pump ( sectional drawing).
4. Replace the antifriction bearings. Fill any open antifriction
bearings without guard disks with grease:
Make sure you use the correct type and mini-
mum amount of grease when lling the bearing
( 9.2.6 Lubricants, Page 37).
Fill the cavities between the rolling elements up to 40 %
with grease.
Wipe off any excess grease with a soft object.
5. Install the pump in the system ( 5 Setup and connection,
Page 14).
7.5 Ordering spare parts
For trouble-free replacement in the event of any faults,
we recommend keeping complete slide-in units or spare
pumps available on site.
The application guidelines conforming to DIN 24296 rec-
ommend provisioning for two years of continuous use
( 9.3 Spare parts for two years of continuous operation
according to DIN 24296, Page 38).
Have the following information ready to hand when order-
ing spare parts ( type plate):
Short designation of the pump
Pump number
Year of manufacture
Part number
Designation
Quantity
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 23
Troubleshooting
8 Troubleshooting
For faults which are not specied in the following table or can-
not be traced back to the specied causes, please consult the
manufacturer.
Possible faults are identied by a fault number in the table
below. This number identies the respective cause and rem-
edy in the troubleshooting list.
Fault Number
Pump not pumping 1
Pumping rate insufcient 2
Pumping rate excessive 3
Pumping pressure insufcient 4
Pumping pressure excessive 5
Pump running roughly 6
Antifriction bearing temperatures too high 7
Pump leaking 8
Motor power uptake excessive 9
Tab. 10 Fault number assignment
Fault number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Cause Remedy
X Supply/suction pipe and/or pressure pipe
closed by armature
Open the armature.
x Automatic aspirator defective ( A25 automatic aspirator operating
manual).
X X Supply/suction pipe not fully opened Open the armature.
X X X X Supply/suction pipe, pump or suction
screen blocked or encrusted
Clean the supply/suction pipe, pump
or suction screen.
X
X
X
Supply/suction pipe cross-section too
narrow
Increase the cross-section.
Remove any encrustations from the
suction pipe.
Open the armature completely.
X Transport and sealing cover still in place Remove the transport and sealing
cover.
Dismount the pump and inspect it for
dry-running damage.
X X X Differential head excessive: NPSH
pump
larger than NPSH
system
Increase the supply pressure.
Consult the manufacturer.
X X
Supply/suction pipe not bled properly or
not lled up completely
Fill up the pump and/or piping
completely and bleed them.
X X
Supply/suction pipe contains air pockets Install the armature for bleeding.
Correct the piping layout.
X X X X Air is sucked in Seal the source of malfunction.
X X X X
Excessive amount of gas: pump is
cavitating
Consult the manufacturer.
24 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Troubleshooting
Fault number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Cause Remedy
X X X Pumped medium temperature too high:
pump is cavitating
Increase the supply pressure.
Lower the temperature.
Consult the manufacturer.
X X X Viscosity or specic gravity of the pumped
medium outside the range specied for
the pump
Consult the manufacturer.
X X Geodetic differential head and/or pipe ow
resistances too high
Remove sediments from the pump
and/or pressure pipe.
Install a larger impeller and consult the
manufacturer.
X X X Pressure-side armature not opened
sufciently
Open the pressure-side armature.
X X X X Pressure pipe blocked Clean the pressure pipe.
X X X X Pump running in the wrong direction Swap any two phases on the motor.
X X X Motor speed insufcient Compare the required motor speed
with the specications on the pump
type plate. Replace the motor if
necessary.
Increase the motor speed if speed
control is available.
X X X X Pump parts worn Replace the worn pump parts.
X X X X Pressure-side armature opened too wide Throttle down at the pressure-side
armature.
Machine the impeller down. Consult
the manufacturer and adjust the
impeller diameter.
X X X Geodetic differential head, pipe ow
resistances and/or other resistances lower
than specied
Throttle down the ow rate at the
pressure-side armature. Observe the
minimum ow rate.
Machine the impeller down. Consult
the manufacturer and adjust the
impeller diameter.
X X Viscosity lower than expected Machine the impeller down. Consult
the manufacturer and adjust the
impeller diameter.
X
X X X
X Motor speed too high Compare the required motor speed
with the specications on the pump
type plate. Replace the motor if
necessary.
Reduce the motor speed if speed
control is available.
X X X X Impeller diameter too large Throttle down the ow rate at the
pressure-side armature. Observe the
minimum ow rate.
Machine the impeller down. Consult
the manufacturer and adjust the
impeller diameter.
X X X X Impeller out of balance or blocked Dismount the pump and inspect it for
dry-running damage.
Clean the impeller.
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 25
Troubleshooting
Fault number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Cause Remedy
X X X Hydraulic parts of the pump dirty, clotted
or encrusted
Dismount the pump.
Clean the parts.
X X X Defective antifriction bearing in bearing
bracket
Replace the antifriction bearing.
X X Defective antifriction bearing in motor Replace the antifriction bearing.
X Lubricant: too much, not enough or
unsuitable
Reduce, top up or replace the lubricant.
X Connecting bolts not tightened correctly Tighten the connecting bolts.
X Mechanical seal worn Replace the mechanical seal.
X Housing seal defective Replace the housing seal.
X Shaft sleeve is penetrated Replace the shaft sleeve and/or O-ring.
X X X X Pump distorted Check the pipe connections and pump
xings.
Check the coupling alignment.
Check the xing of the support foot.
X X Coupling not properly aligned Align the coupling.
X Coupling units worn Replace the coupling units and realign
them.
X X X X Motor running on 2 phases Check the fuse and replace it if
necessary.
Check the cable connections and
insulation.
Tab. 11 Troubleshooting list
26 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Appendix
9 Appendix
9.1 Sectional drawings
9.1.1 Auxiliary connections
Abbreviation Connection
FD Pumped medium / emptying
FF Filling
LO Leak / egress
PM1/PM2 Pressure gauge
FV Bleeding
Tab. 12 Abbreviations of the connection designations
9.1.2 Part numbers and designations
Part no. Designation
102.01 Volute casing
106.01 Suction casing
161.01 Housing cover
161.05 Housing cover
182.01 Foot
210.01 Shaft
230.01 Impeller
321.01 Radial ball bearing
321.02 Radial ball bearing
321.03 Radial ball bearing
321.04 Radial ball bearing
322.01 Cylindrical roller bearing
330.01 Bearing bracket
346.01 Bell housing
360.01 Bearing cover
360.02 Bearing cover
400.01 Gasket
400.02 Gasket
411.01 Seal ring
411.02 Seal ring
411.03 Seal ring
411.04 Seal ring
411.05 Seal ring
411.06 Seal ring
411.37 Seal ring
412.01 O-ring
Part no. Designation
412.10 O-ring
412.11 O-ring
424.01 V-ring
424.02 V-ring
433.01 Mechanical seal
441.01 Shaft seal housing
452.01 Gland
458.01 Retaining ring
461.01 Gland packing
502.01 Split ring
502.02 Split ring
504.01 Spacer ring
507.01 Oil thrower
509.01 Intermediate ring
509.02 Intermediate ring
516.01 Nilos ring
516.02 Nilos ring
525.01 Spacer sleeve
551.01 Spacing washer
551.10 Spacing washer
551.12 Spacing washer
557.01 Balance disk
565.01 Rivet
571.01 Clamp
575.01 Strap
672.01 Vent
681.01 Coupling guard
710.01 Pipe
710.02 Pipe
731.02 Pipe tting
801.01 Flanged motor
855.01 Coupling with spacer piece
894.01 Console
901.01 Hexagon head bolt
901.02 Hexagon head bolt
901.03 Hexagon head bolt
901.04 Hexagon head bolt
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 27
Appendix
Part no. Designation
901.08 Hexagon head bolt
901.09 Hexagon head bolt
902.01 Stud bolt
902.03 Stud bolt
902.05 Stud bolt
902.06 Stud bolt
902.08 Stud bolt
902.10 Stud bolt
903.01 Screw plug
903.02 Screw plug
903.03 Screw plug
903.04 Screw plug
903.05 Screw plug
903.06 Screw plug
903.26 Screw plug
904.02 Grub screw
904.03 Grub screw
908.01 Jacking screw
908.02 Jacking screw
908.10 Jacking screw
914.01 Cheese head screw
914.04 Cheese head screw
914.05 Cheese head screw
914.10 Cheese head screw
920.03 Hexagon nut
920.04 Hexagon nut
920.05 Hexagon nut
920.06 Hexagon nut
920.08 Hexagon nut
920.10 Hexagon nut
922.01 Impeller nut
932.01 Circlip
932.04 Circlip
932.10 Circlip
934.01 Spring washer
936.01 Spring ring
940.01 Shaft key
Part no. Designation
940.02 Shaft key
951.01 Cup spring
971.01 Name plate
Tab. 13 Designations of components according
to part numbers
28 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Appendix
9.1.3 Sectional drawings of the NIM series
672.01
424.02
1
FV
Fig. 9 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal
Base installation
1 Attachment to size-585 bearing
bracket
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 29
Appendix
Fig. 10 Version with split rings
Fig. 11 Attachment of the pump feet to the bell housing
Fig. 12 Version with intermediate ring
FV
672.01
Fig. 13 U1B Packing gland with self-locking
Fig. 14 Wall attachment version
1 2
Fig. 15 Bearing and impeller retention version
1 Bearing bracket size 530
2 Bearing bracket size 585
30 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Appendix
Sizes 300315 and 300400 at bearing bracket 585
PM2
801.01
346.01
855.01
571.01
210.01
932.01
V
551.01
360.02
901.08
321.04
551.10
360.01
420.01
565.01
903.05
971.01
412.10
908.02
411.05
412.01
908.01
575.01
920.10
904.03
902.10
681.01
901.09
940.02
904.02
516.02
914.05
932.10
330.01
321.03
516.01
951.01
PM1
902.05
441.01
914.04
920.05
901.02
901.03
903.03
FF
903.01
903.04
411.04
411.01
902.06 102.01
182.01
502.01
920.06
433.01
230.01
FD
106.01
908.10 940.01
922.01
934.01
412.11 525.01
161.05
411.02
903.02
411.03
901.01
Fig. 16 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal
Base installation
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 31
Appendix
Sizes 300315 and 300400 at bearing bracket 700
PM2
855.01
801.01
346.01
210.01
424.01
571.01
551.01
565.01
914.05
971.01
424.02
914.04
551.12
903.26
507.01
F V
908.01
412.10
908.02
411.37
412.01
904.03
920.10
902.10
575.01
904.02
901.09
681.01
940.02
932.04
321.01
932.01
901.08
360.02
932.10
330.01
322.01
PM1
902.05
441.01
360.01
920.05
901.03
901.02
903.03
X
433.01
903.01
903.04
411.01
411.04
FV
182.01
102.01
920.06
902.06 502.01
230.01 908.10
922.01
934.01
412.11
940.01 161.05
525.01 411.02
903.02
411.03
901.01
106.01
FD
Fig. 17 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal
Base installation
32 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Appendix
Variants for 300315 and 300400 sizes
502.02
Fig. 18 Version with V2 split ring
901.04
920.04
Fig. 19 Attachment of the pump feet to the bell housing
710.01 LO
Fig. 20 Leak/egress on housing cover
411.05 903.05
Fig. 21 X detail on housing cover
903.06 411.06
Fig. 22 C01 connection on volute casing
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 33
Appendix
9.1.4 Sectional drawings of the NAM series
FV
672.01
424.02
1
Fig. 23 U3...D Unbalanced mechanical seal
Base installation
1 Attachment to size-585 bearing
bracket
34 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Appendix
Fig. 24 Version with split rings
Fig. 25 Attachment of the pump feet to the bell housing
Fig. 26 Version with intermediate ring
FV
672.01
Fig. 27 U1B Packing gland with self-locking
Fig. 28 Wall attachment version
1 2
Fig. 29 Bearing and impeller retention version
1 Bearing bracket size 530
2 Bearing bracket size 585
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 35
Appendix
9.2 Technical specications
More technical specications ( order data sheet).
9.2.1 Ambient conditions
Operation under other ambient conditions to be agreed with
the manufacturer
Relative humidity [%] Tempera-
ture [C]
Long-term Short-term
Setup
height
above sea
level [m]
20 to +40 85 100 1000
Tab. 14 Ambient conditions
9.2.2 Preservatives
Use a Valvoline preservative or similar (recommended).
Type of storage Storage
duration
[months]
Preservative
inside/
outside
Renew
[months]
inside/
outside
612 Tectyl 511 M In closed, dry and
dust-free room
> 12 Tectyl 506 EH 48/48
612 Tectyl 542 In open air, central
European climate
> 12 Tectyl 506 EH 48/18
612 Tectyl 542/
Tectyl 506 EH
In open air,
tropical climate,
aggressive
industrial
atmosphere or
close to sea
> 12 Tectyl 506 EH 48/12
Tab. 15 Valvoline preservatives
9.2.3 Sound pressure levels
Measuring conditions:
Distance to the pump: 1 m
Operation: cavitation-free
Motor: IEC standard motor
Tolerance 3 dB
Lower-noise versions of the motors are available if the
expected noise levels exceed the permissible limits.
Sound pressure level [dB] for pump
with motor at speed [min
-1
]
Nominal motor
power PM [kW]
1450 1750 2900 3500
1.5 58 58.5 63 64
2.2 60 60.5 66 67
3.0 62 62.5 68 69
4.0 63 63.5 69 70
5.5 65 65.5 71 72
7.5 66 66.5 72 73
11.0 68 68.5 74 75
15.0 69 69.5 75 76
18.5 70 70.5 76 77
22.0 71 71.5 77 78
30.0 72 72.5 78 79
37.0 73 73.5 79 80
45.0 74 74.5 80 81
55.0 75 75.5 80 81
75.0 76 76.5 81 82
90.0 76 76.5 82 83
110.0 77 77.5 82 83
132.0 78 78.5 83 84
160.0 79 79.5 84 85
200.0 80 80.5 85 86
Tab. 16 Sound pressure levels
36 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Appendix
9.2.4 Tightening torques
Part no. Thread
gage
Quality Tightening
torque [Nm]
901.01
M12
M16
A4-70
45
110
901.02
M12
M16
A4-70
45
110
901.03
M12
M16
M20
8.8
70
170
330
901.04
M20
M24
M30
8.8
330
560
1100
901.08
901.09
M8 4.6 10
902.01 M16 A470 110
914.04
914.05
M6
M8
M10
8.8
10
20
40
914.10 M16 8.8 180
920.03
1)
M16 A470 110
920.04
M20
M24
M30
8.8
330
560
1100
920.05
920.06
920.08
M12
M20
M8
A470
A470
5.8
45
210
12
920.10
M12
M16
M20
5.8
35
80
160
922.01
M24 x 1.5
M30 x 1.5
M36 x 1.5
M48 x 1.5
A4/1.44
A4/1.44
A4/1.44
A4/1.40
175
310
630
1700
Tab. 17 Tightening torques
1) applies only to bearing bracket 585
9.2.5 Cleaning agents
Application area Cleaning agents
Foodstuffs and drinking
water sector
E.g. spirit, Ritzol 155, strong
alkaline soapy solution,
steam jet (for individual
parts only)
Other Benzine, wax solvents,
diesel, parafn, alkaline
cleaners
Tab. 18 Cleaning agents
9.2.6 Lubricants
Manufacturer Brand name Name according
to DIN 51825
Agip Agip GR MU3 K3K20
ARAL Aralub HL3 K3K20
BP BP Energrease
LS3
K3K20
ESSO BEACON 3 K3K20
Fuchs RENOLIT FWA
220
K3K20
Klber MICROLUBE GL
263
K3K20
Mobil-l
Mobilux 3 K3K20
Shell Shell Alvania Fett
R3
K3K20
SKF SKF-Fett LGMT3 K3K20
Tab. 19 Grease types
Size of the
bearing bracket
Short
designation of
the antifriction
bearing
Approx. amount
of grease [g]
530 6410 J C3 35
585 6413 J C3 65
700 NU 2219 ECJ 50
Tab. 20 Minimum amounts for grease lubrication
467.0001 GB 550 018 BA-2006.03 NIM / NAM series 37
Appendix
9.3 Spare parts for two years of
continuous operation according
to DIN 24296
Number of identical pumps (including stand-by pumps)
2 3 4 5 6 or 7 8 or 9 > 9
Part no. Part designation
Set/quantity of spare parts
230.01 Impeller 1 1 1 2 2 3 30 %
210.01
922.01
934.01
936.01
Shaft
Impeller nut
Spring washer or
Spring ring
1)
1 1 2 2 2 3 30 %
321.01
321.02
321.03
321.04
322.01
Groove ball bearing
Groove ball bearing
Groove ball bearing
Groove ball bearing
Cylindrical roller
bearing
2)
1 1 2 2 3 4 50 %
1)
Bearing bracket, complete,
consisting of:
Shaft, bearing, bearing
cover etc.
