Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
NCP For Urinary Retention
Hochgeladen von
Coleen Comelle Huerto60%(5)60% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (5 Abstimmungen)
22K Ansichten5 SeitenThe nursing care plan addresses a patient experiencing urinary retention. The plan involves assessing the patient's history and symptoms, diagnosing the cause as urinary retention related to bladder obstruction, and planning interventions to help the patient empty their bladder sufficiently with a normalized voiding pattern. Interventions include reviewing the patient's medical history, monitoring vital signs and urine output, assisting with urinary drainage procedures if needed, and educating the patient on causes and self-care techniques. The goal is for the patient to understand their condition and void effectively without bladder distention after 8 hours of nursing care.
Originalbeschreibung:
urinary retention
Originaltitel
ncp for urinary retention
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe nursing care plan addresses a patient experiencing urinary retention. The plan involves assessing the patient's history and symptoms, diagnosing the cause as urinary retention related to bladder obstruction, and planning interventions to help the patient empty their bladder sufficiently with a normalized voiding pattern. Interventions include reviewing the patient's medical history, monitoring vital signs and urine output, assisting with urinary drainage procedures if needed, and educating the patient on causes and self-care techniques. The goal is for the patient to understand their condition and void effectively without bladder distention after 8 hours of nursing care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
60%(5)60% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (5 Abstimmungen)
22K Ansichten5 SeitenNCP For Urinary Retention
Hochgeladen von
Coleen Comelle HuertoThe nursing care plan addresses a patient experiencing urinary retention. The plan involves assessing the patient's history and symptoms, diagnosing the cause as urinary retention related to bladder obstruction, and planning interventions to help the patient empty their bladder sufficiently with a normalized voiding pattern. Interventions include reviewing the patient's medical history, monitoring vital signs and urine output, assisting with urinary drainage procedures if needed, and educating the patient on causes and self-care techniques. The goal is for the patient to understand their condition and void effectively without bladder distention after 8 hours of nursing care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
[Type text]
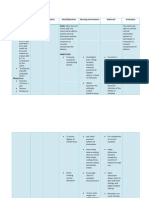
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Urinary
retention
(acute or
chronic)
related to
bladder
obstruction,
Decompens
ation of
detrusor
musculature
Urinary
retention is
the inability
to empty the
bladder.
With chronic
urinary
retention,
you may be
able to
urinate, but
you have
trouble
starting a
stream or
emptying
your
bladder
completely.
You may
urinate
frequently;
you may
feel an
urgent need
to urinate
but have
little
At the end of 8
hours of nursing
care, the patient
will be able to:
Void in
sufficient
amounts
with no
palpable
bladder
distention.
Verbalize
understandi
ng of
causative
factors and
appropriate
interventions
,
Demonstrat
e
techniques/b
ehaviors to
alleviate/pre
vent
retention.
Voiding
pattern
normalized.
Review medical
history for
diagnoses such
as prostatic
hypertrophy,
scarring, recurrent
stone formation
Ask client about
stress
incontinence
when moving,
sneezing,
coughing,
laughing, or lifting
objects.
Monitor vital signs
Suggest
detrusor
muscle
atrophy
and/or
chronic
overdistenti
on because
of outlet
obstruction.
High
urethral
pressure
inhibits
bladder
emptying or
can inhibit
voiding until
abdominal
pressure
increases
enough for
urine to be
involuntarily
lost.
After 8 hours of
nursing intervention
the patient was able
to:
Void in sufficient
amounts with no
palpable bladder
distention.
Verbalize
understanding of
causative
factors and
appropriate
interventions ,
Demonstrate
techniques/beha
viors to
alleviate/prevent
retention.
Voiding pattern
normalized.
.
[Type text]
success
when you
get to the
toilet; or you
may feel
you still
have to go
after you've
finished
urinating.
With acute
urinary
retention,
you can't
urinate at
all, even
though you
have a full
bladder.
Acute
urinary
retention is
a medical
emergency
requiring
prompt
action.
Chronic
urinary
retention
may not
seem life
Observe urinary
stream, size and
force.
Prepare for and
assist with urinary
drainage, such as
emergency
cystostomy.
