Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Week 12 - Compressed Gas Cylinders
Hochgeladen von
pl_raja0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
22 Ansichten1 SeiteWeek 12 - Compressed Gas Cylinders
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenWeek 12 - Compressed Gas Cylinders
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
22 Ansichten1 SeiteWeek 12 - Compressed Gas Cylinders
Hochgeladen von
pl_rajaWeek 12 - Compressed Gas Cylinders
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
AROMATICS PROJECT
SAFETY TOPIC WEEK 12, 2007
COMPRESSED GAS CYLINDERS COMPRESSED GAS CYLINDERS
HAZARDS
Inert gas can rapidly displace oxygen in con-fined spaces, causing
loss of consciousness or death to anyone in those areas.
Flammable gas can ignite and burn rapidly.
A compressed gas cylinder can become a missile if the valve is
damaged.
Compressed gas can cause a pipe or vessel to explode
When directed at a person, compressed gas or oxygen can embed
particles in eyes and skin.
Precautions
Never take compressed gas cylinders into vessels or confined
spaces.
Always remove torches and hoses from confined spaces when not
in use.
Continuously and adequately ventilate confined spaces where inert
welding gases are used.
Make dry chemical fire extinguishers readily available for fire
emergencies.
NO SMOKING rules must be enforced near places where
compressed flammable gas is used and stored.
Protect cylinders and hoses from sparks and slag.
Never permit oil, grease, or other lubricants to contact gas
cylinders, valves, regulators, hoses, or fittings.
Keep valve protection caps on cylinder valves at all times except
when cylinders are connected to regulators.
Never move uncapped cylinders.
Move and secure cylinders in an upright position.
Never introduce compressed gas into a piping system or vessel
without specific instructions, applicable written permits, and relief
valves of proper size.
Never use compressed gas or oxygen for cleaning anything,
including skin or clothing.
Store flammable and non-flammable cylinders separately. They
should be placed at least 20 feet apart or have a 5-foot barrier with a
1-hour fire rating.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Where To Use Red Danger Tape: Aromatics ProjectDokument3 SeitenWhere To Use Red Danger Tape: Aromatics Projectpl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 47 - How To Use Red TapeDokument3 SeitenWeek 47 - How To Use Red Tapepl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weather Protection of Electrical Installations: Aromatics ProjectDokument1 SeiteWeather Protection of Electrical Installations: Aromatics Projectpl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 47 - How To Use Red TapeDokument3 SeitenWeek 47 - How To Use Red Tapepl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weather Protection of Electrical Installations: Aromatics ProjectDokument1 SeiteWeather Protection of Electrical Installations: Aromatics Projectpl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week - 22 - Safe Use of Hand ToolsDokument1 SeiteWeek - 22 - Safe Use of Hand Toolspl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 20 Underground Services and ExcavationDokument1 SeiteWeek 20 Underground Services and Excavationpl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 03 - Slips Trips FallsDokument1 SeiteWeek 03 - Slips Trips Fallspl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 25 Ol2k Exercise CharlieDokument1 SeiteWeek 25 Ol2k Exercise Charliepl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 30 - Scaffold Green TagDokument1 SeiteWeek 30 - Scaffold Green Tagpl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe Use of Hand Gloves: Aromatics ProjectDokument1 SeiteSafe Use of Hand Gloves: Aromatics Projectpl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SKEC - Safety Moment AwardDokument1 SeiteSKEC - Safety Moment Awardpl_raja100% (1)
- Safety Moment Award - HindiDokument1 SeiteSafety Moment Award - Hindipl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 04 - Safe Slinging For LiftingDokument1 SeiteWeek 04 - Safe Slinging For Liftingpl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 02 Electrical SafetyDokument1 SeiteWeek 02 Electrical Safetypl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
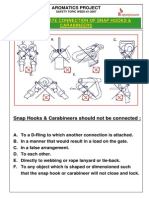
- Week 01 Inappropriate Connection of Snap HookDokument1 SeiteWeek 01 Inappropriate Connection of Snap Hookpl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aromatics Project: Medical Clinic Consultation FormDokument1 SeiteAromatics Project: Medical Clinic Consultation Formpl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 52,01 - Safe Use of Fiber Web Sling KOREANDokument4 SeitenWeek 52,01 - Safe Use of Fiber Web Sling KOREANpl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temporary Electrical Installation: Aromatics ProjectDokument3 SeitenTemporary Electrical Installation: Aromatics Projectpl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 51 - Selection of Hand GlovesDokument3 SeitenWeek 51 - Selection of Hand Glovespl_rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)