1 2
433... Mechanical seal 2 3 4 5 6 7 90 %
461.01 Gland packing rings (set) 4 4 6 6 6 8 40 %
502.01
502.02
Split ring
Split ring
2 2 2 3 3 4 50 %
Various
1)
Seals for pump housing
(set)
Other seals (set)
4 6 8 8 9 12 150 %
Tab. 21 Spare parts for two years of continuous operation
1) Delivered as a mechanical unit (BG) or sales unit (VG)
2) Depending on the size of the bearing bracket
38 NIM / NAM series BA-2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
Appendix
46 7. 00 01 G B 5 50 0 18 B A - 20 06 .0 3 N IM / N A M s er ie s 39
Appendix
40 NIM / NAM series BA -2006.03 467.0001 GB 550 018
1
Operating and Maintenance Instructions VM No.: 490.0023 GB
Edition: 07.03
Ident. No.: 550 299
MELO Retain for future use!
Order No.: Pump Ident. No.:
Machine No.: Pump Type:
Operating data, dimensions and other additional information can be found in the order-specific part of the
documentation.
These operating and maintenance in-
structions contain information from the
pump manufacturer. They may need to
be supplemented by instructions of the
operator company for its personnel.
These instructions do not take account
of specific information relating to opera-
tion and maintenance of the process
plant into which the pump is integrated.
Such information can only be given by
the persons responsible for construc-
tion and planning of the plant (plant
manufacturer).
Such specific instructions relating to
operation and maintenance of the
process plant into which the pump is
integrated have priority over the
instructions of the pump manufac-
turer. The plant manufacturer must
on principle observe the limits of
use!
Refer to the operating instructions of
the plant manufacturer!
Contents
1. General
2. Safety
3. Transportation and Intermediate
Storage
4. Description
5. Installation/Mounting
6. Start-up/Shutdown
7. Maintenance/Repair
8. Operating Faults, Causes and
Remedial Action
9. Associated Documentation
Important note:
This operating and maintenance instructions
are to be supplemented by the order-related in-
formation.
ALLMARINE MELO
2 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
1 General
1.1 Pump designation
The exact designation can be found in the order-spe-
cific documents (see data sheet).
1.2 Proper use
Information on proper use of the pumps is provided in
the technical data sheet.
The pumped liquid must not contain any abrasive con-
stituents nor corrode the pump materials.
1.3 Performance data
The exact performance data can be taken from the or-
der data sheet and/or acceptance test report.
1.4 Warranty
Our warranty for shortcomings in the supply is laid
down in our delivery conditions. No liability will be un-
dertaken for damages caused by non-compliance with
the operating instructions and service conditions.
If at any later datetheoperatingconditions change(e.g.
different fluid conveyed, speed, viscosity, temperature
or supply conditions), it must be checked by us from
case to case and confirmed, if necessary, that the
pump is suited for those purposes. Where no special
agreements were made, pumps supplied by us may,
during the warranty period, only be opened or varied by
us or our authorized contract service workshops; other-
wise our liability for any defects will cease.
1.5 Testing
Prior to leaving our factory, all pumps are subjected to
aleak test. Additional tests will only beperformed onre-
quest.
1.6 Availability
As a matter of principle, we recommend stocking
replacement pumps and withdrawable units (hydraulic
action system) where the supplied pumps are a
decisive factor in maintaining a production or delivery
process. In this way downtimes can be avoided, or
reduced to a minimum.
1.7 Pressure limit
The sumof inlet pressure and maximum delivery pres-
sure must not be greater than the permissible internal
pump pressure (see data sheet).
ALLMARINE MELO
3 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
2 Safety
These operating instructions contain basic safety
instructions for installation, operation and
maintenance. It is therefore essential that they are read
by fitters andall specialist staff andcustomer personnel
prior to installation and start-up. They must always be
kept at hand at the place of installation.
The special safety instructions contained in the other
chapters must be observed in addition to the general
safety instructions in this chapter.
2.1 Identification of safety instructions in the
operating manual
The safety instructions contained in these operating
instructions which represent a danger to personnel if
not complied with are specially marked by the general
danger symbol:
Warning symbol
as per DIN 4844-W9
Warning of danger from electric voltage is indicated as
follows:
Warning symbol
as per DIN 4844-W8
Instructions which are essential to avoid endangering
the machine and its operation are marked by the word
ATTENTION
Instructions affixed directly to the machine such as
S Directional markers
S Signs for fluid connections
must always be observed and maintained in fully
legible condition at all times.
2.2 Personnel qualification and training
The operating, maintenance, inspection and mounting
personnel must be appropriately qualified for the duties
assigned to them. The scope of their responsibilities,
competency and supervisory duties must be closely
controlledby thecustomer. If thepersonnel donot have
the required knowledge, they must be trained and
instructed. If required, this may be provided by the
manufacturer/supplier on behalf of the customer. The
customer must additionally ensure that personnel fully
understand the content of the operating instructions.
2.3 Dangersintheevent of non-compliancewithsafety
instructions
Failure to comply with the safety instructions may result
in danger to persons, and place the environment and
the machine at risk. Non-compliance with the safety
instructions will lead to the loss of any claims for
damages.
Non-compliance may result in the following dangers:
S Failure of important functions of the plant
S Failure of specified methods for maintenance and
servicing
S Danger to persons resulting from electrical,
mechanical and chemical effects
S Danger to the environment resulting fromleakage of
hazardous substances
2.4 Responsible working practices
The safety instructions contained in these operating
instructions, current national accident prevention
regulations, as well as internal working, operating and
safety rules of the customer, must be observed.
2.5 Safety instructions for the user/operator
S Hot or cold machine parts representing a danger
must be protected against accidental contact on
site.
S Protection against accidental contact for moving
parts (such as the coupling) must not be removed
while the machine is in operation.
S When operating pump aggregates in a dust-laden
environment (e.g. milling, chipboard manufacture,
bakeries), the surfaces of the pumps and motors
must be cleaned at regular intervals, depending on
local conditions, in order to maintain the cooling
effect and eliminate the possibility of spontaneous
combustion. Please also see explosion protection
regulations (BGR 104).
S Leakage (e.g. from the shaft seal) of hazardous
substances being handled, such as explosive, toxic
or hot materials, must be discharged in such a way
that no danger to persons or the environment is
created. Legal regulations must be observed.
S Dangers from electrical energy must be eliminated.
For details in this regard, please refer to VDE and
local power company regulations.
ALLMARINE MELO
4 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
2.6 Safety instructions for maintenance, inspection
and installation
The operating company must ensure that all
maintenance, inspection and installation tasks are
performed by authorized and qualified specialist
personnel who have thoroughly studied the operating
instructions.
Work on the machine is only to be carried out when the
machine is at a standstill. The procedure for shutting
down the machine described in the operating
instructions must always be followed.
Pumps or aggregates handling fluids which are
detrimental to health must be decontaminated. All
safety and protective devices must immediately be
refitted and made operational on completion of the
work.
The instructions under Section 6.1, Preparation for
start-up, must be observed before restarting.
2.7 Unauthorized conversion and production of
replacement parts
Conversion or modification of the machines is only
permissible after consultation with the manufacturer.
Original replacement parts and accessories approved
by the manufacturer are intrinsic to safe operation. If
other parts are used the manufacturer cannot be held
liable for the consequences.
2.8 Unacceptable modes of operation
The operational safety of the machine supplied is only
ensured when it is used in accordance with Section 1 of
the operating instructions. The limit values given on the
data sheet must not be exceeded under any
circumstances.
3 Transportation and Intermediate Stor-
age
3.1 Packaging
Attention must be paid to the figurative markings on the
packaging.
The suction and pressure side and all auxiliary connec-
tions must always be closed during transportation and
storage.
The coverings must only be removed im-
mediately before connecting the pipeline.
3.2 Transportation
The pump or pump aggregate is to be safely trans-
ported to the place of installation, if required by means
of lifting gear.
The regulations for lifting loads in accordance with
VBG 9a must be observed. Crane and sling equip-
ment must be adequately dimensioned. Sling
equipment must not be secured to the lifting eyes
of the motor, except as additional protection
against overturning in the event of nose-heavi-
ness.
Transportation to and at the installation site
Make sure that the unit is transported safely and in a
stable position. Overturning due to nose-heaviness
must be prevented.
In the case of units with eye bolts in the covering plate/
sole plate, these can be used to secure the sling equip-
ment when moving the pump unit vertically.
Transport damage
Check the pump for damage on receipt.
Any damage detected must be notified im-
mediately.
ALLMARINE MELO
5 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
3.3 Preservation/Storage of centrifugal pumps
3.3.1 Preservation
In the case of storage or prolonged standstill, the
pumps must be protected against corrosion. In those
cases, an outside and inside preservation is to be pro-
vided. The durability of the protection against corro-
sion, which is limited in time, depends on the composi-
tion of the preservative to be applied and the storage
conditions.
Under normal circumstances the pumps
have no special preservative.
At an additional charge we can, however, supply
pumps and replacement parts ex factory with a preser-
vative adequate to the planned storage period.
3.3.1.1 Outside preservation
The outside preservative should be applied by painting
or spraying with a spray gun.
Points of preservation
All bright and unvarnished parts (e.g. shaft ends, cou-
plings, flange facings, valve and manometer connec-
tions).
3.3.1.2 Inside preservation
(Not required for pumps made of stainless materials.)
Internal preservation is applied by painting, spraying
using spray guns, filling/dipping and subsequent drain-
ing. Finally, the suction and outlet branches as well as
all other supply and discharge branches must be
sealed with dummy flanges or dummy plugs (plastic
caps).
Points of preservation
All bright parts inside the pump (e.g. pump casing in-
side, bearing bracket, shafts, impellers and diffusers).
3.3.1.3 Storage times
Depending on the required storage period and the sur-
roundings, we recommend the use of preservatives
from Valvoline GmbH, Hamburg.
Storage in a closed, dry and dust-free room
Storage time up to 6 months up to 12 months over 12 months
Internal preservation Tectyl 511 M Tectyl 511 M Tectyl 506 EH
External preservation Tectyl 511 M Tectyl 511 M Tectyl 506 EH
Storage in the open-air, central European climate
Storage time up to 6 months up to 12 months over 12 months
Internal preservation Tectyl 542 Tectyl 542 Tectyl 506 EH
External preservation Tectyl 542 Tectyl 506 EH Tectyl 506 EH
Storage in the open-air, tropical climate, aggressive industrial air or
proximity to the sea
Storage time up to 6 months up to 12 months over 12 months
Intermal preservation Tectyl 542 Tectyl 542 Tectyl 506 EH
External preservation Tectyl 506 EH Tectyl 506 EH Tectyl 506 EH
Internal and external preservation must be renewed after 48 months at the latest.
External preservation must be renewed after 18 months at the latest.
Internal preservation must be renewed after 48 months at the latest.
External preservation must be renewed after 12 months at the latest.
Internal preservation must be renewed after 48 months at the latest.
Note: The preservatives listed are to be regarded as a
recommendation. Alternatively, technically equivalent
products from other manufacturers can be used.
When handling preservatives, the safety hints con-
tained in the relevant DINsafety data sheets and those
of the manufacturer must be complied with.
3.3.1.4 Depreservation
Prior to setting the pump in motion, the inside preserva-
tion must be removed.
Environmentally compatible disposal must be en-
sured.
Preservatives can be removed with wax solvents, pe-
troleum ether, diesel, petroleum or alkaline cleaners.
However, the simplest method is to use a steam
cleaner.
Recommendation for Tectyl 506 EH: Allow petro-
leum ether to act for 10 minutes before any further ac-
tion.
Pumps that areusedinthefoodor drinkingwater sector
must be dismantled and thoroughly cleaned prior to de-
preservation.
Asuitable solvent that is compatible with the liquid to be
pumped (drinking water/food) can be used as the
cleaning agent, e.g. Spiritus, Ritzol 155 or suds with a
high alkaline content. Steam cleaning is ideal.
After a prolonged storage period (more
than 6 months), all elastomers (O-rings,
shaft seals) must be checked for elasticity of shape.
Embrittled elastomers must be replaced. EP rubber
elastomers (EPDM) must be replaced on principle.
3.3.2 Storage
During storage of the pump, the suction and outlet
branches and all other supply and discharge branches
must always be closed with dummy flanges or dummy
plugs.
Storage should be in a dry, dust-free room. During stor-
age, the pump should be cranked at least once a
month. During this process, parts such as the shaft and
bearings should change their position.
3.3.3 Monitoring of preservation
The preservation must be checked at regular intervals.
The preserved areas must be inspected every 6
months and re-treated, if necessary.
We cannot accept any liability for defects
that arise due to incorrect preservation
treatment.
ALLMARINE MELO
6 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
4 Description / Principle design of the pump
The pictorial presentation may not correspond with the pump supplied.
The actual design will be stated in the specific order documents.
Pos. no. Description
..................................................
101 Impeller
109 Hub cap
111 Screw
113 Key
118 Sleeve
120 Sleeve
125 Sealing ring
126 V-ring
141 Key
151 Shaft
152 Ball bearing
154 Washer
155 Snap ring
301 Guide vane casing
319 Column pipe
320 O-ring
375 Bearing bush
382 Screw
401 Delivery bend
444 Pipe
451 Stud bolt
453 Screw
464 Plug
503 Bearing housing
504 Screw
506 O-ring
520 Bearing cover
520A O-ring
521 Screw
551 Suction cover
726 Guard
740 Coupling
750 Motor frame
4.1 Series ALLMARINE MELO
seeFig. 4.1
Fig. 4.1
Fig. 4.2
ALLMARINE MELO
7 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
5 Installation/Mounting
5.1 Installation
For installation methods and locations, please see in-
stallation drawing.
Other methods of installation are not permissible
without prior consultation with the manufacturer.
5.1.1 Place of installation
Temperature: min. 20 C
max. +40 C
Relative air humidity:
permanent max. 85 %
temporary max. 100 %
Installation height: max. 1000 m above NN
For data differing from this, please consult the manu-
facturer.
Intensive vibrations in the vicinity of the
pump unit can lead to bearing damage and
must therefore be avoided.
5.1.2 Protective devices
In order to prevent injuries due to burns, at pumping
liquid temperatures higher than 60 C protective de-
vices in accordance with EN 809 must be provided on
site.
5.2 Mode of fastening covering plate/sole plate
Acovering plate/sole plate is used for installation of the
aggregate in the tank.
The tank lid must be constructed in such a
way that it can take the weight of the pump
unit and all operating forces that occur.
Precise details on the shape and dimension of the
covering plate/sole plate are provided in the installation
drawing.
5.2.1 Fixing the pump aggregate
If necessary, a suitable gasket should be fitted by the
customer between the covering plate/sole plate and
the tank lid. Tighten the fastening screws evenly cross-
wise.
The prescribed tightening torque (Section
7.2.3) must be observed.
Precisedetails ontheshapeanddimensionof thefixing
are provided in the installation drawing.