Prepare for
procedures, such
as the following:
laser,
transurethral
microwave
thermotherapy
(TUMT),
Cortherm,
Prostatron, and
transurethral
needle ablation
(TUNA), Urethral
stent, Open
prostate resection
procedures, such
as TURP
Evaluating
degree of
obstruction
and choice
of
intervention.
May be
indicated to
drain
bladder
during acute
episode.
Done to
quickly
create a
wide open
prostatic
fossa,
often
resulting in
immediate
restoration
of normal
urine flow
[Type text]
threatening,
but it can
lead to
serious
problems
and should
also receive
attention
from a
health
professional
.
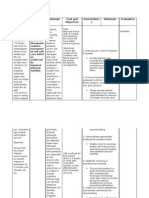
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
[Type text]
S: Ahhewanko. Joke
lang! Di
konamatandaan. Wag
kanatanong ng tanong.
As verbalize by the
patient.
O:
Disorientation to
time
Observed
experience of
forgetting
Scratches his
head when he is
unable to recall
information
Uses alibi that
she is only joking
when she cant
remember
things.
Impaired
memory
related to
neurological
disturbances
Impaired
memory is
directly
related to
effects of
general
medical
condition or
ongoing
effects of
substance.
Depending o
n the areas
of the brain,
the client are
unable to
recall
information,
either
remote or
recent. The
client may
confabulate
to fill in
those lost
memories.
At the end of 2
hours of nursing
care, the patient
will be able to
Verbalize
awareness
of memory
problems;
and
Accept
limitations of
current
condition
Provide
opportunities
for
reminiscence
or recall past
events.
Encourage
ventilation of
feelings of
frustration,
helplessness,
and so forth.
Refocus
attention to
areas of focus
and progress.
Allow the
client to
answer
questions on
his own, but
do not rush
him to answer
it. Make the
client feel that
he can still do
things
independently
.
Monitor
clients
behavior and
Long-term memory may
persist after loss of recent
memory. Reminiscence is
usually an enjoyable activity
for the client.
To lessen feelings of
powerlessness/hopelessness.
It is important to maximize
independent function, assist
the client when memory has
deteriorated further.
To reduce frustration
After 2 hours of
nursing
intervention the
patient was able
to:
The
patient
was able
to
verbalize
awareness
of memory
problems
[Type text]
assist in use
of stress-
management
techniques
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Impaired Physical Mobility RT Neuromuscular Skeletal Impairment.Dokument3 SeitenImpaired Physical Mobility RT Neuromuscular Skeletal Impairment.Abegail Abaygar100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan Risk For Urinary RetentionReginald Julia100% (2)
- Urinary Retention, RevisedDokument2 SeitenUrinary Retention, RevisedKim Beverly100% (5)
- NCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFDokument2 SeitenNCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFNoel Cabamongan88% (8)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDokument3 SeitenImpaired Urinary Eliminationcamziii89% (18)
- NCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSODokument3 SeitenNCP-impaired Urinary Elimination-TAHBSOtinatin9890% (1)
- NCP BPHDokument8 SeitenNCP BPHjyaba0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic71% (7)
- Nursing Care PlanDokument1 SeiteNursing Care PlanSHeenah Qo100% (1)
- NCP Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Tract InfectionsDokument4 SeitenNCP Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Tract InfectionsRaveen mayi89% (9)
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortDokument2 SeitenImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortRis NapolisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Functional Urinary Incontinence NCPDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Functional Urinary Incontinence NCPderic58% (12)
- Acute Pain NCPDokument2 SeitenAcute Pain NCPBobby Valencerina100% (1)
- NCP UtiDokument1 SeiteNCP Utitsunami_cutieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument9 SeitenNursing Care PlanJam AbantaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Acute Pain RT CancerDokument3 SeitenNCP Acute Pain RT CancerCharissa Magistrado De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlansDokument4 SeitenNursing Care PlansanreilegardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDokument1 SeiteNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP OsteomyelitisDokument3 SeitenNCP OsteomyelitisClariss Alota100% (2)
- NCP Chronic ConfusionDokument4 SeitenNCP Chronic ConfusionLyka DianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFDokument2 SeitenNCP Impaired Urinary Elimination CRFAnonymous FgT04krgymNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy NCPDokument9 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy NCPderic88% (8)