5.2.2 Checking the alignment
After aligning and tightening the screws, it must be
possible to turn the pump and drive by hand, without
any strain.
Note: The pump unit should not be welded to the base
for technical installation reasons.
5.3 Checking the coupling alignment
5.3.1 Coupling alignment in case of flanged aggregates
In the case of pumps with flanged drive motor, the
pump and motor are precisely centered in the lantern.
Alignment or re-alignment of the coupling is not requi-
red.
Note: Improper handling, e.g. during transportation,
may impair the alignment between the pump and the
motor. In this case the pump and the motor must be re-
turned to the factory for checking.
5.3.2 Coupling alignment of special designed couplings
(if present)
Refer to the operating instructions of the coupling
manufacturer.
5.4 Space required for maintenance and repair
The pump must be accessible from all
sides in order to be able to carry out
necessary visual inspections.
Adequate space must be provided for maintenance
and repair work, in particular for removal of the drive
motor or of the complete pump aggregate. It must also
be ensured that all pipelines can be attached and
removed without hindrance.
5.5 Laying the pipelines
5.5.1 Nominal widths
The nominal diameters of the pipelines need not
necessarily correspond to those of the inlet and outlet
branch, however, they must not be smaller. Different
nominal diameters of suction branches and suction
pipelines are to be compensated by suitable transition
pieces. Formation of air bags is to be avoided.
Fig. DN 1
Shorter pipelines onthedischargesideare
possible, but may lead to increased noise
development.
Compensators must not generate any un-
acceptable additional forces on the pump
connection branches. Special care is needed in cases
where compensators are used, whose pressurised di-
ameter is greater than the nominal width of the pump
connection branches.
ALLMARINE MELO
8 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
5.5.2 Changes in cross-section and direction
Sudden changes in cross-section and direction, as well
as bends with a bend radius less than 1.5 times the in-
terior pipe width, must be avoided.
5.5.3 Supports and flange connections
All pipelines must be connected to the
pump stress-free in accordance with
VDMA standard sheet 24277.
The permissible pipeline forces must not
be exceeded in any operating status.
Wethereforerecommendonprinciplethat acalculation
of the pipeline forces is performed, which takes into
consideration all operating status (e.g. cold/warm,
empty/full, depressurised/pressurised, etc.).
Pipeline supports must always be free sliding and must
not rust in (check regularly).
How to assess a pipeline connection
To conduct an assessment, the pipeline must be de-
pressurised, completely drained and cooled. The
pumping liquid must be disposed of with respect for the
environment.
S Disconnect the pipeline from the pump at the con-
necting flanges.
S After disconnecting the connecting flanges, the
pipeline must be freely movable in all directions in
the area of expected expansion.
Note: up to 150 mm by hand
from 150 mm with small lever
S The flanges must lie plane-parallel.
5.5.4 Cleaning pipelines prior to attachment
Prior to assembly, all pipeline parts and valves must be
thoroughly cleaned.
No impurities must reach the pump from
the pipeline system (e.g. welding beads,
residues from preservatives, etc.).
Flange gaskets must not protrude inwards. Blanking
flanges, plugs, protectivefilmand/or protectivepaint on
flanges and seals must be removed completely.
Filters on suction side must be cleaned
regularly. We recommend monitoring with
differential manometer and/or contact manometer.
5.5.5 NPSH observation
The NPSHconditions of the systemmust be adaptedto
the respective pump requirement (NPSH
req.
).
Anessential conditionis fulfilledif thesystemNPSHva-
lue (NPSH
avail.
) is at least 0.5 m above the pump
NPSH value (NPSH
req.
). The NPSH
req.
can be taken
from the characteristic curves of the relevant pumps.
The applicable NPSH values in the char-
acteristic curves are for water with 20 C.
For other media and/or temperatures, the NPSH value
may deviate from the characteristic curves.
Uncertainties in the determination of
NPSH conditions, particularly for media
other than water and/or other temperatures, must be
compensated for by increased safety factors (please
consult the manufacturer).
5.5.6 Pressure pipeline
5.5.6.1 Stop valve in the pressure pipeline
A stop valve should be installed in the pressure pipe-
line.
5.5.6.2 Non-return valve in the pressure pipeline
The pump must not run backwards. It is recommended
that a non-return valve is fitted between the pressure
branch and the stop valve.
5.5.6.3 Bleeding
In the pressure pipeline, bleeding facilities should be
provided at the highest point and in front of the non-re-
turn valve.
5.5.7 Auxiliary connections
The positions of the auxiliary connections on the pump
are shown in the installation drawing. All auxiliary
pipelines must be connected in accordance with the
installation drawing, stress-free and sealed.
For the design with pressure pipeline and covering
plate/sole plate, a manometer may be attached to the
pressure pipeline.
Note: Due to unfavorable flowconditions, the pressure
at this point does not correspond to the actual delivery
pressure of the pump, and so must only be applied for
checking functioning (pump running, pump not run-
ning).
5.6 Safety and control devices
5.6.1 Manometers
We recommend to provide suitable pressure gauges in
the inlet and pressure pipelines, and in the pressurized
auxiliary pipelines.
5.6.2 Safety devices in the inlet, delivery and auxiliary
pipelines
Safety devices in the form of stop valves must be
installed in the pipelines, if not already provided, to
allow the pipelines to be shut off and disconnected
during maintenance and repair work.
5.7 Electrical connections
The power supply cables of the drive motor must be
connected by a trained electrician, according to the
motor manufacturers circuit diagram. The valid VDE
regulations, the regulations of the local electricity board
and the operating manual for the motor must be
complied with.
Danger due to electrical power must be excluded and
an EMERGENCY STOP switch in accordance with EN
809 must be provided.
The pump must not run dry, not even
for checking the sense of rotation.
Refer 6.1... Control of drive motor sense of rotation
5.8 Checking the pressure of the system with built-in
pump
If the whole systemwith built-in pump is to be subjected
to a final pressure test, the test pressure must not be
more than the maximum permissible internal pressure
of the pump (see data sheet).
ALLMARINE MELO
9 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
6 Start-up/Shutdown
6.1 Preparations for (initial) start-up
6.1.1 Filling the tank
The tank must be sufficiently filled with delivery fluid be-
fore starting and during operation, in order to maintain
full delivery of the pump. The fluid level is dependent on
the immersion depth of the pump, and must not fall be-
low the minimum.
The minimum suction head must be
300 mm above the impeller.
During bleeding of the pump and the plant, hazardous
or environmentally harmful fluid and gas emerging
must be safely collected and discharged.
6.1.2 Control of drive motor sense of rotation
The sense of rotation of the motor must match the
sense of rotation arrow on the pump. To check the
sense of rotation, the motor can be switched on briefly
when the pump is full.
The pump must not run dry, not even
for checking the sense of rotation.
If the sense of rotation is incorrect, the sense of rotation
of the three phase motor can be reversed by switching
any two phases.
6.2 Start-up
6.2.1 General
Before starting, all filling and venting openings must be
completely closed.
6.2.2 Starting
To avoid overloading the drive motor, the pump should
berunuponly against aclosedpressurestopvalvedur-
ing starting.
6.2.3 Drive
Switch on the motor.
Refer to the operating instructions of the drive motor
manufacturer.
6.2.4 Minimum rate of flow
Immediately after reaching the operating speed, the
pressure-side stop valve must be opened and the
pump operated up to at least the minimum rate of flow
(see data sheet).
6.2.5 Setting the pump power output values
The pressure-side stop valve must be opened until the
required pump power output values are obtained (see
data sheet).
6.2.6 Temperature
In order to prevent injuries due to burns, at pumping
liquid temperatures higher than 60C protective de-
vices in accordance with EN 809 must be provided on
site.
It must be ensured that the pump housing
is evenly heated. Differences in tempera-
turebetweenthetopandbottomof thepump, as well as
sudden temperature changes, should be avoided.
Temperature changes in the material of more than
50C per minute are not permissible.
6.2.7 Spare pump
A spare pump belonging to the plant must always be
kept ready for operation. For these purposes, the stop
valve on the supply side must be completely open. The
stop valve on the outlet side must be opened to such a
degree that the pump, filled and bleeded, has operating
temperature.
In plants in which impermissible tempera-
ture may arise due to failure of the operat-
ing pump, a standby pump of sufficient output must be
provided.
Two independent energy sources must be provided for
the operating and standby pumps.
6.3 Shutdown
S Pressure pipeline
If a non-return valve is installed in the pressure pipe-
line, the stop valve can remain open. Without non-
return valve, the stop valve must be closed.
S Drive
Switchoff themotor. Makesurethepump runs down
smoothly and evenly.
It must be ensured that the pump does not run back-
wards after switching off. Otherwise, the pump may
reach unacceptably high speeds.
6.4 Measures in the event of standstills
Pumped liquid
...
Measures in the event of
brief standstill
Measures in the event of
prolonged standstill
May solidify
+
has a preservative effect
Hear or drain pump Drain pump
May solidify
+
does not have a preserva-
tive effect
Hear or drain pump
Drain and preserve pump
Does not solidify
+
has a preservative effect
- -
Does not solidify
+
does not have a preserva-
tive effect
-
Drain and preserve pump
See section 3.3
ALLMARINE MELO
10 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
7 Maintenance/Repair
7.1 Maintenance
S The instructions in Section 2, Safety, must be
observed in maintenance and repair work.
S Regular monitoring and maintenance of the pump
and the drive motor are essential for optimum ser-
vice life and safety.
7.1.1 General monitoring
1. The pump must not run dry.
2. The pump must not run in cavitation.
3. The minimum delivery rate must always be main-
tained (see Section 6.2..).
4. The drive motor must not be overloaded.
5. The bearing temperature of rolling bearings must
not exceed 120 C.
6. The shaft seal must have no inadmissible leakage.
7. The pump unit must not experience or generate any
undue vibrations (e.g. as a result of incorrect align-
ment). International standardISO10816must bere-
ferred to for assessment.
8. Changes to the normal operating data may indicate
faults. The causes must be established.
9. Installed standby pumps must be started up once a
week.
7.1.2 Maintenance of components
Special maintenance information can be
found in the additional order-related docu-
mentation.
7.1.2.1 Bearing
Note: Bearing replacement can be performed with
pump in place and without dismantling the entire pump,
see Section 7.2.1.2.
The nominal service life of the bearing is designed for a
minimum of 2 years continuous operation, in accord-
ance with DIN ISO 281. The actual usable life may be
lower, due to intermittent operation, high temperature,
low viscosity, vibrations or the like.
The running noises and the temperature in the bearing
area must be checked at regular intervals. We recom-
mend monitoring bearings by means of shock pulse
measurements. If damage to a bearing is detected, the
bearing must be replaced.
The bearing area can become very hot.
Risk of burning if touched!
As a precautionary measure, we recommend that
the ball bearings are replaced every 2 years.
In the event that a type has been supplied with re-
greasable antifriction bearing (see data sheet):
Please refer to the order-related supple-
mentary documentation for details onanti-
friction bearing greases, lubrication intervals and
grease quantities.
7.1.2.2 Bearing
Note: Bearing replacement can be performed with
pump in pace and without dismantling the entire pump,
see Section 7.2.1.2.
7.1.2.3 Shaft seal (if present)
The built-in mechanical seal is maintenance-free.
A maximum dripping rate of 10 g/h may occur during
operation and is normal. If the dripping is heavier, the
shaft seal must be replaced.
A defective shaft seal can cause uncontrolled dis-
charge of pumping liquid.
This constitutes a hazard to people (possibility of
spraying liquid) and to the environment!
7.1.2.4 Coupling (if present)
The condition of the flexible elements in the coupling is
to be checked at regular intervals.
Note: Worn flexible elements are to be replaced.
7.1.2.5 Drive
Refer to the operating instructions of the motor
manufacturer.
ALLMARINE MELO
11 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
7.2 Repair
General
The systemoperator is responsible for ensuring that in-
struction in safety is provided. The personnel must be
made aware of all hazards that can arise in connection
with the pumped liquid or the plant.
Mounting and repair work
Trained Service fitters are available on request to carry
out mounting and repair work.
For all repairs, it must be ensured that the pump is de-
pressurised, completely drained and cool. The motor
must be protected against unintended switching on.
We must refuse acceptance of repair work on pumps
filled with fluid, for the protection of our staff and for
environmental reasons. The expenditures for disposal
with respect to the environment are to be carry by the
customer/operating company.
Hazardous substances
Where repairs are to be carried out on pumps which
have been operated with hazardous substances
and/or environmentally harmful media, the
customer/operator must inform its own personnel on
site, or our personnel where repairs are returned to our
factory or a service workshop, without being
specifically requested to do so.
Together with the request for a Service fitter a
verification of delivery material, for example in the form
of a DIN safety data sheet, must be submitted to us.
Alternatively, you can request a certificate of safety
(form no. 448/191) from our Service department, filling
it out truthfully, correctly and in full. Send the completed
form to the center commissioned with carrying out the
repair, or hand it to our Service fitter.
Hazardous substances are:
S Toxic substances
S Health-endangering substances
S Corrosive substances
S Irritants
S Explosive substances
S Fire-inducing substances
S Highly flammable, easily flammable and normally
flammable substances
S Carcinogenic substances
S Substances impairing fertility
S Genetically distorting substances
S Substances in other ways hazardous to humans
Pumps or units which pump hazardous substances or
substances that are dangerous to the environment
must be completely decontaminated.
7.2.1 Dismounting the centrifugal pump
Before dismounting, the following work must be carried
out:
S Electrical danger must be eliminated! The motor
must be secured against being switched on. If
necessary, the power supply cable must be
disconnected from the motor by an authorized
electrician.
S Close all stop devices in the pressure pipeline.
S Allow the pump housing to cool to ambient
temperature.
S Remove pump aggregate from tank using suitable
lifting gear.
S Detach pressure pipeline and manometer line, if fit-
ted.
S Drain the fluid in flowable condition from the pump.
Note: Use a collecting tank.
S The pump must be depressurized and drained.
S Hazardous substances and/or environmentally
harmful media must be drained off and collected
such that no danger to life and limb is created.
Environmentally compatible disposal must be
ensured.
S Remove auxiliary pipelines, if fitted.
S Dismount manometer lines, manometers and hold-
ing devices.
The pump must be dismounted by a qualified
technician using the pertaining drawings.
To prevent damage, it is especially important to ensure
that the components are dismounted concentrically
and that they are not tilted.
7.2.1.1 Dismounting instructions
Note: See under Dismounting of the bearing, Section
7.2.1.2 if only the bearings are to be dismantled.
Remove the fastening screws and lift the pump off the
oil tank.
1. Remove guard 726.
2. Remove the screws fastening the motor and lift it
off.
3. Pull coupling half 740 off the pump shaft, by
using an extractor, if necessary.
4. Remove the coupling pins.
5. Remove the pipe 444.
6. Remove motor lantern 750 from delivery bend
401.
7. Remove suction cover 551 fromguide vane cas-
ing 301.
8. Remove screws 111 and hub cap 109.
9. Pull off impeller 101 by means of a puller.
10. Pull off sleeve120: Fit an SKFnut (KM11) onthe
sleeve und use a puller.
11. Remove V-ring 126 and bearing cover 520. If
necessary, remove O-ring 520Aand sealing ring
125 from bearing cover.
12. Remove snap ring 155 and washer 154.
ALLMARINE MELO
12 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
13. Press the shaft out from the pump, remove the
shaft towards the impeller side.
14. Pull the sleeve 118 off the shaft: There are
notches on the sleeve for engaging a puller.
15. Remove bearing housing 152 from the delivery
bend.
16. Press bearings 152 out of the bearing housing.
17. Dismantle delivery bend 401, column pipe 319
and guide vane 301. If necessary, pull bearing
bush 375 off the guide vane casing.
7.2.1.2 Dismounting of grooved ball bearings
The entire pump doesnt have to be dismantled, if only
the bearings are to be replaced. Two special tools are
required: one bearing cover and one puller, they arent
supplied with the pump.
1. Remove screws holding the motor and lift it off.
2. Pull the half coupling off the pump shaft and re-
move the coupling pins.
3. Remove V-ring 126 and bearing cover 520. If
necessary, remove O-ring 520A and lip seals
125 from the bearing cover.
4. Remove snap ring 155 and washer 154.
5. Remove bearing housing 503.
6. Push sleeve and bearing cover (specials tools)
onto the pump shaft. Tighten the bearing cover.
7. Tighten the puller to the sleeve and pull the bear-
ing housing with bearings off the shaft.
8. Press bearings 152 out of the bearing housing.
Press against the inner race of the bearings in
order not to damage them.
7.2.2 Mounting the centrifugal pump
Before remounting check all parts for wear
and aging and, as necessary, replace with
original replacement parts.
Clean all parts before mounting. Always fit new
gaskets.
The pump must be mounted by a qualified techni-
cianusingthe pertainingdrawings. The prescribed
tightening torque must be observed.
To prevent damage, it is especially important to ensure
that the components are mounted concentrically and
that they are not tilted.
Mounting instructions:
S For mounting the pump follow backwards the steps
outlined at Section 7.2.1.1.
S For mountingthegroovedball bearings, followback-
wards the steps outlined at Section 7.2.1.2.
S Make sure that clearance between the two half cou-
pling is about 3 mm.
S After tightening the screws, it must be possible to
turn the pump and drive manually without straining
points.
7.2.3 Tightening torque
Note: With poor and lightly greased surfaces, the va-
lues must beincreasedby 10-15%, inorder toreachthe
required performance.
Thread Quality
Tightening
torque
[Nm]
M 6
M 8
M 10
M 12
M 16
8.8
8.8
21.6
43.1
73.5
117.6
When the centrifugal pump has been mounted the
following work must be carried out:
S Install pump aggregate in plant or tank using suit-
able lifting gear.
S Attach pressure pipeline and manometer line, if
fitted.
S Electrical danger must be eliminated! Power supply
cables must only be connected by qualified
electricians. Pay attention to sense of rotation.
S Fill tank with fluid.
Start up pump as per instructions in Section 6.
7.3 Replacement parts
The application guidelines in accordance with DIN 24
296 can be taken as a basis for spare parts stock hold-
ing.
However, for reasons of operational safety, we recom-
mend the stocking of complete insert units or spare
pumps.
Advantage: In the event of damage, a defective unit
can be replaced by a spare unit without great expendi-
ture and in a very short space of time.
7.3.1 Ordering spare/replacement parts
The following details are required for handling orders
for replacement and spare parts:
S Pump abbreviation
S Pump number
S Year of construction
S Part number
S Denomination
S Quantity
refer to name plate
ALLMARINE MELO
13 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
8 Operating Faults, Causes and Remedial Action
8.1 Faults with reference number for cause and remedial action
The table below is intended as a guide to identifying faults and their possible causes.
If faults occur which are not listed here, or which cannot be traced back to the listed causes, we recommend consulting the
factory, or one of our branch offices or sales offices.
The pump must be depressurized and drained when faults are being rectified.
Centrifugal pump faults Reference numbers for cause and remedial action
Delivery rate too low 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 21, 22
Delivery head too low 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 21, 22
Power consumption of pump too high 9, 11, 12, 17, 21, 22, 25
Delivery pressure too high 9, 12
Bearing temperature increased 17, 18, 20, 25
Pump housing leaky 23
Pump not operating smoothly 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 11, 17, 24, 25, 26
Pump gets hot 2, 5, 26
8.2 Causes and remedial action
Ref. no.: Cause Remedial action
1 Delivery head higher than nominal delivery head
of pump.
1. Open stop valve in pressure pipeline until operating point is
reached.
2. Install impeller with larger diameter.
3. Increase rotation speed (turbine, frequenzy control, ...).
2 Pump or pipelines not properly bled or filled. Bleed and top up pump or pipelines.
3 Screen basket/suction strainer or impeller
blocked.
Clean screen basket/suction strainer and impeller.
4 Air pockets forming in pipeline. Perhaps install a vent valve, or lay pipeline differently.
5 NPSH
plant
(inlet) too low. 1. Check fluid level in inlet tank.
2. Open stop valve in inlet pipeline fully.
3. Check inlet flow conditions of pump.
6 Wrong direction of rotation of pump. Reverse polarity of any two phases on motor.
7 Rotation speed too low. Increase rotation speed (turbine, frequenzy control, ...).
8 Excessive wear on inner pump parts. Replace worn parts.
9 Density or viscosity of delivery medium does not
comply with pump design data.
Consult the factory in the event of faults due to non-compliance
with design data.
10 - -
11 Delivery head lower than nominal delivery head
of pump.
1. Regulate operating point with stop valve in pressure pipeline.
2. Turn off impeller in event of continuous overload.
12 Rotation speed too high. Reduce rotation speed (turbine, frequenzy control, ...).
13 - -
14 - -
15 - -
16 - -
17 Pump twisted. Check pipelines for twists in connections.
18 Excessive axial thrust. Clean relief bore holes in impeller.
19 - -
ALLMARINE MELO
14 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
20 Specified coupling half gap not complied with. Set coupling half gap as per installation diagram.
21 Motor voltage incorrect. Use motor with correct voltage.
22 Motor runs only to two phases. 1. Check cable connection.
2. Replace fuses.
23 Screws not tight. 1. Tighten screws.
2. Replace gaskets.
24 Impeller out-of-true. 1. Clean impeller.
2. Re-balance impeller.
25 Groove ball bearing defective. Replace groove ball bearing.
26 Delivery rate below minimum. Increase delivery rate to minimum.
Consult factory
ALLMARINE MELO
15 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
9 Order-specific Documentation
These operating instructions are supplemented by the following documents:
Acceptance of order No.
Data sheet No.
Installation drawing No.
Sectional drawing No.
Part list No.
ALLMARINE MELO
16 VM 490.0023 GB/07.03 - Ident-Nr. 550 299
Notices
Subject to technical alterations.
A Member of the
COLFAX PUMP GROUP
ALLWEILER AG S Werk Radolfzell
Postfach 1140 S 78301 Radolfzell
Allweilerstrae 1 S 78315 Radolfzell
Germany
Tel. +49 (0)7732 86-0
Fax +49 (0)7732 86-436
E-mail: service@allweiler.de
Internet: http://www.allweiler.com
1 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
This instruction is valid for all TRE pump models shown on page 2
Contents Page
List of components 2
Exploded view 3
Ordering code/Service intervals 4
Sectional view 5
Useful tools/Shaft seal-assembly drawing 6
Dismantling/reassembly 7
Pressure relief valve/SealGuard 11
Screw pumps
TRE
Maintenance and Service
Instruction
Ident No 550 811
October 2001
2 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
Before commencing any work, read this instruction carefully! Failure to comply with
these instructions may cause damage and personal injury!
!
Valid for all pumps in sizes: TRE 20,40,80
With code for shaft seal: 18.1 = type carbon
18.2 = type Silicon carbide
18.3 = type Silicon carbide with SealGuard
List of components
For more information about the pumps identification code, technical data and performance we refer to the
TRE Product description. For more information about the pumps installation, Start-up and trouble shooting
we refer to the "Installation and Start-up instruction" for Low Pressure Pumps, ident No 550 802.
Pos Denomination Q-ty G053A Notes
1010 Power rotor 1
1020 Power rotor 1
113 Key 1
122 Ball bearing 1 x
125 Secondary seal 1 x 1
201 Idler rotor 2
202 Idler rotor 2
351 Balancing bush 1
401 Pump body 1
416 Suction flange 1
417 Screw 8
418 Gasket to 1 x
suction flange
423 Gasket to 1 x
discharge flange
427 Discharge flange 1
440 Return valve 1
451 Screw 4
453 Screw 4
462 Plug 1
462A Sealing washer 1 x
463 Plug 1
463A Sealing washer 1 x
501 Front cover 1
506 Gasket 1 x
509 Shaft seal 1 x
537 Deaeration plug 2
537A Washer 2 x
551 Rear cover 1
556 Gasket 1 x
557 Plug 1
557A Washer 1 x
605 O-ring 1 x
608 Valve spindle 1 x
608A Tension pin 1 x
6120 Set screw 1 x
613 Pin 1 x
614 Valve piston 1 x
615 Valve spring 1 x
7310 Compl. Seal 1 2,3
Guard
732 Gas generator 1 2
Explanations:
G053A: Spare parts kit
Notes:
1) For version 18.2 and 18.3
2) For version 18.3 only
3) Including Gasgenerator
Components included
in spare parts set:
3 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
Exploded view
Fig. 1
All work carried out on the pump has to be
performed in such a manner that risks for
personal injury are observed!
When handling liquids that may harm skin
use gloves and/or protective clothing.
!
!
!
!
When handling liquids which may involve
fire hazards appropriate precautions to
avoid danger are to be taken.
In case of failure for a system with elevat-
ing pressure fluid jets may cause injury
and/or damage.
Oil leakage may make the floor slippery
and cause personal injury.
Connecting and disconnecting of electric
cables must be done only by personnel
authorized to do such work.
!
Before any maintenance work, ensure that
the driver is deenergized and the pump
hydraulically isolated.
!
451
501 125
463 463A
537A 537
557A
557
537A
537
506
440
401
556
551
453
(608A)
(614)
(615)
(613)
(6120)
(608)
(605)
462A
462
122
351
113
1020
202
509
418
416
417
423
427
xVxx
xTxx
732
7310
xQxx
xTxx, xQxx
xQxx
xQxx
at 18.1
at 18.2
at 18.3
at 18.2, 18.3
at 18.3
at 18.3
4 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
Recommendation:
For maintenance the following spare
part sets are recommended:
Set: To be used:
G053A Spare parts kit
For service.
Item Spare Parts sets 20 40 80
G053A Spare parts kit with 18.1 70191335 70191335 70191337
Spare parts kit with 18.2 70191336 70191336 70191338
Spare parts kit with 18.3 70191336 70191336 70191338
Part numbers for pump size
Ordering code
Inspection of shaft seal
Excessively leaking shaft seals (more than 10 drops
per hour) should be changed without delay, as the
leakage normally will grow worse and cause addi-
tional damage.
In installations where unplanned shut downs must
be avoided, it is advisable to dismantle the pump for
a thorough inspection and thereby change out shaft
seal and ball bearing, every three years as a max
period.
It is recommended always to have the spares in-
cluded in minor spare part kit G053A available.
Inspection of rotors
A quick inspection of the idler rotors can be made
simply by removing the rear cover. Note that the
driver must be deenergized and the pump hydrauli-
cally isolated before the rear cover is removed.
If a more thorough investigation is needed, proceed
as under Dismantling/Reassembly.
Service intervals
The intervals for inspection and replacement of wear
parts vary greatly with the properties of the pumped
liquid and can only be determined by experience.
Pumping liquid which contains abrasive materials,
or liquid that is corrosive, will significantly reduce
service life and call for shorter service intervals.
Wear will normally show as unnormal:
Vibration
Noise
Loss of capacity
Reduction in flow/pressure
Leakage
!
If the pumps operating temperature exceeds
60C let the pump cool off before any service,
maintenance or dismantling work is com-
menced to avoid burn injury.
5 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
Sectional view
Fig. 2
732
537A 537
7310
(at 18.3)
125 (at 18.2, 18.3)
C - C E - E
463 463A
6 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
d
L
D
Fine
emery
Puller
Screw
spanner
16 mm
Plastic
mallet
Sliding calliper
Oil can
Screw
driver
Mounting tool kit
Shaft seal - assembly drawing
Fig. 4
Useful tools
Fig. 3
Allen key
5 mm and
3 mm
Shaft seal G050 (509)
Version code 18.2
S1 Seat
S2 O-ring
S3 Retainer
S4 Seal ring
S5 Carrier
S6 O-ring
S7 Spring unit
S8 Stop screw
+ Secondary seal 125
Version code 18.3
18.2 + Complete
SealGuard 7310
Version code 18.1
S1 Seat
S2 O-ring
S4 Seal ring
S6 O-ring
S7 Spring unit
S8 Stop screw
Stationary member Rotating member
Front
cover
retaining
tab
Seat slot
S8
Seat retaining lug
S4
S6
S1
S2
S7
S8 S5
S6 S1 S2
S3
S7 S4
S4, S7 is one unit
Stationary member Rotating member
Tool 2
Tool 1
D= 25,5 mm
For dimension and material,
please contact our Service.
Retainer lug
Seat slot
7 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
F.
B.
E.
Remove the shaft
coupling.
Remove the key 113.
Fig. 9 Fig. 10
Dismantling
Turn the electricity OFF.
Close the valves.
Remove the pump
from the system.
ATTENTION
Use appropriate vessels to collect oil spill-
age when removing and opening the pump.
Note the position of the shaft coupling.
Release the stop screw.
A.
C.
Fig. 8
Fig. 7
ON OFF
Fig. 5
D.
Remove the front cover 501 and power
rotor 1020.
Fig. 6
451
113
1020
Remove the
screws 451.
501
8 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
501
1020
G.
L.
Fig. 13 Fig. 14
Fig. 11 Fig. 12
Fig. 15
Separate the front
cover 501 and the
power rotor 1020.
K. 18.2 and 18.3
Place the front cover 501 on a pair of
wooden pieces.
Press out the shaft seal, stationary member
with a suitable tool.
Loosen the shaft seal rotating member.
Remove and inspect the
idler rotors 202.
I.
202
Remove the secondary seal 125 with a
suitable screw driver.
Fig. 16
H. 18.2 and 18.3
501
501
125
Insert two suitable
screw drivers in the
carrier S5 slots and
gently push the
rotating member
S4, S7 off the rotor
shaft.
Loosen the two
stop screws S8
(3 mm Allen key)
on the carrier S5
and pull it off.
at
18.1
at
18.2
18.3
J. 18.1
Rotating
Member
S5
S8
9 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
Reassembly
A.
Fig. 19
Fig. 20
Fig. 17 Fig. 18
Fig. 21
C. 18.1
E.
Fig. 22
Lubricate
the idler rotors 202
and fit them into the pump body 401.
B.
Un-pack a new shaft seal 509.
Check that the O-ring S6 is in place.
18.1 18.2, 18.3
Polish the power rotor shaft
1020 with a fine emery and oil.
Fit the rotating member above
the ball bearing 122 and lock it
with its stop screws S8.
122
D. 18.2 and 18.3
Polish the power rotor shaft
1020 with a fine emery and oil.
Fit the carrier S5 tight against the
ball bearing. Make sure the carrier
is not fitted upside down.
Firmly tight the two stop screws S8.
Lubricate the O-ring S6 in the rotat-
ing member with oil.
Press the rotating member S4, S7
gently on to the rotor shaft and make
sure the driving lugs enters the slots
in the carrier S5.
401
1020
Insert the Power rotor 1020 into the pump
body 401.
F. 18.2 and 18.3
501
125
1 2
Press the Secondary
seal 125 in place with
a suitable tool in two
steps as shown. Use a
column drill machine
as a press tool.
NOTE!
Tool nr 2 has
one end for sizes
025, 032 and one
end for size 038
202
401
Oil can
Emery
S6
S6
S4
S8
S8
S5
S4,S7
Tool 1 Tool 2
S5
Rotating
member
10 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
Fig. 27
Fig. 26
Fig. 23
Fig. 25
Fig. 24
Fig. 28
G. 18.1
Fit the spring unit S7 in place.
Note the position for the Seat
slots and lugs.
(See fig 4.)
Lubricate the O-ring
S2 and put it on the
seat S1. Fit the seat
S1 on top of the
spring unit. Watch
position of the Seat
slots and lugs.
(See fig 4.)
Press the seat gently into the recess in the
front cover 501 with a suitable tool as
shown.
Turn the front cover 501 up-side down. The
seat shall now remain in the cover.
Fit the retainer S3
in place. Note the
position for the
retainer lugs and
cover slots.
(See fig 4.)