- NCP - Acute PainDokument3 SeitenNCP - Acute PainErine Emmanuelle Cawaling Hetrosa100% (1)
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPAlyanna Peñaflorida100% (2)
- To Promote Good Hygiene and Physical Comfort.: Coli (E. Coli), NormallyDokument2 SeitenTo Promote Good Hygiene and Physical Comfort.: Coli (E. Coli), NormallyFran LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP CKDDokument9 SeitenNCP CKDDanica Salinas100% (1)
- Impaired Urinary Elimination Prostate CancerDokument4 SeitenImpaired Urinary Elimination Prostate CancerEji AsouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDokument3 SeitenActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- Spinal Cord Injury NCPDokument2 SeitenSpinal Cord Injury NCPShengxy Ferrer100% (6)
- MS 2 NCP Deep Vein ThrombosisDokument4 SeitenMS 2 NCP Deep Vein ThrombosisRosaree Mae PantojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pain NCPDokument2 SeitenAcute Pain NCPCaren AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument11 SeitenNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- NCPDokument8 SeitenNCPJoseph Anthony Benitez VerzosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDokument5 SeitenNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDokument3 SeitenNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionRosalie Delfin90% (10)
- Infection NCPDokument1 SeiteInfection NCPMsOrangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Dokument2 SeitenImbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Senyorita KHaye100% (1)
- Urinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orDokument4 SeitenUrinary Tract Infection, (UTI) Is An Infection of One orLorebellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Planmjoie_baby6568470100% (6)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPDokument2 SeitenBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Ncp-Angina - Doc NCPDokument1 SeiteNcp-Angina - Doc NCPVanes SaRn67% (3)
- Impaired Physical Mobility CholecystectomyDokument2 SeitenImpaired Physical Mobility CholecystectomyPrincess Danica Purcia100% (1)
- NCP FractureDokument2 SeitenNCP FractureAi Rou100% (1)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDokument2 SeitenNCP Activity Intolerancea22hous0% (1)
- NCP PancreatitisDokument2 SeitenNCP PancreatitisJeanelle GenerosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective CopingDokument2 SeitenIneffective CopingDaryll Romero50% (2)
- N C P For Perioperative Pts.Dokument4 SeitenN C P For Perioperative Pts.Daisy Palisoc100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan (CVA)Dokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan (CVA)Mel Rodolfo50% (2)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDokument5 SeitenNCP Activity IntoleranceRea HashimNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP ConstipationDokument1 SeiteNCP ConstipationGrace_CessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Urinary EliminationDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan Impaired Urinary Eliminationderic86% (14)
- Urinary RetentionDokument6 SeitenUrinary Retentionjakenathanielvelasco50% (2)
- Self Care DeficitDokument2 SeitenSelf Care DeficitSj 斗力上75% (4)
- NCPDokument12 SeitenNCPJonathan Liscano100% (3)
- NCP Psyche 1Dokument7 SeitenNCP Psyche 1Pete SkullNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssessmentDokument2 SeitenAssessmentBriggette AnnangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis May Be Related To Possibly Evidenced byDokument37 SeitenNursing Diagnosis May Be Related To Possibly Evidenced byLea TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary IncontinenceDokument5 SeitenUrinary IncontinencefakrulnersmudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Icu-CcuDokument6 SeitenNCP Icu-CcuJohn CenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Path o PhysiologyDokument1 SeitePath o PhysiologyColeen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLUID and ElectrolytesDokument18 SeitenFLUID and ElectrolytesColeen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CefuroximeDokument4 SeitenCefuroximeColeen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AldazideDokument1 SeiteAldazideColeen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terminal Care What Is Terminal Care?Dokument6 SeitenTerminal Care What Is Terminal Care?Coleen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Claudine Huerto MrsDokument4 SeitenClaudine Huerto MrsColeen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResistorsDokument2 SeitenResistorsColeen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AldazideDokument1 SeiteAldazideColeen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report PaperDokument1 SeiteReport