Lubricate the
O-ring S2 and
put it on the
seat S1. Fit the seat S1
on top of the retainer.
Watch the position of the seat
slots and lugs. (See fig 4.)
Press the seat gently into the recess in the
front cover 501 with a suitable tool as shown.
Turn the front cover 501 up-side down. The
seat shall now remain in the cover.
H. 18.2 and 18.3
501
I.
506
Replace the gasket
506.
Carefully fit the
Front cover 501 on
the pump.
J.
451
Fit the screws
451.
Tight them crosswise,
step by step to avoid
deformation on bearing
outer ring and seal
damages.
Turn the shaft to check
that it moves without
too much force.
K.
113
Fit the key 113 back in place.
Press on the shaft coupling
to its original position.
Tighten the stop screw.
Install the pump
back into the
system and proceed
according to in-
structions under
Start-up in the
Installation manual.
L.
501
S1
S2
S7
501
S1
S2
S3
Tool 1
Tool 1
11 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
1
2
5
7
6
9
8
10
4
3
Gas generator
Note!
Must be open
6
9
1
2
3 1 0
Fig. 29
Pressure relief valve
ATTENTION
Spring tension.
Release spring tension by turning set screw 6120
CCW as much as possible.
Loosen and remove the screws 453.
Separate the valve element from the rear cover
551.
If necessary, replace the gasket 556 and the
O-ring 605.
Reassemble the parts in reverse order. Be careful
to tighten the screws 453 crosswise.
Readjust the valve pressure according to the
Installation and Start-up Instruction for Low
pressure pumps.
453
612
551
605
556
Recharging
1) Disconnect the pipe connector (4) from the
dispenser (2). Remove the check valve (3).
2) Remove the cover disk (10). Remove the gas
generator (9) from the dispenser (2) with a 21
mm socket. Dispose the generator in the recyc-
ling system for batteries, where available. Push
the piston to its filled position, and fill the
dispenser with high-temperature resistant engine
oil. Fit the check valve (3) and the connector (4)
to the dispenser.
3) Feed oil into the hose (5) and seal compartment,
for example with an oil-filled grease gun. Recon-
nect the hose (5) to the connector (4).
4) Fit a new gas generator (9) to the dispenser (2).
Tighten with approx. 2 Nm. Clip on the cover
disk (10).
5) Turn the gas generator set knob (3 mm Allen
key) to no. 6 which will make the oil last for
about 3 months.
Keep away from open fire when
removing the gas generator.
!
SealGuard
For more information about
SealGuard, read the Installa-
tion and start-up Instruction
for SealGuard.
ATTENTION
The SealGuard can be
readjusted or switched off
during operation.
Depending on temperature
and setting, it can take from
hours to a couple of days
after starting, until oil is
being dispensed.
NOTE!
For longer periods of stand-by, the gas gene-
rator set-knob could be set to zero to avoid
unnecessary oil consumption.
6120
Fig. 30
With code for shaft seal: 18.3 = type Silicon carbide
with SealGuard
12 Ident No 550 811
October 2001
Subject to technical alterations
ALLWEILER AG
Postfach 1140 78301 Radolfzell
Allweilerstrae 1 78315 Radolfzell
Germany
Tel. +49 (0) 7732 86-0
Fax +49 (0) 7732 86-436
E-mail: service@allweiler.de
Internet: http://www.allweiler.com
UNIPUMP
Close Coupled Sewage pump
Series K, HK, QSH
Operating Instructions
Herborner Pumpenfabrik J .H. Hoffmann GmbH & Co.
House address:
Littau 3-5
D-35745 HERBORN
info@herborner-pumpen.de
Phone
++49
(2772)
933- 0
Telefax
++49
(2772)
933- 100
Internet
http://www.herborner-pumpen.de
We reserve the right to make technical modifications in line with technological advancements !
A - BA20 GB
A
l so
o
n
th
e
In
te
r n
e
t!
2
1. General information .................................................................................. 3
1.1 Intended application ...................................................................................... 3
1.2 Model designation ......................................................................................... 3
1.3 Technical specifications rating plate ......................................................... 3
1.4 Noise level ...................................................................................................... 4
2. Safety ......................................................................................................... 5
2.1 Marking of safety instructions in the operating manual ............................... 5
2.2 Qualifications and training of personnel ...................................................... 5
2.3 Dangers caused in negligence of safety instructions .................................. 5
2.4 Safety awareness ........................................................................................... 6
2.5 Safety instructions for the operator/user ...................................................... 6
2.6 Safety instructions for maintenance,
inspection and installation work ................................................................... 6
2.7 Unauthorised modifications and use of non-genuine spare parts ............. 6
2.8 Unapproved usage ........................................................................................ 6
3. Transportation........................................................................................... 7
3.1 Transport equipment...................................................................................... 7
4. Description ................................................................................................ 8
4.1 Shaft seal ........................................................................................................ 8
4.1.1 Checking the seal on the tandem arrangement .......................................... 8
4.2 Drive ................................................................................................................ 8
4.2.1 Motor specifications ....................................................................................... 9
5. Erection and installation......................................................................... 10
5.1 Erecting the pump ........................................................................................ 10
5.2 Sectional drawing ........................................................................................ 10
5.2.1 Spare parts ................................................................................................... 13
5.3 Laying the pipelines ..................................................................................... 13
5.3.1 Intake line ..................................................................................................... 13
5.3.2 Discharge line .............................................................................................. 14
5.4 Frost protection ............................................................................................ 14
5.5 Electrical connection ................................................................................... 15
5.6 Checking the direction of rotation ............................................................... 15
5.6.1 Altering the direction of rotation .................................................................. 15
5.7 Start-up mode ............................................................................................... 15
6. Commissioning........................................................................................ 17
7. Maintenance ............................................................................................ 18
7.1 General maintenance instructions .............................................................. 18
7.2 Maintenance instructions following a prolonged shutdown ..................... 19
7.3 Greasing the bearings ................................................................................. 19
7.3.1 Greasing interval table ................................................................................ 19
7.4 Cleaning ....................................................................................................... 20
7.5 Removing the pump ..................................................................................... 20
7.6 Filling and changing the oil - tandem arrangement .................................. 20
7.7 Official acceptance ...................................................................................... 20
General information
3
1. General information
1.1 Intended application
UNIPUMP close coupled sewage pumps with non-clogging-system of Herborner
Pumpenfabrik are suitable for pumping
Contaminated fluids with grain sizes up to 80 mm diameter.
They MUST NOT be used to pump the following:
Combustible or explosive media!
Media containing aggressive chemicals which could damage the
pump material!
NOTE Bronze or stainless steel pump materials are available for pumping
aggressive and abrasive media.
The use of explosion-proof motors is permissible.
1.2 Model designation
Example: 10 / QSH 101 - 1 - 220
Impeller diameter
Number of paddles
Size
Series
Motor output P, e.g. 10 = 10 horsepower
1.3 Technical specifications rating plate
Technical specifications regarding the type of pump used can be taken from either
the brochure, these operating instructions or the rating plate.
We recommend that you make a note of the specifications for the supplied pump, as
shown on the original rating plate, in the following diagram, so that this information is
accessible whenever you need it.
NOTE In case of queries and when ordering spare parts, you will be required
to state the pump type and order no.
General information
4
Key to rating plate
Typ Pump type
Nr. Serial number
Bj. Year of construction
A-Nr. Order no.
Q Rated delivery rate [m/h]
H Rated discharge
head [m]
n Rotary speed [rpm]
mP Power output [kW]
Key to the rating plate on the motor (not shown)
Typ Motor type
Nr. Motor number
U Operating voltage [V]
I Rated current [A]
50Hz/60Hz Frequency [Hz]
P
1
Power input [kW]
P
2
Power output [kW]
n Rotary speed [rpm]
cos Power factor
3~ Three-phase a.c. motor
IP 55 Protection category
Kl.F Insulation category F
Y Type of circuit
NOTE The information on the rating plates may vary depending on the motor
manufacturer!
1.4 Noise level
The maximum noise level is generally determined by the drive motors via air, magnet
and bearing noises.
The system does not exceed the permissible limit curves for electric motors as
specified by VDE 0530 part 9/12.84.
Lowest noise generation during operation is close to Q
OPT
.
Safety - Information
5
2. Safety - Information
(Based on VDMA- Instruction sheet 24292)
The Operating Manual contains fundamental instructions to be observed during
installation, operation and maintenance. Therefore, it is essential that these
instructions are read carefully by both the fitter and the person responsible/user
before installing and starting the unit. The Operating Instruction should always be
available at the location of the unit.
Not only the general instructions listed in this chapter Safety-Information should
be followed carefully, but also the specific safety instructions stated in the other
chapters of the manual.
As soon as the pump as a single machine is part of an entirety of machines,
the superior operating manual should be observed for a total safety inspection.
2.1 Marking of safety instructions in the Operating Manual
All safety instructions stated in this Operating Manual, which may cause
hazards if neglected, are highlighted with a common danger symbol
(specifications DIN 4844-W9).
Warning against dangerous voltage is indicated by this danger symbol
(specifications DIN 4844-W8).
CAUTION refers to safety instructions which may cause damages to the
equipment or affect its functions if neglected.
NOTE Instructions written directly on the equipment, i.e.:
direction of rotation arrow
name plates
must be absolutely followed and kept in a legible condition.
2.2 Qualifications and training of personnel
Operating, maintenance, inspection and installation personnel must prove
qualifications for the respective duties. Areas of responsibility, competence and
personnel supervision should be clearly defined by the user. If the personnel is not
sufficiently qualified, it should be trained and instructed accordingly. Such a training
can be carried out on behalf of the manufacturer/supplier at the request of the user.
Further, the user should ensure that the contents of the Operating Manual is fully
understood by the personnel.
2.3 Dangers caused in negligence of safety instructions
Disregarding safety instructions can cause danger to persons as well as to the
equipment and to the environment. Disregarding safety instructions can invalidate
the right to any damage claims. In particular, disregard for safety instructions may
result in the following hazards:
Failure of important functions of the plant.
Danger to persons by electrical, mechanical or chemical impact.
Danger to the environment by leakage of dangerous substances.
Safety - Information
6
2.4 Safety awareness
The Safety Instructions listed in this Operating Manual, the existing national safety
regulations, as well as any internal operating and safety instructions which apply
in the users own premises should be respected.
2.5 Safety instructions for the user/ operator
Safety guards for moving parts (e.g. ventilator hoods) may not be
removed while the unit is in operation.
Dangers due to electrical energy must be excluded (for details,
please refer to the regulations of the VDE and of the local Power
Supply Company).
Leakage (for example of the mechanical seal) of dangerous liquids
(explosiv, toxic, hot) have to be drained off without dangers for persons
and country. Legal rules must be followed.
2.6 Safety instructions for maintenance, inspection and installation work
The user must ensure that all maintenance, inspection and installation work is
carried out by authorized and qualified personnel, that has familiarized itself
thoroughly with the Operating Manual.
As a rule, all work on the unit should only be carried out when it is switched off. The
procedures described in the Operating Manual for stopping the unit should be
strictly followed.
Pumps or agregates used for pumpi ng harmful substances shoul d be
decontaminated.
Immediately after completion of work, all safety and protective devices should be
refitted and fully functional.
Before re-starting the plant, the instructions for electrical wiring and installation
should be followed again.
2.7 Unauthorized modifications and use of non-genuine spare parts
Modifications or changes to the unit are only authorized upon approval of the
manufacturer. Only genuine spare parts and original accessories will ensure the
safety of the unit. The use of non-genuine spare parts and accessories can result
in the annulments of the liability for damages caused thereby.
2.8 Unapproved usage
The operating safety of the unit is only guaranteed, provided that the unit is used in
accordance with the Safety and Operating Instructions.
Any other usage is not in conformity with the regulations. Consequently, the
manufacturer is not liable for any resulting damages. Unauthorized usage is at the
users risk.
The correct usage of the unit also implies a strict observation of the operating,
maintenance and serving instructions issued by the manufacturer.
The Installation and Operating Manual does not invalidate general
regulations and standards not refered to.
General technical rules should be observed.
2
.
S
a
f
e
t
y
Transportation
7
3. Transportation
Brace the pump to protect it against falls and impact!
Secure the pump to prevent it from tilting!
3.1 Transport equipment
The pump should be transported using slings, taking care to ensure a secure grip.
The lifting gear and slings must be adequately dimensioned for the
weight of the pump!
The pump should be deposited on a sufficiently firm surface which is
completely level.
CAUTION Special care should be taken to ensure that the unit is not top-heavy,
otherwise it could topple over.
The accident prevention regulations and generally recognised technical rules must
be observed.
2
.
S
a
f
e
t
y
Description
8
4. Description
4.1 Shaft seal
On the intake side, all models are sealed with maintenance-free mechanical seals
of wear-resistant materials which have been adapted to suit the respective operating
conditions.
The pump can optionally be fitted with a mechanical seal in a tandem arrangement.
On the discharge side, all motors are equipped with a special seal to protect against
splashes.
CAUTION If the pump is allowed to run dry, the mechanical seal will be destroyed!
4.1.1 Checking the seal on the tandem arrangement
In pumps with a tandem seal, the shaft seal consists of two mechanical seals
arranged one in front of the other.
The oil chamber is filled with lubrication oil for lubrication and cooling.
NOTE The seal can be checked via an electrode.
- Connect the electrode to an electrical level monitor.
- Change the oil after 4000 hours.
- Oil grade in accordance with ISO VG 46 (e.g. Shell Tellus 46).
Circuit example:
Function:
- When the electrode is immersed in an
electrically conductive liquid, a control
voltage of approximately 3 mA will flow.
- By means of a measuring amplifier, the
control current can actuate a control
current relay with a potential-free two-
way contact.
4.2 Drive
The pump is equipped with a three-phase squirrel-cage motor
- Voltages to IEC 38
- Circuit:
- Protection category IP 55
- Insulation category F
The precise motor specifications can be taken from the rating plate.
The motor is cooled via heat dissipation from the cooling fins to the ambient air.
CAUTION Observe the coolant temperature as specified on the rating plate!
50Hz 60Hz
380V
220-240/380-420V 250-277/440-480V < 3kW
380-420V 440-480V > 3kW
400V
230/400V 265/460V < 3kW
400/690V 460V > 3kW
Description
9
4.2.1 Motor specifications
CAUTION Rated output and rated current at a permissible temperature-rise limit
of 80K and cooling temperature of 40C to VDE.
Rated Rated
output [380V] [400V] output [440V] [460V]
[kW] [kW] [kg]
0,75 /K 25 0,55 1,7 1,55 0,66 1,65 1,53 Y 26
1 /K 50 0,75 2,2 2,0 0,9 2,2 2,0 Y 34
1,5 /K 50 1,1 2,85 2,6 1,3 2,8 2,55 Y 38
2 /K 50 1,5 3,8 3,55 1,8 3,7 3,55 Y 41
3 /K 50 2,2 5,4 4,9 2,6 5,3 4,85 Y 49
3 /K 80 2,2 5,4 4,9 2,6 5,3 4,85 Y 70
4 /QSH 101 3,0 7,3 6,7 3,6 7,3 6,7 82
5,5 /QSH 101 4,0 9,4 8,6 4,8 9,3 8,7 89
7,5 /QSH 101 5,5 12,0 11,3 6,6 11,9 11,3 109
10 /QSH 101 7,5 15,6 14,8 9,0 15,8 15,0 121
60Hz
Type Rated current Circuit
Weight
[A] [A]
Rated current
1500 rpm 1800 rpm
50Hz
Rated Rated
output [380V] [400V] output [440V] [460V]
[kW] [kW] [kg]
1 /HK 25 0,75 1,93 1,75 0,9 1,9 1,73 Y 26
1,5 /HK 25 1,1 2,7 2,45 1,32 2,7 2,4 Y 27
3 /HK 50 2,2 4,9 4,6 2,6 4,9 4,55 Y 41
4 /HK 50 3,0 6,3 6,3 3,6 6,4 6,2 50
5,5 /HK 50 4,0 8,6 8,0 4,8 8,4 8,0 57
4 /HK 80 3,0 6,3 6,3 3,6 6,4 6,2 72
5,5 /HK 80 4,0 8,6 8,0 4,8 8,4 8,0 78
7,5 /HK 80 5,5 11,9 10,7 6,6 11,3 10,7 98
10 /HK 80 7,5 16,2 14,1 9,0 15,1 14,2 106
15 /HK 80 11,0 21,0 20,5 13,2 21,5 21,0 149
20 /HK 80 15,0 31,0 27,5 18,0 30,0 28,0 164
Type
50Hz 60Hz
Circuit
[A] [A]
Rated current Rated current
Weight
3000 rpm 3600 rpm
Erection and installation
10
5. Erection and installation
5.1 Erecting the pump
CAUTION For operational safety reasons, the vertical type motor should not be
positioned pointing downwards!
Provide sufficient space for maintenance and repair work!
When ins talling the pump, care s hould be taken to ens ure an
adequate supply of cooling air during operation.
The lifting gear (load hook, crane) required for installation and rem-
oval must be adequately dimensioned for the overall weight of the
pump and must comply with the valid safety regulations.
5.2 Sectional drawing
K 25 ... HK 25
Type F
Type GF
1 2 5 17 7
13 12 11 29
3 44
27 28 48
1 2 5 17 7
13 12 11 29
3 44
27 28 48
Erection and installation
11
K 50 ... HK 50
K 80 ... HK 80
1 2 5 18 3 17 7
12 11 13 44 27 28 48
1 2 11 5 18 3 17 7
12 11 19 13 44 27 28 48
Erection and installation
12
QSH 101
1 Casing
2 Impeller
3 Rear wall
5 Vent plug
7 Motor
11 Casing joint
12 Drain plug
13 Impeller nut
17 Mechanical seal
18 Bush
19 Cover
20 Impeller cap
27 Ball bearing
28 Ball bearing
29 Disc
44 Shaft with rotor
48 Labyrinth disc
63 Disc
64 Seal cover
66 O-ring
67 Mechanical seal
68 O-ring
69 Vent plug
70 Monitoring electrode
71 Vent plug
72 Oil drain plug
73 Oil
74 O-ring
75 Joint ring
81 Casing wear ring
Detail "Y"
Detail "X"
68 71 69 64 70 63
74 75 67 17 66 72 73
Erection and installation
13
NOTE No specific foundation is required for erecting the pump. A flat surface
is adequate.
Anchoring with four fastening bolts.
Only use removable screws to facilitate subsequent removal without
having to loosen the flange connections.
Under no circumstances should studs or foundation anchors be used!
CAUTION When erecting outside, a protective roof should be erected to shield
against the elements.
5.2.1 Spare parts
The specifications for further selection of spare parts are related to the initial need
for a two year operation based on DIN 24 296.
5.3 Laying the pipelines
Attach the intake and discharge line without tension.
5.3.1 Intake line
To avoid air pocket formation:
Lay the intake line with a continuous rise.
The supply line should have a slight gradient towards the pump.
NOTE If local conditions do not permit a continuous rise in the intake line,
provision should be made for complete venting.
Installation of a...
gate valve to close the lines immediately in front of the pump, to allow
the pump to be removed without first draining the lines.
Spare parts
(generally existing)
Number of pumps (including reserve pump)
1 2 3 4 5 6-7 8-9 10-..
Number of replacement parts
Impeller 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 20%
Cover 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 20%
Mechanical seal 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 25%
Ball bearing set 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 25%
Shaft seal ring 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 25%
Split ring 1 2 2 2 3 3 4 50%
Seal set 2 4 6 8 8 9 12 150%
Shaft + accessories 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 20%
Erection and installation
14
5.3.2 Discharge line
The locally valid regulations should be observed when laying the discharge line.
CAUTION When laying the discharge line, provisions should be made for
complete venting.
The discharge line should be installed in a frost-proof area.
Installation of a...
gate valve to close the lines immediately in front of the pump, to allow
the pump to be removed without first draining the lines.
non-return device between the discharge connection and gate valve,
prevents return flow of the pumping medium after shutting off the pump.
5.4 Frost protection
During long periods of shutdown, the pump should be drained if there is a risk of
frost.
Open the drain plug in the casing.
Take care to ensure that the escaping medium does not cause injury or
damage the motor or other components. In systems with hot media,
beware particularly of the risk of scalding.
CAUTION Before commissioning the pump
Close the drain plug in the pump casing.
Erection and installation
15
5.5 Electrical connection
Before commissioning, have the system checked by an expert to verify
that the required electrical safety measures have been implemented.
The earthing, TN system and residual current operated system etc.
must satisfy local regulations and must be inspected by a qualified
electrician to verify proper functioning.
CAUTION The cross-section and voltage drop of the mains supply line must
comply with the relevant regulations (e.g. VDE, VE or local
equivalent). The voltage specified on the pumps rating plate must
match the available mains voltage.
Motors with built-in thermistor temperature sensors:
- Test voltage of PTC thermistor max. 1,5 V!
- Only are able to work in conjunction with a tripping unit!
The pump should be protected by an appropriate back-up fuse (corresponding to
the rated output of the motor). The size of the motor protective circuit breaker should
be 1,05-fold of the current consumption.
5.6 Checking the direction of rotation
For rotary current pumps, the direction of rotation should be conscientiously checked
when commissioning for the first time and at every new location. An incorrect
direction of rotation will impair performance and may damage the pump.
In the case of control systems comprising several pumps, each pump should be
checked individually.
Looking at the motor fan, it should rotate in a clockwise direction.
The di re cti on of rotati on s houl d
match the arrow.
CAUTION Switch the pump off immediately after starting.
If the pump is allowed to run dry, the mechanical shaft seal will be destroyed.
When checking the direction of rotation, the pump should be secured
in such a way as to eliminate the possibility of injuries caused by the
rotating impeller. Never put your hand into the discharge connection
or the intake opening of the pump casing.
5.6.1 Altering the direction of rotation
If the direction of rotation is incorrect, it can be reversed by swapping over two
phases of the supply cable in the control unit.
5.7 Start-up mode
The following motor circuit-breaker settings are required:
For direct starting: set to rated motor current
For Y starting: set to rated motor current x 0.58
Erection and installation
16
Motor connection diagrams:
The incorrect electrical circuit type will cause failure of the electric
motor!
Operating
voltage
(mains )
Motor voltage (motor rating plate)
D
i
r
e
c
t
s
t
a
r
t
i
n
g
S
t
a
r
/
d
e
l
t
a
s
t
a
r
t
i
n
g
or
Commissioning
17
6. Commissioning
Before commissioning, the pump should be inspected and a functional check
carried out. In particular, the following points should be checked:
Have the pump and pipelines been connected in accordance with
regulations?
Does the electrical connection satisfy the valid provisions?
Is the motor circuit-breaker correctly set?
Are the valves required for operation open?
Have the connection cables been installed in accordance with
regulations?
Is the pump correctly seated in the anchor?
Have the covers of the suction- and delivery side been removed before
mounting (only with water supply)?
CAUTION When commissioning, the pump and intake line should be vented
and primed with pumping liquid before starting up!
The shut-off valve in the intake and discharge lines must be fully
open.
If the pump is allowed to run dry, the mechanical shaft seal will be
destroyed.
Do not touch pumps which are used for pumping hot water risk of
burns!
NOTE If the density or flowrate exceeds the designed capacity, care should
be taken to ensure that the motor is not overloaded and that the available
feed height is reached (cavitation!).
Maintenance
18
7. Maintenance
Before starting maintenance work, all poles of the pump should be
disconnected from the mains and secured against re-activation.
When carrying out maintenance and repair work, the safety regulations
governing work in enclosed spaces and the generally recognised
technical rules must be observed.
NOTE The maintenance tips given here are not intended as a guide for carrying
out your own repairs specialised experience is required for this
purpose.
By entering into a maintenance contract with our customer service
department, you can be assured of top quality, expert service at all
times.
7.1 General maintenance instructions
Pumps manufactured by Herborner Pumpenfabrik are established quality products
and are subject to stringent final inspections.
Should you experience a malfunction despite this, under no circumstances should
you attempt to improvise consult our customer service department.
This applies in particular in the case of repeated shutdowns by the overcurrent trip
in the control unit, or in the event of alarms.
To ensure a long service life, the checks and maintenance work outlined below
should be carried out at regular intervals.
Our sales force will be pleased to advise you on special applications and help solve
your pumping problems.
NOTE Within the context of supply agreements, Herborner Pumpenfabrik will
only guarantee its products provided repairs are carried out by authorised
agents and proof is furnished that original spare parts for Herborn pumps
have been used.
6
.
C
o
m
m
i
s
s
i
o
n
i
n
g
7
.
M
a
i
n
t
e
n
a
n
c
e
Maintenance
19
7.2 Maintenance instructions following a prolonged shutdown
NOTE Before switching on the pump and during a prolonged shutdown,
rotate the motor shaft several times by hand on the fan.
7.3 Greasing the bearings
Bearing of the common shaft for the pump and motor
Anti-friction bearings have been greased in the factory
Refer to the greasing interval table for lubrication periods
The grade of lubrication grease which should be used is
STABURAGS NBU 8 EP
CAUTION Avoid over-greasing the bearings.
Grease presses with hydraulic head H to DIN 71412
The quantity of grease dispensed is
approximately 0.2 - 0.4 g per stroke with a high-pressure plunger-
type grease gun
approximately 1.2 g per stroke with a hand-lever grease gun
The quantity of grease required is shown in the greasing interval table.
7.3.1 Greasing interval table
Re-greasing device
Re-greasing device for 4-pole drives from 1.1 kW
Motors with - 0.55 kW and 0.75 kW
- 3000 rpm
- Ship classification
are not suitable for re-greasing.
Motor Ball bearing (drive side) Ball bearing (fan side)
[kW]
Greasing
interval [h]
Quantity of
grease [g]
Greasing
interval [h]
Quantity of
grease [g]
1,1 5000 7 10000 3
1,5 5000 7 10000 3
2,2 5000 10 10000 5
3,0 5000 10 10000 5
4,0 5000 10 10000 5
5,5 4000 16 8000 8
7,5 4000 16 8000 8
Maintenance
20
7.4 Cleaning
When removing or dismantling the pump, it should be cleaned to remove deposits,
if appropriate by mechanical means, in order to ensure perfect operation.
7.5 Removing the pump
Before removing the pump, the motor connection cables should be
disconnected from the terminal box by a qualified electrician.
All shut-off valves in the intake and discharge lines must be closed.
With hot pumping media, the pump casing must have cooled down
to the ambient temperature.
The pump unit must be pressureless and empty. For this purpose,
open the drain plug.
Care must be taken to ensure that escaping medium does not cause
injury or damage to the motor or other components. In case of
systems with hot media, beware particularly of the risk of scalding!
The lifting gear must be adequately dimensioned for the overall
weight of the pump. Observe accident prevention regulations and
general technical regulations.
Deposit the pump on a firm surface and secure to prevent it from
tipping over.
Caution - tilting danger with the loosening of the pump from the
piping network - squeezing danger below the motor!
7.6 Filling and changing the oil - tandem arrangement
The oil chamber between the motor and pump unit is filled with lubrication oil in the
factory. The quantity of oil necessary will be indicated by oil escaping from the vent
opening. Only genuine spare parts must be used for repair purposes.
Approx. 1,5 Litres of oil,
Change the oil after 4,000 hours of operation,
Oil grade in accordance with ISO VG 46 (e.g. Shell Tellus 46).
Do not mix different oils.
Used oil should be disposed of properly in accordance with the local
regulations!
7.7 Official acceptance
The delivered goods may be officially accepted by:
All classification companies
The German Armed Forces quality inspection service or
National technical inspectorates
VEM motors GmbH
Wernigerode
______________________________________________________
Installation, Operating and Maintenance Instructions
Three Phase Asynchronous Motors with Squirrel Cage Rotor
and Slip Ring Rotor, Standard Design 68238 01 englisch
______________________________________________________
1. General
To prevent damage to motors and the driven equipment the procedures laid down in the Operating
and Maintenance Instructions must be followed. Especially to avoid risk of injury, the separately
enclosed Safety Regulations must be adhered to strictly.
Since for reasons of clarity the Operating and Maintenance Instructions cannot contain specific
information with regard to all conceivable special applications and areas with special requirements,
the user himself has to make appropriate protection arrangements during the installation process.
2. Description
The motors have been manufactured in accordance with IEC 34-1, DIN EN 60034-1, DIN VDE
0530 and other appropriate DIN standards. Motors can also be supplied to comply with special
regulations (e.g. Classification Regulations, Regulations for Explosion Protection). Separate
additional instructions apply for the following motor versions:
Roller table motors
Motors in explosion protected design
Motors for marine application on board ship
The details on the relevant Order Confirmation constitute the scope of supply.
3. Protection Standard
The protection standard of the motors is indicated on their rating plate. The protection standard of
additional devices fitted to the motor can be different than the protection standard of the motor.
This needs to be taken into consideration during the installation of the motors. If motors are
installed in the open (Protection Standard IP 44), they should be protected against direct effects
of the climate (freezing of the fan due to direct fall of rain, snow and formation of ice).
4. Type of Construction
The type of construction of the motors is indicated on the rating plate. The motors can be used in
different types of construction only with permission of the manufacturer and if necessary after
modification carried out in accordance with the manufacturers instructions. Especially with types
of construction with vertical shaft the user has to ensure that foreign particles cannot fall into the
fan cowl.
5. Transport & Storage
If possible the motors should only be stored in closed and dry rooms. Outdoor storage under cover
is permitted for a short time only and requires adequate protection against all harmful effects of
the climate. The motors also have to be protected against mechanical damage. Never transport or
store the motors resting on their fan cowls. The eye bolts of the motors together with appropriate
lifting tackle must be used for transport. The eye bolts are intended for the lifting of the motors
only, without any additional parts such as bed plates, gears etc. If eye bolts are removed after
installation, the tapped holes must be blanked off permanently according to the Protection
Standard.
6. Removal of the Transport Safety Device
On motors with transport safety device (roller bearing), the hexagon head screw provided for the
fastening of the transport safety device is to be loosened and taken off together with the transport
safety device. Subsequently the bearing end shield bolt packed in a bag inside the terminal box is
to be screwed into the bearing end shield. If it is necessary for the motor type the bag will also
1
contain a lock washer that is to be placed onto the bearing end shield bolt before screwing it into
the bearing end shield.
7. Installation and Fitting
Since during normal operation of electric motors, temperatures in excess of 100 C can occur on
their surface, any contact with them must be prevented if the motors are installed in accessible
areas. Because of this temperature sensitive parts must never be fitted to them or have contact
with them. In types of construction IM B14 and IM B34 it must be ensured that the maximum
usable screw depth specified in the catalogue is not exceeded, otherwise the winding will be
damaged.
Vent holes must be kept free and the minimum distances stated in the dimensional drawings must
be maintained so that the flow of cooling air is not obstructed. Care must be taken that the
discharged warmed up cooling medium is not sucked up again.
The key in the shaft end is secured by the shaft protective sleeve for transport and storage only.
Because of the danger that the key may be thrown aside, a start-up or a trial run with the key
protected by the shaft sleeve only is strictly forbidden.
Transmission components (such as couplings, pinions or belt pulleys) should be drawn onto the
shaft by means of pull-on devices or by heating-up the part to be drawn onto the shaft. For the
purpose of drawing the transmission components onto the shaft, the shaft ends are provided with
tapped centering holes according to DIN 332 Part 2. Transmission components must never be
driven onto the shaft using hammer blows because the shaft, the bearings and other components
of the motor could be damaged.