PaperColeen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TurpDokument23 SeitenTurpColeen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TurpDokument23 SeitenTurpColeen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument3 SeitenIneffective Airway ClearanceColeen Comelle HuertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thai Book Lesson From Genius SchoolDokument85 SeitenThai Book Lesson From Genius SchoolAlexis L.D (Riker94)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Binary or Genderqueer GendersDokument9 SeitenNon-Binary or Genderqueer GendersJuan SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ppr.1 Circ.5 Gesamp Ehs ListDokument93 SeitenPpr.1 Circ.5 Gesamp Ehs ListTRANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ahsan Menu KolachiDokument12 SeitenAhsan Menu Kolachisalman GtrNoch keine Bewertungen
- MoRTH 1000 Materials For StructureDokument18 SeitenMoRTH 1000 Materials For StructureApurv PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Study Resource WasDokument3 SeitenThis Study Resource WasNayre JunmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copy of HW UMTS KPIsDokument18 SeitenCopy of HW UMTS KPIsMohamed MoujtabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 3 Polymer and Fuel ChemistryDokument10 SeitenUNIT 3 Polymer and Fuel Chemistryld6225166Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Mixing Equipments Used in Flocculation and CoagulationDokument27 Seiten4 - Mixing Equipments Used in Flocculation and Coagulationhadeer osmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coiled Tubing Safety Impact Firing Head (HP) - by DynaDokument16 SeitenCoiled Tubing Safety Impact Firing Head (HP) - by DynamahsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secondary 1 Express English Paper 1 & 2Dokument15 SeitenSecondary 1 Express English Paper 1 & 2Menon HariNoch keine Bewertungen
- ListwarehouseDokument1 SeiteListwarehouseKautilya KalyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Evaluation and Management of The Solitary Pulmonary NoduleDokument21 SeitenDiagnostic Evaluation and Management of The Solitary Pulmonary NoduleGonzalo Leal100% (1)
- Canfield FairDokument3 SeitenCanfield Fairapi-546463844Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Dokument1 SeiteDysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Bheru LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crude TBP Country United Arab Emirates Distillation: MurbanDokument2 SeitenCrude TBP Country United Arab Emirates Distillation: MurbanHaris ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 18: Calculating Food Costs, Selling Prices and Making A ProfitDokument4 SeitenUnit 18: Calculating Food Costs, Selling Prices and Making A Profitkarupukamal100% (2)
- Air MassesDokument22 SeitenAir MassesPrince MpofuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seachem Laboratories, Inc. Safety Data SheetDokument10 SeitenSeachem Laboratories, Inc. Safety Data SheetJorge Restrepo HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Relieving, Normalising and Annealing: Datasheet For Non-Heat-TreatersDokument2 SeitenStress Relieving, Normalising and Annealing: Datasheet For Non-Heat-TreatersGani PateelNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS 11255 - 7 - 2005 - Reff2022 Methods For Measurement of Emission From Stationary Sources Part 7 Oxides of NitrogenDokument10 SeitenIS 11255 - 7 - 2005 - Reff2022 Methods For Measurement of Emission From Stationary Sources Part 7 Oxides of NitrogenPawan SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DocumentDokument6 SeitenDocumentGlennford Loreto SuyatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3M Window Film PR SeriesDokument3 Seiten3M Window Film PR SeriesPhan CrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy, Physiology & Health EducationDokument2 SeitenAnatomy, Physiology & Health Educationsantosh vaishnaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Choke Manifold Procedures 3932324 01Dokument4 SeitenChoke Manifold Procedures 3932324 01Saïd Ben Abdallah100% (1)
- Entrepreneurship Paper 2Dokument3 SeitenEntrepreneurship Paper 2kisebe yusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legg Calve Perthes DiseaseDokument97 SeitenLegg Calve Perthes Diseasesivaram siddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Orientation Grade 11 Revision Term 2 - 2021 FinalDokument16 SeitenLife Orientation Grade 11 Revision Term 2 - 2021 FinalTeeshan VerappenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concepts and Applied Aspect of Sharir RachnaDokument122 SeitenBasic Concepts and Applied Aspect of Sharir RachnaRam Krish100% (1)
- Review Dynamic Earth CoreScienceDokument3 SeitenReview Dynamic Earth CoreScienceVikram BologaneshNoch keine Bewertungen