All components that are to be fitted to the shaft end must be balanced dynamically according to
the balancing system of the motor (full or half key). The rotors of the motor are balanced with half
key; this is indicated by letter H after the serial number on the rating plate. Motors with letter F
after the serial number are balanced with full key. If possible the motors are to be installed in such
a way that they are free from vibrations. With precision balanced motors special instructions are to
be followed. When the installation is completed the user must ensure protection of movable parts
and safety of operation.
Direct coupling to the driven machine requires a particularly accurate alignment. The shafts of both
machines must be in alignment. The shaft height is to be adjusted to that of the driven machine
using appropriate shims.
Belt drives put a lot of stress on the motor because of relatively high radial forces. When
dimensioning belt drives, apart from the instructions and calculation programmes issued by the
manufacturers of the belts, it must be ensured that the radial force permissible at the shaft end of
the motor as stated in our data is never exceeded by the pull and pre-tensioning of the belt. When
pre-tensioning the belt during installation the instructions of the belt manufacturers must be strictly
adhered to.
8. Insulation Check & Replacement of Grease / Bearings
When the motor is first commissioned and especially after extended storage, the insulation
resistance of the winding is to be measured to earth and between phases. The applied voltage can
be max. 500 V. During and immediately after the measurements dangerous voltages are present
at the terminals. Therefore never touch the terminals and follow the operating instructions of the
insulation resistance meter closely! Depending on the rated voltage U
N
, the following minimum
values must be maintained with a winding temperature of 25 C :
Rated Power P
N
Insulation Resistance referred to
kW Rated Voltage kW/V
1 < PN 10 6.3
10 < PN 100 4
100 < PN 2.5
If the minimum values are lower, the winding must be dried properly until the insulation resistance
corresponds to the required value.
When the motor is commissioned after a prolonged period of storage inspect the bearing grease
visually and replace it if hardening and other irregularities occur. If the motors are to be
commissioned by the manufacturer after more than three years following their delivery then the
bearing grease must always be replaced. With motors fitted with covered or sealed bearings the
2
bearings must always be replaced with new bearings of the same type after a storage period of
four years.
9. Commissioning
Please follow the Safety Regulations closely. All work is to be carried out only when there is no
voltage on the motor. The installation must be carried out according to the valid regulations by
qualified skilled personnel. Initially the mains conditions (voltage and frequency) must be
compared with the data on the rating plate of the motor. The dimensions of the connecting cables
must be adjusted in line with the rated currents of the motor.
The connection points of the motor are marked in accordance with DIN VDE 0530 Part 8. In
Section 19 of these instructions the most common circuit diagrams for three phase motors in basic
design are provided, according to which the connection will be implemented. For all other versions,
the special circuit diagrams are glued to the inside of the terminal box cover or placed in the
terminal box. An additional terminal box can be provided for the connection of auxiliary and
protection devices (e.g. anti-condensation heaters); the same regulations apply as for the main
terminal box.
Always start the motors with an over-current protection device that is set in accordance with the
relevant nominal values of the motor (1,05 I
nom
). Otherwise warranty claims with respect to
damaged windings become void. Before the motor is connected for the first time it is
recommended to check the insulation resistances between winding and earth and between phases
(see Section 8). After prolonged storage it is absolutely essential that the insulation resistance is
measured. Before coupling the motor to the driven machine, check the direction of rotation of the
motor to prevent possible damage being caused to the driven machine. If the mains supply with
the phase sequence L1, L2 and L3 is to be wired to the connection points U, V, W, the motor is
rotating clockwise looking at the shaft end. The direction of rotation can be changed by swapping
the connections between 2 phases. For the permissible tightening torques for the terminal board
bolts refer to the table below:
Terminal board Connecting Bolt Thread Permissible Tightening Torque in Nm
16 A M4 1.2 + 0.5
25 A M5 2.5 0.5
63 A M6 4 1
100 A M8 7.5 1.5
200 A M10 12.5 2.5
400 A M12 20 4
630 A M16 / M20 30 4 / 52 4
Before closing the terminal box make absolutely sure that:
- the connection has been made in accordance with the wiring diagram
- all terminal box connections are tightened
- all minimum values of air paths are maintained (larger than 8 mm up to 500 V, larger than 10 mm
up to 750 V, larger than 14 mm up to 1000 V)
- the interior of the terminal box is clean and free from foreign particles
- unused cable entries are blanked off and the threaded plugs with seals are tightened
- the seal in the terminal box cover is clean and tightly glued and all sealing surfaces
are in the correct state to ensure that the relevant Protection Standard is maintained.
Before starting up the motor check that all safety regulations are strictly adhered to, that the
machine is correctly installed and aligned, that all fixing parts and earthing connections are
tightened, that the auxiliary and additional devices are functionally and correctly connected and if a
second shaft end is fitted that the key is secured against being thrown aside.
If possible the motor is to be connected without load. If the motor is running smoothly and without
any abnormal noises, the load of the driven machine is to be applied onto the motor. When the
motor is started up it is recommended to monitor the current consumption if the motor is loaded
with its driven machine so that any possible overloads and asymmetries occurring in the mains can
be recognised immediately. The starter must always be in the starting position during starting.
With slip ring motors the correct running of the brushes must be monitored. They must be
3
absolutely spark-free. Please always observe the Safety Regulations during operation of the motor
and when switching it off.
10. Maintenance
You are once again referred to the Safety Regulations, in particular to isolation, to securing
against reconnection, to checking whether all components connected to a voltage source are in
dead state. If it is necessary to disconnect the motor from the mains for maintenance work
particular care must be taken to ensure that any possibly existing auxiliary circuits (e.g. anti-
condensation heaters, forced ventilators, brakes) are also disconnected from the mains.
If the motor is to be dismantled during maintenance work, the sealing compound on the centering
shoulders is to be removed. When re-assembling the motor these need to be re-sealed using a
suitable motor sealing compound. Existing copper sealing washers must always be refitted.
11. Bearings and Lubrication
The anti-friction bearings of the motors in standard design are filled with anti-friction bearing
grease in the factory (or with sealed bearings by the bearing manufacturer) according to DIN
51825 in compliance with the table below:
Type series Lubricating grease according
to DIN 51825
Lubricating Grease Base
All Squirrel Cage motors
IEC/DIN 56 132T
Asonic GLY 32
or
Progressive standard 56 - 100 Multemp SRL Lithium base
All Squirrel Cage motors
IEC/DIN 132 355 and
Progressive standard 112 315
Forced Ventilated motors
Brake motors KE2R-40 Polyurethane base
Slip ring motors
IEC/DIN and Progressive
Standard
Marine Motors for on board ship K2N-30
Under normal load and climatic conditions, the quality of grease guarantees an operation of the
motor for approx. 10,000 service hours with two pole design and 20,000 service hours with
multipole design. If not otherwise agreed the grease of anti-friction bearing must never be refilled
during this period. However, the condition of the grease should be checked occasionally even
before this time limit. The indicated number of service hours is only valid for operation at rated
speed. If during operation of the motor via an inverter the nominal speed is exceeded then the
regreasing period reduces approximately in the opposite ratio to the increase in the motor speed.
Regrease the bearings only after a thorough cleaning using suitable solvents. The same type of
grease must be used. When replacing the grease only the equivalent types specified by the motor
manufacturer can be used. Please bear in mind that the bearings should only be filled up to about
2/3 of their free space. A complete filling of the bearings and bearing covers with grease leads to
increased bearing temperature and therefore to increased wear.
The regreasing of bearings with regreasing facility is carried out at the grease nipple when the
motor is running using the grease quantity required for the respective motor. For the re-greasing
intervals please refer to the table below:
Frame Size Two pole design Four and multipole design
112 to 280 2,000 hrs. 4,000 hrs.
315 2,000 hrs. 4,000 hrs.
355 2,000 hrs. 3,000 hrs.
The quantities of grease required for the re-greasing are stated in the below table (Please note
that for the first re-greasing approx. twice the amount of grease is required because the grease
lubrication pipes are still empty). The used grease is collected in the grease chamber of the
4
external bearing cap. After approx. 5 re-greasings this old grease should be removed, e.g. as part
of inspection work.
Series
Progressive
standard
Overall
length
Number
of poles
Quantity of
grease in cm
Series
IEC/DIN
Overall
length
Number of poles
Quantity of grease in
cm3
Frame Size D-end ND-end Frame
Size
D-end ND-end
112 all 10 10 LX2, M2 23 20
132 all 17 17 160 L4, 6, 8 23 20
160 all 23 20 M2 23 23
2 23 23 180 M4, L6, 8 23 20
180 4 31 31 L4 23 23
2 31 31 L2 - -
200 4 35 31 200 LX2 31 31
225
2 35 35 L4, 6, 8
LX 6
31 23
4 41 35 M2 31 31
250
2 41 41 225 M4, 6, 8
S4, 8
35 31
4 52 41 M2 35 35
2 52 52 250 M4, 6, 8 41 35
280 4 57 52 2 41 41
S2 57 52 280 4 52 41
315 M2 57 57 2 52 52
VL S4, 6, 8 64 52 4 57 52
M4, 6, 8 78 57 MX2 VL 57 52
2 57 57 315 MY2 VL 57 57
355 4 90 57 MX4, 6, 8 VL 64 52
6,8 90 57 MY4, 6, 8 VL 78 57
12. Slipring Contact System
The slipring contact system is to be inspected at regular intervals. It is advisable to check the slip
rings 2 3 times immediately after commissioning, at intervals of approx. 50 operating hours.
Subsequently regular maintenance is to be carried out at intervals that depend on the relevant
operating conditions.
A thin layer of patina should be formed on the surface of the slip rings. Generally such patina layer
is formed after an operation of between 100 to 500 hours. If intensive scoring or burnt spots on the
slip ring surface occur they must be removed immediately either by cleaning or if necessary by re-
machining. If slight scoring appears it is not necessary to re-machine. The pressure of the carbon
brushes must be checked. It should be between 18.5 kPa and 24 kPa. When replacing the
brushes the same type of brush must always be used. New carbon brushes must be bedded-in.
With box type brush holders care must be taken to ensure that the carbon brushes do not jam due
to contamination. The carbon brushes wear naturally and the abrasion can amount to 3 - 5 mm per
1,000 hours of operation.
13. Draining of condensation water
On installation sites where formation of dew and thus occurrence of condensation water can be
expected inside the motor, the accumulated condensation water has to be drained at regular
intervals through the opening at the lowest point of the end shield. Subsequently the opening must
be closed up again.
14. Cleaning
So that the effects of cooling air are not interferred with, all parts of the motor must be cleaned at
regular intervals. In the majority of cases it is sufficient to clean the machine with compressed air
that is free from water and oil. Especially the vent holes and the spaces between the ribs must be
5
kept clean. The dust generated by natural wear and deposited in the interior of the motor or in the
slip ring space must be removed at regular intervals. It is recommended to include the electric
motors in the regular routine inspections of the driven machine.
15. Motors with Thermal Winding Protection
A continuity test of the thermistor sensor circuit using a test lamp, a hand generator and such like
is strictly prohibited because this would destroy the sensors immediately. If it becomes necessary
to verify the cold resistance of the sensor circuit (at approx. 20C) then the measuring voltage
must never exceed 2.5 V DC. It is recommended to carry out the measurement using a
Wheatsone bridge with a 4.5 V DC supply voltage. The cold resistance of the sensor circuit must
never exceed 810 Ohms; a measurement of the hot resistance is not necessary. With motors that
are fitted with thermal winding protection, care must be taken that when the thermal winding
protection responds and after the cooling down of the motor, no hazards can occur due to
spurious automatic reconnection.
16. Warranty, Repair, Spare Parts
Unless expressly agreed otherwise only our contractual workshops are permitted to carry out
repairs during the warranty period. Other repairs that may potentially be required can also be
carried out by skilled personnel in these workshops. Details about Customer Service network can
be obtained from the manufacturer on request. The spare parts are listed in Section 20 of these
Operating & Maintenance Instructions. Maintenance carried out appropriately (provided it is as
described in Section Maintenance) does not constitute a breach of warranty provisions. The
contractual warranty liability on the part of the manufacturer is not prejudiced by this.
17. Electromagnetic Compatibility
The motors, as non-independently working unit, have been checked with regard to their conformity
with the EMC Standards. It is the responsibility of the equipment operator to ensure by suitable
measures that the apparatus or plant in their entirety comply with the relevant electromagnetic
compatibility standards.
18. Trouble Shooting
General mechanical and electrical faults are to be rectified according to the Schedule in Section
21. All Safety Regulations must be strictly observed when rectifying faults.
6
Terminal board circuits
Single Speed Squirrel Cage Motor : Single Speed Squirrel Cage Motor:
D low voltage Y high voltage
Star Delta Switch Connection:
For Star Delta without bridges,
connection as per the switch scheme
Motor with thermal winding protection
Terminal board connection as above
connection of the tripping device
from
the motor
The connection will be implemented as per
the connection diagramme of the tripping
device
7
Slip ring motor
D low voltage Y high voltage
Stator
Rotor
Rotor connection according to type either via terminals or via brush holder
to the starter
8
20. Construction of the motor
Item No. Bezeichnung Designation
1.01 Lagerschild D-Seite End shield Drive end
1.02 Lagerdeckel, D-Seite, auen Bearing cover, Drive end, external
1.03 Lagerdeckel, D-Seite, innen Bearing cover, Drive end, internal
1.04 Tellerfeder / Wellfeder, D-Seite, nicht bei
Rollenlagern
Disc spring / wave washer, Drive end, not for roller
bearings
1.05 Wlzlager D-Seite Antifriction bearing, Drive end
1.06 V-Ring D-Seite V-type rotary seal, Drive end
1.07 Flanschlagerschild Flange end shield
1.08 Filzring D-Seite Felt ring, Drive end
2.01 Lagerschild N-Seite End shield Non-drive end
2.02 Lagerdeckel, N-Seite, auen Bearing cover, Non-drive end, external
2.03 Lagerdeckel, N-Seite, innen Bearing cover, Non-drive end, internal
2.04 Wlzlager N-Seite Antifriction bearing, Non-drive end
2.05 V-Ring N-Seite V-type rotary seal, Non-drive end
2.06 Wellfeder Wave washer
2.08 Filzring N-Seite Felt ring, Non-drive end
3.01 1 Paar Motorfe 1 pair of motor feet
3.02 Lfter Fan
3.03 Lfterhaube, Kunststoff Fan cowl, plastic
3.04 Lfterhaube, Stahlblech Fan cowl, sheet steel
3.05 Lfterhaube mit Schutzdach Fan cowl with canopy
3.06 Ringschraube Lifting eye bolt
4.01/4.02 Klemmenkastendeckel Terminal box cover
4.03/4.04 Dichtung Klemmenkastendeckel Terminal box cover gasket
4.05/4.06 Klemmenkastenunterteil Terminal box base
4.07 Dichtung Klemmenkastenunterteil Terminal box base gasket
4.08 Klemmenplatte Terminal plate
4.09 Kabeleinfhrung Cable gland
4.10 Verschluschraube Screw plug for gland opening
4.11 Kabeleinfhrung fr thermischen
Wicklungsschutz
Cable gland for thermal winding protection
4.12 Anschlu fr thermischen Wicklungsschutz Terminal for thermal winding protection
4.13 Schelle Clamp
4.14 Verschlustcken Sealing Components
4.15 Zwischenplatte Adapter plate
4.16 Flacher Anschlukasten Flat terminal box
4.17 Normalienbeutel Standard parts bag
5.01 Lufer, komplett Rotor, complete
6.01 Schleuderscheibe, D-Seite Grease thrower ring, Drive end
6.02 Schleuderscheibe, N-Seite Grease thrower ring, Non-drive end
6.03 Labyrinthbuchse, D- u. N-Seite Labyrinth gland, Drive and Non-drive end
6.04 Leitscheibe, D-Seite Guide disc, Drive end
6.05 Leitscheibe, N-Seite Guide disc, Non-drive end
7.01 Schleifringlufer mit Schleifringen Slip ring rotor with slip rings
8.01 Brstenhalter Brush holder
8.02 Brstentrgerplatte mit Brstenbolzen Brush carrier plate with brush rod
8.03 Schutzdeckel fr Schleifringraum Protective cover for slip ring compartment
8.04 Dichtung fr Schutzdeckel Gasket for protective cover
8.05 Deckel fr Lfterhaube Cover for fan cowl
9.01 Klemmenkastendeckel fr
Luferklemmenkasten
Terminal box cover for Rotor Terminal Box
9.02 Dichtung Klemmenkastendeckel fr
Luferklemmenkasten
Gasket for terminal box cover for Rotor Terminal Box
9.03 Klemmenplatte fr Luferanschlu Terminal board for rotor connection
9.04 Klemmenkastenunterteil fr Luferanschlu Terminal box base for rotor connection
9.05 Kabeleinfhrung fr Luferanschlu Cable gland for rotor connection
9.06 Zwischenflansch fr Luferklemmenkasten Adapter flange for rotor terminal box
9.07 Verschluschraube fr Luferanschlu Screw plug for rotor connection
9
Three phase asynchronous motor with squirrel cage rotor / basic version K2.R 56 132T
(example, delivered version may differ in details)
10
Three phase asynchronous motor / basic version K1.R / K2.R 112 - 355
(example, delivered version may differ in details)
11
Three-phase asynchronous motor with slip ring rotor / basic version S11R / SPER, S11H /SPEH
(example, delivered version may differ in details)
12
21. Trouble shooting
21.1 Electrical Faults
Motor doesn't start
Motor runs up heavily
Humming noise during start
Humming noise during operation
Hum in time of the double slip frequency
Excessive warming up at no-load
operation
Excessive warming up at rated output
Excessive warming up of individual winding sections
Possible cause of fault Remedial measure
l l l
Overload Decrease the load
l
Interruption of a phase in the supply
conductor check the switch and the supply conductor
Interruption of a phase in the supply
l l l
conductor after switching-on check the switch and the supply conductor
l
Mains voltage too low, frequency too high check the mains conditions
l
Mains voltage too high, frequency too low check the mains conditions
l l l l
Stator winding misconnected check the winding connections
l l l
Turn-to-turn fault check the winding and the insulation resistance,
repair in authorized service workshop
l l l
Phase-to-phase short circuit check the winding and the insulation resistance,
repair in authorized service workshop
l
Interruption in the squirrel cage winding repair in authorized service workshop
13
21. 2 Mechanical Faults
Dragging noise
Excessive warming up
Strong vibrations
Bearing warming up excessively
Bearing noises
Possible cause of fault Remedial measure
l l l
Rotary parts are dragging Determine the cause, re-align parts
l
Air supply reduced Check the ventilation passages
l
Unbalance of the rotor Take rotor off, re-balance it
l
Rotor not circular, shaft deformed Take rotor off, co-ordinate further measures with the
manufacturer
l
Imperfect alignment Align motor & driven machine, check the coupling
l
Unbalance of the coupled machine Re-balance coupled machine
l
Shocks from the coupled machine Check the coupled machine
l
Irregularities from the gear Check and repair the gear
l
Resonance with the foundation Stiffen the foundation after consultation
l
Changes in the foundation Determine the cause, eliminate it and re-align the machine
l
Too much grease in the bearing Remove excess grease
l
Coolant temperature higher than 40 C Regrease bearing with suitable grease
l
V-type rotary seal or gamma ring are
dragging
Replace V-type rotary seal or gamma ring, maintain the
prescribed installation clearance
l l
Lubrication insufficient Lubricate according to instructions
l l
Bearing is corroded Replace bearing
l l
Bearing clearance too small Use bearing with larger bearing clearance
l
Bearing clearance too large Use bearing with smaller bearing clearance
l
Chatter marks in the bearing track Replace bearing
l
Standstill marks Replace bearing
l
Cylindrical roller bearing operated at
low load
Change the bearing according to manufacturers instructions
l
Coupling pushes or pulls Re-align motor & driven machine
l
Belt tension too high Adjust the belt tension according to instructions
l l
Bearing not aligned or stressed Check the bearing bore, consult the manufacturer
14
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Champion 700 Series Motor Grader Series I Operators Manual Revision 1 8-24-1977 PDFDokument54 SeitenChampion 700 Series Motor Grader Series I Operators Manual Revision 1 8-24-1977 PDFjulianmata77% (13)
- Compressor spare parts catalogueDokument1 SeiteCompressor spare parts catalogueMuhd Khir Razani0% (2)
- Master Plumber Exam Coverage (Philippines)Dokument4 SeitenMaster Plumber Exam Coverage (Philippines)Eugene Micarandayo100% (3)
- ABB AC - Motor 500KW - Final Service ReportDokument4 SeitenABB AC - Motor 500KW - Final Service ReportZi MingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crankshaft Alignment MeasurementDokument1 SeiteCrankshaft Alignment MeasurementmohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- C9200-2 FWG PDFDokument200 SeitenC9200-2 FWG PDFOzcan ErgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allweiler Serie SM ManualDokument48 SeitenAllweiler Serie SM ManualLuvys Garcia MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- WP310LDokument109 SeitenWP310Ljohn smithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behrens PumpsDokument338 SeitenBehrens PumpsClement_Claudiu50% (2)
- Centrifugal Pumps Data Book: Xingang ShipyardDokument1.260 SeitenCentrifugal Pumps Data Book: Xingang ShipyardМихасикNoch keine Bewertungen
- Store Requisition Parts ListDokument20 SeitenStore Requisition Parts ListJuan VizcarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation Manual XW200 - Version02Dokument44 SeitenOperation Manual XW200 - Version02SimonaMauna100% (2)
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsVon EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiid PumpDokument38 SeitenFiid Pumpsridhar100% (1)
- Instruction Manual V-Line Water Cooled Compressor: V105, V150, V200, V250, V375Dokument69 SeitenInstruction Manual V-Line Water Cooled Compressor: V105, V150, V200, V250, V375Dhairya SindhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Reading As ReasoningDokument18 SeitenCritical Reading As ReasoningKyle Velasquez100% (3)
- HMA Valveco Product OverviewDokument16 SeitenHMA Valveco Product OverviewrizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sauer CompressorDokument50 SeitenSauer CompressorSergei KurpishNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMOT Training1Dokument106 SeitenAMOT Training1ShanAris50% (2)
- User Manual XA030 - V01Dokument77 SeitenUser Manual XA030 - V01Виктор СуворовNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSE Etype EN PDFDokument4 SeitenOSE Etype EN PDFAnonymous WLEMufwK7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Viscochief EVT-10C Viscosity Transducer: Marine & Diesel EquipmentDokument18 SeitenViscochief EVT-10C Viscosity Transducer: Marine & Diesel EquipmentИван ПарлапановNoch keine Bewertungen
- ManualDokument134 SeitenManualrpicho100% (2)
- E.190.07.ws GWS382Dokument482 SeitenE.190.07.ws GWS382cengiz kutukcuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imo PumpDokument108 SeitenImo Pumpelmiski nouhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump Iso13709 Api610 bb3 Multistage DVMX Marelli Maintenance Manual EnglishDokument25 SeitenPump Iso13709 Api610 bb3 Multistage DVMX Marelli Maintenance Manual EnglishJuan Pablo Chumba Lara100% (1)
- Sauer & SohnDokument50 SeitenSauer & SohnILLUMINATOR100% (1)
- ALCAP Separator Training CourseDokument9 SeitenALCAP Separator Training CourseGerald Campañano100% (2)
- SJ-GENUIE-SERIES Compressed 2 PDFDokument444 SeitenSJ-GENUIE-SERIES Compressed 2 PDFZawYeLinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal IM PAAE044210-11Dokument496 SeitenInternal IM PAAE044210-11Julia KusovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FuelPurifier WestfaliaDokument193 SeitenFuelPurifier WestfaliaHorst100% (2)
- Manual EVK SealDokument18 SeitenManual EVK Sealpanamajack26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bombas AllweilerDokument14 SeitenBombas AllweilerCARLOS ANDRES CARVAJAL SUAREZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jets Vacuum Product Catalogue Issue H PZFMLDokument34 SeitenJets Vacuum Product Catalogue Issue H PZFMLmkaklin100% (2)
- MAN-BW L16-24 Project-Guide PDFDokument202 SeitenMAN-BW L16-24 Project-Guide PDFJevgenij ChupinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1450 RPM ALLWEILER PumpsDokument51 Seiten1450 RPM ALLWEILER Pumpsengfaridmalk100% (1)
- WARTSILA R32 Diesel Generator PDFDokument44 SeitenWARTSILA R32 Diesel Generator PDFAkhleshNoch keine Bewertungen
- FW Generator Alfa LavalDokument81 SeitenFW Generator Alfa LavalRusuVasileCristian100% (3)
- Operation Manual XA150 Version02 CompressedDokument44 SeitenOperation Manual XA150 Version02 CompressedИван Парлапанов67% (3)
- Mechanical Separation Basics of SeparatorsDokument86 SeitenMechanical Separation Basics of Separatorsalex_alexutzuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manual Installation, Operation, Maintenance Screw Pump Series Type A (Bearings Arranged Externally)Dokument23 SeitenInstruction Manual Installation, Operation, Maintenance Screw Pump Series Type A (Bearings Arranged Externally)Douglas DuarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sperre X-range Compressor Service ManualDokument60 SeitenSperre X-range Compressor Service ManualFelix d souza50% (2)
- Purificadora LO ALFA LAVAL S946 PDFDokument702 SeitenPurificadora LO ALFA LAVAL S946 PDFfrancisco rios100% (4)
- WestfaliaSeparator - 2058-9001-010 OSD6-0196-067 Instruction Manual and Parts v0206Dokument208 SeitenWestfaliaSeparator - 2058-9001-010 OSD6-0196-067 Instruction Manual and Parts v0206Val ShaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allweiler NTTDokument12 SeitenAllweiler NTTSalsa Amorir50% (2)
- Lancashire BoilerDokument28 SeitenLancashire BoilerDr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wartsila Wireless Temperature MonitoringDokument3 SeitenWartsila Wireless Temperature MonitoringVito DigeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALFA LAVAL Manual P605 High Speed SeparatorDokument181 SeitenALFA LAVAL Manual P605 High Speed SeparatorMery A. Dominguez88% (8)
- ACE pump spare parts guideDokument4 SeitenACE pump spare parts guidepetrakou aglaia100% (1)
- Wartsila 8R32Dokument364 SeitenWartsila 8R32BARIS BILMEZ100% (5)
- Instruction Manual for Reciprocating CompressorsDokument185 SeitenInstruction Manual for Reciprocating CompressorsGiovanni Colonna67% (3)
- MAN B W Project Guide L21 31Dokument238 SeitenMAN B W Project Guide L21 31ArdhiKhurniawan83% (6)
- KRAL DS - DL OID 01enDokument28 SeitenKRAL DS - DL OID 01enembasianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pga58 Pga200Dokument14 SeitenPga58 Pga200Anonymous 8rb48tZS100% (1)
- D 10 - Operating Instructions - Ed. 1104Dokument116 SeitenD 10 - Operating Instructions - Ed. 1104Centrifugal Separator100% (1)
- Technical Manual DBDokument27 SeitenTechnical Manual DBRentu Philipose100% (2)
- Napier TC Water Cleaning Procedure SB - 297 - 298 - 307 - 357 - 358 - 397 - CMHO - 050 - 01Dokument5 SeitenNapier TC Water Cleaning Procedure SB - 297 - 298 - 307 - 357 - 358 - 397 - CMHO - 050 - 01jomari saliganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Change CPU status from "STOP" to "STARTDokument1 SeiteChange CPU status from "STOP" to "STARTDimitris Paliktoglou80% (5)
- TDI Catalog TurboStartTwo Brochure PDFDokument4 SeitenTDI Catalog TurboStartTwo Brochure PDFEva Karia colorado MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABC 2ha 2 S LT EnglishDokument166 SeitenABC 2ha 2 S LT EnglishMarcos Romero80% (5)
- Alfa Laval MAB 103Dokument163 SeitenAlfa Laval MAB 103loloNoch keine Bewertungen
- REXROTH ABUKG Filter-Cooler Circulation Circuit With In-Line FilterDokument10 SeitenREXROTH ABUKG Filter-Cooler Circulation Circuit With In-Line FilterJamin S. PanderajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Maintenance ListDokument390 SeitenElectrical Maintenance ListYogendra Kumar SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dunkin Brands Global Parts CML Catalog PDFDokument68 SeitenDunkin Brands Global Parts CML Catalog PDFAmin Santana100% (1)
- wndw3 Print PDFDokument520 Seitenwndw3 Print PDFbryanth9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technology in Supply Chain ManagementDokument8 SeitenTechnology in Supply Chain ManagementjasmineNoch keine Bewertungen
- WELKIN - Price Reference - 2021-07-15Dokument1 SeiteWELKIN - Price Reference - 2021-07-15marcoaparrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- EZSkin v3 User GuideDokument16 SeitenEZSkin v3 User GuidePg1978Noch keine Bewertungen
- By Himanshu Panwar Asst. Prof. Civil Engineering Department AkgecDokument34 SeitenBy Himanshu Panwar Asst. Prof. Civil Engineering Department AkgecAlok0% (1)
- Leadership Learnings From Chhatrapati SHDokument5 SeitenLeadership Learnings From Chhatrapati SHSagar RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- 64-2103 Tweco Pistolas WeldskillDokument6 Seiten64-2103 Tweco Pistolas WeldskillcarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM4320 PDFDokument85 SeitenTM4320 PDFandres cortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- JVC TH-M606 - 603 - SMDokument101 SeitenJVC TH-M606 - 603 - SMCaillouxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ln26r71bd Ln-s2652d Ln26r71b Ln32r71bd LN s3252d DiagramaDokument261 SeitenLn26r71bd Ln-s2652d Ln26r71b Ln32r71bd LN s3252d DiagramaVictor Julio AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unethical Business Pratices in Corporates: March 2016Dokument13 SeitenUnethical Business Pratices in Corporates: March 2016Manju Nadh ChakravadhanulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sop Flower Arrangement in HotelDokument2 SeitenSop Flower Arrangement in HotelwawahalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citrix Xen Desktop Interview Questions and Answers - Citrix Xen Desktop FAQsDokument3 SeitenCitrix Xen Desktop Interview Questions and Answers - Citrix Xen Desktop FAQsAnonymous rNmxZViYaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jobber JR DetailsDokument2 SeitenJobber JR DetailsUrvish PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- KANSAS CITY Hyatt Regency Hotel Walkways CollapseDokument8 SeitenKANSAS CITY Hyatt Regency Hotel Walkways CollapseRafran RoslyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing Sodium Hyposulfite SolutionDokument2 SeitenManufacturing Sodium Hyposulfite SolutionAravind KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- WFT Composite PlugsDokument11 SeitenWFT Composite Plugsahmad haqkim muhamad malackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccim Fee Refund FormDokument1 SeiteCcim Fee Refund FormMohammad ShafiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- AKA DP Close Bus Ring SolutionsDokument2 SeitenAKA DP Close Bus Ring Solutionssun qiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Management: Operating SystemsDokument48 SeitenProcess Management: Operating SystemsvidishsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aggregate Crushing Value Test Lab ReportDokument2 SeitenAggregate Crushing Value Test Lab ReportComr A Y ZarginaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETH Names DivisionsDokument10 SeitenETH Names Divisionsichigo_bleach00Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Data (Design Manual) - EDTRAU342315-D - RXYQ-BYMDokument104 SeitenEngineering Data (Design Manual) - EDTRAU342315-D - RXYQ-BYMignatiusglenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Converting Urban Waste To EnergyDokument11 SeitenConverting Urban Waste To EnergyDéépákNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open-Ended CG Experiments Spark CreativityDokument9 SeitenOpen-Ended CG Experiments Spark CreativityArjun ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Offline Typing Project WorkDokument2 SeitenOffline Typing Project WorkUsman al-HassamNoch keine Bewertungen